Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
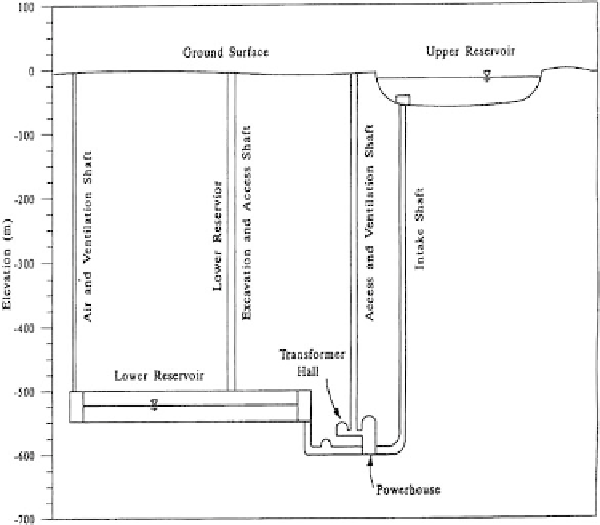
Figure 4: Proposed underground pumped-hydroelectric storage facility layout [7].
low maintenance costs. However, depending on the large capital costs involved,
UPHES might not be a viable option as other technologies begin to develop larger
storage capacities, e.g. fl ow batteries. Currently, no costs have been identifi ed for
UPHES, primarily due to the lack of facilities constructed. A number of possible
cost-saving ideas have been put forward such as using old mines for the lower
reservoir of the facility [7, 9]. Also, if something valuable can be removed to make
the lower reservoir, it can be sold to make back some of the cost.
4.2.3 Disadvantages of UPHES
UPHES incorporates the same disadvantages as PHES (large-scale required, high
capital costs, etc.), with one major exception. As stated previously (see Section 5.1),
the most signifi cant problem with PHES is its geological dependence. As the
lower reservoir is obtained by drilling into the ground and the upper reservoir is at
ground level, UPHES does not have such stringent geological dependences. The
major disadvantage for UPHES is its commercial youth. To date there is very few,
if any, UPHES facilities in operation. Therefore, it is very diffi cult to analyse and
to trust the performance of this technology.
4.2.4 Future of UPHES
UPHES has a very bright future if cost-effective excavation techniques can
be identifi ed for its construction. Its relatively large-scale storage capacities,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search