Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 3
Sequentially homogenization of a heterogeneous microstructure
This condition states that the average strain and stress of the heterogeneous RVE
correlate with the quantities of an analogous homogeneous RVE. Strictly speaking,
a perfect homogenized equation (
9
) of the inhomogeneous microstructure is found if
this condition can be fulfilled. This equation is valid for both the analog homogeneous
RVE and an arbitrarymaterial point within the continuum. This so-called sequentially
homogenization procedure is illustrated in Fig.
3
.
The boundary value problem is solved by the finite element method (FEM). Any
desired structures can be modelled by this procedure. Thereby, the differential equa-
tion (
1
) is converted to its weak form by use of the variational principle.
˃
ij
n
j
−
t
i
δ
u
i
d
−
˃
ij
,
j
δ
u
i
dV
=
0
(11)
V
This equation is numerically solved by discretization [
14
]. The field quantities are
calculated discretely at the nodes of the elements and converge towards the real
solution with increasing mesh refinement.
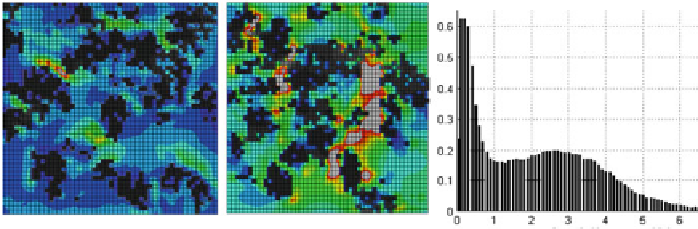
Fig. 4
Left
Inhomogeneous strain distribution in cross sections.
Right
normalized strain distribution
over the whole RVE