Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
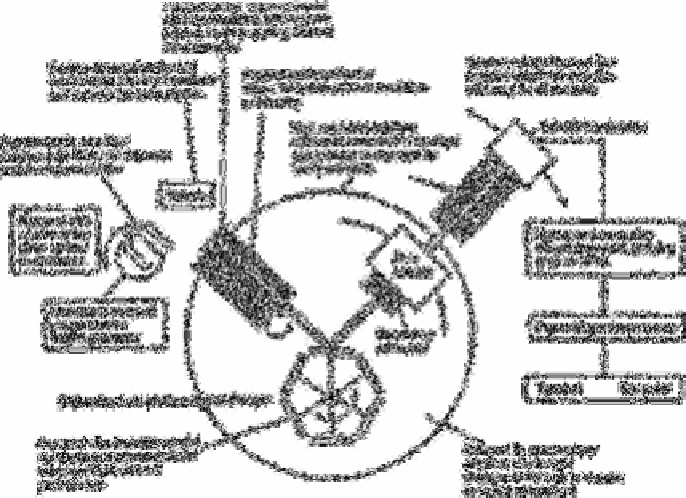
Fig. 1.2
Layout of Philips PW 1404 energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence
spectrometer
Source: Own files
All elements upwards from sodium (z=11) in the periodic table may be determined. The
inclusion of twin excitation sources, which may be switched electronically within a few
seconds, assures optimum sensitivity for all detectable elements. The applicable
concentration range is from per cent to below 1µg L
−1
. As little as 1µg of sample is
sufficient to determine elements at the milligram per litre level; calibration is necessary
only once and is carried out during installation. The calibration will remain unchanged
for a period of at least 12 months. Quantitative analysis is simple and uses the method of
internal standardisation. No external standards are necessary. The method requires no
correction of matrix effects for all elements except those in the range sodium to
phosphorus. Empirical absorption-enhancement correction models may be applied to
these light elements. Sample preparation for solutions and dispersions is very simple,
requiring only a micropipette.
1.1.9
Neutron activation analysis
This is a very sensitive technique whose application in water has been limited to the
determination of iodide in non saline water and bromide in aqueous precipitation. Due to
the complexity and cost of the technique, no water laboratory in the UK has its own
facility for carrying out neutron activation analysis. Instead, samples are sent to one of
the organisations that possess the facilities, eg the Atomic Energy Research
Search WWH ::

Custom Search