Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.1 500 W 1.94 m
diameter turbine with cup
anemometer and wind vane
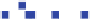
Fig. 6.2 500 W turbine
power curve. 1-min averages
of power output (solid blue
squares) have been placed in
wind speed bins of 0.5 m/s
width, and averaged to give
open red diamonds from
Wright [
1
]
500
400
300
200
100
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
wind speed (m/s)
detail. All the starting measurements described in this chapter come from that tur-
bine. Its power curve, Fig.
6.2
, suggest that it had good low wind performance in that
it has a low cut-in wind speed, defined in IEC 61400-2 as the ''lowest mean wind
speed at hub height at which the wind turbine produces power''. Figure
6.3
, how-
ever, graphically demonstrates that the average starting wind speed is significantly
higher than the cut-in speed. The rest of this chapter analyses rotor acceleration from
rest under the action of the aerodynamic torque caused by the wind. It will be
assumed that the turbine maintains perfect alignment with the wind during starting.
In practice, however, the combination of long starting times, as shown in Fig.
6.4
,


















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search