Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
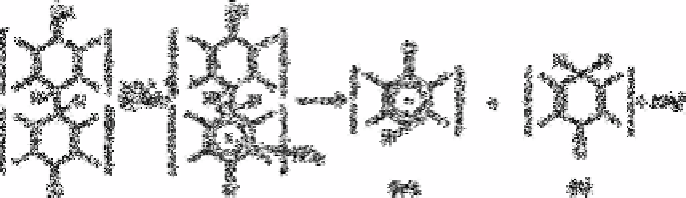
By different oxidative paths, C (coloured species) and L (luminescent compound) are
formed. A subsequent step yields anthraquinone Bianthronyl first degrades via a
bianthronyl—nitronium complex, to anthronyl cation (A
+
) and anthrone (A) and, later, by
different oxidative paths these are transformed into anthraquinone.
The authors differentiated between the final product (λex 286, λem 422nm) and the
anthraquinone (λex 285 420nm), but as can be observed by their spectral characteristics,
these compounds are practically the same.
Resorcinol method
Resorcinol has been proposed as a fluorometric reagent for the determination of nitrate
and nitrite [433]. The author suggested the following mechanism for the reaction of
nitrate: chloride ion catalyses the conversion of nitrate into nitrite, the resultant nitrite
reacts with resorcinol to produce the nitroso compound, which reacts with the excess of
resorcinol to form a reddish violet species. This reaction product exhibits intense
fluorescence in ammoniacal solution and is probably a phenoxazine derivative.
3-amino-1,5 naphthalenedisulphonic acid method
Motomizu
et al.
[434] describe a flow-injection fluorometric method for determining
nitrate in non saline waters. The nitrate is reduced to nitrite in a copperised cadmium
column and the nitrite is reacted with 3-amino-1,5 naphthalenedisulphonic acid to form
the corresponding azoic acid in a flow-injection system; the salt of this acid is fluorescent
in an alkaline medium and the fluorescence is measured. The relative standard deviation
was 0.8% for 10 injections of 2×10
−5
M nitrate, and the detection limit was 1×10
−5
M
nitrate, injection rate was 30 samples/h.
2.62.3
Chemiluminescence methods
Yoshizumi
et al.
[435] described the determination of down to 1µg L
−1
nitrate by a flow
system with a chemiluminescent NOx analyser. Enzymic methods have been used for the
determination of nitrate [436]. These methods are based on the enzymic reduction of
nitrate to nitrite or ammonia. In one method [437] the nitrite is then estimated by the
sulphanilamide-
N
-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride coupling procedure.
Thermal decomposition combined with chemiluminescence analyses has been used to
determine nitrate in deposited aerosol particles [438].

Search WWH ::

Custom Search