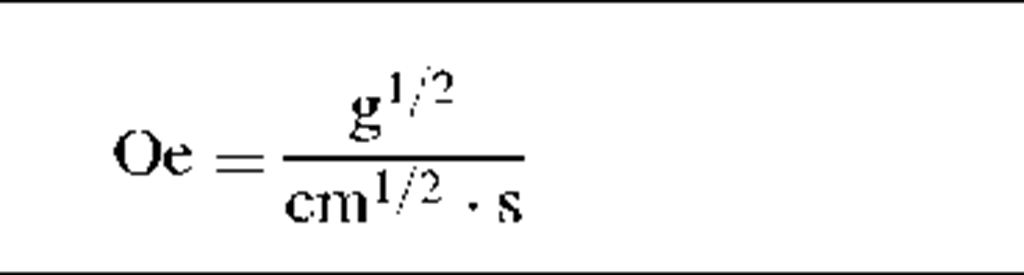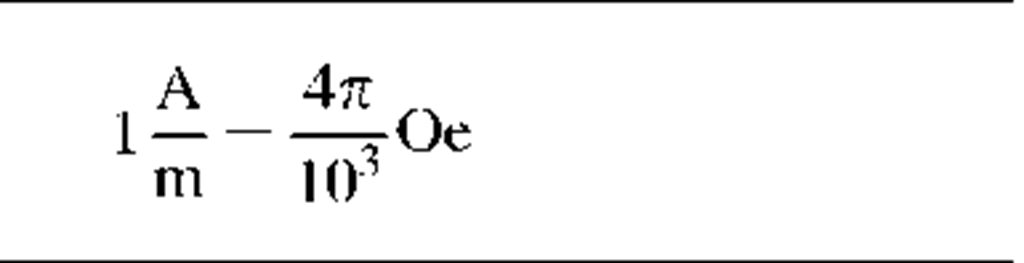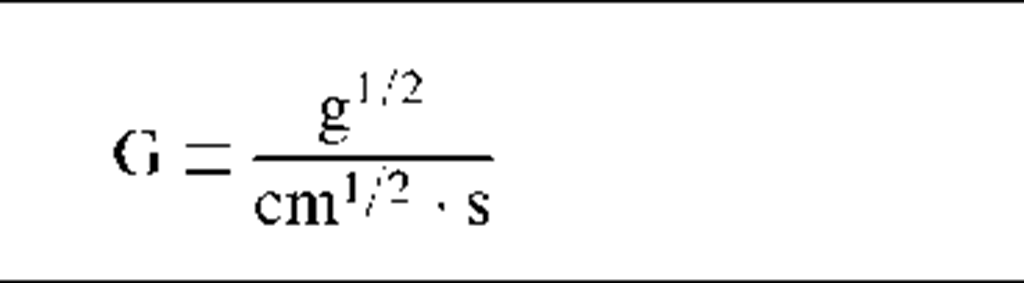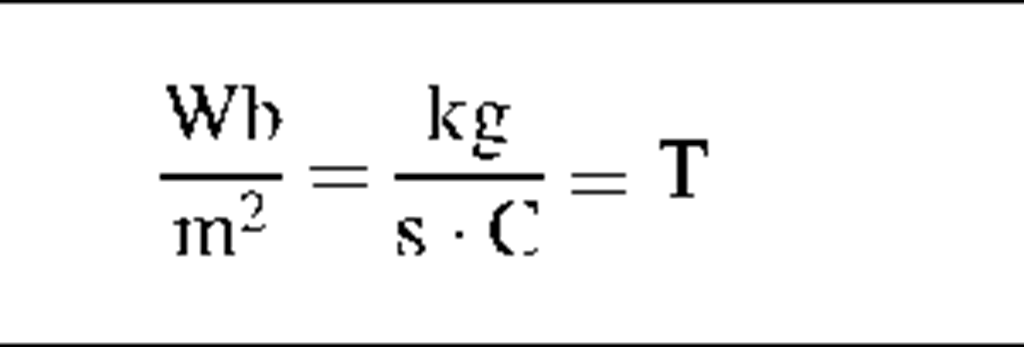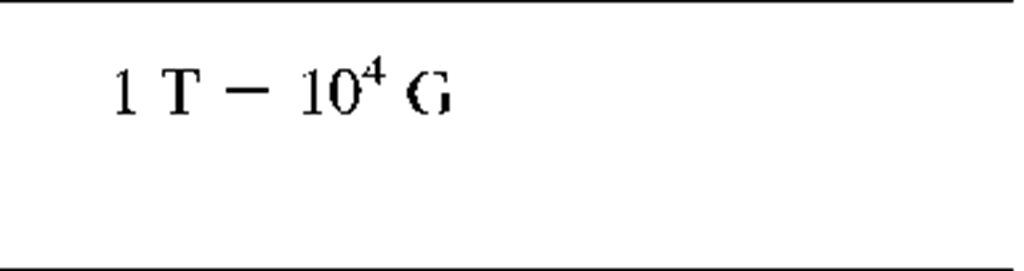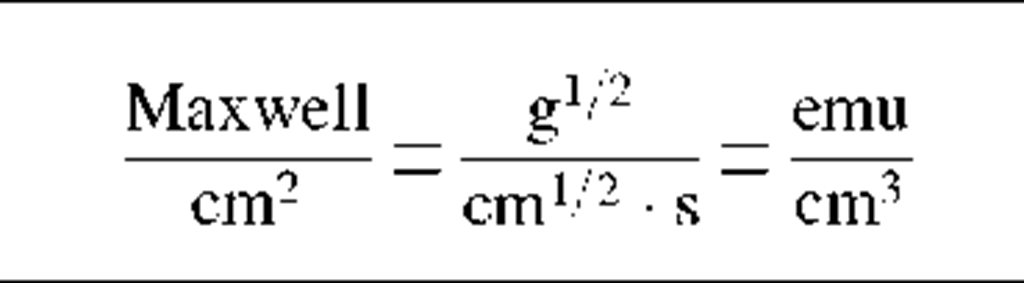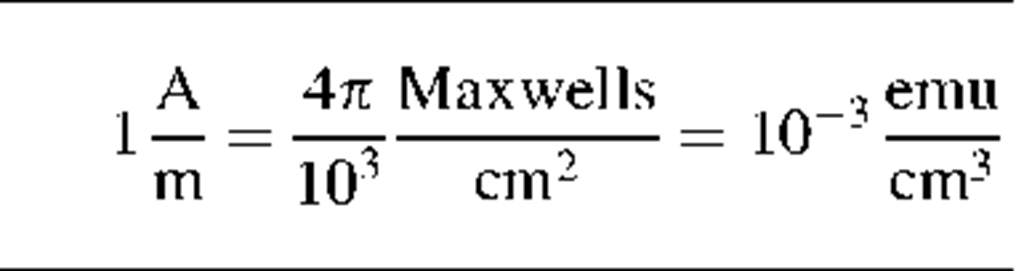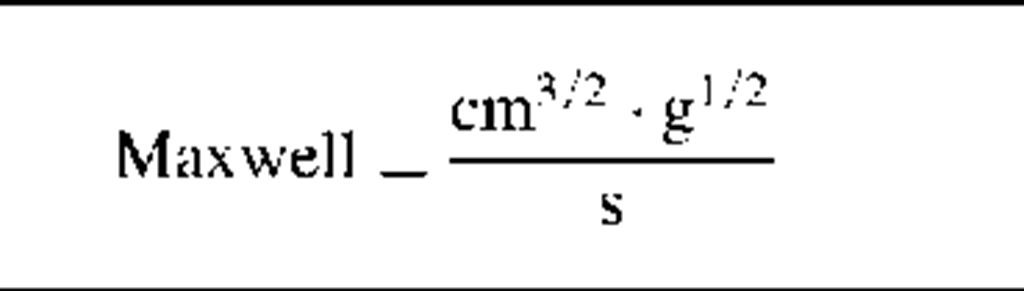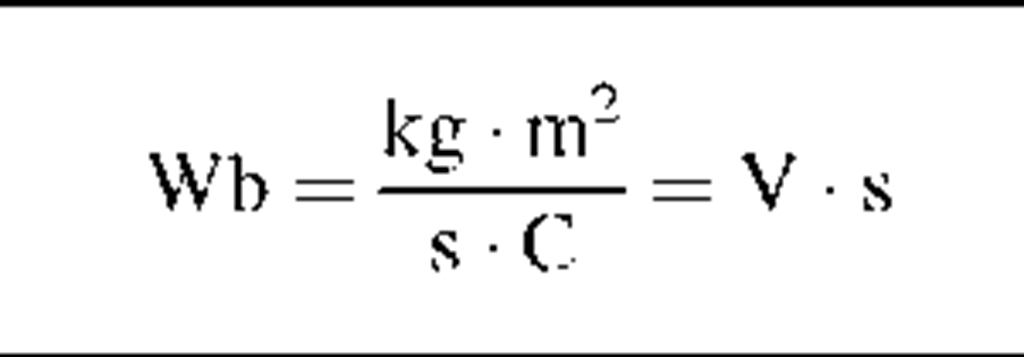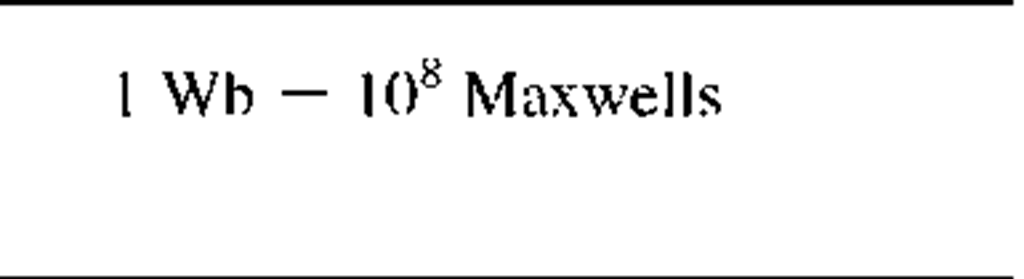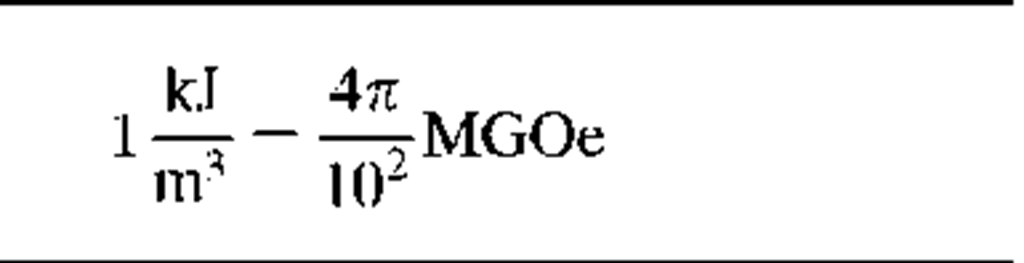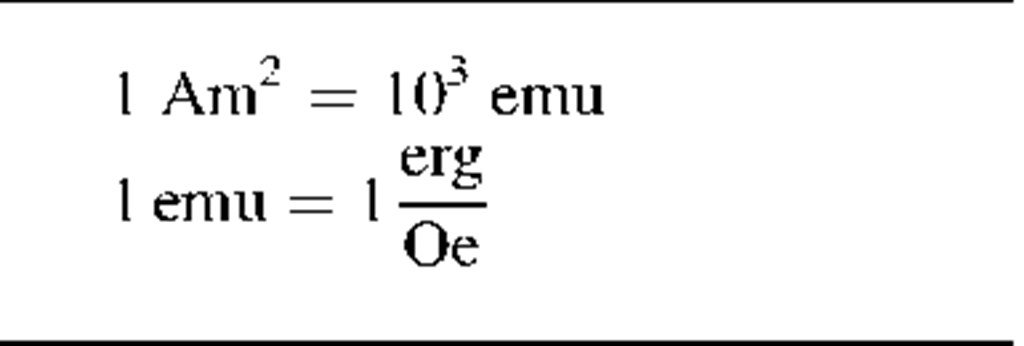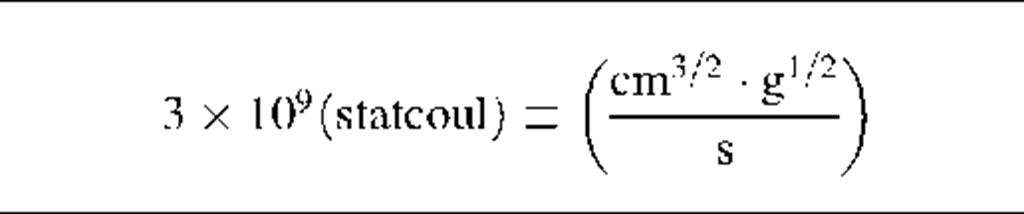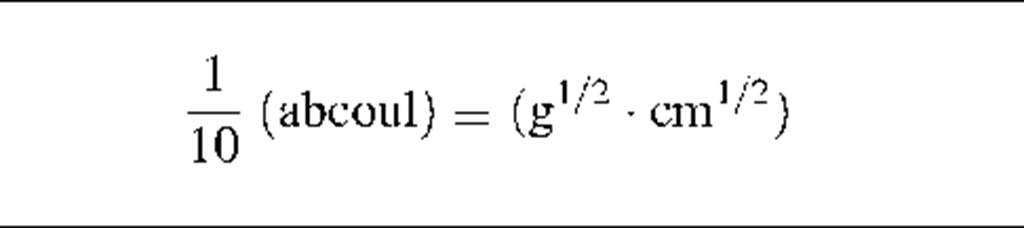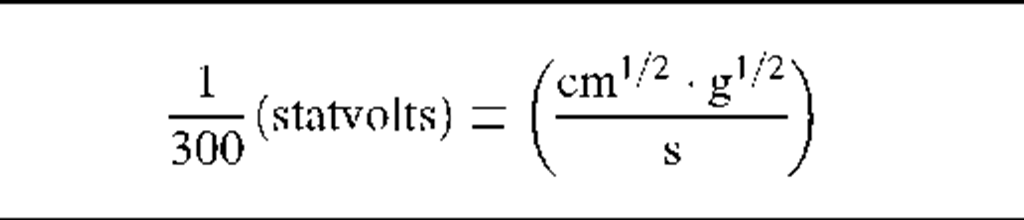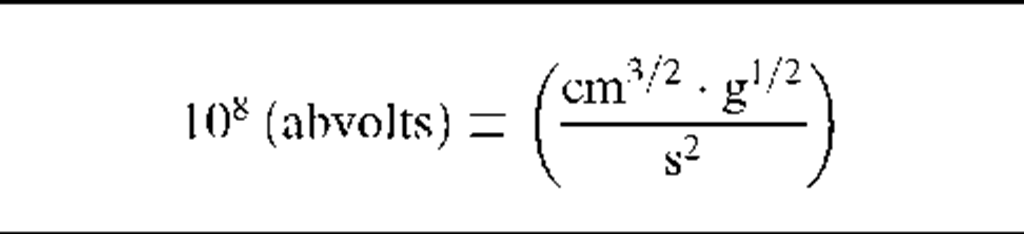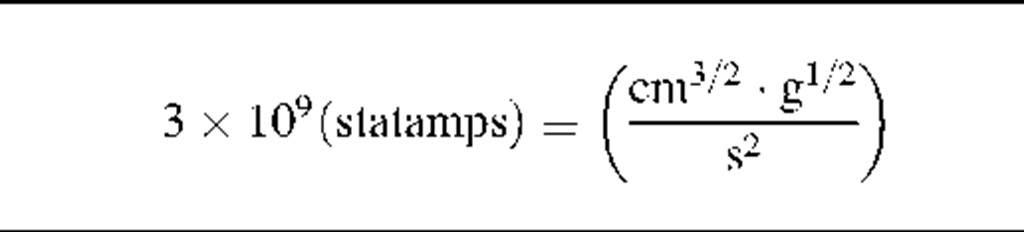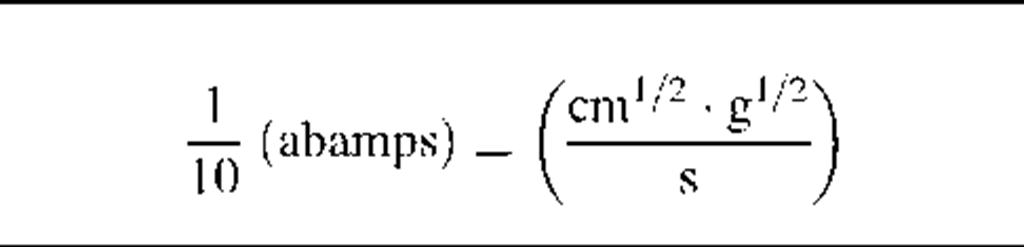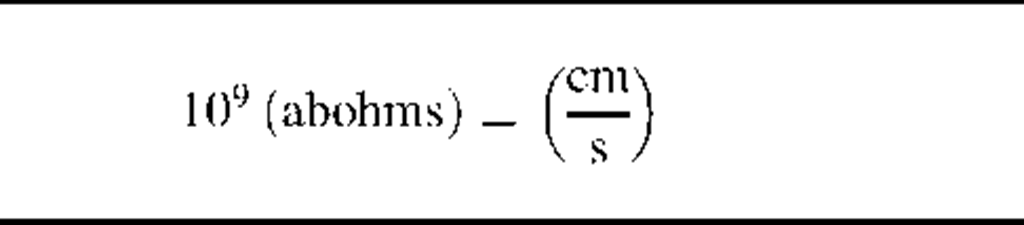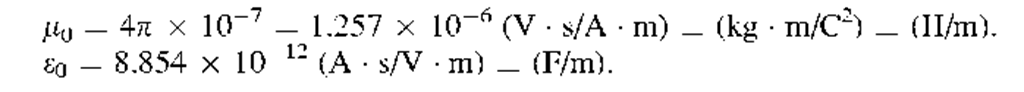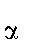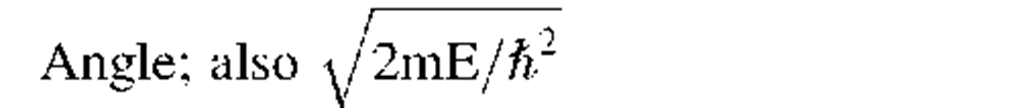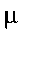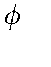Tables (Electronic Properties of Materials) Part 2
Magnetic Units
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
em-cgs units
|
mks (SI) units
|
Conversions
|
|
Magnetic field strength
|
H
|
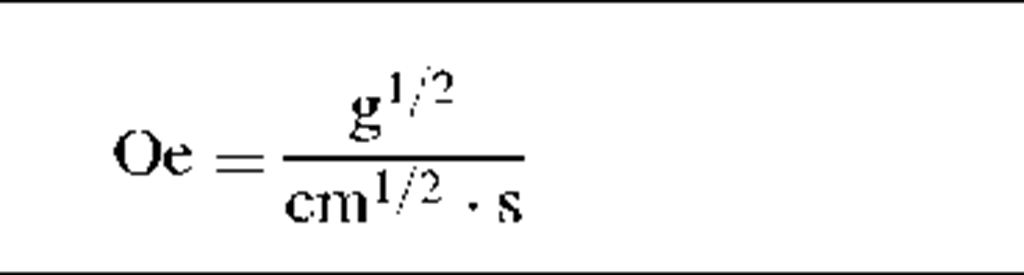 |
 |
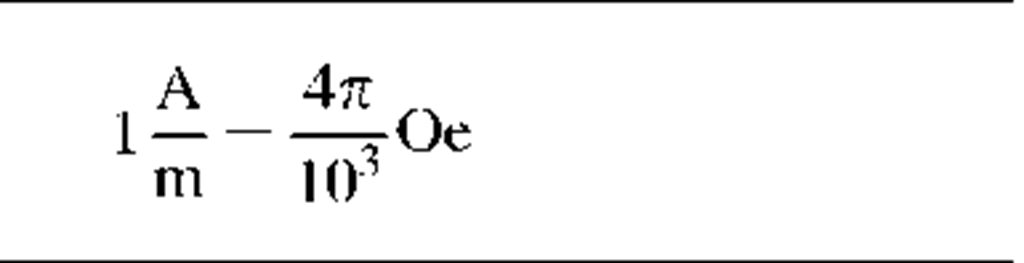 |
|
Magnetic induction
|
B
|
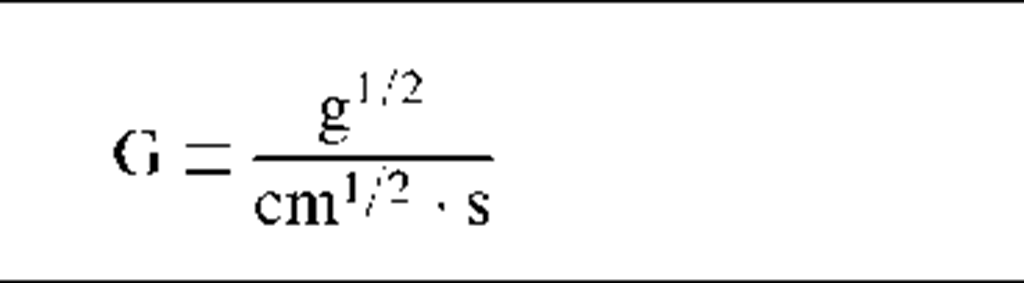 |
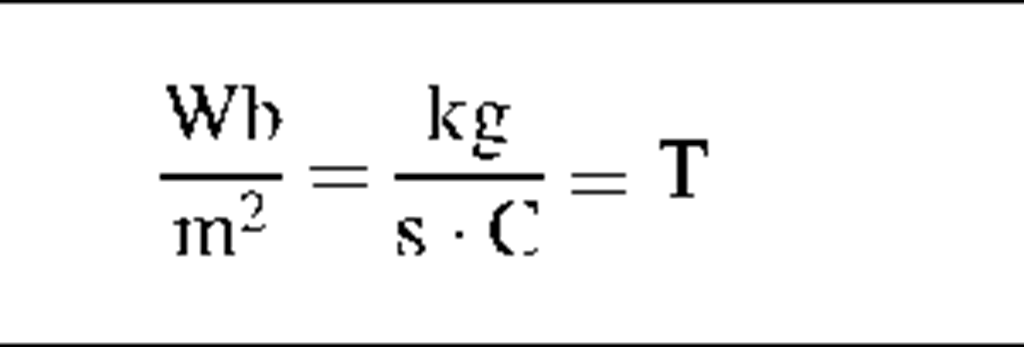 |
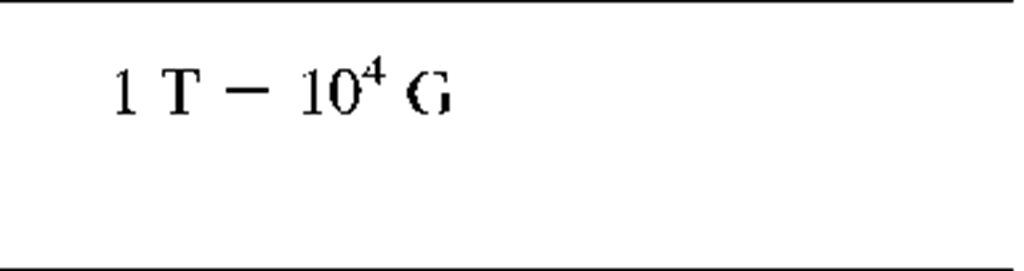 |
|
Magnetization
|
M
|
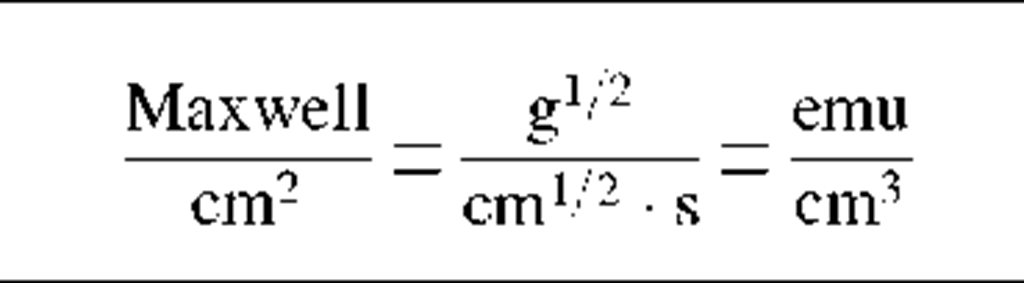 |
 |
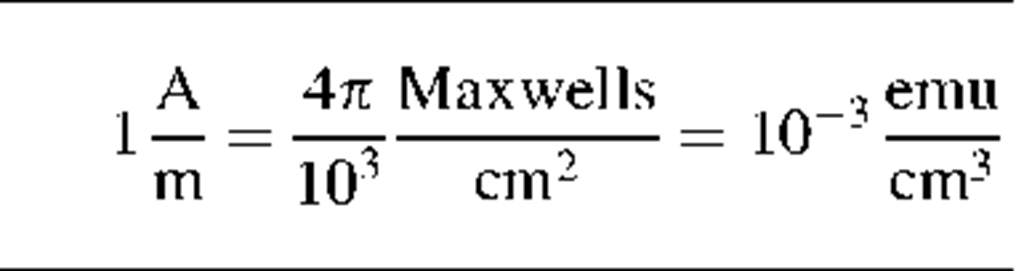 |
|
Magnetic flux
|
*
|
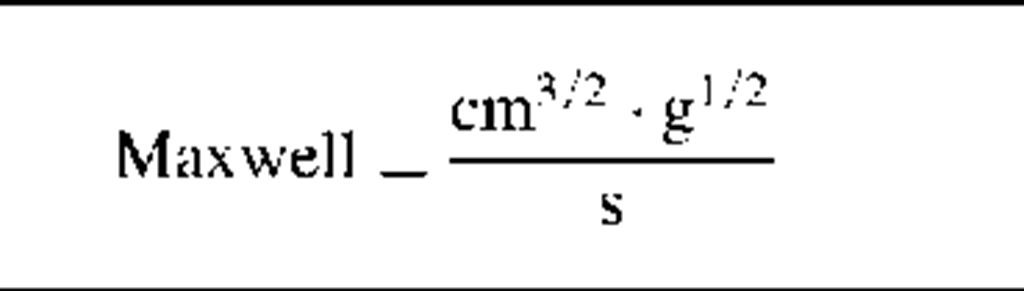 |
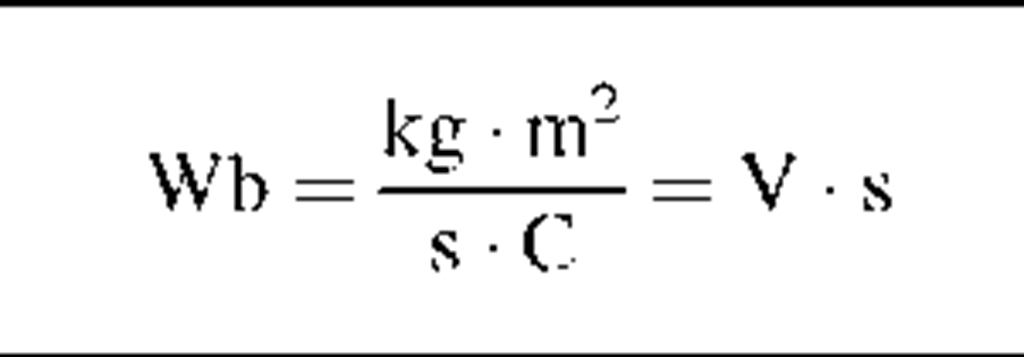 |
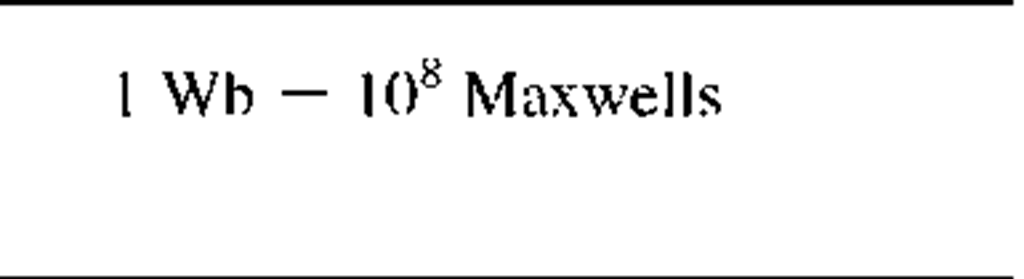 |
|
Susceptibility
|
y,
|
Unities s
|
Unities s
|
 |
|
(Relative) permeability
|
n
|
Unities s
|
Unities s
|
Same value
|
|
Energy product
|
BH
|
MGOe
|
kJ
|
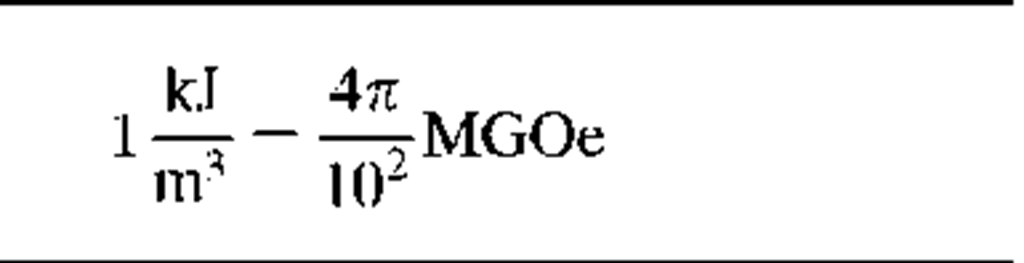 |
|
Magnetic moment
|
Hm
|
emu*
|
Am2
|
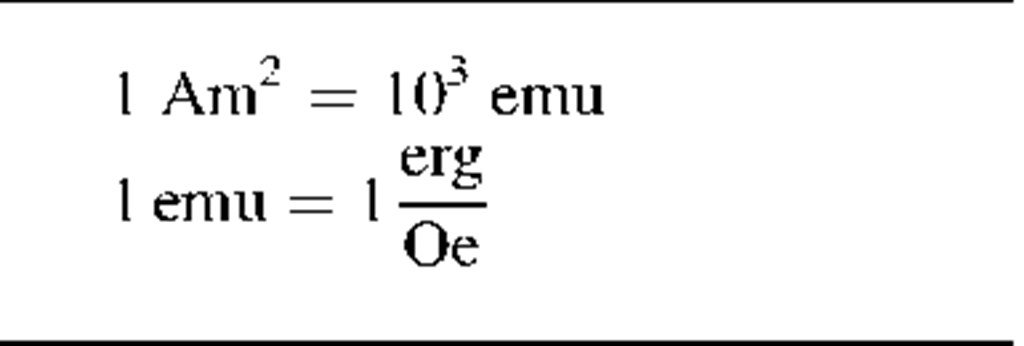 |
*emu = electro magnetic unit (used in USA).
Conversions Between Various Unit Systems
|
SI
|
Electrostatic cgs (esu) units
|
Electromagnetic cgs (emu) units
|
emu-esu conversion
|
|
1(C)
|
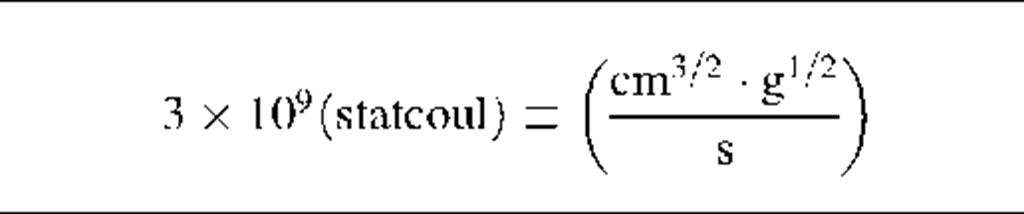 |
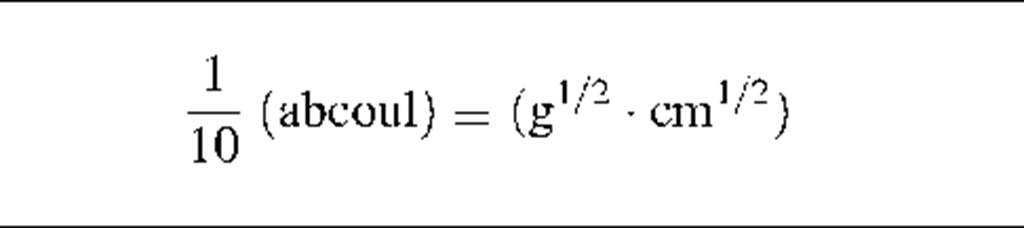 |
1 (abcoul) = f (statcoul)
|
|
1(V)
|
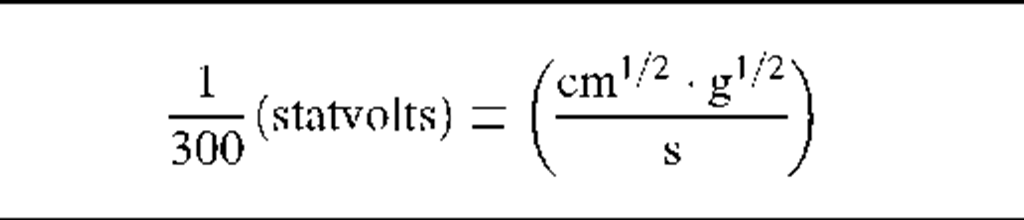 |
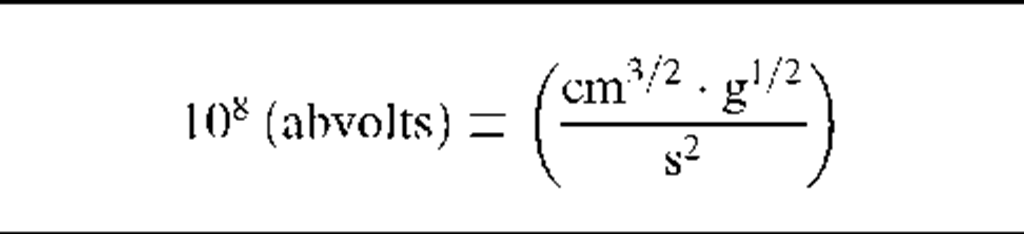 |
1 (abvolt) = i (statvolts)
|
|
1(A)
|
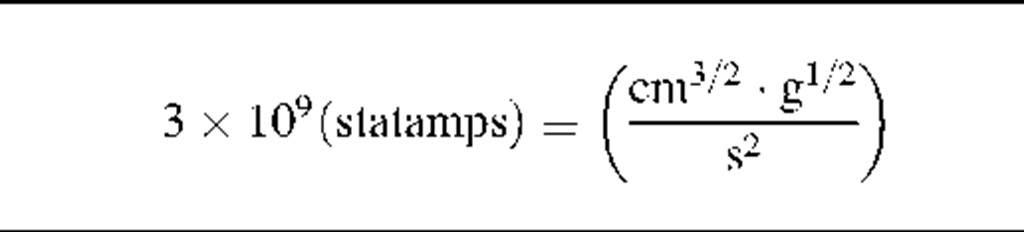 |
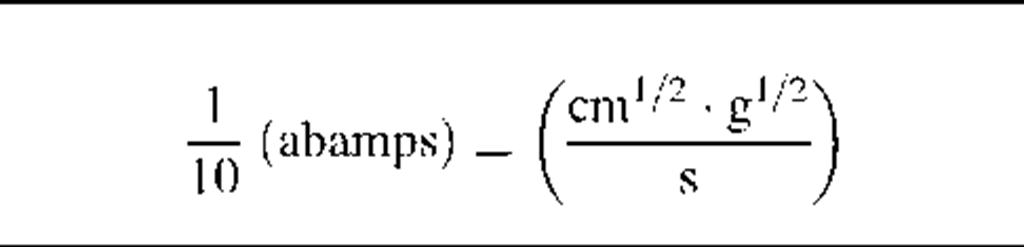 |
1 (abamp) = f (statamps)
|
|
1(Q)
|
 |
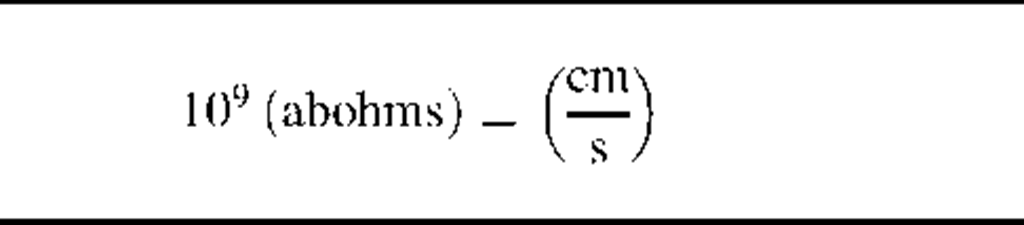 |
1
1 (abohm) = (statohms)
|
Note: The factor "f’ in column four of this table has the value 3 x 1010 (s/cm).
Conversions from the Gaussian Unit System into the SI Unit System
The equations given in this book can be converted from the cgs (Gaussian) unit system into the SI (mks) system and vice versa by replacing the symbols in the respective equations with the symbols listed in the following table. Symbols which are not listed here remain unchanged. It is imperative that consistent sets of units are utilized.
|
Quantity
|
mks (SI)
|
cgs (Gaussian)
|
|
Magnetic induction
|
B
|
B/c
|
|
Magnetic flux
|
f B
|
fB/c
|
|
Magnetic field strength
|
H
|
cH/4p
|
|
Magnetization
|
M
|
cM
|
|
Magnetic dipole moment
|
Mm
|
C^m
|
|
Permittivity constant
|
£0
|
l/4p
|
|
Permeability constant
|
M0
|
4p/c2
|
|
Electric displacement
|
D
|
D/4p
|
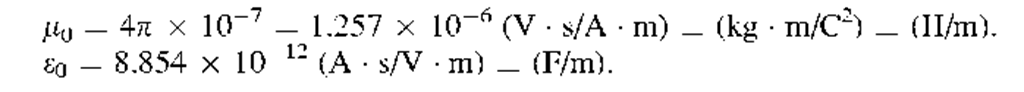
Color Codes of Bands (Rings) on Commercial Resistors
|
First and second
|
|
Fourth color band
|
|
color band
|
Third color band
|
(Tolerances)
|
|
Black —0
|
Black — x 1
|
|
|
Brown —l
|
Brown — x 10
|
Brown —1%
|
|
Red —2
|
Red — x 100
|
Red —2%
|
|
Orange —3
|
Orange — x 1,000 (1K)
|
Orange —3%
|
|
Yellow —4
|
Yellow — x 10 K
|
Yellow —4%
|
|
Green —5
|
Green — x 100 K
|
|
|
Blue —6
|
Blue — x 1,000 K (1 M)
|
|
|
Violet —7
|
Violet — x 10 M
|
|
|
Gray —8
|
Gray — x 100 M
|
|
|
White —9
|
Gold — x .1
|
Gold —5%
|
|
|
Silver — x .01
|
Silver —10% None —20%
|
List of Frequently Used Symbols, as far as they are not already defined in the previous tables.
For example, the symbols for the chemical elements are shown in the previous table. In those cases where a symbol is used more than once, the field of application is indicated, such as: el. = electrical; opt. = optical; mag. = magnetic; th. = thermal.
|
B
|
Magnetic induction (magnetic
|
j
|
Current density
|
|
|
field)
|
JQ
|
Heat flux
|
|
Br
|
Remanence
|
K
|
Thermal conductivity
|
|
C
|
el. Capacitance; mag. Curie
|
k
|
Wave number or wave vector;
|
|
|
constant
|
|
opt: Damping constant
|
|
C
|
Heat capacity (general)
|
L
|
Length
|
|
c
|
opt. Speed of light; th. Specific
|
l
|
Mean free path of electrons
|
|
|
heat capacity
|
M
|
Atomic mass; mag.
|
|
Cp
|
Heat capacity at constant
|
|
Magnetization
|
|
|
pressure
|
m
|
Mass
|
|
cP
|
Molar heat capacity at constant
|
Mr
|
Remanence
|
|
|
pressure
|
n
|
opt. Index of refraction;
|
|
C’v
|
Heat capacity at constant
|
|
th. Amount of substance in mol
|
|
|
volume
|
N(E)
|
Population density of electrons
|
|
Cv
|
Molar heat capacity at constant
|
Ne
|
Number of electrons
|
|
|
volume
|
p
|
momentum
|
|
D
|
Dielectric displacement
|
P
|
Power; el. Dielectric
|
|
D(o)
|
Density of modes
|
|
polarization;
|
|
E
|
Energy
|
|
th. Pressure
|
|
e
|
Electric field strength
|
Q
|
Activation energy
|
|
Ef
|
Fermi energy
|
q
|
Electric charge (general)
|
|
Eg
|
Gap energy
|
R
|
opt. Reflectivity; th. Gas
|
|
Ekin
|
Kinetic energy
|
|
constant
|
|
EMF
|
Electromotoric force
|
T
|
Absolute temperature; opt.
|
|
|
or Electromotive force
|
|
Transmissivity
|
|
exp
|
Exponent, base e
|
t
|
Time
|
|
F
|
Force
|
V
|
Potential energy; el. electric
|
|
F(E)
|
Fermi function
|
|
potential
|
|
fi
|
Oscillator strength
|
v
|
Velocity
|
|
H
|
mag. Magnetic field strength;
|
vg
|
Group velocity
|
|
|
th. Enthalpy
|
W
|
Work; opt. Characteristic
|
|
Hc
|
Coercive field or coercivity
|
|
penetration depth of light
|
|
i
|
 |
Z(E)
|
Density of states
|
|
I
|
Current
|
|
|
Greek Letters
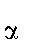 |
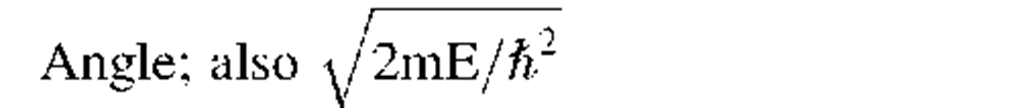 |
 |
opt. Absorbance
th. Expansion coefficient
|
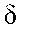 |
Density
|
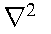 |
See Equation 3.2
|
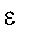 |
Dielectric constant
|
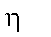 |
Number of energy states; also: efficiency
|
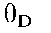 |
Debye temperature
|
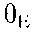 |
Einstein temperature
|
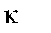 |
opt. Spring constant; th. Compressibility
|
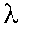 |
Wavelength
|
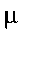 |
el. Mobility of electrons and holes; mag. Permeability
|
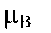 |
Bohr magneton
|
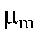 |
Magnetic moment
|
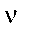 |
Frequency
|
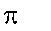 |
3.141….
|
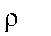 |
Resistivity
|
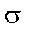 |
Conductivity
|
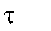 |
Relaxation time
|
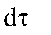 |
Space element
|
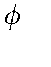 |
el. Work function; opt. Phase difference mag. Magnetic flux
|
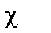 |
el. Electron affinity; mag. Susceptibility
|
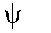 |
Wave function (only space dependent)
|
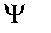 |
Wave function (time and space dependent)
|
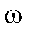 |
Angular frequency
|