Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Cyanogen bromide is then separated by gas chromatography and selectively detected
with an electron capture detector.
It should be noted that the internal standard (nitromethane) must always be introduced
after the addition of cyanide in order to prevent rapid darkening of the solutions, which
causes non-reproducible results. No interferences are caused by oxidising or reducing
substances or by mercury or cadmium at concentrations below 200mg L
−1
. Mercury and
cadmium are, among the metals, the strongest complex-forming agents with bromide.
Even small amounts of aromatic compounds are likely to produce some interferences
owing to their tendency to bind bromine, which is formed by reaction with chlorine
water.
Grandet
et al.
[12] have described a gas chromatographic method for the determination
of µg levels of bromide in potable water.
The application of this technique is discussed under multianion analysis in sections
7.28.3 and 14.1.3.1.
7.7
Chromate and dichromate
7.7.1
Atomic absorption spectrometry
Posta
et al.
[13] have described a high performance flow flame atomic absorption
spectrometric method for the determination of tri- and hexavalent chromium in potable
water, and the preconcentration of hexavalent chromium.
A high performance liquid chromatographic integrator at the output of the flame
atomic absorption spectrometer makes it possible to process simultaneously the signals of
both oxidation states of chromium. Detection limits for tri- and hexavalent chromium are,
respectively, 0.03 and 0.02µg L
−1
.
7.8
Chloride
7.8.1
Titration method
Levy [14] has described a titrimetric procedure for the determination of chloride ions in
the presence of free chlorine. Previous workers have attempted to remove free chlorine
by boiling the sample. This, however, leads to partial decomposition of hypochlorous
acid to hydrochloric acid and oxygen:
Levy [14] overcame this problem by carrying out the reaction at a temperature close to 0°
C and sweeping unhydrolysed chlorine out of solution with a purge of nitrogen before
commencing the determination of chloride ions.
All solutions, except those to be added from burettes, are kept in an ice-bath

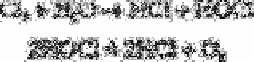
Search WWH ::

Custom Search