Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Culture of the newly
constructed production
cell line
Aliquoted into ampoules
Master
cell bank
1
2
3
4
5
234 5
1
Working cell bank
Number 1
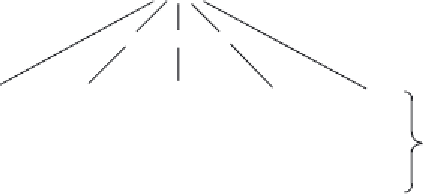
Figure 5.6
The master cell bank/working cell bank system. For simplicity, each bank shown above contains
only fi ve ampoules. In reality, each bank would likely consist of several hundred ampoules. Working cell bank
number 2 will be generated from master cell bank vial number 2 only when working cell bank number 1 is
exhausted and so on
These ampoules are not used directly to seed a production batch. Instead, they are used, as required, to
generate a working cell bank. The generation of a single working cell bank normally entails thawing
a single master cell bank ampoule, culturing of the cells therein and their subsequent aliquoting into
multiple ampoules. These ampoules are then cryopreserved and form the working cell bank. When a
single batch of new product is required, one ampoule from the working cell bank is thawed and used
to seed that batch. When all the vials that compose the fi rst working cell bank are exhausted, a second
vial of the master cell bank is used to generate a second working cell bank, and so on.
The rationale behind this master cell bank/working cell bank system is to ensure an essentially
indefi nite supply of the originally developed production cells for manufacturing purposes. This
is more easily understood by example. If only a single-tier cell bank system existed, containing
250 ampoules, and 10 ampoules were used per year to manufacture 10 batches of product, the
cell bank would be exhausted after 25 years. However, if a two-tier system exists, where a single
master cell bank ampoule is expanded as required, to generate a further 250 ampoule working cell
bank, the entire master cell bank would not be exhausted for 6250 years
The upstream processing element of the manufacture of a batch of biopharmaceutical product
begins with the removal of a single ampoule of the working cell bank. This vial is used to inoculate
a small volume of sterile media, with subsequent incubation under appropriate conditions. This de-
scribes the growth of laboratory-scale starter cultures of the producer cell line. This starter culture
is, in turn, used to inoculate a production-scale starter culture that is used to inoculate the produc-
tion-scale bioreactor (
Figure
5.7). The media composition and fermentation conditions required to














Search WWH ::

Custom Search