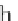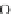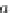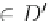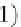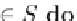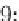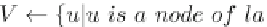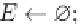Database Reference
In-Depth Information
mining is performed on the set, no frequent subgraph will be produced and as a
result the set is filtered out.
4
Mining Representative Orthogonal Graphs
In this section we will discuss ORIGAMI, an algorithm proposed by Hasan et al.
[
2
], which mines a set of
α
-orthogonal,
β
-representative graph patterns. Intuitively,
two graph patterns are
α
-orthogonal if their similarity is bounded by a threshold
α
.
A graph pattern is a
β
-representative of another pattern if their similarity is at least
β
. The orthogonality constraint ensures that the resulting pattern set has controlled
redundancy. For a given
α
, more than one set of graph patterns qualify as an
α
-
orthogonal set. Besides redundancy control, representativeness is another desired
property,
i.e.
, for every frequent graph pattern not reported in the
α
-orthogonal
set, we want to find a representative of this pattern with a high similarity in the
α
-orthogonal set.
The set of representative orthogonal graph patterns is a compact summary of the
complete set of frequent subgraphs. Given user specified thresholds
α
,
β
∈
[0, 1], the
goal is to mine an
α
-orthogonal,
β
-representative graph pattern set that minimizes
the set of unrepresented patterns.