Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 3-3
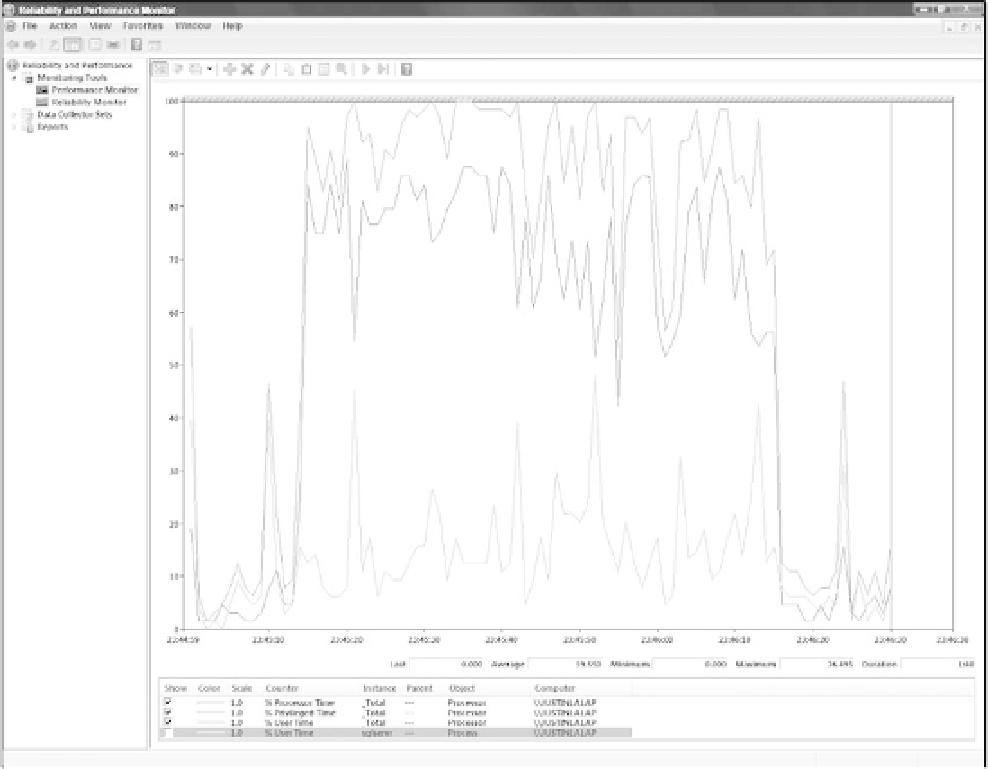
Now that you've confirmed a User Mode process is consuming the CPU time, you can drill down further
by including details from the process object. Here you'll find a counter for each running process. In this
case, adding the process % User Time for
sqlservr.exe
confirms that SQL Server is consuming the CPU
cycles. See Figure 3-4.
Similar to the way % User Mode CPU mirrored the movement on the graph of Total CPU time, the
movement of the
sqlservr.exe
process User Mode CPU time appears to be mirroring the Total User
Mode CPU time, confirming SQL Server as the principal consumer of CPU cycles during this period!
Once SQL Server has been identified as the culprit, SQL Profiler or the reports found in the Performance
Dashboard (available on Service Pack 2 and greater machines) will allow you to identify the longest
running queries/ stored procedures by CPU time. When you've found the resource intensive query, you
can work to optimize through better query design or perhaps by adding an index.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search