The International System of Units (SI)
Rapid advances in science and technology in the 19th and 20th centuries fostered the development of several overlapping systems of units of measurements as scientists improvised to meet the practical needs of their disciplines. The General Conference on Weights and Measures was chartered by international convention in 1875 to produce standards of physical measurement based upon an earlier international standard, the meter-kilogram-second (MKS) system. The convention calls for regular General Conference meetings to consider improvements or modifications in standards, an International Committee of Weights and Measures elected by the Conference (meets annually), and several consultative committees. The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (Bureau International des Poids et Mesures) at Sevres, France, serves as a depository for the primary international standards and as a laboratory for certification and intercomparison of national standard copies.
The 1960 International System (universally abbreviated as SI, from systeme international) builds upon the MKS system. Its seven basic units, from which other units are derived, are currently defined as follows: the meter, defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 second; the kilogram (about 2.2 pounds avoirdupois), which equals 1,000 grams as defined by the international prototype kilogram of platinum-iridium in the keeping of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; the second, the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of radiation associated with a specified transition of the cesium-133 atom; the ampere, which is the current that, if maintained in two wires placed one meter apart in a vacuum, would produce a force of 2 x 10-7 newton per meter of length; the candela, defined as the intensity in a given direction of a source emitting radiation of frequency 540 x 1012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian; the mole, defined as containing as many elementary entities of a substance as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12; and the kelvin, which is 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point (equilibrium among the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases) of pure water.
|
|
Elemental and Derived SI Units |
and Symbols |
|
|
Quantity |
|
SI Units |
|
|
|
|
FORMULA/EXPRESSION |
|
|
|
UNIT |
IN BASE UNITS |
SYMBOL |
|
elemental units |
|
|
|
|
length |
meter |
— |
m |
|
mass |
kilogram |
— |
kg |
|
time |
second |
— |
s |
|
electric current |
ampere |
— |
A |
|
luminous intensity |
candela |
— |
cd |
|
amount of substance |
mole |
— |
mol |
|
thermodynamic temperature |
kelvin |
— |
K |
|
derived units |
|
|
|
|
acceleration |
meter/second squared |
m/s2 |
|
|
area |
square meter |
m2 |
|
|
capacitance |
farad |
A ^ s/V |
F |
|
charge |
coulomb |
A * s |
C |
|
Celsius temperature |
degree Celsius |
K |
°C |
|
density |
kilogram/cubic meter |
kg/m3 |
|
|
electric field strength |
volt/meter |
V/m |
|
|
electrical potential |
volt |
W/A |
V |
|
energy |
joule |
N x m |
J |
|
force |
newton |
kg x m/s2 |
N |
|
frequency |
hertz |
s-1 |
Hz |
|
illumination |
lux |
lm/m2 |
lx |
|
inductance |
henry |
V x s/A |
H |
|
kinematic viscosity |
square meter/second |
m2/s |
|
|
luminance |
candela/square meter |
cd/m2 |
|
|
luminous flux |
lumen |
cd x sr |
lm |
|
magnetic field strength |
ampere/meter |
A/m |
|
|
magnetic flux |
weber |
V x s |
Wb |
|
magnetic flux density |
tesla |
Wb/m2 |
T |
|
plane angle |
radian |
m x m-1=1 |
rad |
|
power |
watt |
J/s |
W |
|
pressure |
pascal (newton/square meter |
) N/m2 |
Pa |
|
resistance |
ohm |
V/A |
n |
|
solid angle |
steradian |
m2 x m-2=1 |
sr |
|
stress |
pascal (newton/square meter |
) N/m2 |
Pa |
|
velocity |
meter/second |
m/s |
|
|
viscosity |
newton-second/square meter |
N x s/m2 |
|
|
volume |
cubic meter |
m3 |
|
Conversion of Metric Weights and Measures
The International System of Units is a decimal system of weights and measures derived from and extending the metric system of units. Adopted by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960, it is abbreviated “SI” in all languages. Below are common equivalents and conversion factors for US customary and SI systems.
|
approximate 1 inch |
common equivalents = 25 millimeters |
conversions accurate within inches x 25.41 |
10 parts per million = millimeters |
|
1 foot |
= 0.3 meter |
feet x 0.30481 |
= meters |
|
1 yard |
= 0.9 meter |
yards x 0.91441 |
= meters |
|
1 mile |
= 1.6 kilometers |
miles x 1.60934 |
= kilometers |
|
1 square inch |
= 6.5 sq. centimeters |
square inches x 6.45161 |
= square centimeters |
|
1 square foot |
= 0.09 square meter |
square feet x 0.0929030 |
= square meters |
|
1 square yard |
= 0.8 square meter |
square yards x 0.836127 |
= square meters |
|
1 acre |
= 0.4 hectare2 |
acres x 0.404686 |
= hectares |
|
1 cubic inch |
= 16 cubic centimeters |
cubic inches x 16.3871 |
= cubic centimeters |
|
1 cubic foot |
= 0.03 cubic meter |
cubic feet x 0.0283168 |
= cubic meters |
|
1 cubic yard |
= 0.8 cubic meter |
cubic yards x 0.764555 |
= cubic meters |
|
1 quart (liq) |
= 1 liter2 |
quarts (liquid) x 0.946353 |
= liters |
|
1 gallon |
= 0.004 cubic meter |
gallons x 0.00378541 |
= cubic meters |
|
1 ounce (avdp)3 |
= 28 grams |
ounces (avdp)3 x 28.3495 |
= grams |
|
1 pound (avdp)3 |
= 0.45 kilogram |
pounds (avdp)3 x 0.453592 |
= kilograms |
|
1 horsepower |
= 0.75 kilowatt |
horsepower x 0.745700 |
= kilowatts |
|
1 millimeter |
= 0.04 inch |
millimeters x 0.0393701 |
= inches |
|
1 meter |
= 3.3 feet |
meters x 3.28084 |
= feet |
Conversion of Metric Weights and Measures
|
1 meter |
= 1.1 yards |
meters x 1.09361 |
= yards |
|
1 kilometer |
= 0.6 mile (statute) |
kilometers x 0.621371 |
= miles (statute) |
|
1 square centimeter |
= 0.16 square inch |
square centimeters x 0.155000 |
= square inches |
|
1 square meter |
= 11 square feet |
square meters x 10.7639 |
= square feet |
|
1 square meter |
= 1.2 square yards |
square meters x 1.19599 |
= square yards |
|
1 hectare2 |
= 2.5 acres |
hectares x 2.47105 |
= acres |
|
1 cubic centimeter |
= 0.06 cubic inch |
cubic centimeters x 0.0610237 |
= cubic inches |
|
1 cubic meter |
= 35 cubic feet |
cubic meters x 35.3147 |
= cubic feet |
|
1 cubic meter |
= 1.3 cubic yards |
cubic meters x 1.30795 |
= cubic yards |
|
1 liter2 |
= 1 quart (liq) |
liters x 1.05669 |
= quarts (liq) |
|
1 cubic meter |
= 264 gallons |
cubic meters x 264.172 |
= gallons |
|
1 gram |
= 0.035 ounce (avdp)3 |
grams x 0.0352740 |
= ounces (avdp)3 |
|
1 kilogram |
= 2.2 pounds (avdp)3 |
kilograms x 2.20462 |
= pounds (avdp)3 |
|
1 kilowatt |
= 1.3 horsepower |
kilowatts x 1.34102 |
= horsepower |
Tables of Equivalents: Metric System Units and Prefixes
|
base unit1 |
|
|
|
QUANTITY |
NAME OF UNIT |
SYMBOL |
|
length |
meter |
m |
|
area |
square meter |
square m, or m2 |
|
|
are (100 square meters) |
a |
|
volume |
cubic meter |
cubic m, or m3 |
|
|
stere (1 cubic meter) |
s |
|
mass |
gram |
g |
|
|
metric ton (1,000,000 grams) |
t |
|
capacity |
liter |
l |
|
temperature |
degree Celsius |
°C |
prefixes designating multiples and submultiples
|
PREFIX |
SYMBOL |
FACTOR BY WHICH UNIT IS MULTIPLIED |
EXAMPLES |
|
|
exa- |
E |
1018 = |
1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
|
|
peta- |
P |
1015 = |
1,000,000,000,000,000 |
|
|
tera- |
T |
1012 = |
1,000,000,000,000 |
|
|
giga- |
G |
109 = |
1,000,000,000 |
|
|
mega- |
M |
106 = |
1,000,000 |
megaton (Mt) |
|
kilo- |
k |
103 = |
1,000 |
kilometer (km) |
|
hecto-, hect- |
h |
102 = |
100 |
hectare (ha) |
|
deca- dec- |
da |
10 = |
10 |
decastere (das) |
|
deci- |
d |
10-1 = |
1 0.1 |
decigram (dg) |
|
centi-, cent- |
c |
10-2 = |
0.01 |
centimeter (cm) |
|
milli- |
m |
10-3 = |
0.001 |
milliliter (ml) |
|
micro-, micr- |
M |
10-6 = |
0.000001 |
microgram (Mg) |
|
nano- |
n |
10-9 = |
0.00000000 |
|
|
pico- |
p |
10-12 = |
0.000000000001 |
|
|
femto- |
f |
10-15 = |
0.000000000000001 |
|
|
atto- |
a |
10-18 = |
0.000000000000000001 |
|
The US was an independent nation for 13 years before the Constitution was signed in 1789, the same year George Washington was elected the country’s first president. In 1781, American Revolutionary leader John Hanson was elected by the Continental Congress “President of the United States in Congress Assembled.” Hanson is thus referred to by some as the first US president, but he was a congressional presiding officer and had none of the presidential powers that would be granted under the Constitution.
British/US System (foot-pound-second, fps)
|
length |
|
|
|
|
|
1 statute mi |
= 5,280 ft |
= 1,760 yd |
= 320 rods |
= 8 furlongs |
|
1 nautical mi |
= 6,076 ft |
= 1.151 mi |
|
|
|
1 furlong |
= 660 ft |
= 220 yd |
= 40 rods |
= 1/8 mi |
|
1 chain (Gunter’s) |
= 66 ft |
= 22 yd |
= 100 links |
= 4 rods |
|
1 rod |
= 16.5 ft |
= 5.5 yd |
= 25 links |
|
|
1 fathom |
= 6 ft |
= 72 in |
|
|
|
1yd |
= 3 ft |
= 36 in |
|
|
|
1 ft |
= 12 in |
|
||
|
1 link (Gunter’s) |
= 0.66 ft |
= 7.92 in |
|
|
|
1 hand |
= 4 in |
|
||
|
1 mil |
= 0.001 in |
|
|
area 1 sq mi 1 acre |
= 640 acres = 10 sq chains |
= 102,400 sq rods = 160 sq rods |
= 3,097,600 = 27,878,400 sq ft sq yd = 4,840 sq yd = 43,560 sq ft |
|
1 sq ft |
= 144 sq in |
|
|
|
volume 1 cu ft 1 cu in |
= 1/27 cu yd = 1/46,656 cu yd |
= 12 board ft = 1/1,728 cu ft |
= 1,728 cu in |
|
1 acre-ft |
= 43,560 cu ft |
= 1,613 cu yd |
|
|
1 board ft |
= 144 cu in |
= 1/12 cu ft |
= 1 super ft (lumber) |
|
1 cord (US) |
= 128 cu ft |
|
|
|
capacity 1 cu ft |
= 7.481 gal (US) |
= 6.229 gal (British) |
|
|
liquid measure (US) |
|
|
|
|
|
1 barrel, oil |
= 42 gal (US) |
= 34.97 gal (British) |
|
|
|
1 gal |
= 0.833 gal (British) |
= 4 quarts |
= 231.00 cu in |
= 128 fl oz |
|
1 quart |
= 1/4 gal |
= 2 pints |
= 57.75 cu in |
= 32 fl oz |
|
1 pint |
= 1/8 gal |
= 1/2 quart |
= 28.88 cu in |
= 16 fl oz |
|
1 gill |
= 1/32 gal |
= 1/4 pint |
= 7.22 cu in |
= 4 fl oz |
|
1 fl oz |
= 1/128 gal |
= 1/16 pint |
= 1.80 cu in |
|
|
dry measure (US) |
|
|
|
|
|
1 bushel |
= 0.97 bushel (British) |
= 4 pecks |
= 2,150.4 cu in |
= 1.24 cu ft |
|
1 peck |
= 1/4 bushel |
= 8 quarts |
= 537.6 cu in |
= 0.31 cu ft |
|
1 quart |
= 1/32 bushel |
= 2 pints |
= 67.2 cu in |
= 1/8 peck |
|
1 pint |
= 1/64 bushel |
= 1/2 quart |
= 33.6 cu in |
|
|
liquid and dry measure (British) |
|
|
|
|
|
1 bushel |
= 1.03 bushels (US) |
= 8 gal |
= 4 pecks = 2,219.36 cu in |
= 1.284 cu ft |
|
1 peck |
= 0.25 bushel |
= 2 gal |
= 8 quarts = 554.84 cu in |
|
|
1 gal |
= 1.20 gal (US) |
= 4 quarts |
= 277.42 cu in |
|
|
1 quart |
= 0.30 gal |
= 2 pints |
= 1/8 peck = 69.36 cu in |
|
|
1 pint |
= 4.80 gills (US) |
= 4 gills |
= 34.68 cu in |
= 20 fl oz |
|
1 gill |
= 1.20 gills (US) |
|
= 8.67 cu in |
= 5 fl oz |
|
1 fl oz |
= 0.96 fl oz (US) |
|
= 1.73 cu in |
|
|
weight |
|
|
|
|
|
1 short ton (US) |
= 0.89 long ton |
= 2,000 lbs |
= 20 short cwt1 |
|
|
1 long ton (British) |
= 1.12 short tons |
= 2,240 lbs |
= 22.4 short cwt1 |
|
|
1 short cwt1 (US) |
= 0.05 short ton |
= 100 lbs |
|
|
|
1 long cwt1 (British) |
= 0.05 long ton |
= 112 lbs |
|
|
|
1 stone (person) |
= 0.14 short cwt1 |
= 14 lbs |
|
|
|
1 lb |
= 0.07 stone (British) |
|
|
|
|
1 oz avoirdupois |
= 437.50 grains |
= 1/16 lb |
= 0.911 oz troy |
|
|
1 oz troy |
= 480.00 grains |
= 1/12 lb |
= 1.097 oz |
|
|
1 grain |
|
= 0.0023 oz |
= 0.0021 oz troy |
|
UNIT SYMBOL ATTRIBUTE MEASURED EXPRESSION IN OTHER UNITS (S = SECOND)
Ampere A current C/s or V/Q
the basic electrical unit of the International System of Units (SI), since 1948 defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures as the constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross section, and placed one meter apart in a vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 x 10-7 newton per meter of length. One ampere is equal to a flow of one coulomb of electricity per second; or, the flow produced in a conductor with a resistance of one ohm by a potential difference of one volt.
farad F capacitance (ability to hold a charge) A x s/V or C/V
the ability of two parallel, oppositely charged plates (a capacitor) to hold an electric charge equals one farad when one coulomb of electricity changes the potential between the plates by one volt.
coulomb C charge A x s
the quantity of electricity transported in one second by a current of one ampere. Approximately equal to 6.24 x 1018 electrons.
watt W power J/s orVxA
one joule of work performed per second; or, the power dissipated in an electrical conductor carrying one ampere current between points at one volt potential difference.
ohm Q resistance V/A or W/A2
resistance of a circuit in which a potential difference of one volt produces a current of one ampere; or, the resistance in which one watt of power is dissipated when one ampere flows through it.
volt V potential W/A or Ax Q
the difference in potential between two points in a conductor carrying one ampere current when the power dissipated between the points is one watt; or, the difference in potential between two points in a conductor across a resistance of one ohm when one ampere is flowing through it.
Temperature Equivalents
Instructions for converting °F into °C or K1, and °C into °F: Find the figure you wish to convert in the second column. If this figure is in °F, the corresponding temperature in °C and K will be found in the third and fourth columns; if the figure is in °C, the corresponding temperature in °F will be found in the first column. To convert a temperature range between two scales, rather than finding equivalent temperatures, see the temperature conversion instructions, below.
|
FAHRENHEIT |
FIGURE |
°CELSIUS |
KELVIN |
°FAHRENHEIT |
FIGURE |
°CELSIUS |
KELVIN |
|
°F) |
TO BE |
(°CENTIGRADE) |
(K) |
(°F) |
TO BE |
(°CENTIGRADE) |
(K) |
|
|
CONVERTED |
(°C) |
|
|
CONVERTED |
(°C) |
|
|
|
-459.67 |
-273.15 |
0 |
+46.4 |
+8 |
-13.33 |
+259.82 |
|
|
|
|
|
+48.2 |
+9 |
-12.78 |
+60.37 |
|
|
-400 |
-240.00 |
+33.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-300 |
-184.44 |
+88.71 |
+50.0 |
+ 10 |
-12.22 |
+260.93 |
|
-459.67 |
-273.15 |
-169.53 |
+103.62 |
+68.0 |
+20 |
-6.67 |
+266.48 |
|
|
|
|
|
+86.0 |
+30 |
-1.11 |
+272.04 |
|
-328.0 |
-200 |
-128.89 |
+144.26 |
+89.6 |
+32 |
0.00 |
+273.15 |
|
-148.0 |
-100 |
-73.33 |
+199.82 |
+104.0 |
+40 |
+4.44 |
+277.59 |
|
|
|
|
|
+122.0 |
+50 |
+10.00 |
+283.15 |
|
-130.0 |
-90 |
-67.78 |
+205.37 |
+140.0 |
+60 |
+15.56 |
+288.71 |
|
-112.0 |
-80 |
-62.22 |
+210.93 |
+158.0 |
+70 |
+21.11 |
+294.26 |
|
-94.0 |
-70 |
-56.67 |
+216.48 |
+176.0 |
+80 |
+26.67 |
+299.82 |
|
-76.9 |
-60 |
-51.11 |
+222.04 |
+194.0 |
+90 |
+32.22 |
+305.37 |
|
-58.0 |
-50 |
-45.56 |
+227.59 |
|
|
|
|
|
-40.0 |
-40 |
-40.00 |
+233.15 |
+212. |
+100 |
+37.78 |
+310.93 |
|
-22.0 |
-30 |
-34.44 |
+238.71 |
+392.0 |
+200 |
+93.33 |
+366.48 |
|
-4.0 |
-20 |
-28.89 |
+244.26 |
+572.0 |
+300 |
+148.89 |
+422.04 |
|
+14.0 |
-10 |
-23.33 |
+249.82 |
+752.0 |
+400 |
+204.44 |
+477.59 |
|
|
|
|
|
+932.0 |
+500 |
+260.00 |
+533.15 |
|
+32.0 |
|
-17.78 |
+255.37 |
+1112.0 |
+600 |
+315.56 |
+588.71 |
|
+33.8 |
+1 |
-17.22 |
+255.93 |
+1292.0 |
+700 |
+371.11 |
+644.26 |
|
+35.6 |
+2 |
-16.67 |
+256.48 |
+1472.0 |
+800 |
+426.67 |
+699.82 |
|
+37.4 |
+3 |
-16.11 |
+257.04 |
+1652.0 |
+900 |
+482.22 |
+755.37 |
|
+39.2 |
+4 |
-15.56 |
+257.59 |
|
|
|
|
|
+41.0 |
+5 |
-15.00 |
+258.15 |
+1832.0 |
+1000 |
+537.78 |
+810.93 |
|
+42.8 |
+6 |
-14.44 |
+258.71 |
+3632.0 |
+2000 |
+1093.33 |
+1366.45 |
|
+44.6 |
+7 |
-13.89 |
+259.26 |
+5432.0 |
+3000 |
+1648.89 |
+1922.05 |
Temperature Equivalents (continued)
All systems of measuring temperature in degrees or units (kelvins) on a scale are based on the interval between the freezing and boiling points of water and differ only in the number of degrees or units into which this interval is divided.
Fahrenheit: interval is divided into 180 degrees (32° to 212°); 0° is at 32° below the freezing point of water.
Rankine: degree is the same as the Fahrenheit degree; 0° is at absolute zero (the theoretical point at which a thermodynamic system has the lowest energy, -459.67 °F). Once common in engineering applications in the US, the Rankine scale is now rarely used.
Celsius: interval is divided into 100 degrees; 0° is at the freezing point of water.
Kelvin: interval is the same as the Celsius degree; 0 K is at absolute zero (the theoretical point at which a thermodynamic system has the lowest energy, -273.15 °C).
Reaumur: interval is divided into 80 degrees; 0° is at the freezing point of water. One of the earliest (1730) temperature scales in widespread use, the Reaumur scale had been supplanted by other scales by the late 19th century.
temperature conversion instructions:2
|
°Fahrenheit |
into |
°Celsius |
subtract 32, divide by 1.82 |
|
°Celsius |
into |
°Fahrenheit |
multiply by 1.8, add 322 |
|
°Celsius |
into |
kelvin |
add 273.15 |
1Because a kelvin is itself a unit of measurement, it is incorrect to use “degree” or the ° symbol with it, as is necessary with the units of the Rankine, Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Reaumur scales. One kelvin is equal to one degree Celsius. 2Instructions are for finding equivalent temperatures; to find the equivalent number of degrees in a temperature range (e.g., tomorrow’s temperature will be 11.0 °F, or 6.1 °C, warmer than today’s temperature), omit the step of adding or subtracting 32.
Cooking Measurements
|
MEASURE |
CONVENTIONAL EQUIVALENTS1 |
METRIC EQUIVALENT |
|
drop |
1/60 teaspoon |
0.08 ml |
|
dash |
V8 teaspoon |
0.62 ml |
|
teaspoon |
8 dashes; V3 tablespoon; Ms fluid ounce |
4.93 ml |
|
tablespoon |
3 teaspoons; 1/2 fluid ounce |
14.79 ml |
|
ounce (weight) |
1/16 pound |
28.35 g |
|
fluid ounce (volume) |
2 tablespoons |
29.57 ml |
|
cup |
8 fluid ounces; 16 tablespoons; V2 pint |
236.59 ml |
|
pound |
16 ounces |
453.6 g |
|
pint |
16 fluid ounces; 2 cups; 1/2 quart |
473.18 ml |
|
quart |
32 fluid ounces; 4 cups; 2 pints; 1/4 gallon |
946.36 ml |
|
gallon |
128 fluid ounces; 16 cups; 8 pints; 4 quarts |
3.785 l |
|
peck |
2 gallons |
7.57 l |
|
bushel |
8 gallons; 4 pecks |
30.28 l |
|
OVEN TEMPERATURE EQUIVALENTS |
||||
|
|
|
AMERICAN OVEN |
FRENCH OVEN TEMPERATURE |
BRITISH “GAS MARK” |
|
|
|
TEMPERATURE |
TERMS AND THERMOSTAT |
OVEN THERMOSTAT |
|
°F |
°C |
TERMS |
SETTINGS |
SETTINGS |
|
160 |
71 |
|
#1 |
|
|
170 |
77 |
|
|
|
|
200 |
93 |
|
tres doux; etuve |
|
|
212 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
221 |
105 |
|
#2 |
|
|
225 |
107 |
very slow |
doux |
|
|
230 |
110 |
|
#3 |
|
|
250 |
121 |
|
|
#1/4 (241 °F) |
|
275 |
135 |
|
|
#1/2 (266 °f) |
|
284 |
140 |
slow |
moyen; modere |
#1(291 °F) |
|
300 |
149 |
|
|
|
|
302 |
150 |
|
#4 |
|
|
320 |
160 |
|
|
#2 (313 °F) |
|
325 |
163 |
|
|
#3 (336 °f) |
|
350 |
177 |
moderate |
assez chaud; bon four |
|
Cooking Measurements
|
OVEN TEMPERATURE EQUIVALENTS |
||||
|
|
|
AMERICAN OVEN TEMPERATURE |
FRENCH OVEN TEMPERATURE TERMS AND THERMOSTAT |
BRITISH “GAS MARK” OVEN THERMOSTAT |
|
°F |
°C |
TERMS |
SETTINGS |
SETTINGS |
|
356 |
180 |
|
#4 (358 °F) |
|
|
375 |
190 |
#5 |
#5 (379 °F) |
|
|
390 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
400 |
205 |
|
#6 (403 °F) |
|
|
410 |
210 |
hot |
chaud |
|
|
425 |
218 |
#6 |
#7 (424 °F) |
|
|
428 |
220 |
|
|
|
|
437 |
225 |
|
|
|
|
450 |
232 |
|
#8 (446 °F) |
|
|
475 |
246 |
very hot |
tres chaud; vif |
#9 (469 °F) |
|
500 |
260 |
#7 |
|
|
|
525 |
274 |
#8 |
|
|
|
550 |
288 |
#9 |
|
|
Spirits Measure
Many specific volumes have varied over time and from place to place, but the proportional relationships within families of measures have generally remained the same. All ounce measures are in US fluid ounces.
|
MEASURE |
CONVENTIONAL EQUIVALENTS METRIC EQUIVALENT |
|
|
pony |
0.75 oz = 34 shot= 1/2 jigger |
22.17 ml |
|
shot/ounce/finger |
1 oz = 11/3 ponies = % jigger |
29.57 ml |
|
jigger |
1.5 oz = 2 ponies = 1V2 shots |
44.36 ml |
|
double |
2 oz = 2 shots |
59.15 ml |
|
triple |
3 oz = 3 shots |
88.72 ml |
|
noggin/imperial gill/drink (whiskey) |
4.8 oz |
142.1 ml |
|
pint |
16 oz = 58 fifth = 1/2 quart |
473.2 ml |
|
quarter yard |
20 oz = 114 pints |
591.5 ml |
|
bottle (champagne or other wine) |
about 25.5 oz or 1^ imperial gallon 750 ml (industry standard) |
|
|
fifth |
25.6 oz = 4/5 quart = 1/5 gallon |
757.1 ml |
|
quart |
32 oz = 1/2 magnum = 1/4 gallon |
946.3 ml |
|
half yard |
40 oz = 21/2 pints |
1.182 l |
|
magnum |
2 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
1.5 l |
|
magnum |
64 oz = 2 quarts = 1/2 gallon |
1.893 l |
|
yard |
80 oz = 5 pints |
2.365 l |
|
jeroboam |
4 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
3l |
|
gallon/double magnum |
128 oz = 4 quarts = 5 fifths = 2 magnums |
3.785 l |
|
rehoboam |
6 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
4l |
|
imperial gallon |
1.20 gallons = % barn gallon = V10 anker |
4.546 l |
|
ale/beer gallon |
1.22 gallons |
4.620 l |
|
methuselah |
8 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
6l |
|
salmanazar |
12 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
9l |
|
barn gallon |
21/2 imperial gallons = % anker |
11.37 l |
|
balthazar |
16 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
12 l |
|
half keg |
5 gallons (type varies) |
varies |
|
nebuchadnezzar |
20 bottles (champagne or other wine) |
15 l |
|
firkin |
9 gallons |
34.07 l |
|
keg |
10 gallons (type varies) |
varies |
|
anker |
60 bottles = 10 imperial gallons = 4 barn gallons |
45.46 l |
|
runlet/rundlet/rudlet |
144 pints = 72 quarts = 18 gallons = 2 firkins |
68.14 l |
|
octave |
15.75 imperial gallons = V8 butt (wine) |
71.60 l |
|
British bottle |
126 bottles = 21 imperial gallons |
95.47 l |
|
aum |
120 quarts = 30 gallons |
113.6 l |
|
barrel (wine) |
126 quarts = 3112 gallons = 3/4 tierce |
119.2 l |
|
barrel (ale/beer) |
144 quarts = 36 gallons = 1/2 puncheon (ale/beer) |
136.3 l |
|
tierce |
168 quarts = 42 gallons = 1/2 puncheon (wine) |
159.0 l |
|
British hogshead (ale/beer) |
54 imperial gallons = 1/2 butt (ale/beer) = 1/4 tun (ale/beer) |
245.5 l |
|
puncheon (ale/beer) |
72 gallons = 2 barrels (ale/beer) |
272.5 l |
|
British hogshead (wine) |
63 imperial gallons = 1/2 butt (wine) = 1/4 tun (wine) |
286.4 l |
|
puncheon (wine) |
84 gallons = 2 tierces |
318.0 l |
|
butt/pipe (ale/beer) |
108 imperial gallons = 1/2 tun (ale/beer) |
491.0 l |
|
butt/pipe (wine) |
126 imperial gallons = 1/2tun (wine) |
572.8 l |
|
tun (ale/beer) |
216 imperial gallons = 4 British hogsheads (ale/beer) = |
982.0 l |
|
|
2 butts (ale/beer) |
|
|
tun (wine) |
252 imperial gallons = 12 British bottles = 2 butts (wine) |
1,146 l |
|
Blackjack |
|||||
|
Number of two-card combinations in a 52-card deck (where aces equal 1 or 11 and face cards equal 10) for each number between 13 and 21 |
Approximate chances of various exceeding 21 |
hands reaching or |
|||
|
TOTAL WITH |
POSSIBLE COMBINATIONS |
TOTAL IN HAND |
CHANCE OF |
CHANCE OF EXCEEDING 21 |
|
|
TWO CARDS |
FROM 52 CARDS |
BEFORE DEAL |
REACHING A |
|
ANY |
|
21 |
64 |
(TWO OR MORE |
COUNT OF |
ONE |
NUMBER |
|
20 |
136 |
CARDS) |
17 TO 21 |
CARD |
OF CARDS |
|
19 |
80 |
(%) |
(%) |
(%) |
|
|
18 |
86 |
16 |
38 |
62 |
62 |
|
17 |
96 |
15 |
42 |
54 |
58 |
|
16 |
86 |
14 |
44 |
46 |
56 |
|
15 |
96 |
13 |
|
38 |
52 |
|
14 |
102 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
118 |
|
|
|
|
|
Poker |
||
|
Number of ways to no wild cards) |
reach and odds of reaching various five-card combinations on a single deal (52-card deck, |
|
|
|
NUMBER OF |
ODDS OF RECEIVING |
|
HAND |
COMBINATIONS |
ON A SINGLE DEAL |
|
royal flush |
4 |
1 in 649,740 |
|
straight flush |
36 |
1 in 72,193 |
|
four of a kind |
624 |
1 in 4,165 |
|
full house |
3,744 |
1 in 694 |
|
flush |
5,108 |
1 in 509 |
|
straight |
10,200 |
1 in 255 |
|
three of a kind |
54,912 |
1 in 47 |
|
two pairs |
123,552 |
1 in 21 |
|
one pair |
1,098,240 |
1 in 2 |
|
Dice |
|||||
|
Probabilities of two-die totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TWO-DIE |
NUMBER OF |
PROBABILITY |
TWO-DIE |
NUMBER OF |
PROBABILITY |
|
TOTAL |
COMBINATIONS |
(%) |
TOTAL |
COMBINATIONS |
(%) |
|
2 |
1 |
2.78 |
8 |
5 |
13.89 |
|
3 |
2 |
5.56 |
9 |
4 |
11.11 |
|
4 |
3 |
8.33 |
10 |
3 |
8.33 |
|
5 |
4 |
11.11 |
11 |
2 |
5.56 |
|
6 |
5 |
13.89 |
12 |
1 |
2.78 |
|
7 |
6 |
16.67 |
total |
36 |
1001 |
Ancient Measures
The standard unit of measure is listed first, with a rough modern equivalent in parentheses. Often, standard units varied over time, so a range is sometimes given. The subdivisions below relate to the standard unit of measure given first.
|
CULTURE |
LENGTH |
WEIGHT |
LIQUID |
|
Egyptian |
cubit (524 mm; 20.62 in) |
kite (4.5-29.9 g; |
cubic cubit (0.14 cubic m; |
|
|
|
0.16-1.05 oz) |
37 gal)1 |
|
|
digit (1/28 of a cubit) |
deben (10 kites) |
khar |
|
|
palm (4 digits) |
sep (10 debens) |
hekat |
|
|
hand (5 digits) |
|
hin |
|
|
small span (12 digits, or 3 palms) |
|
ro |
|
|
large span (14 digits, or 1/2 cubit) |
|
|
|
|
small cubit (24 digits, or 6 palms) |
|
|
|
Babylonian |
kus2 (530 mm; 20.9 in) |
mina (640-978 g; |
ka (99-102 cubic mm; |
|
|
|
23-34 oz) |
3.9-4.0 cubic in) |
|
|
foot (23 kus) |
shekel |
gur(300 ka) |
|
|
shusi (1/30 us) |
|
|
|
Hebrew3 |
|
sacred mina (60 shekels) |
bat4 |
|
|
|
sacred talent (3,000 shekels, or |
hin |
|
|
|
50 sacred minas) |
log |
|
CULTURE |
LENGTH |
WEIGHT |
LIQUID |
|
Hebrew3 |
|
Talmudic mina (25 shekels) |
|
|
(continued) |
|
Talmudic talent (1,500 shekels, or 60 Talmudic minas) |
|
|
Greek |
finger (19.3 mm; 0.76 in) foot (16 fingers) Olympic cubit (24 fingers) |
talent (25.8 kg; 56.9 lb) |
metretes (39.4 l; 10.4 gal) |
|
Roman |
foot (subdivided into the uncia [plural unciae]; V12 ft) |
libra (327.45 g; 11.55 oz) |
sextarius (plural sextarii; 0.53 l; 0.14 gal) |
|
|
pace, or double step (5 ft) |
uncia (1/12 lb) |
amphora (48 sextarii) |
|
|
mille passus (1,000 paces) |
|
|
|
Chinese5 |
chih (25 cm; 9.8 in) chang (3 m; 9.8 ft) |
shih, or tan (60 kg; 132 lb) |
|
1Measures given below the cubic cubit run from small to large. 2Also called the Babylonian cubit. 3The Hittites, Assyrians, Phoenicians, and Hebrews derived their systems from the Babylonians and Egyptians. Hebrew standards were based on the relationship between the mina, the talent (the basic unit), and the shekel. 4Volumes are not definitely known but are listed from largest to smallest. 5The Chinese system of measurement exhibited all the principal characteristics of the Western. It was, however, fundamentally chaotic in that there was no relationship between different types of units, such as those of length and those of volume. It also fluctuated from region to region. The first emperor of China, Shi Huangdi (221-210/09 bc), fixed the basic units given here.
Roman Numerals
Seven numeral-characters compose the Roman numeral system. When a numeral appears with a line above it, it represents the base value multiplied by 1,000. However, because Roman numerals are now seldom utilized for values beyond 4,999, this convention is no longer in use.
|
ARABIC |
ROMAN |
ARABIC |
ROMAN |
ARABIC |
ROMAN |
ARABIC |
ROMAN |
|
1 |
I |
15 |
XV |
170 |
LXX |
1,000 |
M |
|
12 |
II |
16 |
XVI |
180 |
LXXX |
1,001 |
MI |
|
3 |
III |
17 |
XVII |
190 |
XC |
1,002 |
MII |
|
14 |
IV |
18 |
XVIII |
100 |
C |
1,003 |
MIII |
|
15 |
V |
19 |
XIX |
101 |
CI |
1,900 |
MCM |
|
16 |
VI |
20 |
XX |
102 |
CII |
2,000 |
MM |
|
17 |
VII |
21 |
XXI |
200 |
CC |
2,001 |
MMI |
|
18 |
VIII |
22 |
XXII |
300 |
CCC |
2,002 |
MMII |
|
19 |
IX |
23 |
XXIII |
400 |
CD |
2,100 |
MMC |
|
10 |
X |
24 |
XXIV |
500 |
D |
3,000 |
MMM |
|
11 |
XI |
30 |
XXX |
600 |
DC |
4,000 |
MMMMor MV |
|
12 |
XII |
40 |
XL |
700 |
DCC |
5,000 |
V |
|
13 |
XIII |
50 |
L |
800 |
DCCC |
|
|
|
14 |
XIV |
60 |
LX |
900 |
CM |
|
|
Mathematical Formulas
The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter is n (3.141592653589793238462643383279.., generally rounded to 22/7 or 3.1416). It occurs in various mathematical problems involving the lengths of arcs or other curves, the areas of surfaces, and the volumes of many solids.
The American system of numeration for denominations above one million was modeled on a French system, but subsequently the French system changed to correspond to the German and British systems. In recent years, British usage reflects widespread and increasing use of the values of the American system. In the American system each of the denominations above 1,000 millions (the American billion) is 1,000 times the preceding one (one trillion = 1,000 billions; one quadrillion = 1,000 trillions). In the British system the first denomination above 1,000 millions (the British milliard) is 1,000 times the preceding one, but each of the denominations above 1,000 milliards (the British billion) is 1,000,000 times the preceding one (one trillion = 1,000,000 billions; one quadrillion = 1,000,000 trillions).
|
\ |
VALUE IN |
|
|
|
POWERS |
NUMBER |
|
AMERICAN NAME |
OF TEN |
OF ZEROS |
|
billion |
109 |
9 |
|
trillion |
1012 |
12 |
|
quadrillion |
1015 |
15 |
|
quintillion |
1018 |
18 |
|
sextillion |
1021 |
21 |
|
septillion |
1024 |
24 |
|
octillion |
1027 |
27 |
|
nonillion |
1030 |
30 |
|
decillion |
1033 |
33 |
|
undecillion |
1036 |
36 |
|
duodecillion |
1039 |
39 |
|
tredecillion |
1042 |
42 |
|
quattuordecillion |
1045 |
45 |
|
quindecillion |
1048 |
48 |
|
sexdecillion |
1051 |
51 |
|
septendecillion |
1054 |
54 |
|
octodecillion |
1057 |
57 |
|
novemdecillion |
1060 |
60 |
|
vigintillion |
1063 |
63 |
|
googol |
10100 |
100 |
|
centillion |
10303 |
303 |
|
|
VALUE IN |
|
|
|
POWERS |
NUMBER |
|
BRITISH NAME |
OF TEN |
OF ZEROS |
|
milliard |
109 |
9 |
|
billion |
1012 |
12 |
|
trillion |
1018 |
18 |
|
quadrillion |
1024 |
24 |
|
quintillion |
1030 |
30 |
|
sextillion |
1036 |
36 |
|
septillion |
1042 |
42 |
|
octillion |
1048 |
48 |
|
nonillion |
1054 |
54 |
|
decillion |
1060 |
60 |
|
undecillion |
1066 |
66 |
|
duodecillion |
1072 |
72 |
|
tredecillion |
1078 |
78 |
|
quattuordecillion |
1084 |
84 |
|
quindecillion |
1090 |
90 |
|
sexdecillion |
1096 |
96 |
|
septendecillion |
10102 |
102 |
|
octodecillion |
10108 |
108 |
|
novemdecillion |
10114 |
114 |
|
vigintillion |
10120 |
120 |
|
centillion |
10600 |
600 |
Decimal Equivalents of Common Fractions
|
4THS 8THS |
16THS |
32NDS |
DECIMAL |
4THS |
8THS |
16THS |
32NDS |
DECIMAL |
|
|
|
|
0.015625 |
|
|
15 |
30 |
0.9375 |
|
|
|
1 |
0.03125 |
|
|
|
31 |
0.96875 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
0.0625 |
4 |
8 |
16 |
32 |
1 |
|
|
|
3 |
0.09375 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
0.125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
\ |
\ |
5 |
0.15625 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
6 |
0.1875 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
0.21875 |
|
3RDS |
6THS |
12THS |
DECIMAL |
|
12 |
4 |
8 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
1 |
0.833334 |
|
|
|
9 |
0.28125 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
0.166667 |
|
|
5 |
10 |
0.3125 |
|
|
|
3 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
11 |
0.34375 |
|
1 |
2 |
4 |
0.333334 |
|
3 |
6 |
12 |
0.375 |
|
|
|
5 |
0.416667 |
|
|
|
13 |
0.40625 |
|
|
3 |
6 |
0.5 |
|
|
7 |
14 |
0.4375 |
|
|
|
7 |
0.583333 |
|
|
|
15 |
0.46875 |
|
2 |
4 |
8 |
0.666667 |
|
24 |
8 |
16 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
9 |
0.75 |
|
|
|
17 |
0.53125 |
|
|
5 |
10 |
0.833333 |
|
|
9 |
18 |
0.5625 |
|
|
|
11 |
0.916667 |
|
|
|
19 |
0.59375 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
1 |
|
5 |
10 |
20 |
0.625 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
0.65625 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
22 |
0.6875 |
|
5THS |
DECIMAL |
7THS |
DECIMAL |
|
|
|
23 |
0.71875 |
|
1 |
0.2 |
1 |
0.142857 |
|
36 |
12 |
24 |
0.75 |
|
2 |
0.4 |
2 |
0.285714 |
|
|
|
25 |
0.78125 |
|
3 |
0.6 |
3 |
0.428571 |
|
|
13 |
26 |
0.8125 |
|
4 |
0.8 |
4 |
0.571428 |
|
|
|
27 |
0.84375 |
|
5 |
1 |
5 |
0.714285 |
|
7 |
14 |
28 |
0.875 |
|
|
|
6 |
0.857142 |
|
|
|
29 |
0.90625 |
|
|
|
7 |
1 |

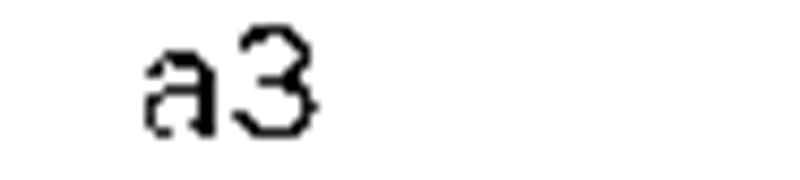
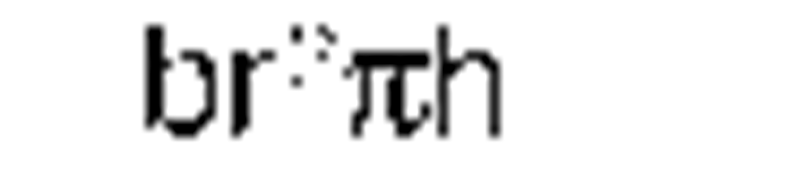
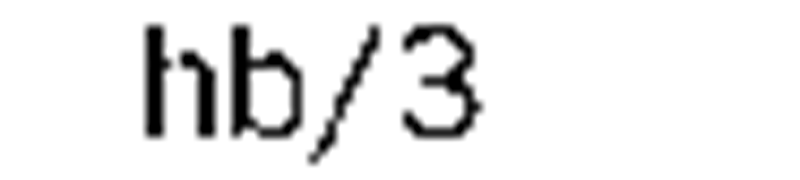
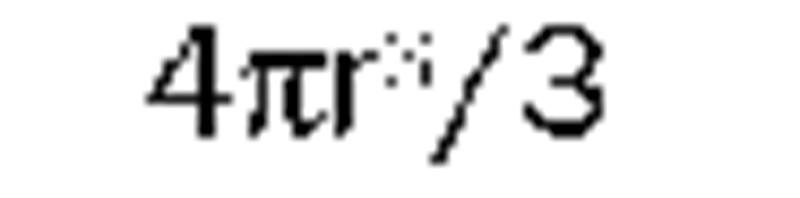
![tmp3A-28_thumb[1][1] tmp3A-28_thumb[1][1]](http://lh4.ggpht.com/_NNjxeW9ewEc/TOtSoHBQW-I/AAAAAAAASSw/Cq29u1eUyAQ/tmp3A28_thumb11_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
