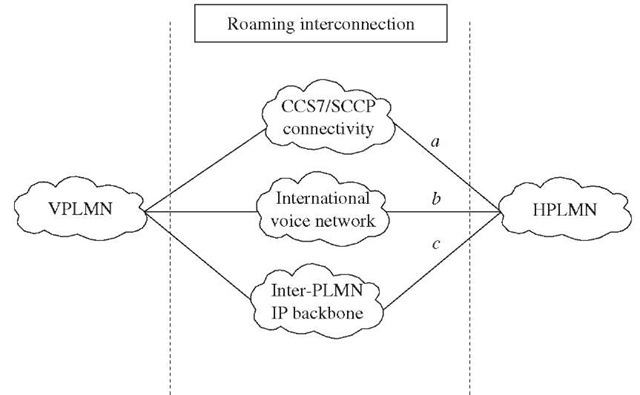
In order to enable roaming, following basic structure should be in place:
1. Inter-PLMN connection. With reference to Figure 1-2, this connection consists of:
(a) CCS7 links (for SCCP MAP traffic) between the VPLMN and the HPLMN. These links are required for information exchange between the HLR in the home network and the VLR in the visited network.
(b) Interconnect links to transport circuit-switched voice and data between the HPLMN and the VPLMN.
Figure 1-2 Inter-PLMN connection.
(c) Packet-switched interconnection to transport packet data between the HPLMN and the VPLMN. Roaming in GSM networks requires (a) and (b) types of interconnection. GPRS roaming requires (a) and (c) types of interconnection. For 3G, all three types of interconnection are required.
2. Agreement. To allow a subscriber to roam and use services in a VPLMN, the two networks (the HPLMN and the VPLMN) must have a roaming agreement in place. The roaming agreement can be a bilateral agreement between two roaming partners or it can be an indirect relationship using a clearinghouse or a roaming broker. The roaming agreement covers several operational and business aspects including interconnection, problem resolution, tariff, pricing, and usage data format and exchange mechanism.
3. Billing. The VPLMN generates usage records for all the services used by a roamer while staying in the network. It then rates the usage records and raises the invoice to the roamer’s HPLMN on the basis of the terms and conditions set in the roaming agreement. The VPLMN also transfers the detailed usage records of each individual roamer to the HPLMN in a specified format. The HPLMN settles the invoices with the VPLMN and charge its own subscriber for the service usage while roaming. The billing and settlement process between two operators can be direct or through a clearinghouse.
4. Testing. Interworking tests are performed before the roaming is commercially launched. This is required to ensure that the user can access all the services provided by the roaming agreement. On-demand and periodic tests are also performed to ensure roaming availability in view of continuous changes in network and services.