The following Frequently Asked Questions, answered by the authors of this topic, are designed to both measure your understanding of the concepts presented in this topic and to assist you with real-life implementation of these concepts.
Q: How can I confirm that my NAT is performing properly?
A: You can start by watching the SmartView Tracker. You could select the FireWall-1 predefined query, or if you are in the All Records view, you will need to enable the NAT fields in the query. Choose View | Query Properties.Then you can select NAT rule number, NAT additional rule number, XlateSrc, and XlateDst. Then you can compare the source/XlateSrc and then destination/XlateDst to determine if NAT is working properly.
If that doesn’t give you what you are looking for, or if the logs in the SmartView Tracker are not what you expect, then you can run an fw monitor command on the firewall to confirm how NAT is working. If you are trying to do a static NAT from IP_A to IP_B, you might set up a filter like this to see if the translation happens in the source:
If that produces too much data, and you want to further filter based on port number, try the following:
The first four entries here show the packet on its way from the client to the server, and the first three inspection points (i, I, and o) show that the source IP address remains the same. Then in the fourth entry, as the packet is leaving the firewall, the source address is translated to 172.16.1.3.You may notice that the source port is also translated, this is how FireWall-1 performs hide NAT.
In the last four entries, you see the return packet from the server to the client. The first inspection of the return packet is destined for the translated address 172.16.1.3 (notice the same source port also).Then the packet is translated back to its original IP and source port for the remainder of the inspection process.
Q: What is the right tool for viewing which rule passes which connections: fw monitor, SMARTView Monitor, or SMARTView Tracker?
A: SmartView Tracker is the only tool that will show you the rule number associated with the log entry.
Q: How would I use the tools described in this topic to troubleshoot a problem where I’m not receiving inbound email?
A: The first thing to check if someone calls with an inbound email problem would be the SmartView Tracker. If a security server is being used, you may see important information in the Info field, such as the virus scanner may not be responding, or the mail server (final MTA) may not be accepting email. If you can’t determine the problem via the logs alone, try to ping, traceroute, and then do a telnet to their external mail server address on port 25 and try to deliver a mail message manually.You might also do the same thing from the firewall to the internal mail server address. If you don’t know the external address of their mail server but do know their domain name, use the nslookup -q=mx domain.com command to find their mail exchanger record. The MX entry with the lowest priority number will be the first attempted. If the solution is still elusive, check that NAT is defined properly and that there are no system resource problems on the firewall preventing processing of inbound mail. Check log files and run an fw monitor and/or tcpdump to find out if there is a virus/ worm causing problems or to determine how far the mail is getting before it is stopped. At this point, it would be a good idea to get a cpinfo, and then as a last resort, try a cpstop/cpstart and/or reboot the firewall to try to get things moving again.
Q: What are the SMTP commands to deliver a mail message manually?
A: Here is a sample connection to a mail server.The commands used to send a message manually are in bold:
Q: How can I test a connection to a Web server with telnet?
A: Most Web servers will listen for connections on port 80, however, there are some exceptions. If you know that this is a standard port 80 HTTP connection, just run telnet www.cisco.com 80, for example, and if you want to verify that you have a connection established, type GET / and press Enter once or twice.You should see HTML scroll across the screen, and then your connection will be closed.
Q: I’m trying to set up synchronization on a Nokia pair, but under ClusterXL in the SmartView Status window it says "Problem!". How can I resolve this?
A: Here are some things for you to check:
■ Run cpconfig on each module and verify that synchronization is enabled; if it is not, enable it and reboot.
■ Run fw tab —t connections —s on both hosts at the same time. If sync is working, you should see a number (under #VALS) that is very similar, within about 200 connections.
■ Ensure that the firewalls are using NTP to synchronize their time. The closer they are to having the same time, the better state sync will work; it is recommended that they are not more than a few seconds off from one another.
■ Ensure that you have the cluster object defined properly:
1. Check that you have the correct Availability mode selected (High Availability or Load Sharing).
2. Check that you have Synchronization enabled and a secure network defined.
■ Run fw ctl pstat and review the sync information displayed on the modules.
■ Run tcpdump on the sync interface to see if sync is working and packets are being sent and received.
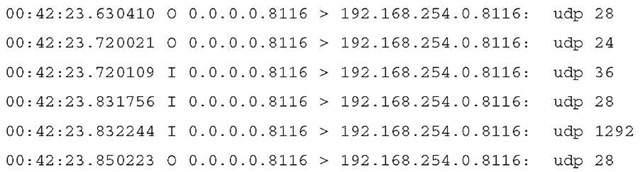
If sync is working properly, you should see output similar to the following by monitoring the sync interface via tcpdump. Notice the second column in the output contains both I and O packets, indicating that there is sync traffic both inbound and outbound on this interface.
Q: How do I use the fw tab command to see how many hosts my firewall has counted?
A: Use the command fw tab —t host_table -s.The output will look something like the following output.The number under #VALS is the current number of hosts counted.