Oxygen cycle Oxygen plays a vital part in the respiration of animals and plants.
1 Oxygen in air
2 Oxygen breathed in by animals
3 Carbon dioxide (a carbon-oxygen compound) bre ath e d out by living things as waste
4 Carbon dioxide absorbed by plants and used in photosynthesis to make carbohydrate foods
5 Surplus oxygen released into the air by plants as waste
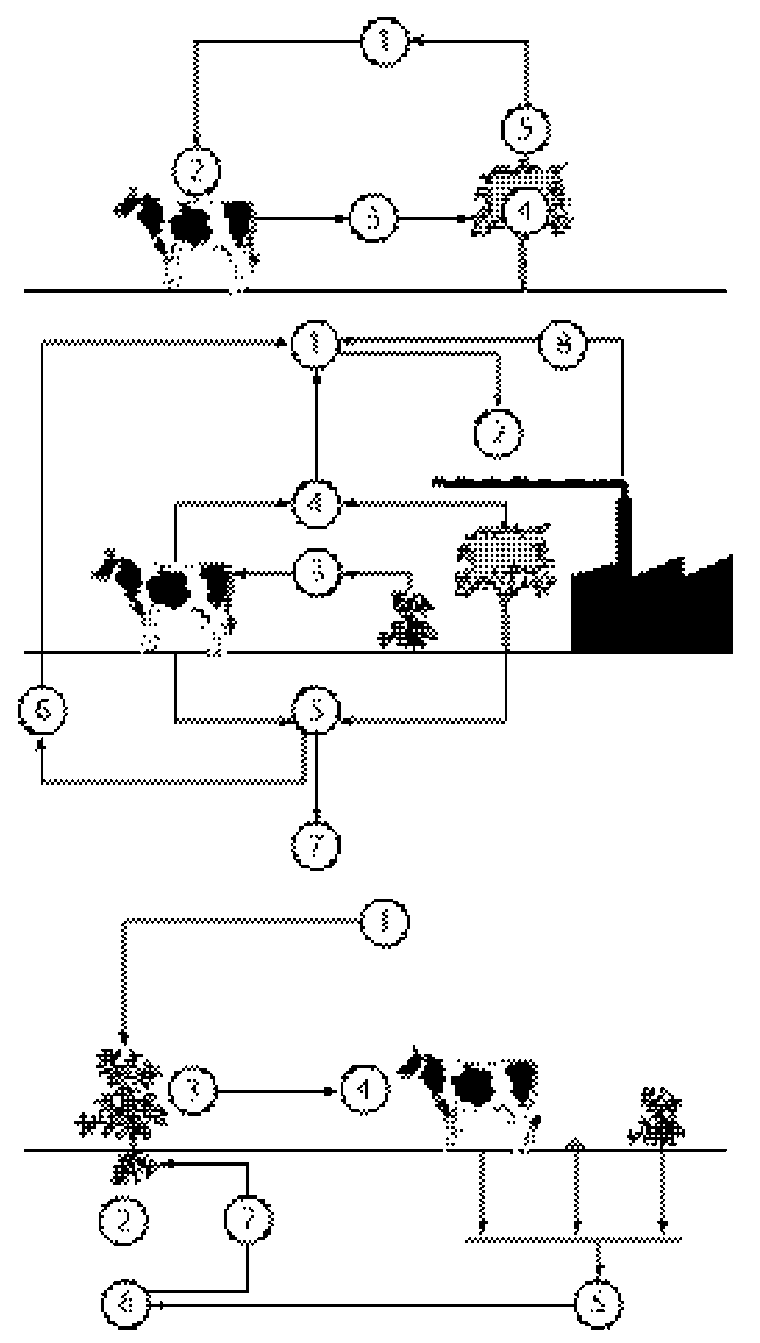
Carbon cycle Plant material is a valuable source of carbon. Oxidizing carbon compounds provide energy for animals and plants.
1 Carbon dioxide (a carbon oxygen compound) in air
2 Carbon dioxide absorbed by plants for making food
3 Plants eaten by animals
4 Carbon dioxide waste breathed out by animals and plants
5 Dead organisms broken down by bacteria
6 These give off carbon dioxide waste
7 Remains of long-dead plants and microscopic organisms forming hydrocarbon fossil fuels: coal, oil, and gas
8 Carbon dioxide released back into the air by burning fossil fuels
Nitrogen cycle As an ingredient in proteins and nucleic acids, nitrogen is vital to all living things.
1 Nitrogen in air
2 Atmospheric nitrogen trapped by some plants’ roots
3 Nitrogen used by plants for making proteins
4 Plant proteins eaten by animals
5 Proteins in dead organisms and body wastes converte d to ammonia by bacteria and fungi
6 Ammonia converted to nitrate by other bacteria
7 Nitrate taken up by plant roots
Sulfur cycle Sulfur is in two of the 20 amino acids which are used by the body to make proteins.
1 Sulfates (sulfur-oxygen compounds) absorbed by plant roots
2 The oxygen in the sulfate is replaced by hydrogen in a plant process that produces certain amino acids
3 Plants eaten by animals
4 Sulfur-containing amino acids of dead plants and animals broken down to hydrogen sulfide (which gives o ffa rotten egg odor) by decomposer micro organisms
5 Sulfur extracted from sulfides by bacteria
6 Other bacteria combine sulfur with oxygen, producing sulfates
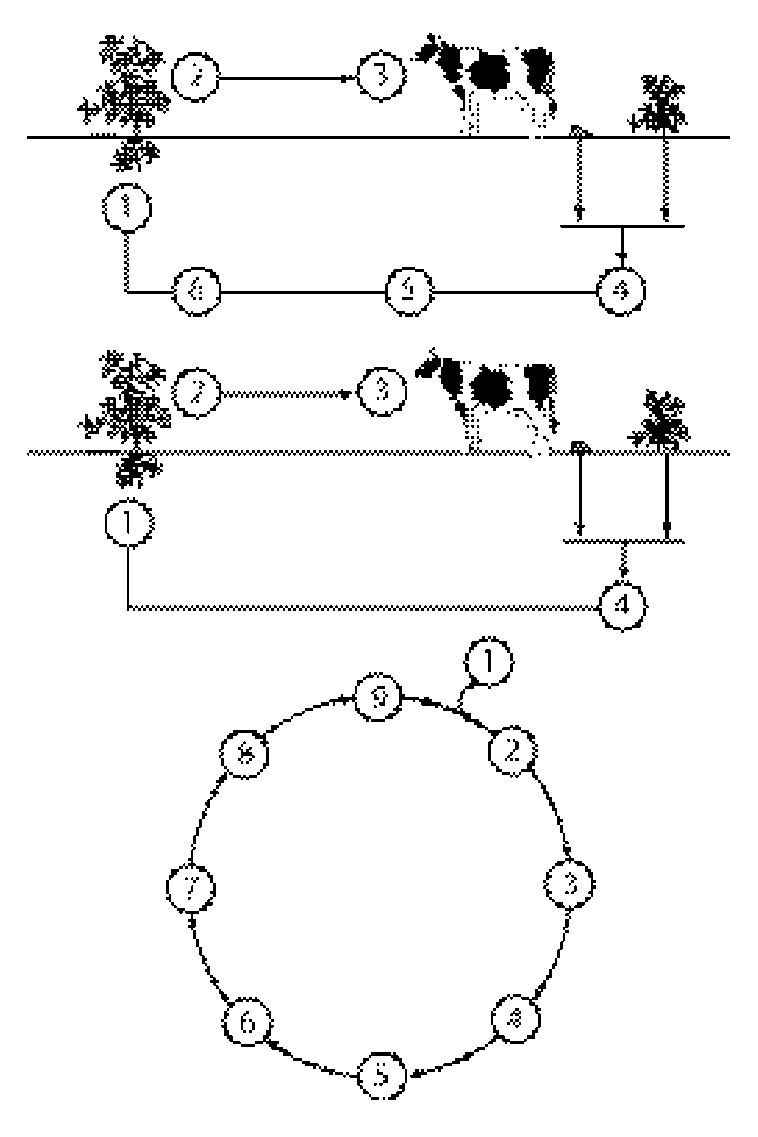
Phosphorus cycle Phosphorus is a vital ingredient of proteins, nucleic acids, and some other compounds found in living things.
1 Phosphates (compounds of phosphorus, hydrogen, and oxygen) absorbed by plant roots
2 Phosphates used by plants in making organic phosphorus compounds
3 Plants eaten by animals
4 Compounds in dead plants and animals broken down to phosphates by microorganisms
Krebs cycle The Krebs or citric acid cycle is the second stage of aerobic respiration in which living things produce energy from foods. It requires oxygen; enzymes (proteins that promote but are not used up in chemical changes) create successive compounds, thus transforming pyruvate to carbon dioxide and water and releasing energy.
1 Acetic acid combines with…
2 Oxaloacetic acid to form…
3 Citric acid. Later changes produce…
4 Aconitic acid
5 Isocitric acid
6 Ketoglutaric acid
7 Succinic acid, carbon dioxide, and energy-rich ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
8 Fumaric acid
9 Malic acid