Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.3 Measured starting
wind speeds for the 500 W
turbine from Wright [
1
].
Average starting wind
speed = 4.8 m/s. The units of
dU/dt are m
2
/s
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
-0.5
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
starting wind speed,
U
s
(m/s)
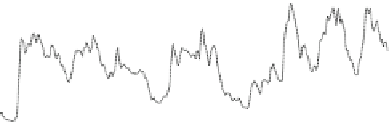
Fig. 6.4 Low speed start of
the 500 W turbine, taken
from Wright [
1
]
Table 6.1 Parameters for
turbine in Fig.
6.1
from
Wright [
1
]
Parameter
Value
Hub radius
0.25 m
0.41 kg m
2
Inertia of composite blades and hub
0.02 kg m
2
Inertia of generator
0.43 kg m
2
Total rotational inertia
Dynamic resistive torque
0.24 Nm
Static resistive torque
0.36 Nm
and the propensity of wind direction changes to increase with decreasing wind
speed, means that most starting sequences will be affected by yaw errors. Yaw is
likely to reduce the starting torque and should lead to the over-prediction of starting
behaviour.
Figure
6.4
shows a typical starting sequences of the 500 W turbine, one of
nearly 200 sequences analysed by Wright [
1
]. Table
6.1
lists the main turbine
parameters related to starting: note that the blade holder made a negligible con-
tribution to the rotor inertia. The difference between the static and dynamic
resistive torque is likely to be caused by friction in the bearings as cogging torque
should be independent of generator speed. Figure
6.4
shows a number of important
features of starting:













































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search