INTRODUCTION
SINA, SOHU, and NETEASE have been regarded as the most successful general Web portals in the Chinese market. However, they have quite different strategies in their business modules, which makes them quite different in terms of their revenue constitution. What are the major reasons and what will be the future direction for Chinese Web portals?
COMPARISON OF SINA, SOHU AND NETEASE
Orientation
Although there are some differences in terms of the orientation between these three leading Chinese Web portals, they are fundamentally quite similar.
SINA definitely wants to be an online media that focuses on the content of the news (information) whilst SOHU’s new media painstakingly emphasizes the differences with SINA. Although Internet news was first advocated in China by SOHU, in 1998, but the first mover SOHU could not keep its seat in the following years. While most people are still debating on whether Web portals definitely need to broadcast news, SINA has successfully become the most successful Chinese media on the Web. On the other hand, SOHU persists with their multi-industry strategy, spending more on their SOHU Merchant and alumni association. After the acquisition of Chinaren, 17173, Focus Real Estate, Goodfeel, SOHU has extended its customer base and aimed to be a portal matrix.
Compared with SINA and SOHU, NETEASE has a unique module that attracts valuable user demographics: large proportion of young and educated users with demonstrated spending power. They have got the diversified revenue streams with the ability to cross-sell services to users across businesses
Content
The following figures show the major channels that have been listed on the corresponding Web sites www.sina.com. cn, www.sohu.com, and www.netease.com.cn Around 70% of the content provided by the three Chinese Web portals is homogenous where the channels have the same orientation, managing module, and contents. The
Figure 1. Orientation of SINA.SOHU and NETEASE
|
SINA |
SOHU |
NETEASE |
|
• SINA is a leading online media and value added service provider (VAS) for China and for Chinese communities worldwide with more than 100 million registered users. • SINA generates revenue from five major business lines including SINA.com (online news and content). SINA Mobile (mobile value-added services), SINA Online (community-based services and games), SINA.net (search and enterprise services), and SINA E-Commerce (online shopping and auctions) • Fiscal 2005 Net revenues of $193.6 million
|
• SOHU.COM is one of China’s top-tier Internet media properties accessed by millions of Chinese for their daily information, communication, and entertainment needs. • SOHU’s business model consists of brand advertising and sponsored search targeting corporate clients, as well as wireless valued added services, e-commerce and online games targeting individual consumers. • The first 3G Chinese Interactive Search Engine Service Provider. • Fiscal 2005 Net revenues of $108.3 million
|
• NetEase operates a leading interactive online and wireless community in China and is a major provider of Chinese language content and services through online games, wireless value-added services, and Internet portal businesses. • NETEASE generates revenues from fees that charge users of their online games and wireless value-added and other fee-based premium services, as well as from selling online advertisements on the NetEase Web sites. • Fiscal 2005 Net revenues of $210 million
|
Figure 2. Contents on SINA front page
|
Forum |
F1 |
Science |
Mobile |
Finance |
Color Message |
OnlineGame |
Cartoon |
Book |
Short Messages |
|
Housing |
Stock |
Education |
Video |
Travel |
Baby sitting |
E-Ladies |
Automobiles |
Shopping Mall |
Enterprise |
|
Life |
Weather |
Alumni |
|
Entertainment |
Chat Room |
Searching |
Recruitment |
Astrology |
I Games |
|
City |
Classification |
Gulf |
Yellow Pages |
Hotels |
Culture |
CDMA |
Auctions |
Club |
|
Figure 3. SOHU business matrix
|
Aggregated content(Channel) |
Communication and community tools |
Search and Directory Services |
|
News |
Alumni Club |
News Search |
|
Business and Finance |
|
Music search |
|
Automobiles |
Blogs |
Picture Search |
|
Real Estate |
Picture Gallery |
Say Board |
|
Sports |
Message Boards |
Map Search |
|
Information Technology |
Instant Messaging Services |
Search Directory |
|
Music |
Shopping Search |
|
|
Women |
||
|
Aside from the above three major businesses, SOHU also provides wireless services,E-Commerce and online games to their customers at the same time. |
||
Figure 4. NETEASE core business constitution
|
Content Channel |
Community and Communication |
Commerce and other Services |
|
News |
|
Online Mall |
|
Entertainment |
POPO(Instant Messaging) |
Website Search |
|
Sports |
Chat |
Yellow Pages |
|
Women’s Topics |
BBS |
Classified Ads |
|
Stocks |
Group-Online Clubs |
Online Learning |
|
Technology |
Alumni Network |
Domain Forwarding |
|
Game Reviews |
Personal Homepages |
Software Downloading |
|
Digital Reviews |
E-Cards |
Online Magazines |
|
Mobile Handset Reviews |
Dating |
|
|
Automobiles |
Matchmaking |
|
|
Real Estate |
Photo Album |
|
|
Business |
Diary |
|
|
Travel |
Blogging |
|
|
Cartoon |
Online Radio |
|
|
Education |
Job Search |
|
|
Health |
|
|
|
Life |
|
|
|
Culture |
|
|
Figure 5. NASDAQ financial performance
|
Company Name |
Market Share(USD) |
Trailing P/E |
|
SINA |
24.16 |
32.21 |
|
SOHU |
18.34 |
23.82 |
|
NETEASE |
56.16 |
15.69 |
|
YAHOO |
39.18 |
24.79 |
|
|
414.86 |
67.81 |
Financial Performances
In this section, P/E is short for the ratio of a company’s share price to its per-share earnings. P/E ratio = market value per share/earnings per share (EPS).
Most of the time, the P/E is calculated using EPS from the last four quarters. This is also known as the trailing P/E. Historically, the average P/E ratio in the market has been around 15-25. This fluctuates significantly depending on economic conditions. The P/E can also vary widely between different companies and industries (iResearch, 2004).
In general, a high P/E suggests that investors are expecting higher earnings growth in the future compared to companies with a lower P/E. It is usually more useful to compare the P/E ratios of one company to other companies in the same industry, to the market in general or against the company’s own historical P/E (www.investopedia.com). A better interpretation of the P/E ratio is to see it as a reflection of the market’s optimism concerning a firm’s growth prospects. The P/E ratio is a much better indicator of a stock’s value than the market price alone.
NETEASE has the highest P/E compared with SINA and SOHU due to its faster revenue growth rate while SOHU has the lowest P/E ratio. The reason comes from the fact that SOHU could neither provide better news than SINA nor better online games than NETEASE.
There are some differences in terms of revenue constitution for the above three companies. Both SINA and SOHU focus more on their online advertisements while NETEASE concentrates their core business on their online games and wireless VAS.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF CHINESE WEB PORTAL
Definition of Web Portal
According to the computing dictionary, (http://computing-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com), a Web portal is a Web “supersite” that provides a variety of services including Web searching, news, white and yellow pages directories, free email, discussion groups, online shopping, and links to other sites. The Web portal was initially used as a search engine and for providing Internet access services. As the market competition became more and more fierce, the Web portal was needed to develop new businesses to attract and sustain Internet users. The Web portal has become a network super market in the virtual world (Zhu, 2004). At the moment, the portal Web site usually provides news, search services, chat room, BBS, free mail box, music, e-commerce, virtual community, online games, free Web pages, and so on.
Web Portal Evolvement Curve
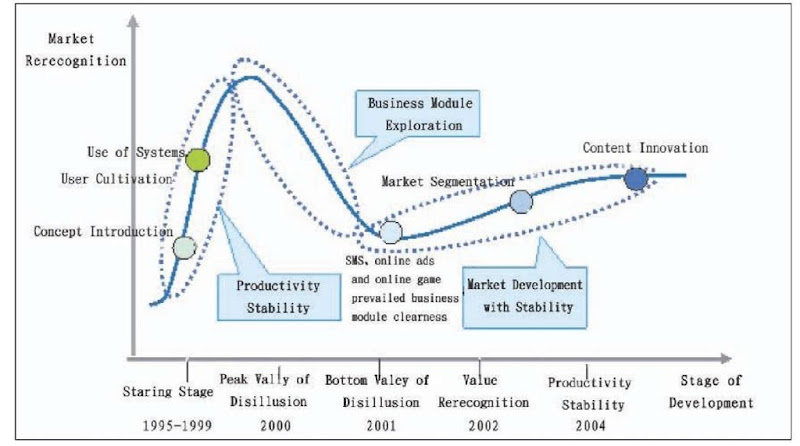
Web portal development stages in China can be described in the following figure (Zhang & Zhu, 2006). 1997 to 1999 is the starting stage for Web portals in China and the user recognition was built then. On February 25, 1998, the first category search engine, SOHU, was developed. At the same time, SINA emerged and became the largest Chinese Web site.
On April 13, 2000, SINA was successfully launched in NASDAQ, NETEASE and SOHU issued stocks at a similar time in July, 2000. The Web portal has come into the peak value expectation overstated stage.
The Internet bubble has collapsed since then. The SINA market share got to its bottom floor of 1.06 USD in October, 2001 (Yahoo Finance, 2001). SOHU’s share even dropped to 60 cents in April, 2001 (Yahoo Finance, 2001). Even worse, NETEASE dropped to 53 cents in June, 2001 (Yahoo Finance, 2001). Due to the error disclosure of its financial report, the exchange of NETEASE was terminated on September 4, 2001 (Yahoo Finance, 2001). The Web portal entered the bottom valley of disillusion.
Figure 6. Revenue constitution for SINA, SOHU and NETEASE(%)
|
Revenue Source |
SINA |
SOHU |
NETEASE |
|
Online advertisements |
43.9 |
65.5 |
14.2 |
|
Non advertisement services |
56.1 |
34.5 |
85.8 |
Figure 6. Revenue constitution for SINA, SOHU and NETEASE(%)
In July, 2002, the three Chinese Web portals issued their Q2 financial reports and announced that they had become profitable since then (Yahoo Finance, 2002). The foundation for their profitability at that time is the short message services (SMS).
The Chinese Internet use touched 68 millions in 2003 (CNNIC, 2006). The three Web portals have made outstanding achievements. The previous rubbish stock, which was worth less than 1 dollar, has come up to over 70 US dollars per share. The profitability business module for the Web portal, which covers SMS, online games, and online advertisements has been clear.
Key Success Factors (KSF)
Grant (2001) has argued that two key factors condition a firms success and subsistence, that is, a firm should provide the products that suit customer’s needs and a firm should discuss two questions for subsistent competition: What is it our customer’s want? What do we have to do for subsistent competition?
Porter (1998) has described the key success factors (KSF) in competitive advantage in the “Five Forces”: the degree of rivalry, the threat of entry, the treat of substitute, buyer power, and supplier power. Although the three Chinese Web portals have their own unique successful stories, there are KSFs that could be classified into three categories.
Clear Profitability Module is a Pre Condition
Any Internet company is an economic entity, while both attention economy and eye ball economy are virtual (Zhu, 2002). A company could survive and consecutively be developed on the basis of faithful profitability module. A successful business module has to support five key factors:3W+2H.
• How to make money—Profitability Module
• How to achieve—Technological availability
• What—Product
• Where—Channel
• Who—Customer
In terms of profitability module, the three Chinese Web portals got their revenue mainly from:
1. online advertisements,
2. fees for experiences (mobile value added services and online games, and
3. purchase (electronic commerce).
The corresponding functionality for the Web portals are their media service, service and application provider functionality.
The development of the Internet in China is somewhat different when compared with global markets. Those differences are even bigger for the Chinese Web portals. Eighty seven percent of revenue for Yahoo comes from their online advertisements (Yahoo financial Report, 2005), while the online ads are not a main stream business for their Chinese counterparts. On the contrary, SMS and online games are quite successful in China.
Figure 7. Web portal development stage in China
Internet Traffic is Foundation for a Web Portal
The three Chinese Web portals began providing their mail box and homepage services with a service fee in2002. SOHU even extended its business into domain name registration. But, in fact, it is not those charged service but SMS, advocated by China Mobile, that became the break through for the profitability sources for those Web portals. At the same time, NETEASE achieved great success on their online game business. As more and more big free mail box services have been introduced to the market, the Web portals have been faced with great challenges from their giant competitors, such as Yahoo and Google.
It has been proven that free service is the best way for online promotion, as the Internet traffic and scalability could be extended by means of free services that are fundamentals for profitability.
Nevertheless, mobile value added service is an exception. The service provider could share the charged service fee with a telecom company, which is a very good profitability module. As the managing cost for mobile networks are relatively high, it is difficult to provide totally free mobile value added service. The customer will need to pay for the traffic fee even though they do not need to pay for the content. Of course the traffic fee for WAP Web sits is also very important.
Going to the Stock Market is a Guarantee for the Development of a Web Portal
It is crucial to find an appropriate time for a company to go to the stock market. The funding obtained in the stock market could be a driver for the consecutive innovation and development for a company. At the same time, it could keep the stability for the core team as well. The anti-risk capability will also be strengthened based on the standardized operations within a company. However, there are some disadvantages to become a public company such as the increase of transparency and managing cost.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS FOR CHINESE WEB PORTALS
The World is Changing
The first global Web portal, Yahoo, made an outstanding achievement in the first quarter of 2005. Their financial report showed that their first quarter revenue in 2005 touched 1.174 billion USD with a net profit of0.205 billion—nearly a 100 percent increase compared with 2004. The business module inside this breaking down revenue is quite simple; 87 percent of the revenue came from their online advertisements (YAHOO financial report,2005).
The previously mentioned success attracts more competitors to share the portal market, including Google, whose revenue reached 1.256 billion USD in the first quarter of 2005, with a net profit of0.369 billion USD (Google financial report, 2005). In May, 2005, Google launched its characteristic services, such as customized homepages, that allowed users to add their personalized content, and such as stock market information, weather forecast, and electronic news preview, and so forth. As early as 2004, Google launched its news searching channel, which could be a symbol for Google to transform to an Internet portal.
Opportunity vs. Challenge
Figure
According to a report from CNNIC (China Internet Networking Information Center), Chinese Internet users have exceeded 100 million at the end of 2005 and reached 111 million. China has become the second largest Internet customer base worldwide and is expected to reach 338 million by 2010.
The newest Nielson/Netratings research report showed that about one fifth of local American Internet users are more liable to read online newspaper rather than traditional printed none.
Figure 8. Profitability module for SINA, SOHU, and NETEASE
|
|
Online advertisements |
Mobile value added services |
Online games |
Electronic Commerce |
|
SINA |
** |
*** |
* |
* |
|
SOHU |
*** |
* |
** |
** |
|
NETEASE |
* |
** |
*** |
|
Huge Potential for Online Advertisement
The Chinese online advertisement market in 2005 was 2.7 billion RMB, while the figure for 2006 will be 4.0 billion RMB. Revenue from TV advertisements for the year 2004 in China was 25.5 billion RMB showing a huge potential for online advertisement. (iResearch, 2004)
Competition will be Intensified for Web Portals
More Internet companies has transformed to become a Web portals in China. TOM and QQ are the two newcomers while at the same time, Microsoft MSN has launched its own Chinese portal, as did YAHOO 3721. It could be expected that more and more Internet companies will compete in the portal market in China.
Web 2.0 Technology
Web 2.0 technology fulfills the real interactions of the Internet, where the information recipient could also be the information maker. Blog, RSS (Really Simple Syndication), and Wiki have been grasped by some of Chinese Internet users. WEB2.0 has fulfilled the entire interaction for the Internet, the information recipient becomes the information producer at the same time. The traditional Web portals, such as SINA,SOHU and NETEASE, will have to meet with the real competitions.
CONCLUSION
Differentiation Competition is the Most Practical Choice for Web Portals
SINA has done their best in the accuracy and fast delivery of SINA news, while NETEASE focuses on providing in-depth news for Internet users in addition to their great success in online games..
At the beginning of2004, NETEASE made fundamental changes on their homepage and optimized each channel in 2005. SOHU emphasized the integration of resource matrix that is a key advantages compared with its competitors.
From Uniformed to Personalized Web Portal
It is customer demand that lead to the development of the Internet and this became Web portals for service integration. It is also consumer demand for finding and getting precise information from an enormous source that gave birth to the search engine. IM (Instant Messaging) tools became popular as the Internet user has demanded sociability.
The uniformed and one-stop services combined with POPUP advertisements and similar news are the current status for Chinese Web portals. The relationship between an Internet site and the user is to rely on each other, that is entertainment and profitability (Zhu, 2004).
Maslow (1943) created his famous hierarchy of needs. Beyond the details of air, water, food, and sex, he laid out five broader layers: the physiological needs, the needs for safety and security, the needs for love and belonging, the needs for esteem, and the need to actualize the self, in that order.
Figure 9. NETEASE Business Report has become a major competitor to SINA News
Table 1. Comparison between uniformed portal and personalized Web portal
|
Phase |
Uniformed portal -1G |
Personalized Portal – 2G |
|
Core Competency |
Editor Based unicast broadcasting |
Personalized based multicast broadcasting |
|
Broadcast Module |
Centralized Control |
P2P (Point to Point)Dialogue |
|
Orientation of Internet user |
Passive |
Active |
|
Roles for Internet users |
Customer, reader, information recipient and user |
Customer, Reader, Information Recipient and user Producer, Writer for User, maker and Broadcaster |
|
Main Content |
Chosen by editors |
Personalized making, Auto choose |
|
Direction for Content |
Coincide with main stream media and commercial profitability |
In pursuit of customization and personalization |
|
Core Application |
News, E-Mail, Searching engine etc |
Borg, RSS, Content Aggregation etc |
|
Interactive Content |
Supplement |
Core |
|
Content Mechanism |
Blocked Edition |
Open Aggregation |
The needs for esteem and the need to actualize oneself are at the moment far away from satisfaction. There are neither geographical closeness between Web sites and their customers, nor do they have psychological closeness (doing well or not makes not too much differences or links to the customer).
With the development of Web 2.0 technology, the traditional uniformed portal will definitely transform itself to a personalized Web portal. Figure 8 shows the differences between an uniformed portal and a personalized Web portal. (Zhang & Zhu, 2006).
With the adoption of WEB2.0 technology, Google has advocated its personal portal, which allows its user to customize news from the New York Times and BBC, weather forecasts, and financial information as long as the user has a Gmail account. The combination of IM, Blog, and RSS is a marvelous and creative idea. It will be the real personal Web portal era when the Internet user can get all their network needs as long as they activate IM after they open their personal computer.
KEY TERMS
Key Success Factors in Competitive Advantage in the “Five Forces”: The degree of rivalry, the threat of entry, the treat of substitute, buyer power, and supplier power.
P/E: Short for the ratio of a company’s share price to its per-share earnings.
P/E Ratio: Market Value per share/Earnings per Share (EPS).
Web Portal: A Web “supersite” that provides a variety of services including Web searching, news, white and yellow pages directories, free e-mail, discussion groups, online shopping and links to other sites.