Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Whereas in structural engineering the design load cases according to [44] apply, some
of the design load cases used in geotechnical engineering differ (see DIN 1054 [50]).
Consistency is ensured by the fact that the characteristic values of the independent
effects are “transferred” at the interfaces, that is the junctions between structure and
subsoil. Those are the action effects resulting from the characteristic values of the
independent actions (see [58] example A.5, and [78]). Therefore, geotechnical
engineering makes use of the design load cases according to DIN 1055-100 [44],
but also the cases specific to geotechnical engineering according to DIN 1054 [50].
The design of foundations to loadbearing structures that have to be analysed according
to second-order theory must include the second-order components in all the analyses
required to satisfy the equilibrium conditions for the deformed structure. Ignoring these
could mean that the required structural reliability is not achieved! This applies in
particular to the foundations of sway structures and hence also to free-standing towers
whose internal forces are calculated according to second-order theory.
In contrast to DIN 1054 [50] 6.1.2, the following procedure is suggested for the
conversion into characteristic internal forces at the soil/structure interface (for an
application see [58] example A.5):
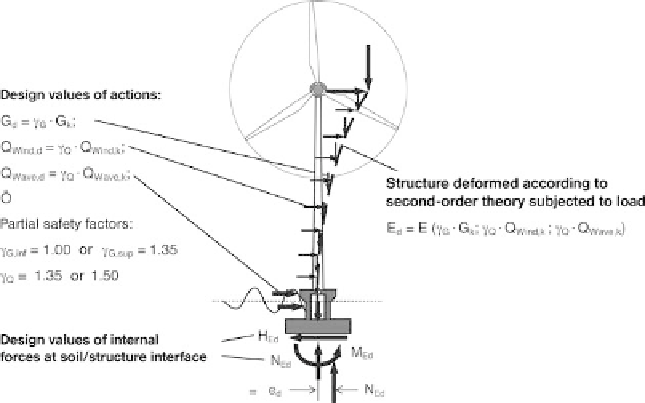
1. Structural Analysis According to Second-Order Theory and Design (see Figure 4.51)
- Calculation of deformation and internal forces with the design values of the
actions (G
d
;Q
imposed,d
;Q
wind,d
; . . . etc.) and the resistances specific to the type
of construction according to DIN 1045-1 [33] 5 and 8.6.1, plus the soil bearing
pressures and uplift resulting from this. In doing so, the equilibrium conditions
for the deformed structure have to be satisfied at the ultimate limit state.
- Calculation of the design values for the subsoil reactions at the underside of the
foundation (N
Ed
;V
Ed
;M
Ed
). Design of the loadbearing structure, including the
Fig. 4.51 Structural analysis according to second-order theory and design