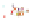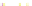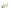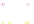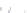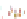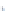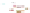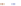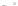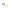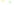Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(c)
(a)
(b)
Nerve Fibers position
Nerve Fibers position
8
x
10
−3
3
x
10
−3
9
10
8
7
2
7
6
5
4
6
1
5
0
4
−1
3
3
−2
2
2
−3
1
0
−4
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
x 10
−3
4
3
2
1
0
−1
−2
−3
−4
1
x 10
−3
x
x
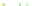
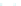
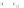
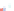
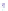
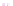
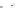
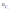
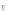
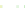
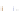
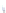
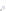
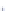
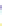
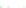
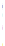
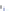
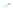
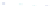
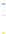
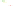
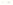
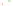
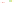
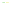
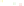
Fig. 4 a
Node positions for a single spiral ganglion inside,
b
and
c
node positions for all the spiral
ganglions for the XY and XZ planes respectively
Ta b l e 2
Conductivity values
for the cochlea structures [
3
]
Conductivity Sm
−
1
Structure
Electrodes
1000
Scala media
1.67
Scala tympani
1.43
Scala vestibuli
1.43
Basilar membrane
0.0625
Reissner membrane
0.00098
Nerve
0.3
Bone
0.156
2.3 Finite Element Method (FEM)
FEM for the given geometry was solved using the COMSOL solver ©. In this para-
graph we briefly review the electrostatic equations solved by the FEM. The different
elements in which the geometry was decomposed are reconnected at nodes. Next the
electric field is approximated at these nodes resulting in a set of algebraic equations.
The basis for the equations is the Poisson equation which gives the electrostatic
potential for a given charge distribution:
−
Δ
u
=
f
,
f
ʩ
(1)
Δ
where
is the Laplacian operator given by:
2
2
2
∂
∂
∂
Δ
=
x
1
+
x
2
+···+
x
d
.
(2)
∂
∂
∂