Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
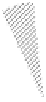
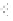
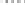
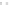
Minas Heavy Oil
Heavy Oil C
M Gas or C Gas
Heavy Oil A
Kerosene
Butane
LNG
Propane
Liquid fuel
Gas fuel
Gas
Treatment-F
Melting-F
Heating-F
(Continuous)
Heating-F
(Batch)
Ladle
Heat
Treatment-F
(Continuous)
Heat
Treatment-F
(Batch)
Mix-Gas & COG
LNG
Propane
Butane
Kerosene
Heavy Oil-A
Heavy Oil-C
Minas Heat
FIGURE 5.83
Relationship between kind of fuel and number of applicants.
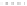
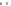
Burner type and Media type
Number of F
27
9
2
8
10
1
1
58
other
Ball
Direct
Firing
Honeycomb
twin
single
Honeycomb
Ball
RT
Ball
Gas Treatment Furnace
Honeycomb
Ball
other
Total
Gas T F
D-Firing
RT
Honeycomb
(twin)
Honeycomb
(single)
FIGURE 5.84
Relationship between kind of burner and number of applicants.
combustion. The results of this field test must be carefully examined to identify the
functional advantages and practicality of the structures.
Combustion methods can be divided into a direct injection method in which fuel
is directly injected into a furnace and an indirect injection method. The combustion
method is selected in accordance with the shape of the furnace, the type of fuel, etc.
The combustion method is the key factor influencing NO
x
emissions, combustion
quality, flame length, and in-furnace temperature distribution. The difference



























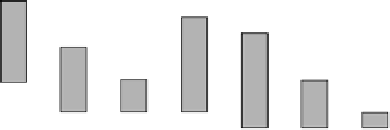
















































































































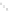











































































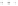


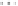





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search