Jersey
Official name: Bailiwick of Jersey. Political status:crown dependency (UK) with one legislative house(States of Jersey [58]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Lieutenant Governor Andrew Ridgway (from 2006). Head of government: Chief Minister Frank Walker (from 2005). Capital: Saint Helier. Official language: English (Jerri-ais, a Norman-French dialect, is spoken by a small number of residents). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Jersey pound (£J) = 100 pence; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = £J 0.50 (the Jersey pound is equivalent in value to the British pound sterling [£]).
Demography
Area: 45.6 sq mi, 118.2 sq km. Population (2007): 89,500. Density(2007): persons persq mi 1,962.7, persons per sq km 757.2. Urban (2001): 28.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.22%; female 50.78%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 17.5%; 15-29, 15.1%; 30-44, 25.1%; 45-59, 21.6%; 60-74, 13.7%; 75-84, 5.0%; 85 and over, 2.0%. Population by place of birth (2001): Jersey 52.6%; UK, Guernsey, or Isle of Man 35.8%; Portugal 5.9%; France 1.2%; other 4.5%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 86.0%, of which Anglican 44.1%, Roman Catholic 14.6%, other Protestant 6.9%, unaffiliated Christian 20.1%; nonreligious/atheist 13.4%; other 0.6%. Major cities (2001; population of parishes): St. Helier 28,310; St. Saviour 12,491; St. Brelade 10,134. Location: western Europe, island in the English Channel.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.5 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.57. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 76.8 years; female 81.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: £J 446,000,000 (income tax 81.4%; import duties 11.2%; stamp duties 3.4%; other 4.0%). Expenditures: £J 466,000,000 (current expenditure 90.8%, of which health 27.4%, education 19.5%, social security 17.7%, public services 5.8%; capital expenditure 9.2%). Production. Agriculture, forestry, fishing (value of export crops in £J ’000; 2005): potatoes 19,700, tomatoes 4,700, flowers (2004) 900; livestock (number of live animals; 2002) 3,970 dairy cattle; fisheries production (metric tons) 2,260 (including whelks 442, brown crabs 438, scallops 231, lobsters 139; from aquaculture 28% [including oysters 580]). Manufacturing: light industry, mainly electrical goods, textiles, and clothing. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2001) 153,000,000 (567,000,000). Gross national income (at 2005 market prices): US$5,800,000,000 (US$66,000 per capita). Households. Average household size (2001) 2.4; median annual household income (2004-05) £J 34,000 (US$62,100); expenditure (2004-05): housing 29.2%, recreation 14.2%, transportation 11.6%, food 9.8%, restaurants and hotels 5.8%. Population economically active (2001): total 48,105; activity rate of total population 55.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [male], 15-59 [female] 81.7%; female 44.1%; unemployed [2006] 2.3%). Public debt: none. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 379. Land use as % of total land area (1997): in temporary and permanent crops 29%, in pasture 22%; overall forest area (2005) 4.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports: n.a. Major import sources (2001): mostly the UK. Exports: agricultural and marine exports (2001) £J 40,626,000 (potatoes 67.4%; greenhouse tomatoes 19.1%; flowers 3.3%; zucchini 3.0%; crustaceans 2.0%; mollusks 2.0%). Major export destinations: mostly the UK.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1995): total length 557 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 74,007; trucks and buses 12,957. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 22,000 (250); telephone landlines (2006): 72,000 (804); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 102,000 (1,148); total Internet users (2004): 27,000 (308).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 16-64 (male) and 16-59 (female) having: no formal degree 34.1%; undergraduate 7.1%; graduate (advanced degree) 4.1%. Literacy (2002): 100%. Health: physicians (2001) 174 (1 per 500 persons); hospital beds (2000) 651 (1 per 133 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 2.4.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none; defense is the responsibility of the UK.
Jordan
Official name: Al-Mamlakah al-Urdunniyah al-Hashimiyah (Al-Urdun) (Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [55]; House of Representatives [110]). Head of state and government: King Abdullah II (from 1999), assisted by Prime Minister Nader Dahabi (from 2007). Capital: Amman. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Jordan dinar (JD) = 1,000 fils; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = JD 0.71.
Demography
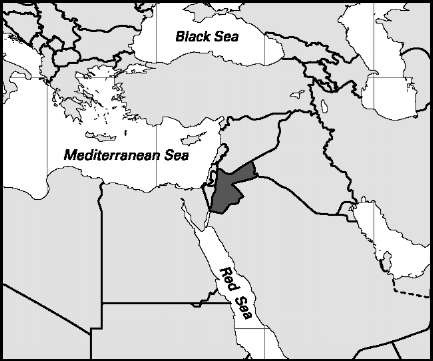
Area: 34,277 sq mi, 88,778 sq km. Population (2007): 5,924,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 172.8, persons per sq km 66.7. Urban (2004): 78.3%. Sex distribution (2004): male 51.46%; female 48.54%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.2%; 15-29, 28.9%; 30-44, 20.7%; 45-59, 8.2%; 60-74, 4.2%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 97.8%, of which Jordanian 32.4%, Palestinian 32.2%, Iraqi 14.0%, Bedouin 12.8%; Circassian 1.2%; other 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Sunni Muslim 95%; Christian 3%; other (mostly Shi’i Muslim and Druze) 2%. Major cities (2004): Amman 1,036,330; Al-Zarqa 395,227; Irbid 250,645; Al-Rusayfah 227,735; Al-Quwaysimah 135,500. Location: the Middle East, bordering Syria, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, the Gulf of Aqaba, Israel, and parts of the emerging Palestinian Autonomous Areas.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 27.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 3.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.71. Life expectancy at birth (2003): male 70.6 years; female 72.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: JD 2,949,800,000 (tax revenue 48.4%, of which sales tax 28.0%, custom duties 8.8%, income and profits taxes 7.4%; foreign grants 27.5%; nontax revenue 22.0%, of which licenses and fees 12.4%; repayments 2.1%). Expenditures: JD 3,102,100,000 (current expenditure 75.0%, of which defense 21.1%, wages 15.0%, social security and pensions 12.9%, oil subsidies 8.4%, interest payments 7.4%; capital expenditure 25.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): tomatoes 598,900, potatoes 172,100, cucumbers 166,200; livestock (number of live animals) 1,890,440sheep, 516,140 goats, 25,000,000chickens; roundwood 265,771 cu m, of which fuelwood 98%; fisheries production 1,071 (from aquaculture 52%). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate ore 6,375,000; potash 1,830,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): chemicals and chemical products 347; bricks, cement, and ceramics 287; food products 232. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 8,967,000,000 (9,792,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 8,480 (30,087,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 3,817,000 (4,426,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 266,521,000 (266,521,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,-000): tourism (2005) 1,441; remittances (2005) 2,500; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 566; official development assistance (2005) 636 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 585; remittances (2005) 349. Population economically active (2003): total 1,293,000; activity rate of total population 23.6% (participation rates: overage 15, 37.9%; female 14.9%; unemployed 14.5%). Gross national income (2006): US$14,595,000,000 (US$2,548 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$6,878,000,000. Households. Average household size (2005)5.4; income per household (2002-03) JD 5,590 (US$7,880); sources of income (2002-03): wages and salaries 45.3%, rentand property income 23.0%, transfer payments 19.9%, self-employment 11.8%; expenditure (2002-03): food and beverages 36.2%, housing and energy 26.4%, transportation and communications 13.2%, education 6.2%, clothing and footwear 4.8%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.0%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 8.4%; overall forest area (2005) 0.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): JD 5,799,200,000 (machinery and apparatus 22.7%, of which transport equipment 9.1%; crude petroleum 13.2%; food products 13.1%; chemicals and chemical products 9.8%; textile yarn and fabric 7.9%). Major import sources: Saudi Arabia 19.8%; China 8.4%; Germany 6.8%; US 6.8%; Italy 3.8%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): JD 2,753,000,000 (domestic exports 83.8%, of which clothing 25.8%, chemicals and chemical products 18.2% [including medicines and pharmaceuticals 5.8%], potash 5.9%, vegetables 4.6%, phosphates 4.3%; reexports 16.2%). Major export destinations: US 31.5%; Iraq 15.7%; India 7.7%; Saudi Arabia 6.0%; Syria 4.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length 788 km; passen-ger-km 2,100,000; metric ton-km cargo 348,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 7,500 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 387,565; trucks and buses 190,188. Air transport (2006; Royal Jordanian airlines only): passenger-km 5,521,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 210,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 265,000 (49); televisions (2004): 1,065,000 (198); telephone landlines (2006): 614,000 (105); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,343,000 (744); personal computers (2005): 355,000 (62); total Internet users (2006): 797,000 (137); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 49,000 (8.8).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling: illiterate 14.0%, literate 4.8%; primary/lower secondary education 36.6%; upper secondary 19.4%; some higher 25.1%, of which advanced degree 2.1%; unknown 0.1%. Literacy (2005): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 91.1%; males literate 95.2%; females literate 87.0%. Health: physicians (2005) 17,569 (1 per 316 persons); hospital beds (2005) 10,141 (1 per 539 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 24.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,299 (vegetable products 91%, animal products 9%); 182% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2005): 100,500 (army 84.6%, navy 0.5%, air force 14.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 5.3%; per capita expenditure US$130.
Background
Jordan shares much of its history with Israel, since both occupied the area known historically as Palestine. Much of present-day eastern Jordan was incorporated into Israel under Kings David and Solomon c. 1000 bc. It fell to the Seleucids in 330 bc and to Muslim Arabs in the 7th century ad. The Crusaders extended the kingdom of Jerusalem east of the Jordan River in 1099. Jordan submitted to Ottoman Turkish rule during the 16th century. In 1920 the area comprising Jordan (then known as the Transjordan) was established within the British mandate of Palestine. Transjordan became an independent state in 1927, although the British mandate did not end until 1948. After hostilities with the new state of Israel ceased in 1949, Jordan annexed the West Bank of the Jordan River, administering the territory until Israel gained control of it in the Six-Day War of 1967. In 1970-71 Jordan was wracked by fighting between the government and guerrillas of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), a struggle that ended in the expulsion of the PLO from Jordan. In 1988 King Hussein renounced all Jordanian claims to the West Bank in favor of the PLO. In 1994 Jordan and Israel signed a full peace agreement. Upon the death of King Hussein in 1999, his son Abdullah took over the throne.
Recent Developments
The Jordanian economy grew in 2007 but was brought in check somewhat by a growing foreign trade deficit and decreased foreign direct investment. Jordan’s central bank reported that GDP growth was 6.0% over data from 2006 and that the rate of inflation fell from 6.25% to 5.40%. As well, public debt grew by little more than 1%. The trade deficit grew by 25.0% in 2007, however, as the value of the country’s imports was more than double that of its exports. Foreign direct investment dropped 75.4%, though compared to 2005 data it grew by 3.5%.
Kazakhstan
Official name: Qazaqstan Respublikasy (Republic of Kazakhstan). Form of government: unitary republic with a parliament consisting of two chambers (Senate [47] and Assembly [107]). Head of state and government: President Nursultan Nazarbayev (from 1990), assisted by Prime Minister Karim Masimov (from 2007). Capital: Astana. Official language: Kazakh (Russian commands equal status at state-owned organizations and local government bodies). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 tenge (T) = 100 tiyn; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 120.62 tenge.
Demography
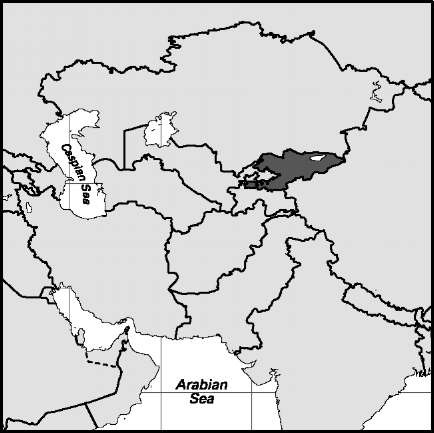
Area: 1,052,100sq mi, 2,724,900sq km. Population (2007): 15,472,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 14.7, persons persq km 5.7. Urban (2006): 57.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.30%; female 51.70%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 23.7%; 15-29, 28.7%; 30-44, 20.7%; 45-59, 16.4%; 60-74,7.9%; 75-84,2.3%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2003): Kazakh 57.2%; Russian 27.2%; Ukrainian 3.1%; Uzbek 2.7%; German 1.6%; Tatar 1.6%; Uighur 1.5%; other 5.1%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (mostly Sunni) 42.7%; nonreligious 29.3%; Christian 16.7%, of which Orthodox8.6%; atheist 10.9%; other 0.4%. Major cities (2004): Almaty 1,175,208; Shymkent (Chimkent) 513,110; Astana 510,533; Qaraghandy (Karaganda) 428,867; Taraz 327,911. Location: central Asia, bordering Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, the Aral Sea, Turkmenistan, and the Caspian Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 19.7 (world avg. 20.3); (2000) within marriage 76.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.90. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 60.6 years; female 72.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: T 1,441,000,000,000 (tax revenue 90.7%, of which corporate taxes 33.8%, VAT 16.9%, social security 11.7%, petroleum taxes 10.0%; nontax revenue 9.3%). Expenditures: T 1,289,300,000,000 (social security 21.1%; education 14.8%; health 10.2%; public order 9.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$2,184,000,-000. Population economically active (2006): total 8,028,900; activity rate of total population 52.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2004] 76.6%; female [2004] 49.0%; unemployed 7.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 9,970,000, potatoes 2,521,000, barley 1,546,000; livestock (number of live animals) 11,410,000 sheep, 5,204,000 cattle, 2,000,000 goats; roundwood 300,800 cu m, of which fuelwood 57%; fisheries production 31,589 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2004): iron ore 20,300,000; bauxite 4,705,600; chromite 3,267,000. Manufacturing (value of production in T ’000,000; 2004): base metals 600,000; food and food products 356,000; coke, refined petroleum products, and nuclear fuel 134,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 66,500,000,000 (59,200,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 86,800,000 (60,277,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 3,945,000 (3,673,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 471,000,000 ([2004] 90,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 10,305,000 (8,906,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 21,855,000,000 (16,472,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$72,388,000,000 (US$4,727 per capita). Households (2001). Average household size (2004) 3.8; sources of income: salaries and wages 72.1%, social benefits 9.2%; expenditure: food and beverages 56.0%, housing 11.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 701; remittances (2006) 187; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 2,674; official development assistance (2005) 141 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 753; remittances (2006) 3,036. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8.4%, in permanent crops 0.05%, in pasture 68.6%; overall forest area (2005) 1.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$12,781,250,000 (machinery and apparatus 26.8%; mineral fuels and lubricants 14.7%; transportation equipment 13.9%; base metals 13.0%; chemicals and chemical products 8.8%). Major import sources (2006): Russia 35.7%; China 20.0%; Germany 7.6%; France 3.5%; Italy 3.3%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$20,096,230,000 (mineral fuels 68.3%; base metals 19.4%; agricultural products [mostly cereals] 3.2%). Major export destinations (2006): Germany 12.5%; Russia 11.3%; China 11.0%; Italy 10.6%; France 7.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length (2004) 13,700 km; passenger-km 12,705,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 191,000,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 90,018 km (paved 93%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 1,204,118; trucks and buses 287,766. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 3,716,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2003) 94,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 5,106,000 (338); telephone landlines (2006): 2,928,000 (191); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 7,834,000 (512); total Internet users (2006): 1,247,000 (81); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 31,000 (2.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/some primary education 9.1%; primary education 23.1%; secondary/some postsecondary 57.8%; higher 10.0%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 99.5%; males literate 99.8%; females literate 99.3%. Health (2006): physicians 57,500 (1 per 266 persons); hospital beds 119,000 (1 per 129 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 13.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,027 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%); 155% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$39.
The Aral Sea was once a large, shallow saltwater lake, straddling the boundary between Kazakhstan to the north and Uzbekistan to the south, that ranked as the world’s fourth largest body of inland water. It nestles in the climatically inhospitable heart of Central Asia, to the east of the Caspian Sea.
Background
Named for its earliest inhabitants, the Kazakhs, the area came under Mongol rule in the 13th century. The Kazakhs consolidated a nomadic empire in the 15th-16th centuries. Under Russian rule by the mid-19th century, it became part of the Kirgiz Autonomous Republic formed by the Soviets in 1920, and in 1925 its name was changed to the Kazakh Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. Kazakhstan obtained its independence in 1991, and during the 1990s it attempted to stabilize its economy.
Recent Developments
In 2007 Kazakhstan continued to have one of the strongest economies in the Commonwealth of Independent States, thanks largely to its oil revenues, though backsliding on democratization was increasingly evident. Kazakhstan became the first state in Central Asia to become a donor to the economic development of its neighbors, promising US$100 million in April to aid the Kyrgyz economy. In addition, a number of Kazakh firms announced plans to invest in industries in Tajikistan. In February, Minister of Environmental Protection Nurlan Iskakov warned thatfor-eign oil firms working in Kazakhstan would face suspension of their activities for alleged failure to observe environmental regulations.
Kenya
Official name: Jamhuri ya Kenya (Swahili); Republic of Kenya (English). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [224]). Head of state and government: President Mwai Kibaki (from 2002), assisted by Prime Minister Raila Odinga (from 2008). Capital: Nairobi. Official languages: Swahili; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Kenya shilling (K Sh) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = K Sh 65.31.
Demography
Area: 224,961 sq mi, 582,646 sq km. Population (2007): 36,914,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 164.1, persons per sq km 63.4. Urban (2005): 20.7%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.90%; female 51.10%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 43.1%; 15-29, 30.2%; 30-44, 15.2%; 45-59, 7.0%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over, 1.0%. Ethnic composition (2004): Kikuyu 21%; Luhya 14%; Luo 13%; Kalenjin 11%; Kamba 11%; Gusii 6%; Meru 5%; other 19%. Religious affiliation (2006): Protestant/independent Christian 66%; Roman Catholic 23%; Muslim 8%; nonreligious 2%; traditional beliefs 1%. Major cities (2004): Nairobi 2,504,400; Mombasa 777,100; Nakuru 256,300; Kisumu 227,100; Eldoret 195,200. Location: eastern Africa, bordering Ethiopia, Somalia, the Indian Ocean, Tanzania, Uganda, and The Sudan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 40.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 25.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.96. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 54.3 years; female 59.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue: KSh 304,705,000,000 (tax revenue 79.7%, of which income and profit taxes 32.6%, VAT 24.9%, excise tax 14.5%; nontax revenue 15.4%; grants 4.9%). Expenditures: K Sh 303,705,000,000 (recurrent expenditure 85.0%, of which wages and salaries 34.3%, interest payments 10.0%; development expenditure 15.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,520,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 4,801,000, corn (maize) 2,906,000, potatoes 980,000, cut flowers (2002) largestsupplier to EU(25%of total market); livestock (number of live animals) 13,883,000 goats, 13,019,000 cattle, 10,033,000 sheep; roundwood 22,356,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 92%; fisheries production 143,274, of which freshwater fish 124,621 (from aquaculture 1%). Miningand quarrying (2004): soda ash 355,380; fluorite 108,000; salt 22,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): food and food products 400; textiles and wearing apparel 245; chemicals and chemical products 142. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 4,864,000,000 (5,035,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (108,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (14,983,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,657,000 (2,703,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.5; expenditure (1993-94): food 42.4%, housing and energy 24.1%, clothing and footwear 9.1%, transportation 6.4%, other 18.0%. Population economically active (2001): total 12,952,000; activity rate of total population 42.1% (participation rates [1998-99]: ages 15-64, 73.6%; female [1997] 46.1%; unemployed 14.6%). Gross national income (2006): US$23,564,000,000 (US$645 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 579; remittances (2004) 464; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 36; official development assistance (2005) 995 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 124. Land use as % of total land area (2000): in temporarycrops 7.9%, in permanent crops 1.0%, in pasture 37.4%; overall forest area 30.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): K Sh 526,870,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 30.7%; petroleum and petroleum products 23.9%; chemicals and chemical products 13.7%; food and live animals 5.2%). Major import sources: UAE 14.7%; India 7.1%; UK 6.5%; South Africa 6.4%; Japan 5.6%. Exports (2006): K Sh 267,900,000,000 (soda ash 35.6%; food 22.4%, of which tea 17.3%, coffee 3.6%; cut flowers 15.7%; petroleum products 2.7%). Major export destinations: Uganda 10.4%; UK 10.1%; The Netherlands 7.3%; Tanzania 6.8%; US 6.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2000): route length 2,700 km; passenger-km 302,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,557,000,000. Roads (2000): total length 63,942 km (paved 12%). Vehicles (2000): passenger cars 244,836; trucks and buses 96,726. Air transport (2004; Kenya Airways only): passenger-km 5,283,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 193,430,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 310,000 (8.8); televisions (2000): 758,000 (25); telephone landlines (2006): 293,000 (8.4); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 6,485,000 (185); personal computers (2004): 330,000 (9.5); total Internet users (2006): 2,770,000 (79).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1998-99). Percentage of population ages 6 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 20.2%; primary education 59.0%; secondary 19.7%; university 1.1%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 16 and over literate 84.3%; males literate 90.0%; females literate 78.5%. Health: physicians (2006) 5,889 (1 per 6,268 persons); hospital beds (2004) 65,971 (1 per 485 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 61.5. Food (2003): daily per capita caloric intake 1,974 (vegetable products 87%, animal products 13%); 85% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 24,120 (army 82.9%, navy 6.7%, air force 10.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$9.
Jomo Kenyatta, an African statesman and nationalist, was the first prime minister (1963-64) and then president (1964—78) of independent Kenya. As president, he encouraged foreign investment from Western and other countries. Largely as a result of his policies, Kenya’s gross national product grew almost fivefold from 1971 to 1981, and its rate of economic growth was among the highest on the continent in the first two decades after independence.
Background
The coastal region of East Africa was dominated by Arabs until it was seized by the Portuguese in the 16th century. The Masai people held sway in the north and moved into central Kenya in the 18th century, while the Kikuyu expanded from their home region in south-central Kenya. The interior was explored by European missionaries in the 19th century. After the British took control, Kenya was established as a British protectorate (1890) and a crown colony (1920). The Mau Mau rebellion of the 1950s was directed against European colonialism. In 1963 the country became fully independent, and a year later a republican government under Jomo Kenyatta was elected. In 1992 Kenyan Pres. Daniel arap Moi allowed the country’s first multiparty elections in three decades, though the balloting was marred by violence and fraud. Political turmoil occurred over the following years.
Recent Developments
The main preoccupation of politicians in Kenya remained the presidential and parliamentary elections that were held in late December 2007. The lastses-sion of the parliament, which opened in March, provided Pres. Mwai Kibaki with the opportunity to emphasize the government’s achievements in the field of primary education and in the allocation of funds to support regional projects. In the final count Kibaki emerged the winner, claiming roughly 47% of the vote to the 44% taken by his opponent, Raila Odinga. Kibaki was immediately sworn in for a second term in office, while opposition leaders expressed outrage and deadly riots erupted, particularly in the shanty-towns around Nairobi. In the ensuing violence throughout the first part of 2008, more than 1,500 people were killed. Odinga and Kibaki agreed to a power-sharing deal to end the violence.
Kiribati
Official name: Republic of Kiribati. Form of government: unitary republic with a unicameral legislature (House of Assembly [42]). Head of state and government: President Anote Tong (from 2003). Capital: Bairiki, on Tarawa Atoll. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Australian dollar ($A) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = $A 1.05.
Demography
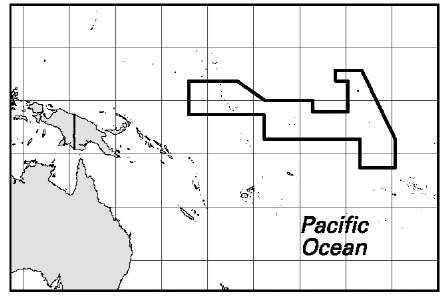
Area: 312.9 sq mi, 810.5 sq km. Population (2007): 95,500. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 341.1, persons per sq km 131.5. Urban (2005): urban 47.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.29%; female 50.71%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 36.9%; 15-29, 28.3%; 30-44, 18.7%; 45-59, 10.7%; 60-74, 4.5%; 75 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): Micronesian 98.8%; Polynesian 0.7%; European 0.2%; other 0.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 55.3%; Kiribati Protestant (Congregational) 35.7%; Mormon 3.1%; Baha’i 2.2%; other/nonreligious 3.7%. Major villages (2005): Betio 12,509; Bikenibeu 6,170; Teaoraereke 3,939; Bairiki 2,766. Location: western Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands (US).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 30.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 8.4 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.20. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 58.7 years; female 64.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: $A 182,369,000 (nontax revenue 35.7%; tax revenue 16.7%; grants 47.6%). Expenditures: $A 78,560,000 (education 25.3%; health 16.7%; economic services 15.6%; defense 7.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2002): US$3,900,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 109,800, bananas 4,939, taro 2,000; livestock (number of live animals) 12,400 pigs, 460,000 chickens; fisheries production 34,012; aquatic plants (all seaweed) production 3,904 (from aqua-culture 100%). Manufacturing: copra (6,194 metric tons produced in 2005), processed fish, clothing, and handicrafts. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 10,000,000 (10,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (9,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2001) 3.2; remittances (2005) 11; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 16; official development assistance (2005) 28. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1999) 2.0. Population economically active (2005): total 36,970; activity rate of total population 40% (participation rates: ages 16 and over [1995] 84.0%; female [1995] 47.8%; unemployed 6.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$130,000,000 (US$1,391 per capita). Households. Average household size (1995) 6.5; expenditure (1996): food 45.0%, nonalcoholic beverages 10.0%, transportation 8.0%, energy 8.0%, education 8.0%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3%, in permanent crops 48%, in pasture, none; overall forest area (2005) 30%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): $A 79,495,000 (food 30.6%; machinery and transport equipment 16.1%; mineral fuels 13.1%; beverages and tobacco 9.8%). Major import sources: Australia 47.8%; Fiji 22.1%; New Zealand 11.1%; Japan 6.0%; China 3.0%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): $A 4,470,000 (domestic exports 82.2%, of which copra 47.3%, shark fins 10.5%, seaweed 8.6%, aquarium fish 7.2%, trepang 5.7%; reexports 17.8%). Major export destinations (2001): Japan 45.8%; Thailand 24.8%; South Korea 10.7%; Bangladesh 5.5%; Brazil 3.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 670 km (paved [1996] 5%). Vehicles (2004; South Tarawa only): passenger cars 610; trucks and buses 808. Air transport (1998): passenger-km 11,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 4,000 (44); telephone landlines (2004): 5,000 (50); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 600 (6.7); personal computers (2004): 1,000 (11); total Internet users (2006): 2,000 (21).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 5 and over having: no schooling/prepri-mary education 11%; incomplete primary 23%; complete primary 34%; incomplete secondary 18%; complete secondary 13%; higher 1%. Literacy (2001): population ages 15 and over literate 94.0%; males literate 93.0%; females literate 95.0%. Health (2004): physicians 20 (1 per 4,455 persons); hospital beds 140 (1 per 680 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 48.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,818 (vegetable products 85%, animal products 15%); 156% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none; defense assistance is provided by Australia and New Zealand.
Background
The islands were settled by Austronesian-speaking peoples before the 1st century ad. In 1765 the British discovered the island of Nikunau; the first permanent European settlers arrived in 1837. In 1916 the Gilbert and Ellice islands and Banaba became a crown colony of Britain; they were later joined by the Phoenix and Line islands. The Ellice Islands declared independence (as Tuvalu) in 1978, and in 1979 the remaining islands became the nation of Kiribati.
Recent Developments
Kiribati experienced economic and environmental pressure in 2007 from annual population growth rates of 2.25%, particularly on South Tarawa, where about half of the population resided. Kiribati had a well-managed Revenue Equalization Reserve Fund, which invested globally, but the fund faced declining returns as the impact of failures in the American sub-prime mortgage market was felt. The government hoped that a joint venture to build high-value fiberglass pleasure craft for the Australian market would be lucrative and long lasting.
North Korea
Official name: Choson Minjujuui In’min Konghwaguk (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea). Form of government: unitary single-party republic with one legislative house (Supreme People’s Assembly [687]). Head of state and government: Chairman of the National Defense Commission Kim Jong Il (from 1998). Capital: P yongyang. Official language: Korean. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 (North Korean) won (W) = 100 chon; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 140.00 won.
Demography
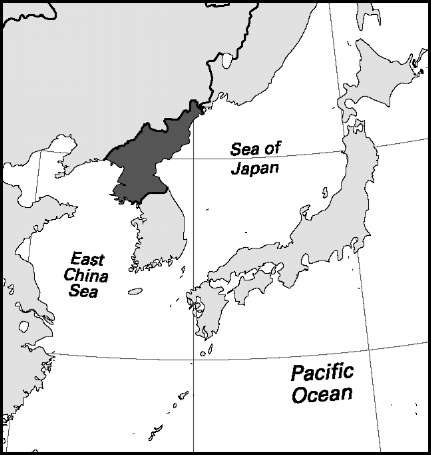
Area: 47,399 sq mi, 122,762 sq km. Population (2007): 23,790,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 501.9, persons per sq km 193.8. Urban (2005): 61.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.49%; female 51.51%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 24.2%; 15-29, 22.8%; 30-44, 25.5%; 45-59, 15.0%; 60-74, 10.5%; 75 and over, 2.0%. Ethnic composition (1999): Korean 99.8%; Chinese 0.2%. Religious affiliation (2005): mostly nonreligious/atheist; autonomous religious activities almost nonexistent. Major cities (2005): P’yongyang (urban agglomeration) 3,351,000; Namp’o (urban agglomeration) 1,102,000; Hamhung (urban agglomeration) 804,000; Ch’ongjin (1993) 582,480; Kaesong (1993) 334,433. Location: eastern Asia, bordering China, Russia, the Sea of Japan (East Sea), South Korea, and the Yellow Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 16.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.15. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.7 years; female 74.2 years.
National economy
Budget (1999). Revenue: W 19,801,000,000 (turnover tax and profits from state enterprises). Expenditures: W 20,018,200,000 ([1994] national economy 67.8%, social and cultural affairs 19.0%, defense 11.6%). Population economically active (2003): total 10,708,000; activity rate of total population 48.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64,67.4%; female 39.4%; unemployed [2000] 24.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 2,582,000, potatoes 2,070,000, corn (maize) 2,062,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,200,000 pigs, 2,740,000 goats, 570,000 cattle; roundwood 7,297,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 79%; fisheries production (2003) 268,700 (from aquaculture 24%). Mining and quarrying (2005): iron ore (metal content) 1,400,000; magne-site 1,200,000; phosphate rock 300,000. Manufacturing (2006): cement 6,155,000; steel semimanufactures (1994) 2,700,000; coke 2,000,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 21,974,000,000 (21,974,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 22,800,000 (22,666,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 7,340,000 (7,340,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (4,200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 545,000 (1,091,000). Households. Average household size (1999) 4.6. Public debt (external, outstanding; 2000): US$12,500,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$25,600,000,000 (US$1,108 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 90; official development assistance (2005) 62. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): FDI (2001-04 avg.) 1.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 22.4%, in permanent crops 1.7%, in pasture 0.4%; overall forest area (2005)51.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$2,718,472,000 ([2002; excludes trade with South Korea] food, beverages, and other agricultural products 19.3%; mineral fuels and lubricants 15.5%; machinery and apparatus 15.4%; textiles and clothing 10.4%). Major import sources: China 39.8%; South Korea 26.3%; Russia 8.2%; Thailand 7.6%; Singapore 2.7%. Exports (2005): US$1,338,281,000 ([2002; excludes trade with South Korea] live animals and agricultural products 39.3%; textiles and wearing apparel 16.7%; machinery and apparatus 11.6; mineral fuels and lubricants 9.5%). Major export destinations: China 37.3%; South Korea 25.4%; Japan 9.8%; Thailand 9.3%; Russia 0.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 5,235 km. Roads (2004): total length 25,185 km (paved 12%). Vehicles (1990): passenger cars 248,000. Air transport (2004): passenger-km (2002) 35,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 3,563,000 (160); telephone landlines (2004): 980,000 (44).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1987-88). Percentage of population ages 16 and over having attended or graduated from postsecondary-level school 13.7%. Literacy (1997): 95%. Health: physicians (2003) 74,597 (1 per 299 persons); hospital beds (2002) 292,340 (1 per 76 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 24.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,419 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 127% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,106,000 (army 85.9%, navy 4.2%, air force 9.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GNI (2004): 8.1%; per capita expenditure US$80.
Background
According to tradition, the ancient kingdom of Cho-son was established in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula, probably by peoples from northern China, in the 3rd millennium bc and was conquered by China in 108 bc. The kingdom was ruled by the Yi dynasty from 1392 to 1910. That year Korea was formally annexed by Japan. It was freed from Japanese control in 1945, at which time the USSR occupied the area north of latitude 38° N and the US occupied the area south of it. The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) was established as a communist state in 1948. North Korea launched an invasion of South Korea in 1950, initiating the Korean War, which ended with an armistice in 1953. Under Kim Il-sung, North Korea became one of the most harshly regimented societies in the world, with a state-owned economy that failed to produce adequate food. In the late 1990s, under Kim Il-sung’s successor, Kim Jong Il, the country endured a serious famine; as many as a million Koreans may have died.
Recent Developments
North Korea showed signs in 2007 that it might be willing to give up its nuclear programs if the price was right. The first breakthrough came in February when North Korea agreed to shut down its decrepit light-water nuclear reactor in exchange for a modest package of economic assistance. A second breakthrough came in October when the North agreed to disable the reactor and submit a list of all remaining nuclear programs by the end of the year. However, North Korean negotiators hinted that they might not reveal how many weapons the North had and also refused to admit to having a uranium-enrichment program. Furthermore, in September 2007 Israeli warplanes bombed a site deep in Syrian territory that Israel later claimed was a nuclear-weapons facility. In April 2008 US officials released video evidence that they claimed proved both the facility’s illicit purpose (the Syrians had claimed that it was an unused military warehouse) and that the technology in it had come directly from North Korea, further heightening tensions. North Korea had failed to meet the 31 December deadline but appeared to comply in May 2008 after the video release.
South Korea
Official name: Taehan Min’guk (Republic of Korea). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [299]). Head of state and government: President Lee Myung Bak (from 2008), assisted by Prime Minister Han Seung Soo (from 2008). Capital: Seoul. Official language: Korean. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 South Korean won (W) = 100 chon; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = W 1,050.33.
Demography
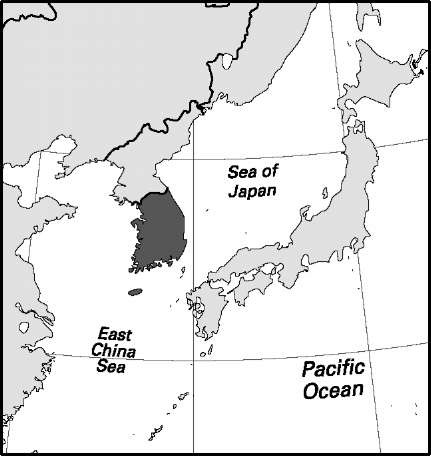
Area: 38,486 sq mi, 99,678 sq km. Population (2007): 48,456,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,259.1, persons persq km 486.1. Urban (2005): 81.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.97%; female 50.03%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 18.6%; 15-29, 22.5%; 30-44, 26.0%; 45-59, 19.2%; 60-74, 10.7%; 75-84, 2.5%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): Korean 97.7%; Japanese 2.0%; US white 0.1%; Han Chinese 0.1%; other 0.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Christian 43%, of which Protestant 17%, independent Christian 16%, Roman Catholic 9%; traditional beliefs 15%; Buddhist 14%; New Religionist 14%; Confucianist 10%; other 4%. Major cities (2005): Seoul 9,820,171; Pusan 3,523,582; Inch’on 2,531,280; Taegu 2,464,547; Taejon 1,442,856. Location: northeast Asia, bordering North Korea, the Sea of Japan (East Sea), and the Yellow Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.13. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 75.1 years; female 81.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: W 191,447,000,000,000 (current revenue 99.3%, of which tax revenue 79.6%, nontax revenue 19.7%; capital revenue 0.7%). Expendi-tures:W 184,922,000,000,000 (current expenditure 86.7%; capitalexpenditure 13.3%). Publicdebt (2005): US$240,000,000,000. Production(metrictonsexcept as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 6,305,000, cabbages 3,068,000, tangerines, man-darins,andsatsumas620,300,greenonions543,000, pears 431,464; livestock (number of live animals) 9,382,000 pigs, 2,484,000 cattle, 119,181,000 chickens; roundwood 4,877,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 51%; fisheries production (2005) 2,075,301 (from aquaculture 21%); aquatic plants production (2005) 636,366 (from aquaculture 98%). Mining and quarrying (2005): feldspar 508,644; iron ore (metal content) 131,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): electrical machinery and apparatus 31,583, of which televisions, radios, telecommunications equipment, and electronic parts 25,223; transportation equipment 26,027, of which automobiles 12,660, ship and boat construction 6,050, automobile parts 5,938; chemicals and chemical products 16,296, of which paints, soaps, and pharmaceuticals 8,040, industrial chemicals 7,131; textiles, wearingap-parel, and footwear 11,646, of which textiles 6,878. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 371,011,000,000 (371,011,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004)3,191,000(82,116,000);crudepe-troleum (barrels; 2005) none ([2004] 828,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 90,627,000 (60,701,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (29,611,000,000). Households (2001). Average household size (2005) 2.9; annual income per house-hold(2006)W32,303,000(US$33,800);sourcesofin-come: wages 84.2%, other 15.8%; expenditure: food and beverages 26.3%, transportation and communications 16.3%, education 11.3%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$871,992,000,000 (US$18,147 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 23,743,000; activity rate of total pop-ulation49.3%(participation rates: ages 15-64,66.4%; female 41.5%; unemployed [July 2007] 3.2%).Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,660; remittances (2006) 917; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 5,145. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 15,314; remittances(2006)4,245; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 3,487. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 16.7%, in permanent crops 2.0%, inpasture0.6%;overallforestarea (2005)63.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$178,827,000,000 (electric and electronic products 17.5%; nonelectrical machinery and transport equipment 17.5%; crude petroleum 12.9%; chemicals and chemical products 9.2%; food and live animals 4.7%). Major import sources.Japan 20.3%; US 13.9%; China 12.3%; Saudi Arabia 5.2%; Germany 3.8%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): US$193,817,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 44.7%; transport equipment 17.8%; chemicals and chemical products 9.2%; textile yarn, fabrics 5.6%). Major export destinations. China 18.1%; US 17.7%; Japan 8.9%; Hong Kong 7.6%; Taiwan 3.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length (2001) 6,819 km; passenger-km 31,004,200,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,336,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 100,279 km (paved 87%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 10,464,827; trucks and buses 4,041,527. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 69,276,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 7,433,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2000): 18,500,000 (396); televisions (2004): 22,915,000 (477); telephone landlines (2006): 26,866,000 (556); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 40,197,000 (832); personal computers (2005): 25,685,000 (532); total Internet users (2006): 34,120,000 (706); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 14,043,000 (291).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through lower secondary 29%; upper secondary/higher vocational 45%; university 26%. Literacy (2001): total population ages 15 and over literate 97.9%; males literate 99.2%; females literate 96.6%. Health (2005): physicians 85,369 (1 per 564 persons); hospital beds (2004) 353,289 (1 per 136 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2003) 7.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,040 (vegetable products 83%, animal products 17%); 157% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 687,000 (army 81.5%, navy 9.2%, air force 9.3%); US military forces (2006) 29,500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.6%; per capita expenditure US$430.
The Unification Church is a religious movement founded in Pusan, South Korea, by the Reverend Sun Myung Moon in 1954. Known for its mass weddings, the church teaches a unique Christian theology.
Background
Civilization in the Korean Peninsula dates to the 3rd millennium bc (see background of Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, above). The Republic of Korea was established in 1948 in the southern portion of the Korean peninsula. In 1950 North Korean troops invaded South Korea, precipitating the Korean War. UN forces intervened on the side of South Korea, while Chinese troops backed North Korea in the war, which ended with an armistice in 1953. The devastated country was rebuilt with US aid, and South Korea prospered in the postwar era, developing a strong export-oriented economy. It experienced an economic downturn in the mid-1990s that affected many economies in the area.
Recent Developments
South Korea was anything but the “Land of the Morning Calm” as voters went to the polls in December 2007 to elect their first CEO president, Lee Myung-bak. Despite questions concerning Lee’s involvement in a financial scandal, Koreans showed a preference for pragmatism over populism by overwhelmingly voting for the former Hyundai executive and mayor of Seoul. This election focused less on anxieties over North Korea and more on economic issues such as creating jobs and making home prices more affordable. Pres. Roh Moo Hyun traveled to Pyongyang in early October to meet with his Northern counterpart, Chairman Kim Jong Il, a full seven years after the first North-South summit. Aside from a vague pledge to replace the armistice agreement with a peace treaty to formally bringthe Korean Wartoanend,thesummitdid little to reduce military tensions, but it did underscore the fact that North-South economic cooperation had skyrocketed in recent years. In the Kaesong Industrial Complex in North Korea, just across the demilitarized zone, more than 20,000 North Koreans were working for South Korean companies. In August the North-South railway line was reconnected for the first time since the division of the Korean peninsula in 1945.
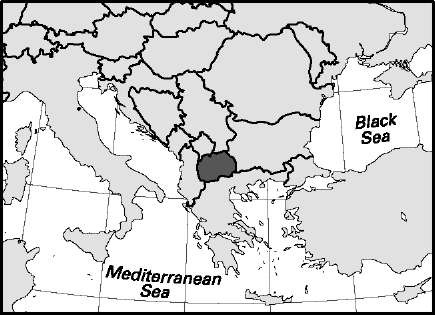
Kosovo
Official name: Republika e Kosoves (Albanian); Re-publika Kosovo (Serbian) (Republic of Kosovo). Form of government: multiparty transitional republic with one legislative house (Assembly of the Republic [120]). Chief of state: President Fatmir Sejdiu (from 2008; final authority rests with UN Interim Administrator Lamberto Zannier [from 2008]). Head of government: Prime Minister Hashim Thagi (from 2008). Capital: Pristina. Official languages: Albanian; Serbian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; US$1 = €0.63 (1 Jul 2008).
Demography
Distribution (2006): male 50.90%; female 49.10%. Age breakdown (2003): under 15, 32.2%; 15-59, 58.7%; 60 and over 9.1%. Ethnic composition (2008): Albanian 92.0%; Serb 5.3%; other 2.7%. Religious affiliation (2006): Muslim 91.0%; Orthodox 5.5%; Roman Catholic 3.0%, Protestant 0.5%. Major cities (2003): Pristina 165,844; Prizren 107,614; Fer-izaj 71,758; Mitrovice 68,929; Gjakove 68,645. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Serbia, Macedonia, Albania, and Montenegro.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.3 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 53.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2003): 3.00. Life expectancy at birth (2004; Albanian population only): male 69.8 years; female 71.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: €758,000,000 (varied taxes on imported goods at border [including customs and VAT] 69.0%; donor assistance 16.0%; other internal revenue [mostly income tax] 9.0%). Expenditures: €717,000,000 (current expenditure 73.2%; development expenditure 26.8%). Population economically active (2006): total 680,000(participation rates: ages 15-64, 33.0%; female 33.0%; unemployed 44.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): wheat 273,377, hay 186,959, corn (maize) 142,140; livestock (number of live animals) 351,800 cattle, 151,200 sheep, 2,386,000 chickens; roundwood 400,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 98%. Manufacturing (2006): cement, bricks, and tiles for reconstruction of housing; food; beverages. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 3,971,000,000 (2,155,000,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 6,530,000 (n.a.). Gross national income (2005): US$3,364,000,000 (US$1,640 per capita). Households. Average household size (2003) 6.5; sources of income (2005): wages and salaries 58.0%, remittances 13.0%, self-employment 9.0%, pensions 8.0%; expenditures (2002): food 42.5%, energy 9.5%, clothing and footwear 8.3%, transportation 8.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 32; remittances (2006) 586; foreign direct investment (2004-06 avg.) 488. Disbursements for (US$’000,000; 2006): tourism 78; remittances 126. Land use as % of total land area (2005): intemporarycrops 12.9%, in permanent crops 0.5%, in pasture 11.2%; overall forest area 41.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): €1,305,900,000 (food and live animals 17.5%; mineral fuels 16.6%; machinery and apparatus 12.5%; iron and steel [all forms] 7.5%; motor vehicles 5.8%). Major import sources: Macedonia 19.7%; Serbia 14.6%; Germany 9.4%; Turkey 7.4%; China 5.7%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): €110,800,000 (iron and steel [all forms] 30.2%; other base and fabricated metals 17.8%; mineral fuels 7.7%; food and live animals 7.7%). Major export destinations: Serbia 18.9%; Bulgaria 12.2%; Italy 11.4%; Albania 11.4%; Macedonia 8.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 430 km. Roads (2005): total length 1,924 km (paved 87%). Air transport (2005; Pristina airport only): passenger arrivals 452,362, passenger departures 478,258. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Telephone landlines (2006): 135,000 (65); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 540,000 (259); total Internet users (2006): 50,000 (24); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 4,700 (2.3).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25-49 having: no formal schooling 3.5%; incomplete/complete primary education 46.0%; incomplete/complete secondary 45.0%; higher 5.5%. Literacy (2000): population ages 15 and over literate 93.5%; males literate 97.7%; females literate 89.9%. Health (2005): physicians 2,500 (1 per 822 persons); hospital beds 5,308 (1 per 387 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 12.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (February 2008): NATO-led Kosovo Force 15,900.
Background
The Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes was created after the collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I. The country signed treaties with Czechoslovakia and Romania in 1920-21, marking the beginning of the Little Entente. In 1929 an absolute monarchy was established, the country’s name was changed to Yugoslavia, and it was divided into regions without regard to ethnic boundaries. Axis powers invaded Yugoslavia in 1941, and German, Italian, Hungarian, and Bulgarian troops occupied it for the rest of World War II. In 1945 the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was established; it included the republics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. Its independent form of communism under Josip Broz Tito’s leadership provoked the USSR. Internal ethnic tensions flared up in the 1980s, causing the country’s ultimate collapse. In 1991-92 independence was declared by Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina; the new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (containing roughly 45% of the population and 40% of the area of its predecessor) was proclaimed by Serbia and Montenegro. Still fueled by long-standing ethnic tensions, hostilities continued into the 1990s. Despite the approval of the Dayton Peace Agreement (1995), sporadic fighting continued and was followed in 1998-99 by Serbian repression and expulsion of ethnic populations in the province of Kosovo. In September-October 2000, the battered nation of Yugoslavia ended the autocratic rule of Pres. Slobodan Milosevic. In April 2001 he was arrested and in June extradited to The Hague to stand trial for war crimes, genocide, and crimes against humanity committed during the fighting in Kosovo. In February 2003 both houses of the Yugoslav federal legislature voted to accept a new state charter and change the name of the country from Yugoslavia to Serbia and Montenegro. Henceforth, defense, international political and economic relations, and human rights matters would be handled centrally, while all other functions would be run from the republican capitals, Belgrade and Podgorica, respectively. The move was seen as an acknowledgment that Serbia and Montenegro had little in common, and a provision was included for both states to vote on independence after three years; Serbia declared its independence in June 2006, shortly after Montenegro severed its federal union with Serbia. From 1999 an autonomous region administrered by the UN, Kosovo declared its independence from Serbia on 17 Feb 2008.
Recent Developments
The independence declaration was obviously the major news of 2008 in Kosovo. The country was immediately recognized by the US, Turkey, and most of the members ofthe EU, including the UK, France, and Germany. However, in addition to Serbia, the list of countries that refused to recognize Kosovo included Russia, China, Spain, Greece, and Cyprus. Kosovo’s economic and social situation was mixed in 2007. The Central Banking Authority of Kosovo reported that GDP grew 4.6% and that there was a budget surplus, while inflation rose only 2.0%. According to the World Bank, however, 37% of Kosovo’s population were considered poor, and 15% lived in extreme poverty. A UN report showed that 57% of those living in extreme poverty were under the age of 25, and unemployment for those under 25 was 40%.
Kuwait
Official name: Dawlat al-Kuwayt (State of Kuwait). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative body (National Assembly [50]). Head of state and government: Emir Sheikh Sabah al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah (from 2006), assisted by Prime Minister Sheikh Nassar Muhammad al-Ahmad al-Sabah (from 2006). Capital: Kuwait (city). Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Kuwaiti dinar (KD) = 1,000 fils; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = KD 0.26.
Demography
Area: 6,880 sq mi, 17,818 sq km. Population (2007): 3,294,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 478.8, persons per sq km 184.9. Urban (2005): 98.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 62.69%; female 37.31%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 24.3%; 15-29, 26.8%; 30-44, 34.2%; 45-59, 11.6%; 60-74, 2.7%; 75-84, 0.3%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2005): Arab 57%, of which Kuwaiti 35%; Bedouin 4%; non-Arab (primarily Asian) 39%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 74%, of which Sunni 59%, Shi’i 15%; Christian 13%, of which Roman Catholic 9%; Hindu 10%; Buddhist 3%. Major cities (2005): Qalib al-Shuyukh 179,264; Al-Sal-imiyah 145,328; Hawalli 106,992; Kuwait (city) 32,403 (urban agglomeration 1,810,000). Location: the Middle East, bordering Iraq, the Persian Gulf, and Saudi Arabia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 1.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 3.00. Life expectancy at birth (2004): male 75.9 years; female 77.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue:KD 12,346,700,000 (oil revenue 93.8%). Expenditures: KD 6,315,200,000 (defense 20.9%; transfers 18.5%; public utilities 14.0%; education 8.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$668,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$111,464,000,000 (US$40,114 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): tomatoes 55,750, cucumbers and gherkins 37,260, potatoes 20,740; livestock (number of live animals) 900,000 sheep, 150,000 goats, 5,000 camels; fisheries production 5,222 (from aquaculture 6%). Mining and quarrying (2005): sulfur 700,000; lime 49,800. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): refined petroleum products 2,701; chemicals and chemical products 533; fabricated metal products 319. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 41,256,000,000 (41,256,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 927,100,000 ([2004] 320,700,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 35,425,000 (12,683,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 9,700,000,000 (9,700,000,000). Population economically active (2004): total 1,634,315, of which Kuwaiti 18.3%, non-Kuwaiti 81.7%; activity rate of total population 59.4% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 76.4%; female [2002] 25.7%; unemployed 2.2%). Households. Average Kuwaiti household size (2004) 4.8; average non-Kuwaiti household size (2004) 5.0; sources of income (1986): wages and salaries 53.8%, self-employment 20.8%, other 25.4%; expenditure (2000): housingand energy 26.8%, food 18.3%, transportation and communications 16.1%, household furnishings 14.7%, clothing and footwear 8.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 165; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 20. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,277; remittances (2006) 2,648; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 57. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.8%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 7.6%; overall forest area (2005) 0.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): KD 3,722,234,000 (transport equipment 23.1%; machinery and apparatus 16.9%; food 12.4%; chemicals and chemical products 8.7%). Major import sources: Germany 11.5%; US 10.8%; Saudi Arabia 7.9%; China 6.8%; Japan 6.4%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): KD 8,428,100,000 (crude petroleum and petroleum products 93.3%; chemicals and chemical products 3.8%; reexports 1.7%). Major export destinations: Japan 20.0%; South Korea 14.0%; US 12.0%; Singapore 11.0%; Taiwan 10.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 5,720 km (paved [1999] 81%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 848,590; trucks and buses 172,219. Air transport (2003-04): passenger-km 6,681,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 223,514,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 482,000 (168); televisions (2004): 1,040,000 (392); telephone landlines (2005): 510,000 (190); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 2,380,000 (886); personal computers (2005): 600,000 (223); total Internet users (2006): 817,000 (295); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 25,000 (8.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling: illiterate 6.2%, literate 37.9%; primary education 12.7%; lower secondary 20.8%; upper secondary 11.7%; higher 10.7%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 84.4%; males literate 85.7%; females literate 82.8%. Health (2003): physicians 4,718 (1 per 526 persons); hospital beds 5,215 (1 per 476 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 8.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,420 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 172% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 15,500 (army 71.0%, navy 12.9%, air force 16.1%); US troops for Iraqi support (2007) 10,000-20,000. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.8%; per capita expenditure US$1,370.
Background
Faylakah Island, in Kuwait Bay, had a civilization dating back to the 3rd millennium bc that flourished until 1200 bc. Greek colonists resettled the island in the 4th century bc. Abd Rahim of the Sabah dynasty became sheikh in 1756, the first of a family that continues to rule Kuwait. In 1899, to thwart German and Ottoman influences, Kuwait gave Britain control of its foreign affairs. Following the outbreak of war in 1914, Britain established a protectorate there. In 1961, after Kuwait became independent, Iraq laid claim to it. British troops defended Kuwait, the Arab League recognized its independence, and Iraq dropped its claim. Iraqi forces invaded and occupied Kuwait in 1990, and a US-led military coalition drove them out in 1991. The destruction of many of Kuwait’s oil wells complicated reconstruction efforts.
Recent Developments
The year 2007 was marked by tensions in the Kuwaiti government. Having increased in importance after playing a pivotal role in January 2006 in removing the ailing emir and replacing him with Emir Sabah al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah, the parliament attempted to play a greater role in government and function as an elected body. There were even unsuccessful calls for a constitutional monarchy. Kuwaiti social and economic concerns were focused on revision of the educational system; improved health, water, and electricity services; and implementation of long-term planning in the fields of housing and employment. The government began a campaign to encourage Kuwaitis to work in the private sector—in 2008, foreign workers made up an estimated 97% of the total private-sector labor force. Planning continued for the construction of a new US$19 billion oil refinery, the largest of its kind in the Middle East.
Kyrgyzstan
Official name: Kyrgyz Respublikasy (Kyrgyz); Respub-lika Kirgizstan (Russian) (Kyrgyz Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Supreme Council [90]). Head of state: President Kurmanbek Bakiyev (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Igor Chudinov (from 2007). Capital: Bishkek. Official languages: Kyrgyz; Russian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 som (KGS) = 100 tyiyn; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = KGS 36.43.
Demography
Area: 76,641 sq mi, 198,500 sq km. Population (2007): 5,317,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 69.4, persons per sq km 26.8. Urban (2003): 33.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.03%; female 50.97%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 31.5%; 15-29, 29.8%; 30-44, 18.8%; 45-59, 12.0%; 60-74, 5.7%; 75-84, 1.9%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2005): Kyrgyz 67.4%; Uzbek 14.2%; Russian 10.3%; Hui 1.1%; Uighur 1.0%; other 6.0%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (mostly Sunni) 60.8%; Christian 10.4%, of which Russian Orthodox 7.7%; nonreligious 21.6%; atheist 6.3%; other 0.9%. Major cities (1999): Bishkek 750,327; Osh 208,520; Jalal-Abad 70,401; Tokmok 59,409; Kara-Kol 47,159. Location: central Asia, bordering Kazakhstan, China, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.3 (world avg. 20.3); (1994) within marriage 83.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.69. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 63.5 years; female 72.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: KGS 20,368,100,000 (tax revenue 80.3%, of which VAT 34.8%, income tax 8.6%, profit tax 6.3%; nontax revenue 17.7%; grants 2.0%). Expenditures: KGS 20,143,700,000 (administration, defense, and police 30.5%; education 24.4%; social security 14.2%; health 11.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,670,-000,000. Population economically active (2005): total 2,260,600; activity rate of total population 43.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2002] 68.7%; female 42.9%; unemployed 8.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): potatoes 1,141,000, wheat 950,100, corn (maize) 437,300; livestock (number of live animals) 2,965,220 sheep, 1,034,890 cattle, 347,178 horses; roundwood (2005) 27,300 cu m, of which fuelwood 66%; fisheries production 27 (from aquaculture 74%). Mining and quarrying (2004): mercury 488; antimony 20; gold 22,000 kg. Manufacturing (value of production in KGS ’000,000; 2004): base and fabricated metal products 24,330; food and tobacco products 6,811; cement, bricks, and ceramics 3,574. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 15,145,000,000 (11,817,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 64,000 (961,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 397,000 (475,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 542,000 (667,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 88,000 (541,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 29,000,000 (798,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.3; income per capita of household (2003) KGS 9,270 (US$212); sources of income (1999): wages and salaries 29.2%, self-employment 25.6%, other 45.2%; expenditure (1990): food and clothing 48.0%, health care 13.1%, housing 5.9%. Gross national income (2006): US$2,712,000,000 (US$516 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 73; remittances (2005) 322; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 56; official development assistance (2005) 193 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 58; remittances (2005) 122. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.0%, in permanent crops 0.3%, in pasture 49.2%; overall forest area (2005) 4.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$717,000,000 (mineral fuels 25.3%, of which refined petroleum 17.3%; chemicals and chemical products 14.2%; machinery and apparatus 12.9%; food products 7.9%). Major import sources (2006): Russia 38.0%; China 14.4%; Kazakhstan 11.6%; US 5.7%; Uzbekistan 3.8%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): US$581,700,000 (gold 44.6%; refined petroleum 8.2%; raw cotton 7.3%; food 6.4%). Major export destinations (2006): Switzerland 26.2%; Kazakhstan 20.5%; Russia 19.4%; Afghanistan 9.4%; China 4.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length (2000) 424 km; passenger-km 45,300,000; metric ton-km cargo 714,900,000. Roads (1999): total length 18,500 km (paved 91%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 196,339. Air transport (2005; Kyrghyzstan Airlines, Altyn Air Airlines, and Itek Air only): passenger-km 368,080,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,014,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 68,000 (13); televisions (2004): 955,000 (185); telephone land-lines (2005): 440,000 (84); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 541,000 (103); personal computers (2005): 100,000 (19); total Internet users (2006): 298,000 (56); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 2,500 (0.5).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: primary education 6.3%; some secondary 18.3%; completed secondary 50.0%; some postsecondary 14.9%; higher 10.5%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.7%; males literate 99.3%; females literate 98.1%. Health: physicians (2004) 13,996 (1 per 363 persons); hospital beds (2004) 26,040 (1 per 195 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 29.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,027 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 157% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 12,500 (army 68.0%, air force 32.0%); US troops (2006) 1,600; Russian troops (2006) 1,000. Militaryexpenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.1%; per capita expenditure US$15.
Background
The Kyrgyz, a nomadic people of Central Asia, settled in the Tian Shan region in ancient times. They were conquered by Genghis Khan’s son Jochi in 1207. The area became part of the Qing empire of China in the mid-18th century. The region came under Russian control in the 19th century, and its rebellion against Russia in 1916 resulted in a long period of brutal repression. Kirgiziya became an autonomous province of the USSR in 1924 and was made the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic in 1936. Kyrgyzstan gained independence in 1991. In the 1990s it struggled with its democratization process and with establishing a thriving economy.
Recent Developments
The political situation in Kyrgyzstan continued to worsen in 2007, and there was general agreement that the 2005 “Tulip Revolution” had been a failure. Frequent demonstrations called for Pres. Kurmanbek Bakiyev’s resignation, usually on grounds of corruption and favoritism. Another reason for disenchantment was continuing economic stagnation, and increasing numbers of Kyrgyz citizens were forced to find work abroad. In January Bakiyev signed constitutional amendments that expanded the powers of the president. In September the Constitutional Court declared the amendments unconstitutional on the grounds that they had not been confirmed by popular referendum. Official results of the October referendum showed 80% of voters approved the new amendments, but observers from NGOs reported numerous cases of ballot-box stuffing.
Laos
Official name: Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao (Lao People’s Democratic Republic). Form of government: unitary single-party people’s republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [115]). Chief of state: President Choummaly Sayasone (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Boua-sone Bouphavanh (from 2006). Capital: Vientiane (Viangchan). Official language: Lao. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 kip (KN) = 100 at; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = KN 8,675.00.
Demography
Area: 91,429 sq mi, 236,800 sq km. Population (2007): 5,859,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 64.1, persons per sq km 24.7. Urban (2005): 27.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.81%; female 50.19%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 39.4%; 15-29, 28.3%; 30-44,17.0%; 45-59, 9.5%; 60-74, 4.4%; 75 and over, 1.4%. Ethnic composition (2005): Lao 54.6%; Khmou 10.9%; Hmong 8.0%; Tai 3.8%; Phu Tai (Phouthay) 3.3%; Lue 2.2%; Katang 2.1%; Makong 2.1%; other 13.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs 49%; Buddhist 43%; Christian 2%; nonreligious/other 6%. Major cities (2003): Vientiane 194,200 (urban agglomeration [2005] 702,000); Savannakhet 58,200; Pakxe 50,100; Xam Nua 40,700; Muang Khammouan 27,300. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering China, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and Myanmar (Burma).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 34.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.77. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 53.1 years; female 57.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2003-04). Revenue: KN 3,282,000,000,000 (tax revenue 72.5%, of which sales tax 18.9%, excise tax 13.6%; grants 14.2%; nontax revenue 13.3%). Expenditures: KN 4,261,000,000,000 (capital expenditure 51.1%, of which foreign-financed 34.2%; current expenditure 48.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,971,000,000. Population economically active (2005): total 2,778,000; activity rate of total population 66.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 81.3%; female 50.2%; unofficially unemployed [2004] 7.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 2,350,000, sweet potatoes 248,000, sugarcane 230,000, ramie 1,800; livestock (number of live animals) 1,827,000 pigs, 1,272,000 cattle, 1,097,000 water buffalo; roundwood 6,335,968 cu m, of which fu-elwood 94%; fisheries production 107,800 (from aquaculture 72%). Miningand quarrying(2005): limestone 560,000; gypsum 250,000; refined copper 30,480. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1999): food and food products 22; wearingapparel 14; tobacco products 8. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 3,430,000,000 ([2004] 762,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 290,000 (290,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (126,000). Gross national income (2006): US$3,270,000,000 (US$568 per capita). Households. Average household size (2005)5.9; average annual income per household (1995) KN 3,710 (US$371); expenditure (1990): food and nonalcoholic beverages 46.2%, transportation and communications 17.9%, household furnishings 8.1%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco 6.4%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 146; remittances (2005) 1.0; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 23; official development assistance (2005) 296. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2001) 0.1; remittances (2005) 1.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.2%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 3.8%; overall forestarea (2005) 69.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$505,900,000 ([2003] consumption goods 49.2%; construction and electrical equipment 12.0%; materials for garment assembly 10.6%; machinery and apparatus 10.2%; mineral fuels 10.2%). Major import sources:Thailand 60%; China 9%; Vietnam 9%; Singapore 4%; Germany 3%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$361,100,000 (garments 26.9%; electricity 26.9%; wood products [mostly logs and timber] 18.6%). Major export destinations: Thailand 19.0%; Vietnam 17.0%; France 8.0%; Germany 6.0%; UK 5.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 24,000 km (paved 16%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 16,320; trucks and buses 4,200. Air transport (2004): passenger-km 216,300,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 33,000 (5.8); televisions (2003): 321,000 (59); telephone landlines (2005): 75,000 (13); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 638,000 (108); personal computers (2005): 100,000 (17); total Internet users (2005): 26,000 (4.6); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 200 (0.03).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 32.8%; incomplete primary education 21.6%; complete primary 18.2%; lower secondary 11.4%; upper secondary 6.2%; higher 9.8%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 72.7%; males literate 82.5%; females literate 63.2%. Health (2005): physicians 5,000 (1 per 1,129 persons); hospital beds 6,736 (1 per 838 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 85.2.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 29,100 (army 88.0%, air force 12.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 0.4%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Background
The Lao people migrated into Laos from southern China after the 8th century ad, displacing indigenous tribes. In the 14th century Fa Ngum founded the first Laotian state, Lan Xang. Except for a period of rule by Burma (1574-1637), the Lan Xang kingdom ruled Laos until 1713, when it split into three kingdoms. France gained control of the region in 1893. In 1945 Japan seized it and declared Laos independent. The area reverted to French rule after World War II. The Geneva Conference of 1954 unified and granted independence to Laos. Communist forces took control in 1975, establishing the Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Laos held its first election in 1989 and promulgated a new constitution in 1991. Although its economy was adversely affected by the mid-1990s Asian monetary crises, it realized a longtime goal in 1997 when it joined the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
Recent Developments
The economy of Laos continued to grow steadily in 2007, with a growth rate of about 6.8%. This expansion was driven to a large extent by foreign direct investment, particularly in the natural resource and industry sectors through the ongoing construction of a number of large hydropower dams (Nam Theun 2, Nam Ngum 2, and Se Kaman 3) and the development of mining activities. Without these large hydropower and mining projects, Laos’s GDP growth rate would have averaged nearly 2 points lower between 2003 and 2006. The continued rapid growth of the mining industry was expected; in its five-year plan (2006-11), the Ministry of Trade and Handicrafts envisioned annual growth of nearly 11.5% in mineral production. The negative social and environmental impacts of these projects remained concerning, however.
Latvia
Official name: Latvijas Republika (Republic of Latvia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (Parliament, or Saeima [100]). Chief of state: President Valdis Zatlers (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Ivars Godmanis (from 2007). Capital: Riga. Official language: Latvian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 lats (Ls; plural lati) = 100 santimi; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 0.45 Ls.
Demography
Area: 24,938 sq mi, 64,589 sq km. Population (2007): 2,274,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 91.2, persons per sq km 35.2. Urban (2004): 68.0%. Sex distribution (2004): male 46.08%; female 53.92%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 14.8%; 15-29, 22.5%; 30-44, 21.2%; 45-59, 19.3%; 60-74, 15.6%; 75-84, 5.5%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2004): Latvian 58.8%; Russian 28.6%; Belarusian 3.8%; Ukrainian 2.6%; Polish 2.5%; Lithuanian 1.4%; other 2.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Orthodox 29%, of which Russian 16%, Latvian 13%; Roman Catholic 19%; Lutheran 14%; nonreligious 26%; atheist/other 12%. Major cities (2006): Riga 722,485; Daugavpils 108,091; Liepaja 85,477; Jelgava 66,051; Jurmala 55,408. Location: eastern Europe, bordering Estonia, Russia, Belarus, Lithuania, and the Baltic Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.7 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 56.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -4.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.29. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 65.9 years; female 76.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: Ls 2,522,202,000 (social security contributions 25.4%; VAT 19.3%; nontax revenue 19.0%; income taxes 17.3%; excises 9.4%). Expenditures: Ls 2,600,612,000 (social security and welfare 28.1%; education 16.5%; health 9.4%; police 6.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; March 2007): US$1,224,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 676,500, potatoes 658,200, sugar beets 519,900; livestock (number of live animals) 435,700 pigs, 371,100 cattle; roundwood 12,842,600 cu m, of which fuelwood 7%; fisheries production 151,160. Mining and quarrying (2005): peat 675,866; limestone 420,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food and food products 245; sawed and planed wood 206; wood products (excluding furniture) 130. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 4,680,000,000 (6,786,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (98,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (1,240,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (1,663,000,000). Households (2004). Average household size (2006) 2.5; annual disposable income per household Ls 3,037 (US$5,624); sources of income: wages and salaries 64.7%, pensions and transfers 25.1%, self-employment 9.4%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 34.1%, transportation and communications 18.5%, housing and energy 12.6%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 15.4%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 9.8%; overall forest area (2005) 47.4%. Gross national income (2006): US$19,531,000,000 (US$8,532 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 1,135,000; activity rate of total population 49.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 69.5%; female 48.3%; unemployed [October 2006-June 2007] 6.7%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 341; remittances (2006) 481; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 402. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 584; remittances (2006) 30; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 59.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): Ls 4,834,713,000 (machinery and apparatus 19.7%; mineral fuels 15.6%; food and food products 11.7%; transport vehicles 10.8%; base and fabricated metals 9.2%; chemicals and chemical products 8.3%). Major import sources: Germany 13.8%; Lithuania 13.7%; Russia 8.6%; Estonia 7.9%; Poland 6.3%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): Ls 2,871,401,000 (wood and wood products [mostly sawn wood] 26.9%; base and fabricated metals [mostly iron and steel] 13.2%; food and food products 12.2%; textiles and clothing 9.0%). Major export destinations: Lithuania 10.8%; Estonia 10.8%; Germany 10.3%; UK 10.1%; Russia 8.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length (2005) 2,270 km; passenger-km 892,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 19,779,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 51,759 km (paved 39%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 742,447; trucks and buses 123,757. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 1,478,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 31,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 228,000 (99); televisions (2003): 1,992,000 (857); telephone landlines (2006): 657,000 (287); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,184,000 (955); personal computers (2005): 566,000 (245); total Internet users (2006): 1,071,000 (468); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 110,000 (48).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004; employed population only). Percentage of population ages 15-74 having: none/unknown through complete primary education 12.3%; secondary 25.0%; vocational 40.0%; higher 22.7%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate, virtually 100%. Health (2006): physicians 8,341 (1 per 273 persons); hospital beds 20,728 (1 per 110 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 7.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,875 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%); 147% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 5,238 (army 34.7%, navy 13.1%, air force 4.9%, headquarters/administrative 47.3%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.7%; per capita expenditure US$119.
Background
Latvia was settled by the Balts in ancient times. It was conquered by the Vikings in the 9th century and later dominated by its German-speaking neighbors, who Christianized the people in the 12th-13th centuries. By 1230 German rule was established. From the mid-16th to the early 18th century, the region was split between Poland and Sweden, but by the end of the 18th century all of Latvia had been annexed by Russia. Latvia declared its independence after the Russian Revolution of 1917, but in 1940 the Soviet Red Army invaded. Held by Nazi Germany in 1941-44, the country was recaptured by the Soviets and incorporated into the Soviet Union. Latvia gained its independence in 1991 with the breakup ofthe Soviet Union; throughout the 1990s it sought to privatize the economy and build ties with Western Europe.
Recent Developments
Latvia’s foreign relations in 2007 developed along anticipated lines. The EU extended the Schengen passport-free travel zone to Latvia, and Canada permitted Latvians visa-free travel. Given the unpopularity of the war in Iraq, in late June the Latvian unit returned home, but 260 peacekeepers were later sent to join the 100 already in Afghanistan. Agreement was reached in March on a border treaty with Russia, though it remained controversial in Latvia because it affirmed the borders imposed by the Soviet regime and accepted the seizure of Latvian border counties by the USSR. Domestically, Latvia experienced an
Lebanon
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-Lubnaniyah (Lebanese Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [128]). Chief of state: President Michel Suleiman (from 2008). Head of government: Prime Minister Fouad Siniora (from 2005). Capital: Beirut. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Lebanese pound (LBP) = 100 piastres; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = LBP 1,506.50.
Demography
Area: 4,016 sq mi, 10,400 sq km. Population (2007): 4,099,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,021, persons per sq km 394.1. Urban (2005): 86.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.99%; female 51.01%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 28.6%; 15-29, 26.2%; 30-44, 21.2%; 45-59, 13.7%; 60-74, 7.9%; 75-84, 2.1%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 84.5%, of which Lebanese 71.2%, Palestinian 12.1%; Armenian 6.8%; Kurd 6.1%; other 2.6%. Religious affiliation (1995): Muslim 55.3%, of which Shi’i 34.0%, Sunni 21.3%; Christian 37.6%, of which Catholic 25.1% (Maronite 19.0%, Greek Catholic or Melchite 4.6%), Orthodox 11.7% (Greek Orthodox 6.0%, Armenian Apostolic 5.2%), Protestant 0.5%; Druze 7.1%. Major cities (2003): Beirut (urban agglomeration; 2005) 1,777,000; Tripoli 212,900; Sidon 149,000; Tyre (Sur) 117,100; Al-Nabatiyah 89,400. Location: the Middle East, bordering Syria, Israel, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.92. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 70.2 years; female 75.2 years. overheated economy. Though gross domestic product grew by an estimated 25%, the growth was offset somewhat by 13% inflation.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: LBP 6,984,200,000,000 (tax revenue 69.7%, of which VAT revenues 24.2%, customs and excise revenues 18.1%; nontax revenue 30.3%). Expenditures: LBP 7,802,200,000,000 (general expenditures 54.7%; interestexpenditures 45.3%, of which foreign 25.7%, domestic 19.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; April 2007): US$20,417,000,-000. Gross national income (2006): US$21,662,-000,000 (US$5,342 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): potatoes 511,400, tomatoes 277,000, oranges 235,600; livestock (number of live animals) 430,000 goats, 340,000 sheep, 90,000 cattle; round-wood 88,504 cu m, of which fuelwood 92%; fisheries production 4,601 (from aquaculture 18%). Mining and quarrying (2005): lime 14,000; salt 3,500; gypsum 1,700. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1998): food and food products 345; cement, bricks, and ceramics 212; wood and wood products 188, of which furniture (including metal furniture) 135. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 9,183,000,000 (10,581,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) none (4,309,000). Population economically active (2004): total 1,170,800; activity rate of total population 30%(participation rates: ages 15-64 [1997] 49.2%; female 21.2%; unemployed 8.2%). Households. Average household size (2004)4.3; average annual income per household (1994; Beirut only) LBP 2,400,000 (US$1,430); expenditure (2002): food, beverages, and tobacco 28.3%, health and education 17.2%, housing and energy 16.7%, household furnishings 7.4%, transportation and communications 7.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,432; remittances (2005) 4,924; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,024; official development assistance (2005) 248 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,878; remittances (2005) 4,233; FDI (2001-05 avg.)431. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporarycrops 16.6%, in permanent crops 14.0%, in pasture 1.6%; overall for-estarea (2005) 13.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$9,339,900,000 (mineral products 23.8%; electrical equipment 11.4%; food and live animals 10.3%; chemicals and chemical products 8.8%; transportation equipment 8.7%). Major import sources: Italy 10.4%; France 8.4%; China 7.9%; Germany 7.0%; US 5.9%. Exports (2005): US$1,879,800,000 (electrical equipment 16.7%; base metals 14.7%; precious metal jewelry and stones [significantly gold and pearls] 11.9%; food and live animals 10.7%; chemicals and chemical products 8.7%). Major export destinations: Syria 10.0%; Iraq 9.5%; UAE 8.2%; Saudi Arabia 7.4%; Switzerland 6.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 7,300 km (paved 85%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 1,370,897; trucks and buses 102,394. Airtransport (2006; Middle East Airlines only): passenger-km 1,940,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 29,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 634,000 (158); televisions (2004): 1,269,000 (320); telephone landlines (2006): 681,000 (178); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,103,000 (288); personal computers (2005): 409,000 (102); total Internet users (2006): 950,000 (248); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 170,000 (44).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 4 and over having: no formal education/unknown 13.7%; incomplete primary education 3.2%; primary 54.2%; secondary/vocational 15.5%; upper vocational 1.7%; higher 11.7%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 88.3%; males literate 93.6%; females literate 83.4%. Health (2004): physicians 10,304 (1 per 364 persons); hospital beds (2006) 9,786 (1 per 414 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 24.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,916 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 152% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 72,100 (army 97.1%, navy 1.5%, air force 1.4%); UN peacekeeping troops (June 2007) 13,300; Syrian troops ended 29-year presence in April 2005. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.5%; per capita expenditure US$280.
Background
Much of present-day Lebanon corresponds to ancient Phoenicia, which was settled c. 3000 bc. In the 6th century ad, Christians fleeing Syrian persecution settled in what is now northern Lebanon and founded the Maronite Church. Arab tribesmen settled in southern Lebanon and by the 11th century had founded the Druze faith. Lebanon was later ruled by the Mamluks. In 1516 the Ottoman Turks seized control; the Turks ended the local rule of the Druze Shihab princes in 1842. After the massacre of Maronites by Druze in 1860, France forced the Ottomans to form an autonomous province for the Christian area, known as Mount Lebanon. Following World War I, it was administered by the French military, but by late 1946 it was fully independent. After the Arab-Israeli War of 1948-49, Palestinian refugees settled in southern Lebanon. In 1970 the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) moved its headquarters there and began raids into northern Israel. The Christian-dominated Lebanese government tried to curb them, and in response the PLO sided with Lebanon’s Muslims in their conflict with Christians, sparking a civil war by 1975. In 1982 Israeli forces invaded in an effort to drive Palestinian forces out of southern Lebanon. Israeli troops withdrew from most of Lebanon in 1985, leaving the conflict unresolved, but later returned. A cease-fire, agreed to in 1996, was broken in 1997 when Israeli soldiers and Lebanon’s Hezbollah forces clashed.
Recent Developments
Political problems associated with choosinga newpresident for Lebanon arose in 2007. Bickering continued between the parliamentary majority, which insisted on an independent president, and the minority, which was pushing for a pro-Syrian president. On 24 November Gen. Emile Lahoud’s nine-yearextended term as president came to an end, but no one was elected to replace him, and Prime Minister FouadSiniora was made acting president. In the thick of continuing political conflict, two parliamentary deputies were killed. In September deputy Antoine Ghanem of the Christian Phalange Party was killed in a car bombing in Beirut; his death came just a few months after another car bomb had killed Walid Eido, a deputy of the Sunni-dominated Future Movement. Both belonged to the pro-government majority bloc in the parliament and were against the imposition of Syrian policies in Lebanon. In December a car bomb killed Gen. Frangois al-Hajj, the operations chief of the Lebanese army. In May 2008 the Muslim extremist organization Hezbollah took up arms against the government in protest against decisions that made its private telephone network illegal and thatsoughtto remove the head of airport security for his ties to the group. The worst violence since the civil war ensued, leaving at least 65 dead in a week of fighting before the government reversed the decisions in question.
Lesotho
Official name: Lesotho (Sotho); Kingdom of Lesotho (English). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [33]; National Assembly [120]). Chief of state: King Letsie III (from 1996). Head of government: Prime Minister Bethuel Pakalitha Mosisili (from 1998). Capital: Maseru. Official languages: Sotho; English. Official religion: Christianity. Monetary unit: 1 loti (plural maloti [M]) = 100 lisente; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = M 7.92 (the South African rand is accepted as legal tender within Lesotho).
Demography
Area: 11,720sq mi, 30,355 sq km. Population (2007): 2,008,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 171.3, persons persq km 66.2. Urban (2006): 23.7%. Sexdis-tribution (2006): male 48.69%; female 51.31%. Age breakdown (2001): under 15, 35.8%; 15-29, 31.2%; 30-44, 14.7%; 45-59, 10.0%; 60-74, 6.0%; 75 and over, 2.1%; unknown 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Sotho 80.3%; Zulu 14.4%; other 5.3%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 91.0%, of which Roman Catholic 37.5%, unaffiliated Christian 23.9%, Protestant (mostly Reformed and Anglican) 17.7%, independent Christian 11.8%; traditional beliefs 7.7%; other 1.3%. Major urban centers (2004): Maseru 178,300; Maputsoe 36,200; Mafeteng 36,000; Tey-ateyaneng 23,700; Hlotse 23,400. Location: southern Africa, surrounded by South Africa.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 25.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 22.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.28. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 40.4 years; female 39.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue: M 4,080,300,000 (tax revenue 82.7%, of which customs receipts 49.3%, income and profit tax 17.9%, sales tax 13.3%; nontax revenue 11.8%; grants 5.5%). Expenditures: M 3,762,300,000 (education and community services 29.9%; health and social security 12.8%; public order 10.1%; defense 5.6%; interest payments 4.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$647,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): potatoes 98,770, corn (maize) 76,090, sorghum 15,828; livestock (number of live animals; 2006) 1,000,000 sheep, 790,000 goats, 650,000cattle; roundwood 2,053,000cu m,ofwhich fuelwood 100%; fisheries production 46 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2005): diamonds 37,000 carats. Manufacturing (value of manufactured exports; US$’000,000; 2002): apparel and clothing accessories 233.7; footwear 23.9; television receivers 13.8. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 250,000,000 (244,500,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2003) none (100,000). Population economically active (2003): total 640,000; activity rate of total population 35.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 60.8%; female 45.0%; unemployed [2005] 50%). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.1; expenditure (2000): food and nonalcoholic beverages 39.9%, household furnishings 17.0%, clothing and footwear 15.6%, transportation 7.8%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$1,748,000,000 (US$876 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 30; remittances (2005) 327; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 39; official development assistance (2005) 69. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 27; remittances (2005) 17. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.9%, in permanent crops 0.1%, in pasture 65.9%; overall forest area (2005) 0.3%.
Foreign trade
(1999; food products 15.3%; unspecified commodities 84.7%). Major import sources (2004): Customs Union of Southern Africa (CUSA; mostly South Africa) 73.4%; Asian countries 23.6%. Exports (2004): M 4,652,000,000 (clothing 74.4%; telecommunications equipment 3.3%; footwear 2.8%). Major export destinations (2004): North America (mostly the US) 74%; EU 16%; CUSA (mostly South Africa) 9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): length 2.6 km. Roads (1999): total length 5,940 km (paved 18%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 12,610; trucks and buses 25,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 80,000 (41); telephone landlines (2005): 48,000 (24); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 298,000 (150); personal computers (2005): 1,000 (0.5); total Internet users (2005): 52,000 (26); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 50 (0.02).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education 22%; incomplete primary 40%; complete primary 17%; secondary and higher 21%. Literacy (2000-04): total population ages 15 and over literate 81.4%; males literate 73.7%; females literate 90.3%. Health (2003): physicians 140 (1 per 16,298 persons); hospital beds 1,025 (1 per 2,226 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 81.3.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,000 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$17.
Background
Bantu-speaking farmers began to settle the area in the 16th century, and a number of chiefdoms arose. The most powerful organized the Basotho in 1824 and obtained British protection in 1843, as tension between the Basotho and the South African Boers increased. The area became a British territory in 1868 and was annexed to the Cape Colony in 1871. The colony’s effort to disarm the Basotho resulted in revolt in 1880, and four years later it separated from the colony and became a British High Commission Territory. In 1966 it declared its independence. A new constitution (1993) ended seven years of military rule. In the late 20th century, Lesotho suffered from internal political problems and a deteriorating economy.
Recent Developments
An estimated one in five people faced the prospect of food shortages in Lesotho in late 2007. Planting of crops had declined because of a lack of resources, and the HIV/AIDS pandemic reduced available labor, but the main cause of the food crisis was the drought (the country’s worst in 30 years), which early in the year ravaged the low-lying areas west of the mountains, where most crops were grown.
Liberia
Official name: Republic of Liberia. Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [30]; House of Representatives [64]). Head of state and government: President Ellen Johnson-Sir-leaf (from 2006). Capital: Monrovia. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Liberian dollar (L$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = L$63.50.
Demography
Area: 37,743 sq mi, 97,754 sq km. Population (2007): 3,750,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 99.4, persons per sq km 38.4. Urban (2005): 58.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.72%; female 50.28%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 42.7%; 15-29, 28.4%; 30-44, 15.3%; 45-59, 9.0%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Kpelle 18.9%; Bassa 13.1%; Grebo 10.3%; Gio (Dan) 7.4%; Kru 6.9%; Mano 6.1%; Loma 5.3%; Kissi 3.8%; Krahn 3.7%; Americo-Liberian 2.4% (descendant from freed US slaves); other 22.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs 40%; Christian (mostly Protestant/independent Christian) 40%; Muslim 20%. Major cities (2003): Monrovia 550,200 (urban agglomeration [2005] 936,000); Zwedru 35,300; Buchanan 27,300; Yekepa 22,900; Harper 20,000. Location: western Africa, bordering Guinea, Cote d’Ivoire, the North Atlantic Ocean, and Sierra Leone.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 44.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 21.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per child-bearing woman; 2006): 6.02. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 38.0 years; female 41.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: US$83,300,000 (tax revenue 87.2%, of which import duties 34.7%, income and profit taxes 34.7%, maritime revenue 10.7%, taxes on goods and services 6.6%; nontax revenue 8.0%; grants 4.8%). Expenditures: US$81,400,000 (current expenditures 88.3%, of which wages 48.5%, goods and services 28.4%, interest on debt 2.2%; development expenditures 11.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,115,000,000. Population economically active (2003): total 1,182,000; activity rate 36.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.0%; female 39.8%; unemployed [2006] 85%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 483,440, sugarcane 255,000, oil palm fruit 183,000; livestock (number of live animals) 220,000 goats, 210,000 sheep, 130,000 pigs; roundwood 6,141,423 cu m, of which fuelwood 95%; fisheries production 10,000. Mining and quarrying (2005): diamonds 10,000 carats (UN sanctions on exports of rough diamonds from 2001 ended in April 2007); gold 16 kg. International maritime licensing (registration fees earned; 2006): more than US$8,000,000. Manufacturing (value of sales in L$’000; January-June 2005): cement 417,224; beer 328,207; carbonated beverages 205,564. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 330,000,000 (330,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) negligible (146,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.1; expenditure (1998): food 34.4%, housing 14.9%, clothing 13.8%, household furnishings 6.1%. Gross national income (2006): US$546,-000,000 (US$153 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): remittances (2005) 620; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 157; official development assistance (2005) 236. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): remittances (2005) 598; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 66. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.0%, in permanent crops 2.3%, in pasture 20.8%; overall forest area (2005) 32.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$273,600,000 (petroleum and petroleum products 33.2%; food, beverages, and tobacco 21.2%, of which rice 9.0%; machinery and transportation equipment 16.4%). Major import sources (2004): South Korea 38.1%; Japan 21.9%; Singapore 12.6%; Croatia 4.8%. Exports (2005): US$112,200,000 (rubber 88.0%; cocoa beans 5.1%). Major export destinations (2004): US 61.4%; Belgium 29.5%; China 5.3%; France 1.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2007): route length 78 km. Roads (2003): total length 10,600 km (paved 6%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 17,100; trucks and buses 12,800. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,100 (0.7); televisions (2001): 69,000 (25); telephone landlines (2002): 6,900 (2.5); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 160,000 (53).
Education and health
Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 58.9%; males literate 75.2%; females literate 42.7%. Health: physicians (2004) 103 (1 per 27,255 persons); hospital beds (2001) 2,751 (1 per 1,003 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 155.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,078 (vegetable products 96%, animal products 4%); 114% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,400; UN peacekeeping troops (August 2007) 13,900. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2003): 11%; per capita expenditure US$16.
Background
Africa’s oldest republic, Liberia was established as a home for freed American slaves under the American Colonization Society, which founded a colony at Cape Mesurado in 1821. In 1822 Jehudi Ashmun, a Methodist minister, became the director of the settlement and Liberia’s real founder. Joseph Jenkins Roberts, Liberia’s first nonwhite governor, proclaimed Liberian independence in 1847 and expanded its boundaries, which were officially established in 1892. In 1980 a coup led by Samuel K. Doe marked the end of the Americo-Liberians’ long political dominance over the descendants of indigenous Africans. A rebellion in 1989 escalated into a destructive civil war in the 1990s. A peace agreement was reached in 1996, and elections were held in 1997.
Recent Developments
Former Liberian president Charles Taylor’s war-crimes trial for murder, rape, and enlistment of child soldiers began in June 2007 in The Netherlands. It was expected that testimony would incriminate important members of the political class. The trial continued in 2008 with sensational testimony, including the assertion from one of Taylor’s aides that African peacekeepers and UN personnel were killed and eaten on Taylor’s orders. Although the UN Security Council extended the mandate of its peacekeeping force until September 2008, itcutthe mission’s strength by 20% and also reduced the size of its police force. Economic conditions improved slightly. In April 2007 the Security Council lifted its ban on Liberian diamond exports, imposed in 2001 to reduce the export of illegal “blood diamonds” that had helped finance the civil war.
Libya
Official name: Al-Jamahiriyah al-’Arabiyah al-Libiyah al-Sha’biyah al-Ishtirakiyah al-’Uzma (Socialist People’s Libyan Arab Jamahiriya). Form of government: authoritarian state with one policy-making body (General People’s Congress [468]). Chief of state: Muammar al-Qaddafi (de facto; from 1969); Secretary of the General People’s Congress Zentani Muhammad al-Zentani (de jure; from 1992). Head of government: Secretary of the General People’s Committee (Prime Minister) Al-Baghdadi Ali al-Mahmudi (from 2006). Capital: Tripoli. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetaryunit: 1 Libyan dinar(LD) = 1,000 dirhams; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = LD 1.18.
Demography
Area: 679,362 sq mi, 1,759,540 sq km. Population (2007): 6,342,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 9.3, persons per sq km 3.6. Urban (2005): 84.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.93%; female 48.07%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 30.1%; 15 -29, 32.2%; 30-44, 19.8%; 45-59, 11.4%; 60-74, 5.3%; 75-84, 1.0%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 87.1%, of which Libyan 57.2%, Bedouin 13.8%, Egyptian 7.7%, Sudanese 3.5%, Tunisian 2.9%; Amazigh (Berber) 6.8%, of which Arabized 4.2%; other 6.1%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 96.1%; Orthodox 1.9%; Roman Catholic 0.8%; other 1.2%. Major cities (2005): Tripoli 911,643 (urban agglomeration 2,098,000); Banghazi 685,367 (urban agglomeration 1,114,000); Misratah (2003) 121,669. Location: northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt, The Sudan, Chad, Niger, Algeria, and Tunisia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 26.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 3.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 23.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.34. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 74.3 years; female 78.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: LD 37,433,000,000 (oil revenues 92.9%). Expenditures.LD 18,319,000,000 (development expenditures 54.0%; current expenditures 46.0%, of which wages and salaries 24.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,-900,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): tomatoes 212,800, olives 211,300, potatoes 195,000; livestock (number of live animals) 4,500,000 sheep, 1,265,000 goats, 47,000 camels; roundwood 652,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 82%; fisheries production 46,339 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): lime 250,000; gypsum 175,000; salt 40,000. Manufacturing (value of production in LD ’000,000; 1996): base metals 212; electrical equipment 208; petrochemicals 175. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 20,202,000,000 (20,202,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2002) none (4,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 642,800,000 ([2004] 125,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 16,419,000 (9,288,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 6,816,000,000 (5,746,000,000). Households. Average household size (2006) 5.9. Population economically active (2003): total 2,137,000; activity rate of total population 37.9% (participation rates: ages 15 to 64, 56.7%; female 24.7%; unemployed [2004] 30.0%). Gross national income (2006): US$50,107,000,000 (US$8,298 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 250; remittances (2005) 15; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 12; official development assistance (2005) 14 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 680; remittances (2005) 914. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.0%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 7.6%; overall forest area (2005) 0.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$8,768,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 48.0%; food and live animals 14.1%; chemicals and chemical products 4.0%). Major import sources: Europe 63.1%, of which Italy 18.3%, Germany 12.0%, UK 4.1%; Japan 8.3%; Arab countries 6.1%. Exports (2004): US$20,600,000,000 (hydrocarbons [mostly crude petroleum] 95.7%). Major export destinations: Europe 90.5%, of which Italy 39.3%, Germany 18.3%, Spain 13.3%, Turkey 8.3%; Asian countries 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 83,200 km (paved 57%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 552,700; trucks and buses 195,500. Air transport (2003): passenger-km 825,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 259,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2000): 717,000 (133); telephone landlines (2006): 483,000 (81); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 3,928,000 (658); personal computers (2005): 130,000 (21); total Internet users (2005): 232,000 (40).
Education and health
Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 84.1%; males literate 93.4%; females literate 74.2%. Health: physicians (2004) 7,405 (1 per 775 persons); hospital beds (2002) 21,400 (1 per 256 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 24.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,885 (vegetable products 88%, animal products 12%); 152%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
The Qattara Depression is an arid Libyan Desert (Eastern Saharan) basin in northwestern Egypt. It covers about 7,000 sq mi (18,100 sq km) of salt lakes and marshes and descends to 435 ft (133 m) below sea level. During World War II, because it was impassable to military traffic, the depression formed a natural anchor at the southern end of the British defense lines at El-Alamein against the final advance of Field Marshal Erwin Rommel’s German army in July 1942. In the late 1970s oil deposits were discovered in the southern part of the depression.
Background
Greeks and Phoenicians settled the area in the 7th century bc. It was conquered by Rome in the 1st century bc and by Arabs in the 7th century ad. In the 16th century the Ottoman Turks combined Libya’s three regions under one regency in Tripoli. In 1911 Italy claimed control of Libya, and by the outbreak of World War II, 150,000 Italians lived there. It became an independent state in 1951. The discovery of oil in 1959 brought wealth to Libya. A decade later a group of army officers led by Muammar al-Qaddafi deposed the king and made the country an Islamic republic. Under Qaddafi’s rule it supported the Palestinian Liberation Organization and terrorist groups, bringing protests from many countries, particularly the US. Intermittent warfare with Chad during the 1970s and ’80s ended with Chad’s defeat of Libya in 1987. International relations in the 1990s were dominated by the consequences of the 1988 bombing of an American airliner over Lockerbie, Scotland; the US accused Libyan nationalists of the deed and imposed a trade embargo on Libya, endorsed by the UN in 1992.
Recent Developments
After nearly eight years of political and legal squabbles, in 2007 the case was settled involving five Bulgarian nurses and one Palestinian doctor who had been sentenced to death by Libyan courts on charges of having infected 426 Libyan children with HIV/AIDS. In July all six, who said that they were tortured to give false confessions, were released and flown to Bulgaria, where Bulgarian Pres. Georgi Purvanov immediately issued them a general pardon. Independent experts maintained that the charges were unfounded, and Saif ul-Islam al-Qaddafi, the son of Libyan leader Muammar al-Qaddafi, later disclosed in a TV interview that the case was “contrived” and that the police investigation involved “manipulation” of information. In October Libya was elected as a nonper-manent member of the Un Security Council for a period of two years. Also in October, Libya’s conciliatory initiative to bring all of the parties involved in the Dar-fur crisis in The Sudan to the negotiating table faltered as key rebel figures refused to attend. It was announced that 12 concessions would be awarded to foreign companies for offshore gas prospecting, and in May Libya signed a US$900 million contract with British Petroleum to drill for oil and gas—an indication that rapprochement between Libya and the West was continuing.
Liechtenstein
Official name: Furstentum Liechtenstein (Principality of Liechtenstein). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Diet [25]). Chief of state: Prince Hans Adam II (from 1989). Head of government: Otmar Hasler (from 2001). Capital: Vaduz. Official language: German. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Swiss franc (CHF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CHF 1.02.
Demography
Area: 62.0 sq mi, 160.5 sq km. Population (2007): 35,300. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 569.4, persons per sq km 219.9. Urban (2003): 21.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.29%; female 50.71%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 17.6%; 15-29, 18.9%; 30-44, 25.3%; 45-59, 21.7%; 60-74, 11.5%; 75-84, 3.9%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2004): Liechtensteiner 65.7%; Swiss 10.4%; Austrian 5.9%; Italian 3.5%; German 3.4%; Turkish 2.6%; other 8.5%. Religious affiliation (2002): Christian 83.9%, of which Roman Catholic 76.0%, Protestant 7.0%, Orthodox 0.8%; Muslim 4.1%; nonreligious/other/unknown 12.0%. Major cities (2005): Schaan 5,811; Vaduz 5,047; Triesen 4,643; Balzers 4,436; Eschen 4,076. Location: central Europe, between Austria and Switzerland.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 81.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.51. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 77.7 years; female 83.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: CHF 1,068,400,000 (current revenue 72.0%, of which taxes and duties 55.4%, investment income 10.9%, charges and fees 3.8%; capital revenue 28.0%). Expenditures: CHF 1,048,500,000 (current expenditure 74.5%, of which financial affairs 21.7%, social welfare 17.3%, education 12.3%, general administration 7.7%, public safety 4.5%, transportation 3.0%; capital expenditure 25.5%). Public debt: none. Population economically active (2005): total 15,667; activity rate of total population 44.8% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 54.3%; female [2003] 41.4%; unemployed [2004] 2.4%). Households. Average household size (2003) 2.5. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): grapes 157; significantly market gardening, other crops include cereals and apples; livestock (number of live animals) 6,000 cattle, 3,000 pigs, 2,900 sheep; roundwood 22,167 cu m, of which fu-elwood 19%. Manufacturing (2004): small-scale precision manufacturing includes optical lenses, electron microscopes, electronic equipment, and high-vacuum pumps. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 67,800,000 (353,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none ([2003] 13); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (50,000). Gross national income (2006): US$2,893,000,000 (US$82,826 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 25%, in pasture 31%; overall forest area (2005) 43%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CHF 1,909,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 31.4%; fabricated metals 15.2%; glass [all forms] and ceramics 6.5%; iron and steel 5.6%; chemicals and chemical products 5.1%). Major direct import sources: Germany 42.1%; Austria 32.5%; Italy 5.4%; US 3.8%; France 2.7%. Exports (2005): CHF 3,227,000,000 (machinery and apparatus [mostly electronic products and precision tools] 31.1%; fabricated metals 15.7%; motor vehicles and parts 10.3%; chemicals and chemical products 8.4%; glass and ceramic products [including lead crystal and specialized dental products] 8.3%). Major direct export destinations: Germany 21.2%; US 16.2%; France 11.6%; Austria 10.2%; Italy 7.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 18.5 km. Roads (2006): total length 250 km (paved 100%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2006) 24,293; trucks and buses (2003) 2,560. Air transport: the nearest scheduled airport service is through Zurich, Switzerland. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 18,000 (517); televisions (2002): 17,000 (510); telephone land-lines (2006): 20,000 (575); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 29,000 (820); total Internet users (2006): 22,000 (627); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 10,000 (285).
Education and health
Compulsory 22.9%; lower vocational 44.5%; higher vocational/teacher training 13.8%; university 6.6%; unknown 9.2%. Literacy: virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2005) 79 (1 per 441 persons); hospital beds (1997) 108 (1 per 288 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 4.7.
Military
Total active duty personnel: none; Liechtenstein has had no standing army since 1868; defense is the responsibility of Switzerland.
Background
The Rhine plain was occupied for centuries by two independent lordships of the Holy Roman Empire, Vaduz and Schellenberg. The principality of Liechtenstein, consisting of these two lordships, was founded in 1719 and remained part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was included in the German Confederation (1815-66). In 1866 it became independent, recognizing Vaduz and Schellenberg as unique regions forming separate electoral districts. An almost 60-year ruling coalition dissolved in 1997, and the prince urged adoption of constitutional reforms.
Recent Developments
Liechtenstein in August 2007 began work on modernizing its justice system. There was particular concern about the placement of detainees waiting to be deported, as Liechtenstein had to address several issues to come into compliance with the European Convention on Human Rights. Although Liechtenstein had made progress in the area, it remained on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development blacklist of uncooperative tax havens.
Lithuania
Official name: Lietuvos Respublika (Republic of Lithuania). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (the Seimas [141]). Head of state: President Valdas Adamkus (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Gediminas Kirkilas (from 2006). Capital: Vilnius. Official language: Lithuanian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 litas (LTL; plural litai) = 100 centai; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = LTL 2.18.
Demography
Area: 25,212 sq mi, 65,300 sq km. Population (2007): 3,375,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 133.9, persons per sq km 51.7. Urban (2006): 66.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 46.59%; female 53.41%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 16.7%; 15-29, 22.1%; 30-44, 22.4%; 45-59, 18.2%; 60-74,14.2%; 75-84, 5.3%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2001): Lithuanian 83.5%; Polish 6.7%; Russian 6.3%; Belarusian 1.2%; Ukrainian 0.7%; other 1.6%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 79.0%; Orthodox 4.8%, of which Old Believers 0.8%; Protestant 1.0%; nonreligious 9.5%; unknown/other 5.7% Major cities (2006): Vilnius 554,400; Kaunas 358,100; Klaipeda 185,900; Siau-liai 128,400; Panevezys 114,600. Location: eastern Europe, bordering Latvia, Belarus, Poland, Russia, and the Baltic Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.2 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 71.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -4.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.26. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 65.4 years; female 77.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: LTL 17,960,900,000 (tax revenue 59.2%, of which VAT 36.4%, income tax 22.2%; social security contributions 32.0%; other [including grants] 8.8%). Expenditures: LTL 17,817,400,000 (social security and welfare 40.4%; wages and salaries 18.3%; grants and subsidies 17.3%). Gross national income (2006): US$28,630,-000,000 (US$8,400 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 1,379,400, barley 948,300, potatoes 894,688; livestock (number of live animals) 1,114,700 pigs, 800,300 cattle; roundwood 6,045,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 19%; fisheries production 141,798 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 1,242,200; peat 535,000; sulfur 74,277. Manufacturing (value added in LTL ’000,000; 2005): food and beverages 2,569; refined petroleum products 2,077; textiles 1,395. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 18,912,000,000 (12,079, 000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (263,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 2,200,000 (63,500,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2003) 6,715,000 (1,942,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (2,929,000,000). Public debt (external outstanding; March 2006): US$3,156,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 1,588,300; activity rate of total population 46.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 67.4%; female 49.5%; registered unemployed 5.6%). Households (2005). Average household size (2004) 2.5; average annual per capita disposable household income: LTL 6,956 (US$2,508); sources of income: wages and salaries 56.6%, transfers 22.6%, self-employment 13.7%; expenditure: food and beverages 39.1%, transportation and communications 13.9%, housing and energy 12.0%, clothing and footwear 8.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 921; remittances (2006) 622; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 628. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 744; remittances (2006) 54; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 131. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 24.3%, in permanent crops 0.7%, in pasture 15.5%; overall forest area (2005) 33.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): LTL 42,974,600,000 (mineral fuels [mostly crude petroleum] 25.6%; machinery and apparatus 17.9%; transport equipment 11.7%; agricultural and food products 8.1%; chemicals and chemical products 7.8%). Major import sources: Russia 27.8%; Germany 15.2%; Poland 8.3%; Latvia 3.9%; The Netherlands 3.7%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): LTL 32,807,300,000 (mineral fuels [mostly refined petroleum] 27.5%; agricultural and food products 12.6%; machinery and apparatus 12.4%; textiles and clothing 9.4%; transport equipment [mostly auto components] 8.3%). Major export destinations: Russia 10.4%; Latvia 10.3%; Germany 9.4%; France 7.0%; Estonia 5.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 1,771 km; passenger-km 430,500,000; metric ton-km cargo 12,896,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 79,497 km (paved 89%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 1,455,276; trucks and buses 121,086. Airtransport (2006): passenger-km 1,200,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,682,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 371,000(108); televisions (2004): 1,785,000 (519); telephone landlines (2006): 792,000(232); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,718,000 (1,381); personal computers (2005): 616,000 (180); total Internet users (2006): 1,083,000 (317); broadband Internetsubscribers (2006): 369,000 (109).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no schooling through complete primary education 14.7%; lower secondary 18.0%; higher secondary 28.2%; vocational/technical 19.3%; higher 19.8%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate: virtually 100%. Health (2006): physicians 13,510 (1 per 251 persons); hospital beds 27,114 (1 per 125 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 6.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,530 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%); 178% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 13,510 (army 74.8%, navy 5.2%, air force 8.9%, active reserve 11.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$90.
Background
Lithuanian tribes united in the mid-13th century to oppose the Teutonic knights. Gediminas, one of the grand dukes, expanded Lithuania into an empire that dominated much of Eastern Europe in the 14th through 16th centuries. In 1386 the Lithuanian grand duke became the king of Poland, and the two countries remained closely associated until Lithuania was acquired by Russia in the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. Occupied by Germany during World War I, it declared its independence in 1918. In 1940 the Red Army gained control of Lithuania. Germany occupied it again in 1941-44, but the USSR regained control in 1944. With the breakup of the USSR, Lithuania became independent in 1991. It signed a border treaty with Russia in 1997, and it joined the European Union and NATO in 2004.
Recent Developments
In an effort to reduce Lithuania’s dependency on Russian energy resources, Vilnius encouraged closer energy collaboration in Europe in 2007. In February the Baltic states and Poland agreed to build a new nuclear power station in Lithuania. In Vilnius in October, the Baltic states and Black Sea regions were encouraged to bypass Russia and secure a reliable supply route for Caspian Sea oil. The GDP grew 18.1% in 2007, largely due to the significant increase in foreign direct investment (FDI) in Lithuania. By the beginning of 2008, FDI had reached more than US$73 billion.
Luxembourg
Official name: Groussherzogtum Letzebuerg (Luxem-bourgian); Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (French); Grossherzogtum Luxemburg (German) (Grand Duchy of Luxembourg). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative body (Chamber of Deputies [60]). Chief of state: Grand Duke Henri (from 2000). Head of government: Prime Minister Jean-Claude Juncker (from 1995). Capital: Luxembourg. Official language: none; Luxembourgian (national); French (used for most official purposes); German (lingua franca). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 999 sq mi, 2,586 sq km. Population (2007): 467,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 467.5, persons per sq km 180.6. Urban (2005): 82.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.52%; female 50.48%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 18.6%; 15-29, 17.9%; 30-44, 24.4%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74, 12.4%; 75-84, 5.2%; 85 and over, 1.3%. Ethnic composition (nationality; 2005): Luxembourger 60.4%; Portuguese 14.8%; French 5.0%; Italian 4.1%; Belgian 3.5%; German 2.3%; English 1.0%; other 8.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 90%; Protestant 3%; Muslim 2%; Orthodox 1%; other 4%. Major cities (2001): Luxembourg 76,688; Esch-sur-Alzette 27,146; Dudelange 17,320; Differdange 10,248; Schifflange 7,849. Location: western Europe, bordering Belgium, Germany, and France.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.1 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 72.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.70. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 76.2 years; female 82.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €6,392,568,500 (indirect taxes 48.6%; direct taxes 46.2%; other 5.2%). Expenditures: €6,476,725,500 (current expenditure 89.7%; development expenditure 10.3%). Public debt (2006): negligible. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 71,750, barley 52,850, potatoes 19,330; livestock (number of live animals) 185,235 cattle, 90,147 pigs; roundwood 276,618 cu m, of which fuelwood 5%. Mining and quarrying (2004): limited quantities of limestone and slate. Manufacturing (value added in €’000,000; 2004): base metals 420; rubber and plastic products 324; fabricated metal products 232. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 3,203,000,000 (6,140,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (129,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (2,533,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (1,430,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$32,911,000,000 (US$71,336 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 202,700; activity rate of total population 45.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 66.6%; female 42.4%; unemployed [June 2005-May 2006] 4.4%). Households. Average household size (2005) 2.5; income per household (2002) €61,800 (US$55,600); sources of income (1992): wages and salaries 67.1%, transfer payments 28.1%, self-employment 4.8%; expenditure (2004): food, beverages, and tobacco 21.4%, housing and energy 21.0%, transportation and communications 20.0%, entertainment and culture 8.1%, household goods and furniture 8.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,614; remittances (2006) 1,292; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2002-05 avg.) 3,895. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,976; remittances (2006) 7,533; FDI (2002-05 avg.) 4,106. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 23.9%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 25.1%; overall forest area (2005) 33.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): €14,140,200,000 (machinery and apparatus 17.4%; transport equipment 14.5%; mineral fuels 12.3%; base and fabricated metals 10.6%; chemicals and chemical products 10.0%). Major import sources: Belgium 34.8%; Germany 27.0%; France 11.9%; The Netherlands 6.3%; Italy 3.0%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): €10,175,600,000 (base and fabricated metals [mostly iron and steel] 28.8%; machinery and apparatus 19.6%; chemicals and chemical products 6.6%; transport equipment 6.3%). Major export destinations: Germany 26.1%; France 17.3%; Belgium 11.4%; Italy 6.4%; UK 5.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 275 km; passenger-km 272,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 420,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 2,894 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 307,265; trucks and buses 26,203. Air transport (2006; Luxair only): passenger-km 516,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 115,000 (253); televisions (2003): 70,000 (156); telephone landlines (2006): 247,000 (524); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 714,000 (1,516); personal computers (2005): 290,000 (634); total Internet users (2006): 339,000 (720); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 93,000 (202).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through primary education 19%; lower secondary 10%; upper secondary/higher vocational 56%; higher 15%. Literacy (2005): virtually 100%. Health (2004): physicians 1,591 (1 per 285 persons); hospital beds 3,045 (1 per 149 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 2.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 4,713 (vegetable products 65%, animal products 35%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 900 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.8%; per capita expenditure US$584.
Background
At the time of Roman conquest (57-50 bc), Luxembourg was inhabited by a Belgic tribe. After ad 400, Germanic tribes invaded the region. Made a duchy in 1354, it was ceded to the house of Burgundy in 1443 and to the Habsburgs in 1477. In the mid-16th century it became part of the Spanish Netherlands. It was made a grand duchy in 1815. After an uprising in 1830, its western portion became part of Belgium, while the remainder was held by The Netherlands. In 1867 the European powers guaranteed the neutrality and independence of Luxembourg. In the late 19th century it exploited its extensive iron-ore deposits. It was invaded and occupied by Germany in both world wars. It abandoned its neutrality by joining NATO in 1949; it had joined the Benelux Economic Union in 1944. A member of the European Union, its economy has continued to expand. On 7 Oct 2000, Grand Duke Jean abdicated power in favor of his son, Crown Prince Henri, after 36 years on the throne.
Recent Developments
Luxembourg’s economy was ranked the fourth most competitive in the world in 2007. While more than 80% of goods produced in Luxembourg were exported to the EU, the country was working actively to diversify its trade internationally. Luxembourg continued to work to develop its infrastructure and housing stock, and a new airport terminal was opened in May 2008.
Macau
Official name: Aomen Tebie Xingzhengqu (Chinese); Regiao Administrativa Especial de Macau (Portuguese) (Macau Special Administrative Region). Political status: special administrative region (China) with one legislative house (Legislative Council [29]). Chief of state: President Hu Jintao of China (from 2003). Head of government: Chief Executive Edmund Ho Hau-wah (from 1999). Capital: Macau. Official languages: Chinese; Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 pataca (MOP) = 100 avos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = MOP 8.03.
Demography
Area: 11.1 sq mi, 28.6 sq km. Population (2007): 527,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 47,477, persons per sq km 18,427. Urban (2006): virtually 100%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.82%; female 51.18%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 15.2%; 15-29, 25.6%; 30-44, 26.3%; 45-59, 23.0%; 60-74, 6.6%; 75-84, 2.6%; 85 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (by place of birth; 2006): mainland China 47.1%; Macau 42.5%; Hong Kong 3.7%; Philippines 2.0%; Portugal 0.3%; other 4.4%. Religious affiliation (1996): nonreligious 60.9%; Buddhist 16.8%; Buddhist/Taoist/Confucianist 13.9%; Roman Catholic 6.7%; Protestant 1.7%. Major city (2006): Macau 502,133. Location: eastern Asia, bordering China and the South China Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.1 (world avg. 20.3); (2004) within marriage 82.7%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.1 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.00. Life expectancy at birth (2001-04): male 77.5 years; female 82.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:MOP 19,345,000,000 (revenue from gambling tax 78.8%; stamp duties 3.8%; property income tax 3.8%). Expenditures: MOP 17,703,000,000 (current expenditure 52.4%; specific accounts 25.5%; capital expenditure 22.1%). Land use as % of total land area (2004): “green area” 21.6%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$14,902,000,000 (US$31,207 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2003): eggs 1,100,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2004) 700,000 chickens; fisheries production (2005) 1,500. Quarrying (value added in MOP ’000; 2003): 17,139. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): wearing apparel 240; textiles 56; furniture 35. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 1,668,000,000 ([2004] 2,124,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (719,000). Public debt (long-term, external; 2004): US$3,100,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 275,500; activity rate of total population 56.6% (participation rates: ages 14-64, 70.8%; female 46.6%; unemployed [January-March 2007] 3.2%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,757; remittances (2004) 72; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 443. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): remittances (2004) 132. Households (2002-03). Average household size (2006) 3.0; annual income per household MOP 183,648 (US$22,862); expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 31.4%, housing and energy 29.9%, education, health, and other services 19.2%, transportation and communications 9.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): MOP 31,340,300,000 (consumer goods 38.2%; capital goods 18.5%; mineral fuels 9.7%). Major import sources: China 43.1%; EU 13.1%; Japan 10.9%; Hong Kong 10.0%; US 4.1%. Exports (2005): MOP 19,823,300,000 (domestic exports 72.5%, ofwhich machine-knitted clothing 40.4%, machine-woven clothing 25.7%; reexports 27.5%). Major export destinations: US 48.7%; EU 17.1%, of which Germany 5.9%; China 14.9%; Hong Kong 9.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 362 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 67,384; trucks and buses 5,780. Air transport (2006; Air Macau only): passenger-km 3,039,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 193,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 164,000 (347); televisions (2003): 130,000 (292); telephone landlines (2006): 177,000 (381); cellular telephonesubscribers (2006): 636,000 (1,374); personal computers (2005): 160,000 (338); total Internetusers(2006): 200,000(432); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 92,000 (183).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 6.2%; incomplete primary education 10.7%; completed primary 22.5%; incomplete secondary 24.9%; completed secondary 21.4%; higher technical 1.7%; university 12.6%. Literacy (2003): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 94.5%; males literate 97.2%; females literate 92.0%. Health (2005): physicians 1,032 (1 per 473 persons); hospital beds 984 (1 per 496 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 2.7.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2004): up to 1,000 Chinese troops; Macau residents are prohibited from entering military service.
Background
Portuguese traders first arrived in Macau in 1513, and it soon became the chief market center for the trade between China and Japan. It was declared a Portuguese colony in 1849 and an overseas territory in 1951. In December 1999 Portugal returned Macau to Chinese rule.
Recent Developments
Development in the gaming industry continued in Macau with the opening in August 2007 of the Venetian Macao, the world’s largest casino, and in February 2008 of the Ponte 16 resort, which brought the number of casinos in Macau to 29. Gaming revenue for 2008 was projected to exceed US$10 billion, slightly lower than the US$10.4 billion earned in 2007.
Macedonia
Official name: Republika Makedonija (Macedonian); Republika e Maqedonise (Albanian) (Republic of Macedonia [member of the UN under the name The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia]). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a unicameral legislature (Assembly [120]). Head of state: President Branko Crvenkovski (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Nikola Gruevski (from 2006). Capital: Skopje. Official languages: Macedonian; Albanian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: denar (MKD); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 39.16 MKD.
Demography
Area: 9,928sq mi, 25,713sq km. Population (2007): 2,044,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 205.9, persons per sq km 79.5. Urban (2005): 68.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.95%; female 50.05%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 20.5%; 15-29, 23.8%; 30-44, 21.8%; 45-59, 18.8%; 60-74, 11.5%; 75-84, 3.2%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2002): Macedonian 64.2%; Albanian 25.2%; Turkish 3.9%; Rom (Gypsy) 2.7%; Serbian 1.8%; Bosniac 0.8%; other 1.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Orthodox 65%; Sunni Muslim 32%; Roman Catholic 1%; other (mostly Protestant) 2%. Major municipalities (2002): Skopje 467,257; Kumanovo 103,025; Bitola 86,408; Prilep 73,351; Tetovo 70,841. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Kosovo, Serbia, Bulgaria, Greece, and Albania.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 87.5%. Death rate per I,000 population (2006): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.57. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.3 years; female 76.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:MKD 92,805,000,000 (tax revenue 90.8%, of which social contributions 30.8%, VAT 29.2%, excise taxes 12.7%, income and profit tax II.8%; nontax revenue 9.2%). Expenditure: MKD 92,228,000,000 (transfers 55.0%, wages and salaries 24.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,613,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 333,900, grapes 265,700, potatoes 186,700; livestock (number of live animals) 1,200,000 sheep, 265,000 cattle; roundwood 822,000cu m, of which fu-elwood 81%; fisheries production 1,114 (from aquaculture 78%). Mining and quarrying (2005): copper (metal content) 21,800. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): food products 186; textiles 89; glass and glass products 57. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 6,271,000,000 (7,933,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (9,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 7,245,000 (7,551,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (6,090,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 807,000 (821,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (70,000,000). Households. Average household size (2002) 3.6; sources of income (2000): wages and salaries 54.2%, transfers 22.6%; expenditure: food 38.4%, transportation and communications 9.7%, fuel 8.2%, beverages and tobacco 7.6%. Population economically active (2006): total 891,679; activity rate 55.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 61.4%; female 39.5%; unemployed 36.0%). Gross national income (2006): US$6,251,000,000 (US$3,070 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 84; remittances (2005) 226; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 174; official development assistance (2005) 185 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 60; remittances (2005) 16. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 22.3%, in permanent crops 1.8%, in pasture 24.8%; overall forestarea (2005) 35.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$3,228,000,000 (mineral fuels 19.2%; machinery and transport equipment 17.4%; food and live animals 10.6%; chemicals and chemical products 10.3%). Major import sources: Russia 13.2%; Germany 10.4%; Greece 9.2%; Serbia and Montenegro 8.2%; Bulgaria 7.3%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$2,041,270,000 (clothing and accessories 27.3%; iron and steel 26.2%; food and live animals 8.2%; mineral fuels 8.0%; tobacco [all forms] 5.0%). Major export destinations: Serbia and Montenegro 22.5%; Germany 17.8%; Greece 15.3%; Italy 8.3%; Croatia 4.0%.
Ottoman Empire from 1371 to 1912. The north and center of the region were annexed by Serbia in 1913 and in 1918 became part of what was later known as Yugoslavia. When Yugoslavia was partitioned by the Axis powers in 1941, Yugoslav Macedonia was occupied principally by Bulgaria. Macedonia again became part of Yugoslavia in 1946. After Croatia and Slovenia seceded from Yugoslavia, fear of Serbian dominance drove Macedonia to declare its independence in 1991. Because of Greek objections to the newstate using the name of an ancient Greek province, it entered the UN as “the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.”
Recent Developments
The disagreement with Greece over Macedonia’s name remained unresolved, though diplomats of both countries agreed in May 2007 to start a fresh round of talks. The European Union, disappointed at the slow pace of reform in the country, declined to set a date for thestart of accession talks with Macedonia, though in April 2008, EU officials stated that the naming controversy should not be an impediment to Macedonian membership. Earlier in the month, however, Greece vetoed Macedonia’s bid to join NATO over the dispute.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length (2004) 699 km; passenger-km 94,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 531,000,000. Roads (2000): length 12,522 km (paved 58%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 307,581; trucks and buses 33,002. Air transport (2005; Macedonian Airlines only): passenger-km 266,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 111,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 189,000 (93); televisions (2003): 507,000 (250); telephone land-lines (2006): 491,000 (241); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,417,000 (696); personal computers (2005): 451,000 (221); total Internet users (2006): 268,000 (132); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 37,000 (18).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: less than full primary education 18.1%; primary 35.0%; secondary 36.9%; postsecondary and higher 10.0%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 10 and over literate 96.1%; males literate 98.2%; females literate 94.1%. Health: physicians (2001) 4,459 (1 per 452 persons); hospital beds (2002) 9,757 (1 per 207 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 8.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,955 (vegetable products 79%, animal products 21%); 149% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 10,890 (army 89.6%, air force 10.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.2%; per capita expenditure US$62.
Background
Macedonia has been inhabited since before 7000 bc. Part of itwas incorporated intoa Roman province inad 29. Itwassettled bySlavic tribes by the mid-6th century ad. Seized by the Bulgarians in 1185.
Madagascar
Official name: Repoblikan’i Madagasikara (Malagasy); Republique de Madagascar (French) (Republic of Madagascar). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [90]; National Assembly [127]). Heads of state and government: President Marc Ravalomanana (from 2002), assisted by Prime Minister Charles Rabemananjara (from 2007). Capital: Antananarivo. Official languages: French; English; Malagasy is the national language. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 ariary (MGA) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = MGA 1,592.00.
Demography
27.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.72%; female 50.28%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 44.1%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44, 15.7%; 45-59, 8.4%; 60-74, 3.7%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Malagasy 95.9%, of which Merina 24.0%, Betsi-misaraka 13.4%, Betsileo 11.3%, Tsimihety 7.0%, Sakalava 5.9%; Makua 1.1%; French 0.6%; Comorian 0.5%; Reunionese 0.4%; other 1.5%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs 42%; Protestant (significantly Lutheran) 27%; Roman Catholic 20%; Sunni Muslim 2%; other 9%. Major cities (2001): Antananarivo 1,403,449; Toa-masina 179,045; Antsirabe 160,356; Fianarantsoa 144,225; Mahajanga 135,660. Location: island in the Indian Ocean, east of the mainland of southern Africa.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 38.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 30.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.29. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 59.9 years; female 63.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:MGA 1,653,000,000,000 (tax revenue 53.7%, of which import duties 26.9%, VAT 10.5%; grants 40.6%; nontax revenue 5.7%). Expendi-tures:MGA 2,045,000,000,000 (current expenditure 50.2%; capital expenditure 49.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,178,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): paddy rice 3,400,000, sugarcane 2,446,000, cassava 2,144,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2006) 9,687,300 cattle, I,600,000 pigs, 3,000,000 geese; roundwood II,238,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 98%; fisheries production 144,900 (from aquaculture 6%). Mining and quarrying (2005): chromite ore 105,000; graphite 15,000; sapphires (export volume) 4,700 kg. Manufacturing (value in US$’000,000; 2004): beverages 107; wearing apparel 57; fabricated metal products 35. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 990,000,000 (990,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (10,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) none ([2004] 3,480,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 321,000 (602,000). Population economically active (2005): total 9,844,100; activity rate of total population 52.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 88.1%; female 49.6%; unemployed 2.8%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 62; remittances (2005) 3; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 59; official development assistance (2005) 929. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 25; remittances (2005) 8. Households. Average household size (2003-04) 4.6; expenditure (2000): food, beverages, and tobacco 50.1%, housing and energy 18.2%, transportation 8.0%. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$5,414,000,000 (US$283 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.1%, in permanent crops 1.0%, in pasture 41.3%; overall forest area (2005) 22.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$1,760,300,000 (petroleum [all forms] 18.3%; textiles 17.9%; food and live animals 11.4%; chemical products 8.6%). Major import sources: China 17.8%; Bahrain 16.4%; France 13.2%; South Africa 5.7%; US 3.6%. Exports (2006): US$1,008,200,000 (textiles and wearing apparel 25.0%; shellfish 13.4%; petroleum [all forms] 8.0%; vanilla 4.7%; cloves 2.7%). Major export destinations: France 39.5%; US 15.0%; Germany 6.0%; Italy 4.2%; UK 3.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2003) 901 km; (2000) passenger-km 24,471,000; (2000) metric ton-km cargo 27,200,000. Roads (1999): total length 49,827 km (paved 12%). Vehicles (1998): passenger cars 64,000; trucks and buses 9,100. Air transport (2005; Air Madagascar only): passenger-km 1,177,875,000; metric ton-km cargo 15,365,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 141,000 (7.6); televisions (2002): 410,000 (25); telephone landlines (2006): 130,000 (6.8); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,046,000 (55); personal computers (2005): 102,000 (5.5); total Internet users (2006): 110,000 (5.8).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003-04). Percentage of population ages 25-59 (male) and 25-49 (female) having: no formal schooling 20.4%; incomplete primary education 33.6%; complete primary 13.2%; incomplete secondary 23.0%; complete secondary 6.4%; higher 3.4%. Literacy (2006): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 70.7%; males literate 76.5%; females literate 65.3%. Health (2004): physicians 1,861 (1 per 9,998 persons); hospital beds 9,303 (1 per 2,000 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 58.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,046 (vegetable products 91%, animal products 9%); 136% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 13,500 (army 92.6%, navy 3.7%, air force 3.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$3.
Background
Indonesians migrated to Madagascar about ad 700. The first European to visit the island was Portuguese navigator Diogo Dias in 1500. Trade in arms and slaves allowed the development of Malagasy kingdoms at the beginning of the 17th century. The Me-rina kingdom became dominant in the 18th century and in 1868 signed a treaty granting France control over the northwestern coast. In 1895 French troops took the island, and Madagascar became a French overseas territory in 1946. As the Malagasy Republic, it gained independence in 1960. It severed ties with France in the 1970s, taking its present name in 1975. A new constitution was adopted in 1992. The country has since been both politically and economically unstable.
Recent Developments
After winning election to a second five-year term in office in December 2006, Pres. Marc Ravalomanana pushed through a number of amendments to the Madagascar constitution in 2007. They included reducing the size of the National Assembly from 160 to 127 seats, ending the autonomy of Madagascar’s provinces, and giving the president increased powers, including authority to make laws directly if a state of emergency were declared. More than 70% of those who voted in a national referendum held in April supported the constitutional changes, though the parliamentary opposition called for a boycott.
Malawi
Official name: Republic of Malawi. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [193]). Head of state and government: President Bingu wa Mutharika (from 2004). Capital: Lilongwe. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Malawi kwacha (MK) = 100 tambala; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = MK 140.51.
Demography
Area: 45,747 sq mi, 118,484 sq km. Population (2007): 13,603,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 373.7, persons per sq km 144.3. Urban (2005): 17.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.65%; female 50.35%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 47.3%; 15-29, 27.6%; 30-44, 12.9%; 45-59, 7.5%; 60-74, 3.8%; 75-84, 0.8%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Chewa 34.7%; Maravi 12.2%; Ngoni 9.0%; Yao 7.9%; Tumbuka 7.9%; Lomwe 7.7%; Ngonde 3.5%; other 17.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant/independent Christian 55%; Roman Catholic 20%; Muslim 20%; traditional beliefs 3%; other 2%. Major cities (2006): Blantyre 744,734; Lilongwe 706,322; Mzuzu 142,128; Zomba 107,195; Karonga (1998) 27,811. Location: southeastern Africa, bordering Tanzania, Mozambique, and Zambia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 42.4 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.82. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 42.8 years; female 41.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:MK 103,298,600,000 (tax revenue 52.9%, of which VAT 16.7%, income tax 11.7%, excises 7.3%, import tax 6.4%; grants 38.7%; nontax revenue 8.4%). Expenditures: MK 110,943,-700,000(current expenditure 76.3%; capital expenditure 21.0%; other 2.7%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 2,100,000, cassava 2,075,000, potatoes 1,800,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,900,000 goats, 750,000 cattle, 456,300 pigs; roundwood (2005)5,661,000cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production (2005) 59,595 (from aqua-culture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 28,000; gemstones (including rubies and sapphires) 1,400 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): food products 62; beverages 28; chemicals and chemical products 11. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,270,000,000 (1,262,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 70,000 (57,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (275,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 26.0%, in permanent crops 1.5%, in pasture 19.7%; overall forest area (2005) 36.2%. Population economically active (2003): total 5,707,000; activity rate of total population 46.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 88.0%; female 49.7%). Households (2004-05). Average household size 4.5; average annual household income MK50,904 (US$467); expenditure: food 55.6%, housing and energy 20.6%, transportation and communications 6.6%. Gross national income (2006): US$2,194,000,000 (US$162 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$496,600,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 23; remittances (2005) 1.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 9.2; official development assistance (2005)575. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 47; remittances (2005) 1.0.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): MK 70,500,000,000 (chemicals and chemical products 16.6%; machinery and apparatus 15.4%; refined petroleum products 11.3%; road vehicles 10.5%; food 7.9%). Major import sources (2004): South Africa 40.4%; India 7.9%; Tanzania 4.9%; Zambia 4.4%; US 3.6%. Exports (2004): MK 52,627,000,000 (tobacco 42.3%; sugar 15.0%; tea 9.8%; cotton 4.2%; reexports 4.0%). Major export destinations (2004): South Africa 13.4%; US 12.2%; Germany 11.9%; Egypt 8.6%; UK 6.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 797 km; passenger-km 29,523,000; metric ton-km cargo 26,055,000. Roads (2003): total length 15,451 km (paved 45%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 22,500; trucks and buses 57,600. Air transport (2005; Air Malawi only): passenger-km 201,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,364,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 22,000 (1.7); televisions (2003): 65,000 (5.2); telephone landlines (2005): 103,000 (7.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 532,000 (41); personal computers (2005): 25,000 (1.9); total Internet users (2006): 60,000 (4.5); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 400 (0.03).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education/unknown 33.5%; incomplete primary education 24.2%; complete primary 27.9%; secondary and university 14.4%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 64.3%; males literate 77.1%; females literate 51.9%. Health: physicians (2004) 266 (1 per 46,644 persons); hospital beds (1998) 14,087 (1 per 735 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 93.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,231 (vegetable products 97%, animal products 3%); 125% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 5,300 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$1.
Background
Inhabited since at least 8000 bc, the region was settled by Bantu-speaking peoples between the 1st and the 4th century ad. About 1480 they founded the Mar-avi Confederacy, which encompassed most of central and southern Malawi. In northern Malawi the Ngonde people established a kingdom about 1600. The slave trade flourished during the 18th-19th centuries. Britain established colonial authority in 1891, and the area became known as Nyasaland in 1907. The colonies of Northern and Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland formed a federation (1951-53), which was dissolved in 1963. The next year Malawi achieved independence. In 1966 it became a republic, with Hastings Banda as president. In 1971 Banda was designated president for life, and he ruled until he was defeated in multiparty elections in 1994. A new constitution was adopted in 1995.
Recent Developments
A bumper corn (maize) harvest for the second consecutive year helped Malawi’s recovery in 2007 from long periods of drought and made it possible in May to supply Zimbabwe with US$120 million of the cereal. In Augustan additional 10,000 tons were provided for drought-stricken Lesotho and Swaziland. The granting in April of a mining license to a subsidiary of an Australian company to develop uranium deposits near Lake Malawi was viewed as a positive economic development, though critics were concerned about its impact on the environment and public health.