Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
[37]. Taking this objective into account, this model should satisfy the following
conditions:
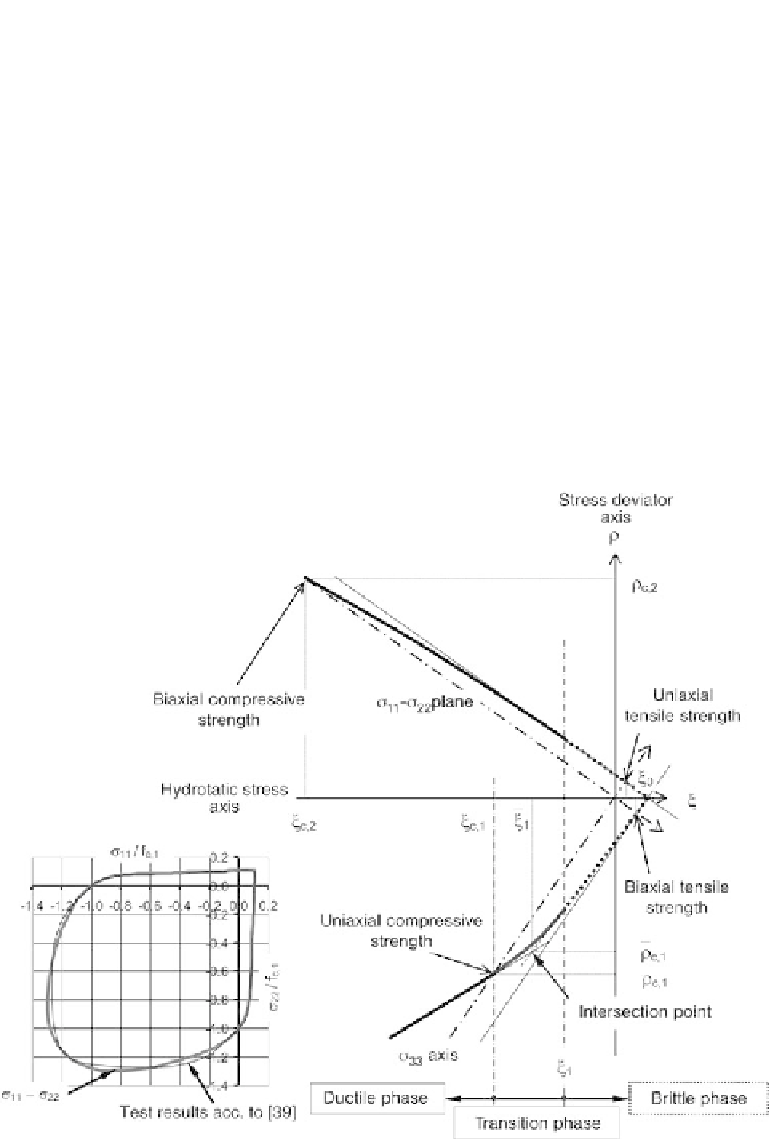
1. Fractures occur in zones with principal tensile stresses close to the tensile strength.
Rankine's failure hypothesis can be used in these zones (“brittle phase”).
2. As the hydrostatic pressure increases, so the failure modes change (hybrid failure
behaviour). The failure meridians gradually curve towards the hydrostatic stress axis
(“transition phase”).
3. Shear failures can be expected at high hydrostatic pressures. They can be
described with meridians at a shallow angle to the hydrostatic stress axis
(“ductile phase”). The design approach for confined columns according to
[42]. can be employed in order
to describe the principal meridians
mathematically.
This results in a failure surface that is similar to a Rankine failure surface for positive
and small negative mean stresses and gradually changes to an elliptically curved failure
surface for larger negative mean stresses.
Fig. 3.15 Three-phase model, principal meridian intersection curve, biaxial stress intersection curve