Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
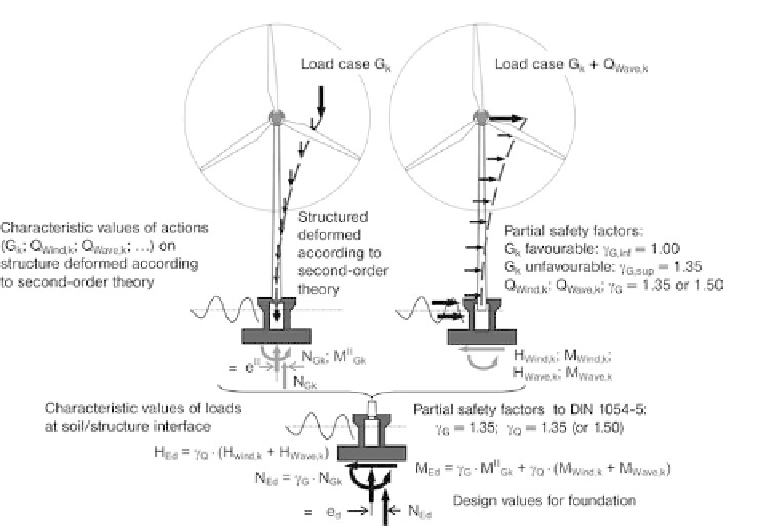
Fig. 4.52 Foundation design
foundation (!), on the basis of DIN 1045-1 [33] in conjunction with DIN 1055-
100 [44].
2. Design of Foundation (see Figure 4.52)
- Calculation of the characteristic values of the independent effects (loads) at the
soil/structure interface (N
Gk
,M
Gk
,H
Gk
;N
imposed,k
,M
imposed,k
,H
imposed,k
;N
wind,k
,
M
wind,k
,H
wind,k
; . . . etc.) with the equilibrium conditions for the loadbearing
structure deformed according to second-order theory.
- Calculation of the design values of the loads on the subsoil (N
Ed
;V
Ed
;M
Ed
or N
d
and T
d
) and geotechnical analyses (safety against ground failure, safety against
sliding, . . .) according to DIN 1054 [50].
Design of structural components
A compact tower foundation is calculated as a circular or annular slab. In order to avoid
lifting of the perimeter and to increase the core radius, a layer of soft material is placed
beneath the central area (inside diameter D
i
1/3
outside diameter D
a
). Further, the
aim is to make sure that no uplift occurs at the soil/structure interface under
characteristic actions (which traditionally corresponds to a full load made up of
permanent, imposed, wind and, if applicable, sea state loads). See [8] for details
regarding design, construction details and reinforcement in tower foundations.