Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
furnace, the emission behavior of volatile matter can be simulated. Under such
variable factors as the types of coal, the temperature of combustion air, and the
oxygen content, the oxygen ratio, tests are conducted by means of sampling and
Exhaust gas
Filter
to Gas anal
y
zers
Coal feeder
in
out
N
2
Cooling water
Air
Air
Cooling water
Sampling port
in
out
Natural gas
Sampling probe
Window
Water cooled section
Air+O
2
120mm
Thermocouple
Thermocouple
2108mm
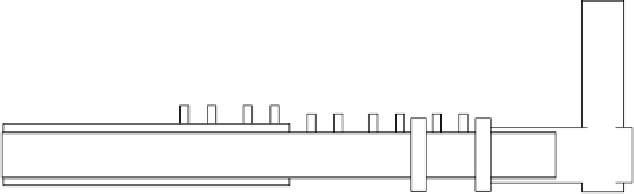
FIGURE 2.95
Outline of horizontal reaction furnace of pulverized coal of high temperature
and high oxygen content.
analysis of reacting particles and gases and by optical measurement of instantaneous
particle temperature.
temperature of particles and the reaction ratio of volatile matter (VM) and fixed
carbon (FC) in the direction of the center of furnace under the test conditions: the
kind of coal (WT coal); the air temperature (1300 K); the oxygen ratio (0.8); and
the oxygen content (21%). This figure shows that pulverized coal, when injected
into the furnace, abruptly emits volatile matter and burns, and according to the
elevating particles temperature, O
2
is consumed and CO
2
, CO, and H
2
are generated.
As shown in this figure, as abrupt emission of volatile matter occurs under such
high temperature reaction as these test conditions, we assumed the following rate
constant model (2.28) for quantitative evaluation of emission rate of volatile matter
from the ratio of remaining volatile matter in reacting particles obtained by the first
sampling port.
x
t
=
k
(2.28)
where
x
is the reaction ratio of volatile matter,
t
is the time, and
k
is the reaction
rate constant.
E
RT
p
−
kk
=
0
exp
(2.29)
















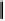








Search WWH ::

Custom Search