Uruguay
Official name: Republica Oriental del Uruguay (Oriental Republic of Uruguay). Form of government: republic with two legislative houses (Senate [31]; Chamber of Representatives [99]). Head of state and government: President Tabare Ramon Vazquez Rosas (from 2005). Capital: Montevideo. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 peso uruguayo (UYU) = 100 centesimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = UYU 19.35.
Demography
Area: 68,679 sq mi, 177,879 sq km. Population (2007): 3,340,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 48.6, persons per sq km 18.8. Urban (2004): 91.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.67%; female 51.33%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 23.2%; 15-29, 22.8%; 30-44, 20.5%; 45-59, 16.1%; 60-74, 11.4%; 75-84, 4.7%; 85 and over, 1.3%. Ethnic composition (2006): white (mostly Spanish, Italian, or mixed Spanish-Italian) 87.4%; black/part-black 8.4%; Amerindian/part-Amerindian 3.0%; other/unknown 1.2%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 54.0%; Protestant 11.0%; Mormon 3.0%; Jewish 0.8%; nonreligious/atheist 26.0%; other 5.2%. Major cities (2004): Montevideo 1,269,552; Salto 99,072; Paysandu 73,272; Las Piedras 69,222; Rivera 64,426. Location: southern South America, bordering Brazil, the South Atlantic Ocean, and Argentina.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2002) within marriage 42.9%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.99. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 72.5 years; female 79.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: UYU 82,343,000,000 (tax revenue 67.9%, of which taxes on goods and services 49.1%; social security contributions 20.5%; nontax revenue 11.6%). Expenditures: UYU 89,947,000,000 (general public services 39.3%, of which public debt payments 22.6%; social security and welfare 19.0%; education 14.2%; health 7.9%; defense 5.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$7,866,-000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 1,300,000, soybeans 632,000, beef 516,000; livestock (number of live animals) 11,956,000 cattle, 9,712,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 5,702,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 35%; fisheries production (2005) 125,953. Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 1,185,000; clays 64,450; gold 3,151 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): food products 411; refined petroleum products 261; pesticides, soaps, and pharmaceuticals 106. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 8,183,000,000 (8,265,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (1,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (15,437,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 2,021,000 (1,538,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (111,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.1; average annual income per household (2005) UYU 177,264 (US$7,242). Population economically active (2006): total 1,580,400; activity rate 47.7% (participation rates: ages 14-64, 72.7%; female 43.5%; unemployed [June 2006-May 2007] 10.1%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$18,801,000,000 (US$5,640 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 594; remittances (2006) 115; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 368; official development assistance (2005) 73 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 252; remittances (2006) 3.0; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 9.8. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.8%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 77.4%; overall forest area (2005) 8.6%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$4,775,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 27.5%; machinery and appliances 16.0%; chemicals and chemical products 12.7%; food, beverages, and tobacco products 8.7%; transport equipment 7.4%). Major import sources: Argentina 22.6%; Brazil 22.6%; Venezuela 12.6%; China 7.3%; US 6.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$3,952,000,000 (beef 23.7%; hides and leather goods 8.6%; dairy products, eggs, and honey 6.9%; textiles and wearing apparel 6.8%; rice 5.5%; plastics and rubber products 5.1%). Major export destinations: Brazil 14.7%; US 13.2%; Argentina 7.6%; Russia 5.7%; Germany 4.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length (2005) 2,073 km; passenger-km 11,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 297,000,000. Roads (2006): length 8,696 km (paved 40%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 523,866; trucks and buses 84,354. Air transport (2006; PLUNA only): passenger-km 1,096,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 264,000 (79); televisions (2003): 838,000 (252); telephone landlines (2006): 987,000 (296); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,330,000 (699); personal computers (2005): 450,000 (135); total Internet users (2006): 756,000 (227); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 107,000 (32).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: 0-3 years of education 7.7%; 4-6 years 32.1%; 7-9 years 18.4%; 10-12 years 22.7%; incomplete/complete higher 19.1%. Literacy (2003): population ages 15 and over literate 98.0%; males literate 97.6%; females literate 98.4%. Health: physicians (2006) 13,705 (1 per 243 persons); hospital beds (2003) 6,661 (1 per 499 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 12.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,576 (vegetable products 76%, animal products 24%); 187% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 25,100 (army 67.7%, navy/coast guard 19.9%, air force 12.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.3%; per capita expenditure US$67.
Background
The Spanish navigator Juan Dfaz de Solfs sailed into the Rfo de la Plata in 1516. The Portuguese established Colonia in 1680. Subsequently, the Spanish established Montevideo in 1726, driving the Portuguese from theirsettlement; 50 years later Uruguay became part of the Viceroyalty of the Rfo de la Plata. It gained independence from Spain in 1811. The Portuguese regained it in 1821, incorporating it into Brazil as a province. A revolt against Brazil in 1825 led to its being recognized as an independentstate in 1828. It battled Paraguay in 1865-70. For much of World War II Uruguay remained neutral. The presidential office was abolished in 1951 and replaced with a nine-member council. The country adopted a new constitution and restored the presidential system in 1966. A military coup occurred in 1973, but the country returned to civilian rule in 1985. The 1990s brought a general upturn in the economy.
Recent Developments
The year 2007 was another one of steady economic growth for Uruguay, but the political climate was heated. GDP grew by a very solid 5.6%, and unemployment hovered around 9.5%, but inflation, which was running at 8.5%, was considerably above the central bank target range. The tax-reform program that was passed in January to help alleviate povertyand address inequality created an income tax that affected many businesspeople. The government faced increased pressure from public-sector unions demanding higher wages and from students and teachers opposed to the government’s educational-reform project. The bitter conflict with Argentina over two pulp paper plants constructed on the Uruguayan side of the Rfo Uruguay had not been resolved by mid-2008, even as one of the plants was given permission by the Uruguayan govern-mentto begin production in November 2007.
Uzbekistan
Official name: Uzbekiston Respublikasi (Republic of Uzbekistan). Form of government: republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [100]; Legislative Chamber [120]). Head of state and government: President Islam Karimov (from 1990), assisted by Prime Minister Shavkat Mirziyayev (from 2003). Capital: Tashkent (Toshkent). Official language: Uzbek. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: sum (UZS; plural sumy); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = UZS 1,310.02.
Demography
Area: 172,700 sq mi, 447,400 sq km. Population (2007): 27,372,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 158.5, persons per sq km 61.2. Urban (2006): 35.9%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.56%; female 50.44%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 32.9%; 15-29, 30.3%; 30-44, 19.6%; 45-59, 11.2%; 60-74, 4.3%; 75 and over, 1.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Uzbek 78.3%; Tajik 4.7%; Kazakh 4.1%; Tatar 3.3%; Russian 2.5%; Karakalpak 2.1%; other 5.0%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (mostly Sunni) 76.2%; Russian Orthodox 0.8%; Jewish 0.2%; nonreli-gious 18.1%; other 4.7%. Major cities (2007): Tashkent 1,959,190; Namangan 446,237; Andijon 321,622; Samarqand 312,863; Buxoro 249,037. Location: central Asia, bordering Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz-stan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Turkmenistan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.4 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.91. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 61.2 years; female 68.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:UZS 6,406,000,000,000 (taxes on income and profits 20.2%; VAT 17.3%; taxes on propertyand resources 12.2%; excise taxes 10.2%). Expenditures: UZS 6,331,000,000,000 (health and education 34.4%; social security 27.0%; national economy9.0%; centralized investments8.1%). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.6; income per household (1995) UZS 35,165 (US$1,040); sources of income (2006): self-employment and rent 55.1%, wages and salaries 29.8%, transfers 15.1%; expenditure (1995): food and beverages 71.0%, clothing and footwear 14.0%, recreation 6.0%. Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$3,343,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 5,996,305, seed cotton 3,600,300, tomatoes 1,583,571; livestock (number of live animals) 10,034,000 sheep, 7,044,600 cattle, 1,973,100 goats, 16,600 camels; roundwood 26,700 cu m, of which fuelwood 69%; fisheries production (2005) 5,425 (from aquaculture 70%). Mining and quarrying (2004): copper (metal content) 80,000; uranium (metal content) 2,016; gold 93,000 kg. Manufacturing (value of production in UZS ’000,000,000; 2006): nonferrous metals 2,705; mineral fuels 2,487; machinery and metalworking products 1,986. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 49,300,000,000 (47,000,000,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 2,699,000 (2,633,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 39,465,000 ([2004] 31,504,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 6,145,000 (5,852,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 62,500,000,000 (48,400,000,000). Population economically active (2004): total 9,945,500; activity rate of total population 38.7% (participation rates [2001]: ages 16-59 [male], 16-54 [female] 70.4%; female 44.0%; unemployed [official rate; 2006] 0.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$16,108,000,000 (US$507 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 28; remittances (2003) 600; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 53; official development assistance (2005) 206 (commitments). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 11.0%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 52.2%; overall forest area (2005) 8.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$4,395,900,000 (machinery and metalworking products 40.3%; chemicals and chemical products 15.0%; base metals 10.4%; food products 8.1%). Major import sources: Russia 27.8%; South Korea 15.2%; China 10.4%; Kazakhstan 7.3%; Germany 7.1%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$6,389,800,000 (cotton fiber 17.2%; energy products [including natural gas and crude petroleum] 13.1%; base metals [significantly gold] 12.9%; machinery and apparatus 10.1%). Major export destinations: Russia 23.7%; Poland 11.7%; China 10.4%; Turkey 7.7%; Kazakhstan 5.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 3,950 km; pas-senger-km 2,352,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 19,300,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 84,400 km (paved 85%). Vehicles (1994): passenger cars 865,300; buses 14,500. Air transport (2006): pas-senger-km 4,700,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 79,400,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 50,000 (1.9); televisions (2003): 7,232,000 (280); telephone landlines (2005): 1,794,000 (67); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 720,000 (27); total Internet users (2006): 1,700,000 (63); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 8,300 (0.3).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education/unknown 2.5%; incomplete primary education 9.0%; primary 7.3%; secondary 66.0%; higher 15.2%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 99.3%. Health (2005): physicians 70,159 (1 per 371 persons); hospital beds 135,143 (1 per 193 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 70.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,201 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 114% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 55,000 (army 73%, air force 27%); German troops 163. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.4%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Background
Genghis Khan’s grandson Shibaqan received the territory of Uzbekistan as his inheritance in the 13th century ad. His Mongols ruled over nearly 100 mainly Turkic tribes, who would eventually intermarry with the Mongols to form the Uzbeks and other Turkic peoples of central Asia. In the early 16th century, a federation of Mongol-Uzbeks invaded and occupied settled regions, including an area called Transoxania that would become the Uzbeks’ permanent homeland. By the early 19th century the region was dominated by the khanates of Khiva, Bukhara, and Quqon, all of which eventually succumbed to Russian domination. The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic was created in 1924. In June 1990 Uzbekistan became the first Central Asian republic to declare sovereignty. It achieved full independence from the USSR in 1991. During the 1990s its economy was considered the strongest in Central Asia, though its political system was deemed harsh.
Recent Developments
Throughout 2007 the Uzbek leadership sought to reverse the country’s worsening economy. In February Pres. Islam Karimov told his cabinet that Uzbekistan urgently needed to expand its output of oil and natural gas and to improve the tax-collection rate by fighting the “shadow” economy. The population had been driven to rely on this shadow economy by Kari-mov’s previous restrictions on the import of consumer goods, which the country could not produce for itself. Despite his comments, however, the import restrictions remained. Throughout the year various officials called for increased domestic and foreign investment in the Uzbek economy. In March Foreign Minister Vladimir Norov asserted that the economy was stable and growing and that foreign investment was increasing. Official statistics seemed to bear this out, as the State Committee on Statistics claimed that in 2007 GDP rose by 9.5%, while industrial output rose by 12.1% and agricultural output by 6.1%. As well, official unemployment dropped by 9.0%. In August the Uzbek authorities liquidated the Uzbek-US Zeravshan-Newmont gold-extraction venture and gave its assets to a local firm, sending a discouraging signal to potential foreign investors.
Vanuatu
Official name: Ripablik blong Vanuatu (Bislama); Republique de Vanuatu (French); Republic of Vanuatu (English). Form of government: republic with a single legislative house (Parliament [52]). Chief of state: President Kalkot Mataskelekele (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Ham Lini (from 2004). Capital: Port Vila. Official languages: Bislama; French; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: vatu (Vt); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Vt 96.21.
Demography
Area: 4,707 sq mi, 12,190 sq km. Population (2007): 226,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 48.0, persons persq km 18.5. Urban (2003): 22.8%. Sex distribution (2003): male 51.40%; female 48.60%. Age breakdown (1999): under 15, 42.2%; 15-29, 26.9%; 30-44, 17.0%; 45-59, 8.8%; 60-74, 3.7%; 75 and over, 1.4%. Ethnic composition (1999): Ni-Vanuatu (Melanesian) 98.7%; European and other Pacific Islanders 1.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 70%, of which Presbyterian 32%, Anglican 13%, Adventist 11%; Roman Catholic 13%; traditional beliefs (John Frum cargo cult) 5%; other 12%. Major towns (2004): Port Vila 36,900; Lu-ganville 12,300. Location: island group in Oceania, between the South Pacific Ocean and the Coral Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 23.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.77. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 61.0 years; female 64.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Vt 8,795,800,000 (tax revenue 83.5%, of which VAT 32.0%, tax on international trade 27.4%; nontax revenue 9.9%; foreign grants 6.6%). Expenditures: Vt 7,964,200,000 (wages and salaries 53.0%; goods and services 21.6%; transfers 11.1%; interest payments 4.4%; other [including technical assistance] 9.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$71,900,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): coconuts 315,000, copra 34,500, bananas 14,040; livestock (number of live animals) 152,000 cattle, 62,000 pigs, 12,000 goats; roundwood (2005) 119,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 76%; fisheries production (2005) 151,080. Mining and quarrying: small quantities of coral-reef limestone, crushed stone, sand, and gravel. Manufacturing (value added in Vt ’000,000; 1995): food, beverages, and tobacco 645; wood products 423; fabricated metal products 377. Energy production (consump-tionj: electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 44,000,000 (44,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (29,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.6%, in permanent crops 7.0%, in pasture 3.4%; overall forest area (2005) 36.1%. Population economically active (1999): total 76,370; activity rate of total population 40.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 75.1%; female 44.9%; unemployed [2000] 1.7%). Gross national income (2006): US$344,000,000 (US$1,556 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.7; sources of income (1985): wages and salaries 59.0%, self-employment 33.7%; expenditure (1990; Port Vila and Luganville only): food and nonalcoholic beverages 30.5%, housing and energy 20.7%, transportation 13.2%, health and recreation 12.3%, tobacco and alcohol 10.4%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 74; remittances (2006) 11; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 14; official development assistance (2005) 39. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11; remittances (2006) 18; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 0.8.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): Vt 17,645,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 25.9%; food and live animals 18.3%; mineral fuels 11.9%; chemicals and chemical products 9.6%). Major import sources (2005): Australia 41.3%; New Zealand 13.9%; Fiji 8.0%; Singapore 7.1%; France 3.4%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): Vt 5,130,000,000 (domestic exports 71.2%, of which kava 13.6%, beef 9.1%, copra 6.3%, timber 6.0%, cocoa 5.4%; reexports 28.8%). Major export destinations (2005; domestic exports): EU 34.8%; Australia 14.7%; New Caledonia 7.5%; Japan 5.2%; New Zealand 1.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 1,070 km (paved 24%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 2,600; trucks and buses 4,400. Air transport (2005; Air Vanuatu only): passenger-km 220,861,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,647,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 2,000 (9.5); televisions (2004): 2,700 (13); telephone landlines (2005): 7,000 (32); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 13,000 (59); personal computers (2005): 3,000 (14); total Internet users (2005): 8,000 (38); broadband Internet subscribers (2004): 20 (0.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 18.0%; incomplete primary education 20.6%; completed primary 35.5%; some secondary 12.2%; completed secondary 8.5%; higher 5.2%, of which university 1.3%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 74%. Health (2004): physicians 29 (1 per 7,138 persons); hospital beds (2003) 397 (1 per 511 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 55.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,025 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 113% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none; in 2005 Vanuatu had a paramilitary force of about 200.
Background
The islands of Vanuatu were inhabited for at least 3,000 years by Melanesian peoples before being discovered in 1606 by the Portuguese. They were rediscovered by French navigator Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 and then explored by English mariner Capt. James Cook in 1774 and named the New Hebrides. Sandalwood merchants and European missionaries arrived in the mid-19th century; they were followed by British and French cotton planters. Control of the islands was sought by both the French and British, who agreed in 1906 to form a condominium government. During World War II a major Allied naval base was on Espfritu Santo; the island group escaped Japanese invasion. The New Hebrides became the independent Republic of Vanuatu in 1980. Much of the nation’s housingwas ravaged bya hurricane in 1987.
Recent Developments
Vanuatu enjoyed continued political stability and a steady 3% rate of economic growth in 2007. The value of primary commodities (coconut oil, kava, copra, and beef), which contributed about 20% to total exports, increased with the resumption of kava exports, and growing demand for copra was expected to generate higher incomes for the 65% of the population that depended on agriculture. The commodities sector was also expected to grow as a result of the government’s successful use of coconut-oil-based biofuel for power generation and the planned use of biofuel in the government’s vehicle fleet. Vanuatu’s tourism was growing rapidly as a result of investment in hotels and increased airline services from major markets.
Vatican City State
Official name: State of the Vatican City (Holy See). Form of government: ecclesiastical. Chief of state: Pope Benedict XVI (from 2005). Head of government: Secretary of State Tarcisio Cardinal Bertone (from 2006). Capital: Vatican City. Languages: Italian; Latin. Religion: Roman Catholic. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 0.17 sq mi, 0.44 sq km. Population: (2007): 930. Density: (2007): persons per sq mi 5,471, persons per sq km 2,114. Location: southern Europe, within the commune of Rome, Italy. Annual budget: US$209,000,000. Industries: banking and finance; printing; production of a small amount of mosaics and uniforms; tourism.
Background
Vatican City, the independent papal state, is the smallest independent state in the world. Its medieval and Renaissance walls form its boundaries except on the southeast, at St. Peter’s Square. Within the walls is a miniature nation, with its own diplomatic missions, newspaper, post office, radiostation, banking system, army of more than 100 Swiss Guards, and publishing house. Extraterritoriality of the state extends to Castel Gandolfo, summer home of the Pope, and to several churches and palaces in Rome proper. Its independent sovereignty was recognized in the Lateran Treaty of 1929. The pope has absolute executive, legislative, and judicial powers within the city. He appoints the members of the Vatican’s government organs, which are separate from those of the Holy See. The state’s many imposing buildings include St. Peter’s Basilica, the Vatican Palace, and the Vatican Museums. Frescoes by Michelangelo and Pinturicchio in the Sistine Chapel and Raphael’s Stanze are also there. The Vatican Library contains a priceless collection of manuscripts from the pre-Christian and Christian eras.
Recent Developments
There was an intense calendar of foreign initiatives in 2007, which included formal visits from US Pres. George W. Bush and British Prime Minister Tony Blair, as well as visits by the presidents of both Israel and the Palestinian Authority to Vatican City. The plight of Roman Catholics in China was also a focus of Vatican attention, with calls for Beijing to restrain action against priests not affiliated with the state-recognized Chinese Patriotic Catholic Association. Finally, stronger ties were pursued with the Muslim faith, adherents of which were announced in March 2008 to outnumber Roman Catholics for the first time in history.
Venezuela
Official name: Republica Bolivariana de Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela). Form of government: federal multiparty republic with a unicameral legislature (National Assembly [167]). Head of state and government: President Hugo Chavez Frias (from 2002). Capital: Caracas. Official language: Spanish; 31 indigenous Indian languages were made official in May 2002. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 bolivar fuerte (BsF) = 100 centimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = BsF 2,147.30 (the bolivar fuerte replaced the bolivar [Bs] 1 Jan 2008, at the rate of 1 BsF = Bs 1,000).
Demography
Area: 353,841 sq mi, 916,445 sq km. Population (2007): 26,024,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 73.5, persons per sq km 28.4. Urban (2005): 93.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.52%; female 50.48%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 32.1%; 15-29, 26.9%; 30-44, 20.5%; 45-59, 13.2%; 60-74, 5.5%; 75-84, 1.5%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 63.7%; local white 20.0%; local black 10.0%; other white 3.3%; Amerindian 1.3%; other 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 84.5%; Protestant 4.0%; nonreligious/other 11.5%. Major cities (urban agglomerations) (2001/2005): Caracas 1,836,000 (2,913,000); Maracaibo 1,609,000 (2,255,000); Valencia 1,196,000 (2,451,000); Barquisimeto 811,000 (1,029,000); Ciudad Guayana 629,000. Location: northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, the North Atlantic Ocean, Guyana, Brazil, and Colombia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 21.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.1 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.59. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.0 years; female 76.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: Bs 117,326,000,000,000 (petroleum income 52.9%, of which royalties 37.5%, taxes 13.0%; nonpetroleum income 47.1%, of which VAT 22.4%). Expenditures: Bs 117,255,000,000 (current expenditure 75.0%; development expenditure 22.8%; other 2.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$29,317,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 8,895,000, corn (maize) 2,375,000, rice 1,115,000; livestock (number of live animals) 16,615,000 cattle, 110,000,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 4,906,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 78%; fisheries production (2005) 492,210 (from aquaculture 5%). Mining and quarrying (2005): iron ore (metal content) 13,200,000; bauxite 5,900,000; phosphate rock (gross weight) 392,000. Manufacturing (value added in Bs ’000,000,000; 2004): food products 8,122; iron and steel 3,022; refined petroleum 2,890. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 99,200,000,000 (73,400,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 8,200,000 ([2004] none); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 1,175,000,000 ([2004] 373,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 56,645,000 (21,738,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 24,975,000,000 (24,975,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 641; remittances (2006) 300; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,320. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,281; remittances (2006) 253; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 732. Households. Average household size (2005) 4.5; average annual household income (2006) Bs 13,848,000 (US$6,450); expenditure (2002): food and nonalcoholic beverages 27.3%, housing and energy 13.5%, transport 10.5%, expenditures in cafes and hotels 9.0%. Gross national income (2006): US$177,866,000,000 (US$6,540 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 12,379,700; activity rate of total population 45.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 68.7%; female 38.6%; unemployed [July 2006-June 2007] 9.4%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.9%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 20.7%; overall forest area (2005) 54.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$32,226,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 20.7%; road vehicles and parts 14.5%; chemicals and chemical products 10.4%). Major import sources (2005): US 31.6%; Colombia 11.0%; Brazil 9.1%; Mexico 6.9%; Panama 3.9%. Exports (2006): US$65,210,000,000 (petroleum [all forms] 89.6%; iron and steel [all forms] 2.7%; aluminum [all forms] 2.1%). Major export destinations (2005): US 50.9%; Puerto Rico/US Virgin Islands 7.8%; Netherlands Antilles 7.2%; Canada 2.4%; Colombia 1.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2005) 768 km; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 22,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 96,200 km (paved 34%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 2,466,000; trucks and buses 677,000. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 2,578,700,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,100,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 1,981,000 (80); televisions (2004): 5,000,000 (201); telephone landlines (2006): 4,217,000 (164); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 18,790,000 (733); personal computers (2005): 2,475,000 (98); total Internet users (2006): 4,160,000 (162); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 538,000 (21).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of head-of-household population having: no formal schooling 10.2%; primary education or less 38.5%; some secondary 36.9%; completed secondary/higher 14.4%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 93.0%; males literate 93.3%; females literate 92.7%. Health (2003): physicians 35,756 (1 per 722 persons); hospital beds 74,866 (1 per 345 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 23.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,417 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 131% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 82,300 (army 41.3%, navy 22.2%, air force 8.5%, national guard 28.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$60.
Background
In 1498 Christopher Columbus sighted Venezuela; in 1499 the navigators Alonso de Ojeda, Amerigo Vespucci, and Juan de la Cosa traced the coast. A Spanish missionary established the first European settlement at Cumana c. 1520. In 1718 it was included in the Viceroyalty of New Granada and was made a captaincy general in 1731. Venezuelan Creoles led by Francisco de Miranda and Simon Bolivar spearheaded the South American independence movement, and though Venezuela declared independence from Spain in 1811, that status was not assured until 1821. Military dictators generally ruled the country from 1830 until the overthrow of Marcos Perez Jimenez in 1958. A new constitution adopted in 1961 marked the beginning of democracy. As a founding member of OPEC, it enjoyed relative economic prosperity from oil production during the 1970s, and its economy has remained dependent on the world petroleum market. The leftist president Hugo Chavez promulgated a new constitution in 1999, and he was reelected in 2002; a period of great political and economic tumult ensued.
Recent Developments
In November 2007 Venezuela’s National Assemblyap-proved modifications to the 1999 constitution that would increase the power of the national executive and central government. One of the changes would allow for the indefinite reelection of the president, and another would end the central bank’s autonomy. Venezuela’s GDP grew 23.6% in 2007 and for the first time exceeded US$200 billion. The nonpetroleum sector grew at a rate of 9.5% in 2007, though the petroleum sector contracted by 4.2%. Inflation between the beginning of 2007 and April 2008 reached 32.7%, one of the higher rates among less-developed economies. Petroleum remained central to Venezuela’s economy. Over the past decade reserves of sweet crude had declined, and heavy-oil projects in the Orinoco Basin had become more important. In May 2007 Pres. Hugo Chavez unilaterally modified the contracts under which foreign companies exploited four heavy-oil projects. The administration of US Pres. George W. Bush was frustrated over the increasing volume of cocaine trafficked through Venezuela. In Moscow Chavez proclaimed, “Either we break US imperialism or US imperialism will definitely break the world.”
Vietnam
Official name: Cong Hoa Xa Hoi Chu Nghia Viet Nam (Socialist Republic of Vietnam). Form of government: socialist republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [493]). Head of state: President Nguyen Minh Triet (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung (from 2006). Capital: Hanoi. Official language: Vietnamese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 dong (VND) = 10 hao = 100 xu; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = VND 16,844.50.
Demography
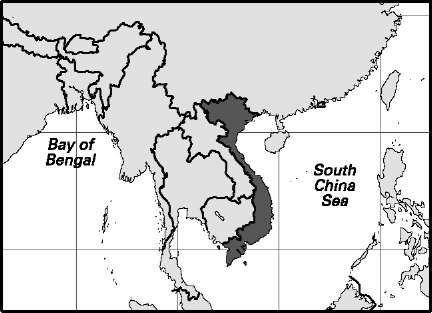
Area: 127,882 sq mi, 331,212 sq km. Population (2007): 87,375,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 683.2, persons per sq km 263.8. Urban (2005): 27.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.14%; female 50.86%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 27.9%; 15-29, 30.1%; 30-44, 22.2%; 45-59, 12.1%; 60-74,5.4%; 75-84,1.9%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (1999): Vietnamese 86.2%; Tho (Tay) 1.9%; Montagnards 1.7%; Thai 1.7%; Muong 1.5%; Khmer 1.4%; Nung 1.1%; Miao (Hmong) 1.0%; Dao 0.8%; other 2.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Buddhist 48%; New-Religionist (mostly Cao Dai and Hoa Hao) 11%; traditional beliefs 10%; Roman Catholic 7%; Protestant 1%; nonreligious/atheist 20%; other 3%. Major cities (urban agglomeration) (2004/2005): Ho Chi Minh City 3,452,100 (5,065,000); Hanoi 1,420,400 (4,164,000); Haiphong 591,100 (1,873,000); Da Nang 459,400. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering China, the Gulf of Tonkin, the South China Sea, the Gulf of Thailand, Cambodia, and Laos.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.94. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.8 years; female 73.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:VND 166,900,000,000,000 (tax revenue 71.2%, of which VAT 24.6%, corporate taxes 22.3%, taxes on trade 19.8%; nontax revenues 27.6%; grants 1.2%). Expenditures: VND 190,200,000,000,000 (current expenditures 61.9%, of which social services 28.3%, economic services 5.5%, interest payment 3.2%; capital expenditures 38.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$16,513,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$56,583,000,000 (US$656 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 35,826,000, sugarcane 15,679,000, cassava 7,714,000; livestock (number of live animals) 26,855,300 pigs, 6,510,800 cattle, 2,921,000 buffalo, 64,380,000 ducks; roundwood (2005) 31,587,212 cu m, of which fuelwood 83%; fisheries production (2005) 3,367,200 (from aquaculture 43%); aquatic plants production (2005) 30,000 (from aquaculture 100%). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock 800,000; tin (metal content) 3,500. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2000): food products 736; cement, bricks, and pottery 418; wearing apparel 376. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 53,320,000,000 ([2004] 46,029,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 32,400,000 (14,900,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 131,200,000 ([2004] negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 335,000,000 (11,358,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 6,342,000,000 (6,342,000,000). Population economically active (2004): total 43,242,000; activity rate 52.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 77.7%; female 49.0%; unemployed [2006] 4.8%). Households (2004). Average household size 4.4; average annual income per household (1997-98) VND 15,494,000 (US$1,165); sources of income: wages and salaries 32.7%, self-employment 27.0%, agriculture 22.6%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 53.5%, transportation and communications 10.8%, household furnishings 9.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,880; remittances (2006) 4,800; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,516; official development assistance (2005) 1,887 (commitments). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 21.2%, in permanent crops 7.5%, in pasture 2.1%; overall forest area (2005) 39.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$31,500,000,000 (machinery equipment [including aircraft] 17.5%; petroleum products 11.5%; iron and steel 8.3%; garments and leather 7.2%; cloth 6.0%). Major import sources (2006): China 16.5%; Singapore 14.0%; Taiwan 10.7%; Japan 10.5%; South Korea 8.6%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$26,500,000,000 (crude petroleum 22.1%; garments 17.1%; footwear 10.5%; fish, crustaceans, and mollusks 9.4%; electronic products 4.1%). Major export destinations (2006): US 19.7%; Japan 13.1%; Australia 9.2%; China 7.6%; Singapore 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 2,600 km; passenger-km 4,580,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,948,400,000. Roads (2004): total length 137,359 km (paved 44%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars, trucks, and buses 600,000. Airtransport(2005-06): passenger-km 11,787,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 251,100,000. Communications, in total units(units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 1,530,000 (19); televisions (2003): 15,938,000 (197); telephone landlines(2005): 15,845,000(188); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 9,593,000 (114); personal computers (2005): 1,174,000 (14); total Internet users (2005): 10,711,000(130); broadband Internetsubscribers (2005): 210,000(2.5).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 18 and over having: no formal education 9.0%; primary education 29.2%; lower secondary 32.5%; upper secondary 24.9%; incomplete/complete higher 4.3%; advanced degree 0.1%. Literacy (2003): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 94.0%; males literate 95.8%; females literate 92.3%. Health (2006): physicians 52,800 (1 per 1,633 persons); hospital beds 198,400 (1 per 434 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 26.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,892 (vegetable products 87%, animal products 13%); 157% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 455,000 (army 90.5%, navy 2.9%, air force 6.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 6.0%; per capita expenditure US$38.
Background
A distinct Vietnamese group began to emerge c. 200 bc in the independent kingdom of Nam Viet, which was annexed to China in the 1st century bc. The Vietnamese were under continuous Chinese control until the 10th century ad. The southern region was gradually overrun by Vietnamese from the north in the late 15th century. The area was divided into two parts in the early 17th century, with the northern part known as Tonkin and the southern part as Cochin China. In 1802 the northern and southern parts of Vietnam were unified under a single dynasty.
Following several years of attempted French colonial expansion in the region, the French captured Saigon in 1859 and later the rest of the area, controlling it until World War II. The Japanese occupied Vietnam in 1940-45 and declared it independent at the end of World War II, a move the French opposed. The French and Vietnamese fought the First Indochina War until French forces with US financial backing were defeated at Dien Bien Phu in 1954; evacuation of French troops ensued.
Following an international conference at Geneva, Vietnam was partitioned along the 17th parallel, with the northern part under Ho Chi Minh and the southern part under Bao Dai; the partition was to be temporary, but the reunification elections scheduled for 1956 were never held. Bao Dai declared the independence of South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam), while the Communists established North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam). The activities of North Vietnamese guerrillas and pro-communist rebels in South Vietnam led to US intervention and the Vietnam War. A cease-fire agreement was signed in 1973, and US troops were withdrawn. The civil war soon resumed, and in 1975 North Vietnam invaded
South Vietnam and the South Vietnamese government collapsed. In 1976 the two Vietnams were united as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. From the mid-1980s the government enacted a series of economic reforms and began to open up to Asian and Western nations. During the 1990s the US moved to normalize relations with it.
Recent Developments
In January 2007 Vietnam became the World Trade Organization’s 150th member, and in October the country was elected to nonpermanent membership on the UN Security Council. These events set the context for an intense year of diplomacy. Pres. Nguyen Minh Triet visited Beijing in May, resulting in a joint communique that stressed long-term trade and economic cooperation and addressed territorial issues. In a speech delivered in California in June, Triet promoted bilateral trade and investment and reached out to the Vietnamese-American community. Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung visited India in July to cement a strategic partnership, then focused on trade and investment the following month on trips to Indonesia, the Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar (Burma), and Brunei. In September Dung made stops in Russia, Poland, and the Czech Republic before addressing the UN General Assembly. Meanwhile President Triet attended the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit in Australia and made a side visit to New Zealand.
Virgin Islands (US)
Official name: Virgin Islands of the United States. Political status: organized unincorporated territory of the US with one legislative house (Senate [15]). Chief of state: US President George W. Bush (from 2001). Head of government: Governor John deJongh, Jr. (from 2007). Capital: Charlotte Amalie. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
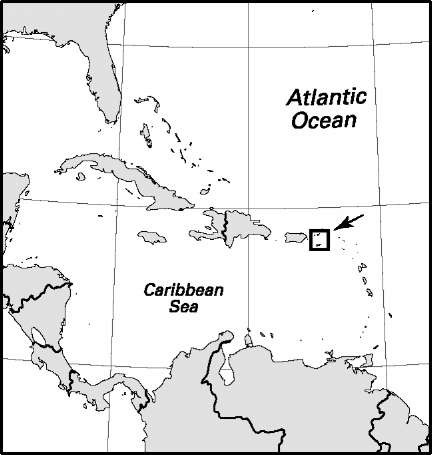
Area: 136 sq mi, 353 sq km. Population (2007): 113,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 830.9, persons per sq km 320.1. Urban (2006): 94.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 47.71%; female 52.29%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 22.4%; 15-29, 18.8%; 30-44, 20.0%; 45-59, 21.3%; 60-74, 13.4%; 75 and over, 4.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 76.2%; white 13.1%; mixed race 3.5%; Asian 1.1%; other 6.1%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 96.3%, of which Protestant 51.0% (including Anglican 13.0%), Roman Catholic 27.5%, independent Christian 12.2%; nonreligious 2.2%; other 1.5%. Major towns (2000): Charlotte Amalie 11,004 (urban agglomeration 18,914); Christiansted 2,637; Frederiksted 732. Location: northeastern Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.0 (world avg. 20.3); (1998) within marriage 30.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.17. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.2 years; female 83.1 years.
National economy
Budget. Revenue (2006): US$718,700,000 (income tax 54.1%; corporate taxes 25.8%). Expenditures (2004): US$592,000,000 (direct federal expenditures 100%). Public debt (2005-06): US$1,150,-000,000. Production. Agriculture, forestry, fishing (value of sales in US$’000; 2002): ornamental plants and other nursery products 799, livestock and livestock products 775 (notably cattle and calves and hogs and pigs), vegetables 340 (notably tomatoes and cucumbers); livestock (number of live animals; 2006) 8,000 cattle, 4,000 goats, 3,200 sheep; fisheries production (2005) 1,269 metric tons. Mining and quarrying: sand and crushed stone for local use. Manufacturing (value of sales in US$’000; 2002): beverages and tobacco products 44,766; stone, clay, and glass products 32,939; computer and electronic products 22,875. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 996,100,000 (926,400,000); coal (metric tons; 2002) none (290,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2002) none (149,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2002) 18,801,000 (1,588,000). Households (2004). Average household size 2.5; average annual income per household US$37,201; sources of income (1999): wages and salaries 73.9%, transfers 10.0%, self-employment 8.8%; expenditures (2001): housing 38.8%, food and beverages 12.5%, transportation 11.1%, education and communications 7.1%. Population economically active (2004): total 44,299; activity rate of total population 39.7% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 53.1%; female 52.7%; unemployed [2007] 5.9%). Gross domestic product (at 2006 market prices): US$3,080,000,000 (US$27,300 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 1,466. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporarycrops 6%, in permanentcrops 3%, in pasture 9%; overall forest area (2005) 28%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$10,243,300,000 (foreign crude petroleum 85.3%; other [significantly manufactured goods] 14.7%). Major import sources: US 11.3%; other countries (mostly Venezuela) 88.7%. Exports (2005): US$10,476,300,000 (refined petroleum 89.5%; unspecified [significantly rum and watches] 10.5%). Major export destinations: US 95.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 1,257 km (paved 95%). Vehicles (2006): registered vehicles 69,330. Cruise ships (2006-07): passenger arrivals I,900,253. Air transport (2006-07; St. Croix and St. Thomas airports only): passenger arrivals 676,039. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 15,000 (134); televisions (2000): 65,000 (594); telephone landlines (2006): 65,000 (576); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 80,000 (713); total Internet users (2005): 30,000 (268); broadband Internetsubscribers (2005): 3,000 (27).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 0.5%; incomplete primary to incomplete secondary 39.1%; complete secondary 29.8%; some higher II.9%; undergraduate 13.8%; advanced degree 4.9%. Health (2005): physicians 165 (1 per 680 persons); hospital beds (main hospitals on St. Thomas and St. Croix only ) 320 (1 per 350 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 7.9.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): no domestic military force is maintained; the US is responsible for defense and external security.
Background
The Virgin Islands of the US probably were originally settled byArawak Indians, but they were inhabited by the Caribs when Christopher Columbus landed on St. Croix in 1493. St. Croix was occupied by the Dutch, English, French, and Spanish and was at one time owned by the Knights of Malta. Denmark occupied St. Thomas, St. John, and St. Croix and established them as a Danish colony in 1754. The US purchased the Danish West Indies in 1917 for US$25 million and changed the name to the Virgin Islands. They were administered by the US Department of the Interior from 1931. In 1954 the Organic Act of the Virgin Islands created the current governmental structure, and in 1970 the first popularly elected governor took office. The area suffered extensive damage by hurricanes in 1995.
Recent Developments
The US Virgin Islands Water and Power Authority in January 2007 presented a US$1.2 billion, 10-year plan designed to break its dependence on oil-fired generation by substituting increasing amounts of renewable energy. Officials called for 20% of the dependency’s fuel needs to be met using renewable energy sources, including wind and solar energy and, after a March 2008 government visit to Nevis, geo-thermal operations.
Yemen
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-Yamaniyah (Republic of Yemen). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Consultative Council [111]; House of Representatives [301]). Head of state: President Major General ‘Ali ‘Abdallah Salih (from 1990). Head of government: Prime Minister ‘Ali Muhammad Mujawar (from 2007). Capital: Sanaa. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Yemeni rial (YR) = 100 fils; valuation (1 Jul 2008): US$1 = YR 198.95.
Demography
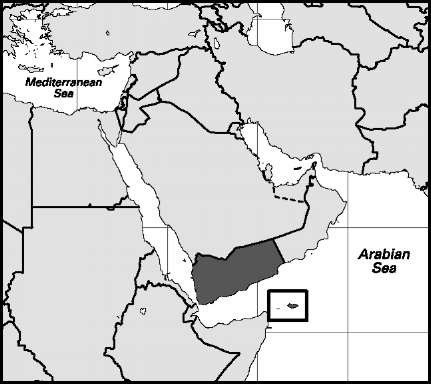
Area: 203,891 sq mi, 528,076 sq km. Population (2007): 22,231,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 109.0, persons per sq km 42.1. Urban (2006): 28.6%. Sex distribution (2004): male 50.99%; female 49.01%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 45.6%; 15-29, 29.5%; 30-44,12.8%; 45-59, 6.9%; 60-74, 3.8%; 75-84,1.0%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 92.8%; Somali 3.7%; black 1.1%; Indo-Pakistani 1.0%; other 1.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim, nearly 100%, of which Sunni 58%, Shi’i 42%. Major cities (2004): Sanaa 1,707,586; Aden 589,419; Ta’izz (2001) 450,000; Al-Hudaydah (2001) 425,000; Al-Mukalla (2001) 165,000. Location: the Middle East, bordering Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, and Saudi Arabia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 42.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 34.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.58. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 60.2 years; female 64.1 years.
National economy
6.0%). Expenditures: YR 1,405,000,000,000 (transfers and subsidies 31.2%; wages and salaries 26.0%; interest on debt 6.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,717,000,000. Population economically active (2004): total 4,244,000; activity rate of total population 21.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 41.8%; female 12.1%; unemployed 16.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sorghum 401,843, potatoes 226,366, tomatoes 211,734, khat (qat) 147,444 (khat’s (qat’s) agricultural and nonagricultural contribution is about 10% of total GDP; khat(qat) cultivation employs nearly 15% of the labor force); livestock (number of live animals) 8,197,024 sheep, 8,041,955 goats, 1,463,700 cattle, 347,145 camels; roundwood 366,885 cu m, of which fuelwood 100%; fisheries production 229,660. Mining and quarrying (2005): salt 90,000; gypsum 38,000. Manufacturing (value added in YR ’000,000; 2006): food and beverages 121,761; cement, bricks, and ceramics 34,294; tobacco 26,556. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 5,336,900,000 (3,624,500,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 133,000,000 ([2005] 31,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 2,804,000 (4,047,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 38,000,000,000 (n.a.). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporarycrops 2.9%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 30.4%; overall forest area (2005) 1.0%. Gross national income (2006): US$17,083,000,000 (US$786 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 7.1; income per household (1998) YR 29,035 (US$217); expenditures (1999): food and nonalcoholic beverages 43.8%, tobacco and khat (qat) 14.8%, housing and energy 13.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 181; remittances (2005) 1,283; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 24; official development assistance (2005) 336. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 167; remittances (2005) 109.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): YR 1,043,119,407,000 (crude and refined petroleum 24.8%; food and live animals 19.2%; machinery and apparatus 13.7%; base and fabricated metals 10.2%; transport equipment 9.7%). Major import sources: UAE 22.0%; Saudi Arabia 9.7%; Switzerland 9.1%; China 7.3%; Kuwait 6.7%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): YR 1,316,197,658,000 (crude and refined petroleum 91.7%; food and live animals 3.9%, of which fish 2.0%; machinery and apparatus 1.3%). Major export destinations: India 24.0%; China 22.5%; Thailand 14.4%; UK 5.9%; US 5.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2006): total length 71,300 km (paved 9%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 522,437; trucks and buses 506,766. Air transport (2002): pas-senger-km 1,598,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2005) 67,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2006): 236,000 (11); televisions (2003): 6,780,000 (359); telephone landlines (2005): 968,000 (47); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,978,000(139); personal computers (2005): 300,000 (14); total Internet users (2006): 270,000 (13).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling 46.0%; reading and writing ability 31.5%; primary education 12.0%; secondary 7.2%; higher 3.3%. Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 53.0%; males literate 74.7%; females literate 52.4%. Health (2006): physicians 5,980 (1 per 3,495 persons); hospital beds 14,413 (1 per 1,450 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 59.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,926 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 109% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 66,700 (army 90.0%, navy 2.5%, air force 7.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 7.0%; per capita expenditure US$50.
Background
Yemen was the home of ancient Minaean, Sabaean, and Himyarite kingdoms. The Romans invaded the region in the 1st century ad. In the 6th century it was conquered by Ethiopians and Persians. Following conversion to Islam in the 7th century, it was ruled nominally under a caliphate. The Egyptian Ayyubid dynasty ruled there from 1173 to 1229, after which the region passed to the Rasulids. From 1517 through 1918, the Ottoman Empire maintained varying degrees of control, especially in the northwestern section. A boundary agreement was reached in 1934 between the northwestern imam-controlled territory, which subsequently became the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen), and the southeastern British-controlled territory, which subsequently became the People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen (South Yemen). Relations between the two Yemens remained tense and were marked by conflict throughout the 1970s and 1980s. Reaching an accord, the two officially united as the Republic of Yemen in 1990. Its 1993 elections were the first free, multiparty general elections held in the Arabian Peninsula, and they were the first in which women participated. In 1994, after a two-month civil war, a new constitution was approved.
Recent Developments
According to the UN High Commissioner for Refugees, more than 20,000 people entered Yemen illegally from East Africa in 2007, leaving poverty and war behind, and at least 400 died along the way, with as many missing and feared dead. The number entering in the first two months of 2008 alone topped 8,700. A mosque was firebombed in April 2007 by two unidentified attackers, who doused people with gasoline before lighting them on fire. In July a suicide bomber attacked a convoy of Spanish tourists, killing seven Spaniards and two Yemenis at the Queen of Sheba temple in Marib. Yemen continued to work with US special forces based in Djibouti to fight al-Qaeda, members of which were thought to travel throughout Yemen.
Zambia
Official name: Republic of Zambia. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [158]). Head of state and government: President Rupiah Banda (acting; from 2008). Capital: Lusaka. Official language: English. Official religion: none; however, in 1996 Zambia was declared a Christian nation per the preamble of a constitutional amendment. Monetary unit: 1 Zambian kwacha (K) = 100 ngwee; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = K 3,210.00.
Demography
Area: 290,585 sq mi, 752,612 sq km. Population (2007): 11,477,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 39.5, persons per sq km 15.2. Urban (2006): 36.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.75%; female 50.25%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 46.2%; 15-29, 30.6%; 30-44,13.4%; 45-59, 6.1%; 60-74, 3.0%; 75-84,0.6%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Bemba 21.5%; Tonga 11.3%; Lozi 5.2%; Nsenga 5.1%; Tumbuka 4.3%; Ngoni 3.8%; Chewa 2.9%; other 45.9%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 82.4%, of which Roman Catholic 29.7%, Protestant (including Anglican) 28.2%, independent Christian 15.2%, unaffiliated Christian 5.5%; traditional beliefs 14.3%; Baha’i 1.8%; Muslim 1.1%; other 0.4%. Major cities (2000): Lusaka 1,084,703; Ndola 374,757; Kitwe 363,734; Kabwe 176,758; Chingola 147,448. Location: southern Africa, bordering Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Namibia, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 41.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 21.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.39. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 38.0 years; female 38.2 years.
National economy
Tax 18.0%, VAT 10.9%, excise taxes 5.6%; nontax revenue 1.4%). Expenditures: K 9,248,000,000,000 (current expenditures 77.1%; capital expenditures 20.3%; other 2.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 2,700,000, cassava 950,000, corn (maize) 865,000, fresh-cut flowers (value of sales; 2000) US$21,000,000; livestock (number of live animals) 2,600,000 cattle, 1,270,000 goats, 340,000 pigs; roundwood (2005) 8,053,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 90%; fisheries production (2005) 70,125 (from aquaculture 7%). Mining and quarrying (2005): copper (metal content) 447,000; cobalt (metal content) 9,300; amethyst 1,100,000 kg. Manufacturing (2005): cement 435,000; refined copper 399,000; vegetable oils (2001) 11,800. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 8,512,000,000 (8,281,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 233,000 (153,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (3,938,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 490,000 (528,000). Households. Average household size (2005) 5.1; average annual income per household (2004) K 6,024,360 (US$1,261); expenditure (1993-94): food, beverages, and tobacco 57.1%, transportation and communications 9.6%, housing and energy 8.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 164; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 165; official development assistance (2005) 945. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 94; remittances (2006) 24. Population economically active (2000): total 3,165,200; activity rate of total population 32.0% (participation rates: ages 12-64, 55.8%; female 41.3%; unemployed 12.7%). Gross national income (2006): US$10,339,000,000 (US$884 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,085,000,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.1%, in permanent crops 0.04%, in pasture 40.4%; overall forest area (2005) 57.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$2,017,000,000 (chemicals and chemical products 16.4%; nonelectrical machinery and equipment 16.2%; printed matter 11.8%; petroleum [all forms] 9.5%; road vehicles 7.6%). Major import sources:South Africa 46.2%; UK 14.2%; Saudi Arabia 7.1%; Zimbabwe 6.0%; France 2.9%. Exports (2004): US$1,461,000,000 (copper 43.1%; cobalt 15.9%; food and live animals 9.5%; cotton 8.2%). Major export destinations: South Africa 25.6%; UK 17.0%; Switzerland 16.0%; Tanzania 7.4%; Democratic Republic of the Congo 7.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (1998): length (2005) 2,173 km; passenger-km 586,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 702,000,000. Roads (2001): total length 91,440 km (paved 22%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 157,000; trucks and buses 81,000. Air transport (2006; Zambian Airways Limited only): passenger-km 56,609,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 55,000 (5); televisions (2003): 551,000 (51); telephone landlines (2006): 93,000 (7.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,663,000 (140); personal computers (2005): 131,000 (11); total Internet users (2006): 500,000 (42); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,300 (0.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001-02). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 14.7%; some primary education 33.4%; completed primary 19.7%; some secondary 22.0%; completed secondary 5.9%; higher 4.3%. Literacy (2006): population ages 15 and over literate 68.0%; males literate 76.3%; females literate 59.8%. Health: physicians (2004) 1,264 (1 per 8,672 persons); hospital beds (2004) 21,924 (1 per 500 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 100.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,642 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 90% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 15,100 (army 89.4%; air force 10.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$4.
Background
Archaeological evidence suggests that early humans roamed present-day Zambia one to two million years ago. Ancestors of the modern Tonga tribe reached the region early in the 2nd millennium bc, but other modern peoples from Congo and Angola reached the country only in the 17th and 18th centuries. Portuguese trading missions were established early in the 18th century. Emissaries of Cecil Rhodes and the British South Africa Co. concluded treaties with most of the Zambian chiefs during the 1890s. The company administered the region known as Northern Rhodesia until 1924, when it became a British protectorate. It was part of the Central African Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasa-land in 1953-63. In 1964 Northern Rhodesia became the independent republic of Zambia. A constitutional amendment was passed in 1990 allowing opposition parties; the following years were filled with political tension.
Recent Developments
In January 2007 Pres. Levy Mwanawasa launched Zambia’s Fifth National Development Plan, which focused on improving health, education, and the infrastructure and encouraging foreign investment. In April China made Zambia a loan of US$39 million to repair flood damage, and in May Zambia received US$50 million from Western donors to help clean up pollution created by mining. In June the United Kingdom agreed to provide about US$800 million to relieve poverty over the next decade. The country’s decaying railway system received US$250 million from the UK, South Africa, and the US to connect copper mines in Zambia and eventually to link Zambia’s railway system with Angola’s Benguela Railway, while in October Japan agreed to help further improve Zambia’s infrastructure.
Zimbabwe
Official name: Republic of Zimbabwe. Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [93]; House of Assembly [210]). Head of state and government: President Robert Mugabe (from 1987). Capital: Harare. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 (new third) Zimbabwe dollar (Z$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Z$1,081,091.75 (the [new third] Z$ replaced the [new second] Z$ 6 Sep 2007, at the rate of 1 [new third] Z$ = [new second] Z$1,200; the [new second] Z$ had replaced the [old] Z$ on 1 Aug 2006, at the rate of 1 [new second] Z$ = [old] Z$1,000; in September 2007 the black-market value was nearly [new third] Z$250,000 = US$1).
Demography
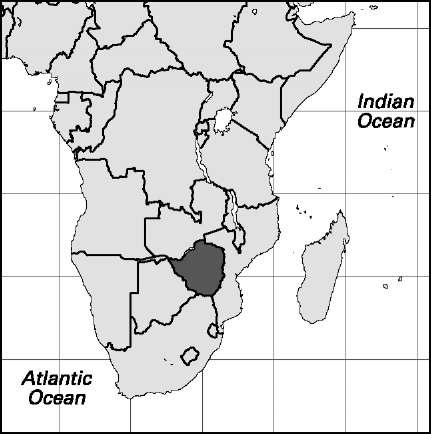
Area: 150,872 sq mi, 390,757 sq km. Population (2007): 12,311,000. Density (2007): persons persq mi 81.6, persons per sq km 31.5. Urban (2006): 36.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.95%; female 50.05%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.6%; 15-29, 35.2%; 30-44, 14.5%; 45-59, 7.7%; 60-74, 3.8%; 75 and over, 1.2%. Ethnic composition (2003): Shona 71%; Ndebele 16%; other African 11%; white 1%; mixed race/Asian 1%. Religious affiliation (2005): African independent Christian 38%; traditional beliefs 25%; Protestant 14%; Roman Catholic 8%; Muslim 1%; other (mostly unaffiliated Christian) 14%. Major cities (2002): Harare 1,444,534; Bulawayo 676,787; Chitungwiza 321,782; Mutare 170,106; Gweru 141,260. Location: southern Africa, bordering Mozambique, South Africa, Botswana, Namibia, and Zambia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 28.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 21.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.18. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 40.2 years; female 38.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:(old)Z$8,071,700,000,000 (tax revenue 96.2%, of which income tax 50.5%, sales tax 29.4%, customs duties 11.5%, excise tax 3.5%; nontax revenue 3.8%). Expenditures: (old) Z$9,630,900,000,000 (current expenditures 87.3%, of which goods and services 52.1%, transfer payments 21.7%, interest payments 13.5%; development expenditure 12.7%). Population economically active (2003): total 5,542,000; activity rate of total population 43.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 74.0%; female 44.0%; unemployed [2006] 70%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 3,600,000, corn (maize) 900,000, seed cotton 280,000; livestock (number of live animals) 5,400,000 cattle, 3,000,000 goats, 610,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 9,107,600 cu m, of which fuelwood 89%; fisheries production (2005) 15,452 (from aquaculture 16%). Miningand quarrying (2005): chromite 614,720; asbestos 122,000; nickel (metal content) 8,556. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1998): beverages 171; foodstuffs 148; textiles 99. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 9,908,000,000 (11,948,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 3,398,000 (3,435,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (594,000). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,222,-000,000. Households. Average household size (2004) 4.5; income per household (1992) (old) Z$1,689 (US$332); expenditure (1995): food 33.6%, housing 17.3%, beverages and tobacco 16.0%, household durable goods 7.5%. Gross national income (2006): US$1,734,000,000 (US$131 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$ 000,000): tourism (2005) 99; remittances (2005) 500-1,300; foreign direct investment(2001-05 avg.) 29; official development assistance (2005) 220 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 131. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8.3%, in permanent crops 0.3%, in pasture 44.5%; overall forest area (2005) 45.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$1,989,000,000 (fuel and electricity 23.3%; machinery and transport equipment 21.0%; chemicals and chemical products 20.2%; food 8.1%). Major import sources: South Africa 50.5%; Botswana 4.3%; UK 4.0%; Zambia 2.5%; US 1.9%. Exports (2004): US$1,679,700,000 (gold 15.6%; tobacco 13.5%; ferroalloys 11.0%; platinum 10.4%; cotton lint 7.3%; horticultural products [including cut flowers] 5.0%). Major export destinations: South Africa 30.2%; Switzerland 6.0%; UK 5.9%; China 4.8%; Germany 4.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 3,077 km; passenger-km (1998) 408,223,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,377,000. Roads (2002): total length 97,267 km (paved 19%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 570,866; trucks and buses 84,456. Air transport (2006; Air Zimbabwe only): passenger-km 671,185,000; metric ton-km cargo 8,547,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 166,000 (14); televisions (2004): 610,000 (50); telephone landlines (2006): 332,000 (25); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 833,000 (64); personal computers (2005): 850,000 (71); total Internet users (2006): 1,220,000 (93); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 10,000 (0.8).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1992). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 22.3%; primary 54.3%; secondary 13.1%; higher 3.4%. Literacy (2006): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 92.4%; males literate 95.5%; females literate 89.3%. Health: physicians (2004) 2,086 (1 per 5,792 persons); hospital beds (1996) 22,975 (1 per 501 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 52.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,794 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 97%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 29,000 (army 86.2%, air force 13.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$11.
Background
Remains of Stone Age cultures dating back 500,000 years have been found in the Zimbabwe area. The first Bantu-speaking peoples reached it during the 5th-10th centuries ad, driving the San (Bushmen) inhabitants into the desert. Asecond migration of Bantu-speakers began c. 1830. During this period the British and Afrikaners moved up from the south, and the area came under the administration of the British South Africa Co. in 1889-1923. Called Southern Rhodesia (1911-64), it became a self-governing British colony in 1923. The colony united in 1953 with Nyasaland (Malawi) and Northern Rhodesia (Zambia) to form the Central African Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasa-land. The federation dissolved in 1963, and Southern Rhodesia reverted to its former colonial status. In 1965 it issued a unilateral declaration of independence considered illegal by the British government, which led to economic sanctions against it. The country proclaimed itself a republic in 1970 and called itself Rhodesia in 1964-79. In 1979 it instituted limited majority rule and changed its name to Zimbabwe Rhodesia. It was granted independence by Britain in 1980 and became Zimbabwe. Robert Mugabe, Zimbabwe’s first prime minister, became president in 1987. Although a multiparty system was established in 1990, Mugabe’s rule became more and more autocratic.
Recent Developments
After a year in which Morgan Tsvangirai and his opposition Movement for Democratic Change (MDC) had been campaigning for “mass action” to effect regime change, Pres. Robert Mugabe in 2007 banned political rallies across Zimbabwe. Further attempts by the opposition to mount demonstrations were blocked by police, and in March MDC leaders in Harare were arrested. Tsvangirai drove to the police station where his supporters were being held and was himself arrested and savagely beaten. In late March 2008, the presidential election was contested. In the weeks leading up to the poll, there were reports of widespread violence and intimidation by supporters of Mugabe. After delaying the publication of the election results, which MDC supporters insisted showed that Tsvangirai had won the office outright, the electoral commission claimed that a runoff was required. Tsvangirai withdrew, however, after weeks of violence against his supporters. Mugabe won the presidency unopposed, but by September the issue of leadership of the country had not been resolved.
Antarctica
The Arctic regions may be defined in physical terms (astronomical [north of the Arctic Circle], climatic [above the 10 °C(50 °F)Julyisotherm],orvegetational [above the northern limit of the tree line]) or in human terms (the territory inhabited by the circumpolar cultures). The region includes portions of Canada, the US, Russia, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Iceland, and Greenland (partof Denmark). The Arctic Ocean, 14.09 million sq km (5.44 millionsq mi) in area, constitutes abouttwo-thirds of the region. The land area consists of permanent ice cap, tundra, or taiga. The population of peoples belonging to the circumpolar cultures (2007 est.) is about 530,000 (Aleuts [in Russia and Alaska], more than 4,000; Athabascans [in North America], 45,000; Inuits [or Eskimos, in Russian Chukhotka, North America, and Greenland], 160,000; Sami [or Lapps, in Northern Europe], 70,000; and 41 indigenous peoples [in the Russian North], 250,000). International organizations concerned with the Arctic include the Arctic Council, the Inuit Circumpolar Council, and the Indigenous Peoples’ Secretariat. In 2007 Arcticsea ice melted dramatically. The new record-low ice extent, set in September, was 4.13 million sq km (1.59 million sq mi). This extent of sea ice was 23% less than that recorded in 2005, when the previous record low was set, and 39% below the long-term average from 1979to2000. InAugusta Russian research team used manned submersibles to place a Russian flag on the seabed at the North Pole. The US, Canada, and Denmark challenged Russia’s claim. The US Geological Survey estimated that the Arctic held 25% of the world’s undiscovered oil and natural gas reserves. The Northwest Passage became ice free for a short period of time in 2007, the first occurrence in recorded history of a completely open passage. Canada, which maintained that the passage through the Arctic archipelago was a domestic waterway, announced that it was building eight Arctic patrol ships and began work on a deepwater port at the eastern entrance to the Northwest Passage. In 2007 the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released a report confirming that the Arctic had experienced the greatest warming of any region on the planet.
Membership in International Organizations
African Union (AU; formerly [until 2002] Organization for African Unity)
Founded: 1963. Members: 52 countries of Africa (all except Morocco), Western Sahara. Web site: <www.africa-union.org>.
Andean Community
Founded: 1969. Members: Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru; associate members Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, Uruguay; observer states Mexico, Panama. Web site: <www.comunidadandina.org>.
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Founded: 1989. Members: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, US, Vietnam. Web site: <www.apec.org>.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Founded: 1967. Members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar (Burma), Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam. Web site: <www.aseansec.org>.
Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM)
Founded: 1973. Members: Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas (Community member only), Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago; associate members Anguilla, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands.
Web site: <www.caricom.org>.
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
Founded: 1994. Members: Burundi, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Rwanda, Seychelles, The Sudan, Swaziland, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe. Web site: <www.comesa.int>.
Commonwealth (also called Commonwealth of Nations)
Founded: 1931. Members: United Kingdom and 52 other countries, all of which were once under British rule or administratively connected to another member country (Fiji was suspended in December 2006); Nauru is a Special Member. Web site: <www.thecommonwealth.org>.
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) Founded: 1991. Members: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine. Web site: <www.cisstat.com>.
Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP) Founded: 1996. Members: Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, East Timor, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal, Sao Tome and Prfncipe; observer states Equatorial Guinea, Mauritius. Web site: <www.cplp.org>.
Council of Europe
Founded: 1949. Members: 47 European and former Soviet countries; observer states Canada, Japan, Mexico, US, Vatican City. Web site: <www.coe.int>.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
Founded: 1975. Members: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Cote d’Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo. Web site: <www.ecowas.int>.
European Free Trade Association (EFTA) Founded: 1960. Members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland. Web site: <www.efta.int>.
Founded: 1950. Members: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, The Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, UK. Web site: <www.europa.eu.int>.
Founded: 1975. Members: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, UK, US, EU. Web site: <www.g8.utoronto.ca>.
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Founded: 1981. Members: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE.
Web site: <www.gcc-sg.org/eng/index.php>.
Latin American Integration Association (ALADI) Founded: 1980. Members: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela. Web site: <www.aladi.org>.
League of Arab States (Arab League) Founded: 1945. Members: Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, The Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, UAE, Yemen; observer states Eritrea, Venezuela. Web site:
<www.arableagueonline.org/las/index_en.jsp>. Nordic Council of Ministers Founded: 1971. Members: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, autonomous regions of Greenland, Faroe Islands, Aland Islands. Web site: <www.norden.org>.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Founded: 1949. Members: Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, UK, US. Web site: <www.nato.int>.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
Founded: 1960. Members: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, The Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, UK, US. Web site: <www.oecd.org>.
Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE)
Founded: 1973. Members: 54 countries of Europe and Central Asia, plus Canada and the US. Web site: <www.osce.org>.
Organization of American States (OAS) Founded: 1948. Members: all 35 independent countries of the Western Hemisphere (Cuba’s participation has been denied since 1962); 61 permanent observer states (including the EU). Web site: <www.oas.org>.
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
Founded: 1960. Members: Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Venezuela; Indonesia announced in May 2008 that it would withdraw at the end of 2008. Web site: <www.opec.org>.
Organization of the Islamic Conference (OIC) Founded: 1969. Members: 56 Islamic countries (mainly in Africa and Asia), Palestinian Authority; observer states Bosnia and Herzegovina, Central African Republic, Russia, Thailand, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.
Web site: <www.oic-oci.org>.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF; formerly [until 2000] South Pacific Forum)
Founded: 1971. Members: Australia, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, New Zealand, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu.
Web site: <www.forumsec.org>.
Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC; formerly South Pacific Commission)
Founded: 1947. Members: American Samoa, Australia, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, France, French Polynesia, Guam, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Pitcairn Islands, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, US, Vanuatu, Wallis and Futuna. Web site: <www.spc.int>.
Union of South American Nations (UNASUR/UNASUL) Founded: 2004. Members: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela. Web site: <www.comunidadandina.org>.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
Founded: 1985. Members: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka; observer states Australia, China, EU, Iran, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mauritius, Myanmar (Burma), US. Web site: <www.saarc-sec.org>.
Southern African Development Community (SADC) Founded: 1980. Members: Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe. Web site: <www.sadc.int>.
Southern Common Market (MERCOSUL/MERCOSUR) Founded: 1991. Members: Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay; associate members Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela. Web site: <www.mercosur.int/msweb>.
Founded: 1945. Members: 192 countries. Web site: <www.un.org>.
World Trade Organization (WTO) Founded: 1995. Members: 152 member countries worldwide; 31 observer states as of May 2008. Web site: <www.wto.org>.
Secretaries-General of the United Nations
The UN General Assembly appoints the Secretary-General to a five-year term on the recommendation of the 15-member Security Council; permanent members of the Security Council have veto power over nominees. The Secretary-General balances diverse and sometimes conflicting duties in the various roles of diplomat, advocate, administrator, and civil servant. The Secretary-General has a broad mandate, being able to marshal resources and advocacy on issues as various as peace efforts around the globe and disease prevention and treatment. Internet resource: <www.un.org>.
|
SECRETARY GENERAL |
TERM |
|
|
Sir Gladwyn Jebb (acting) (UK) |
1945- |
1946 |
|
Trygve Lie (Norway) |
1946- |
1952 |
|
Dag Hammarskjold (Sweden) |
1953- |
1961 |
|
U Thant (Burma, now Myanmar) |
1961- |
1971 |
|
Kurt Waldheim (Austria) |
1972- |
1981 |
|
Javier Perez de Cuellar (Peru) |
1982- |
-1991 |
|
Boutros Boutros-Ghali (Egypt) |
1992- |
1996 |
|
Kofi Annan (Ghana) |
1997- |
2006 |
|
Ban Ki-moon (South Korea) |
2007- |
The International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC) was established by the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court on 17 Jul 1998. The statute that created the ICC went into force on 1 Jul 2002; the court was fully operational as of July 2003. As of June 2008,the ICC has 106 member countries.
Philippe Kirsch (Canada)
Akua Kuenyehia (Ghana)
Rene Blattmann (Bolivia)
Luis Moreno-Ocampo (Argentina)
List A—elected as experts in criminal law and procedure
Bruno Cotte (France) Fatoumata Dembele Diarra (Mali) Adrian Fulford (United Kingdom) Daniel David Ntanda Nsereko (Uganda) Elizabeth Odio Benito (Costa Rica)
Georghios M. Pikis (Cyprus) Song Sang-Hyun (Republic of Korea) Sylvia Steiner (Brazil) Ekaterina Trendafilova (Bulgaria)
List B—elected as experts in international law and human rights law
Rene Blattmann (Bolivia)
Hans-Peter Kaul (Germany)
Philippe Kirsch (Canada)
Erkki Kourula (Finland)
Akua Kuenyehia (Ghana)
Navanethem Pillay (South Africa)
Mauro Politi (Italy)
Fumiko Saiga (Japan)
Anita Usacka (Latvia)
Silvana Arbia (Italy)
United Nations Membership by Date of Admission
|
COUNTRY DATE |
OF ADMISSION |
|
|
Argentina |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Belarus |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Brazil |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Chile |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
China1 |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Cuba |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Denmark |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Dominican Rep. |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Egypt |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
El Salvador |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
France |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Haiti |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Iran |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Lebanon |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Luxembourg |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
New Zealand |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Nicaragua |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Paraguay |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Philippines |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Poland |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
USSR (later Russia) |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Saudi Arabia |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Syria |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Turkey |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Ukraine |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
UK |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
US |
24 Oct |
1945 |
|
Greece |
25 Oct |
1945 |
|
India |
30 Oct |
1945 |
|
Peru |
31 Oct |
1945 |
|
Australia |
1 Nov |
1945 |
|
Costa Rica |
2 Nov |
1945 |
|
Liberia |
2 Nov |
1945 |
|
Colombia |
5 Nov |
1945 |
|
Mexico |
7 Nov |
1945 |
|
South Africa |
7 Nov |
1945 |
|
Canada |
9 Nov |
1945 |
|
Ethiopia |
13 Nov |
1945 |
|
Panama |
13 Nov |
1945 |
|
Bolivia |
14 Nov |
1945 |
|
COUNTRY DATE OF ADMISSION |
||
|
Venezuela |
15 Nov |
1945 |
|
Guatemala |
21 Nov |
1945 |
|
Norway |
27 Nov |
1945 |
|
The Netherlands |
10 Dec |
1945 |
|
Honduras |
17 Dec |
1945 |
|
Uruguay |
18 Dec |
1945 |
|
Ecuador |
21 Dec |
1945 |
|
Iraq |
21 Dec |
1945 |
|
Belgium |
27 Dec |
1945 |
|
Afghanistan |
19 Nov |
1946 |
|
Iceland |
19 Nov |
1946 |
|
Sweden |
19 Nov |
1946 |
|
Thailand |
16 Dec |
1946 |
|
Pakistan |
30 Sep |
1947 |
|
Yemen |
30 Sep |
1947 |
|
Myanmar |
19 Apr |
1948 |
|
Israel |
11 May |
1949 |
|
Indonesia |
28 Sep |
1950 |
|
Albania |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Austria |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Bulgaria |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Cambodia |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Finland |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Hungary |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Ireland |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Italy |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Jersey |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Jordan |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Laos |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Libya |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Nepal |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Portugal |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Romania |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Spain |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Sri Lanka |
14 Dec |
1955 |
|
Morocco |
12 Nov |
1956 |
|
The Sudan |
12 Nov |
1956 |
|
Tunisia |
12 Nov |
1956 |
|
Japan |
18 Dec |
1956 |
|
Ghana |
8 Mar |
1957 |
|
COUNTRY DATE OF ADMISSION |
||
|
Malaysia |
17 Sep |
1957 |
|
Guinea |
12 Dec |
1958 |
|
Benin |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Burkina Faso |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Cameroon |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Central African Rep. |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Chad |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Dem. Rep. of the |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Congo |
|
|
|
Rep. of the Congo |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Cote d’lvoire |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Cyprus |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Gabon |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Madagascar |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Niger |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Somalia |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Togo |
20 Sep |
1960 |
|
Mali |
28 Sep |
1960 |
|
Senegal |
28 Sep |
1960 |
|
Nigeria |
7 Oct |
1960 |
|
Sierra Leone |
27 Sep |
1961 |
|
Mauritania |
27 Oct |
1961 |
|
Mongolia |
27 Oct |
1961 |
|
Tanzania |
14 Dec |
1961 |
|
Burundi |
18 Sep |
1962 |
|
Jamaica |
18 Sep |
1962 |
|
Rwanda |
18 Sep |
1962 |
|
Trinidad and Tobago |
18 Sep |
1962 |
|
Algeria |
8 Oct |
1962 |
|
Uganda |
25 Oct |
1962 |
|
Kuwait |
14 May |
1963 |
|
Kenya |
16 Dec |
1963 |
|
Malawi |
1 Dec |
1964 |
|
Malta |
1 Dec |
1964 |
|
Zambia |
1 Dec |
1964 |
|
The Gambia |
21 Sep |
1965 |
|
Maldives |
21 Sep |
1965 |
|
Singapore |
21 Sep |
1965 |
|
Guyana |
20 Sep |
1966 |
|
Lesotho |
17 Oct |
1966 |
|
COUNTRY DATE OF ADMISSION |
||
|
Botswana |
17 Oct |
1966 |
|
Barbados |
9 Dec |
1966 |
|
Mauritius |
24 Apr |
1968 |
|
Swaziland |
24 Sep |
1968 |
|
Equatorial Guinea |
12 Nov |
1968 |
|
Fiji |
13 Oct |
1970 |
|
Bahrain |
21 Sep |
1971 |
|
Bhutan |
21 Sep |
1971 |
|
Qatar |
21 Sep |
1971 |
|
Oman |
7 Oct |
1971 |
|
United Arab |
9 Dec |
1971 |
|
Emirates |
|
|
|
The Bahamas |
18 Sep |
1973 |
|
Germany |
18 Sep |
1973 |
|
Bangladesh |
17 Sep |
1974 |
|
Grenada |
17 Sep |
1974 |
|
Guinea-Bissau |
17 Sep |
1974 |
|
Cape Verde |
16 Sep |
1975 |
|
Mozambique |
16 Sep |
1975 |
|
Sao Tome |
16 Sep |
1975 |
|
and Principe |
|
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
10 Oct |
1975 |
|
Comoros |
12 Nov |
1975 |
|
Suriname |
4 Dec |
1975 |
|
Seychelles |
21 Sep |
1976 |
|
Angola |
1 Dec |
1976 |
|
Samoa |
15 Dec |
1976 |
|
COUNTRY DATE OF ADMISSION |
||
|
Djibouti |
20 Sep |
1977 |
|
Vietnam |
20 Sep |
1977 |
|
Solomon Islands |
19 Sep |
1978 |
|
Dominica |
18 Dec |
1978 |
|
St. Lucia |
18 Sep |
1979 |
|
Zimbabwe |
25 Aug |
1980 |
|
St. Vincent and |
16 Sep |
1980 |
|
the Grenadines |
|
|
|
Vanuatu |
15 Sep |
1981 |
|
Belize |
25 Sep |
1981 |
|
Antigua and |
11 Nov |
1981 |
|
Barbuda |
|
|
|
St. Kitts and Nevis |
23 Sep |
1983 |
|
Brunei |
21 Sep |
1984 |
|
Namibia |
23 Apr |
1990 |
|
Liechtenstein |
18 Sep |
1990 |
|
Estonia |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
North Korea |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
South Korea |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
Latvia |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
Lithuania |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
Marshall Islands |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
Federated States |
17 Sep |
1991 |
|
of Micronesia |
|
|
|
Armenia |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Azerbaijan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Kazakhstan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
COUNTRY |
DATE OF ADMISSION |
|
|
Kyrgyzstan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Moldova |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
San Marino |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Tajikistan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Turkmenistan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Uzbekistan |
2 Mar |
1992 |
|
Bosnia and |
22 May |
1992 |
|
Herzegovina |
|
|
|
Croatia |
22 May |
1992 |
|
Slovenia |
22 May |
1992 |
|
Georgia |
31 Jul |
1992 |
|
Czech Republic |
19 Jan |
1993 |
|
Slovakia |
19 Jan |
1993 |
|
Macedonia2 |
8 Apr |
1993 |
|
Eritrea |
28 May |
1993 |
|
Monaco |
28 May |
1993 |
|
Andorra |
28 Jul |
1993 |
|
Palau |
15 Dec |
1994 |
|
Kiribati |
14 Sep |
1999 |
|
Nauru |
14 Sep |
1999 |
|
Tonga |
14 Sep |
1999 |
|
Tuvalu |
5 Sep |
2000 |
|
Serbia |
1 Nov |
2000 |
|
Switzerland |
10 Sep |
2002 |
|
East Timor |
27 Sep |
2002 |
|
(Timor-Leste) |
|
|
|
Montenegro |
28 Jun |
2006 |
1The Republic of China (Taiwan) held the seat until 25 Oct 1971, when UN Res. 2758 gave the membership and a seat on the Security Council to the People’s Republic of China. 2Macedonia is known in the UN as The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.