Solomon Islands
Official name: Solomon Islands. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (National Parliament [50]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Nathaniel Waena (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Derek Sikua (from 2007). Capital: Honiara. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Solomon Islands dollar (SI$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SI$7.72.
Demography
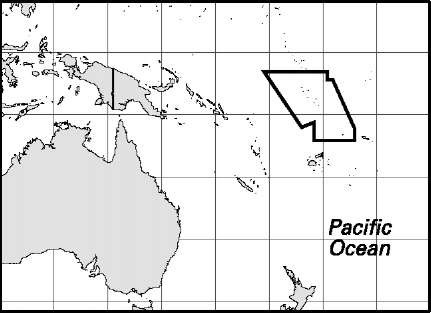
Area: 10,954 sq mi, 28,370 sq km. Population (2007): 495,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 45.2, persons per sq km 17.4. Urban (2005-06): 16.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.53%; female 48.47%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 40.0%; 15-29, 28.7%; 30-44,17.9%; 45-59, 8.5%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75 and over, 1.0%. Ethnic composition (2002): Melanesian 93.0%; Polynesian 4.0%; Micronesian 1.5%; other 1.5%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 70%, of which Anglican 32%, Adventist 10%; Roman Catholic 18%; traditional beliefs 5%; other 7%. Major towns (2004): Honiara 57,600; Gizo 6,200; Auki 4,700; Buala 2,900. Location: southwestern Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 30.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 26.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.78. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.4 years; female 75.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:SI$946,200,000 (tax revenue 73.0%, of which VAT 17.9%, logging duties 13.6%, import duties 9.3%, corporate tax 8.2%; nontax revenue 13.9%; grants 13.1%). Expenditures: SI$911,100,000 (current expenditure 90.5%, of which wages 27.3%, debt service 13.9%; capital expenditure 9.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$148,100,000. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$411,000,000 (US$849 per capita). Households (2005-06). Average household size 6.2; average annual income per household US$3,129; sources of income: home production (mostly food preparations and handicrafts) 36.9%, wages and salaries 26.6%, transfers 8.8%, self-employment 7.8%; expenditure: food 53.5%, housing 15.8%, transportation 6.8%. Population economically active (2006): total 201,000; activity rate of total population 41.0% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 68.8%; female 38.3%; unemployed [2003] 15.2%). Production (metric tons exceptas noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): coconuts 276,000, oil palm fruit 162,290, sweet potatoes 88,723; livestock (number of live animals) 53,000 pigs, 13,500 cattle, 230,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 692,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 20%; fisheries production 29,597; aquatic plants production (2005) 120 (from aquaculture 100%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gold 10 kg. Manufacturing (2006): coconut oil 59,000, copra 21,214, palm oil 5,427. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 68,000,000 (55,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (57,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2.0; remittances (2006) 2.0; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -3.0; official de-velopmentassistance (2005) 198. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5.0; remittances (2006) 6.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.6%, in permanent crops 2.1%, in pasture 1.4%; overall forest area (2005) 77.6%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; ci.f.): US$250,613,000 (machinery and transport equipment 24.7%; petroleum [all forms] 21.7%; food 14.1%; construction materials 10.0%). Major import sources: Australia 25.3%; Singapore 23.4%; Japan 7.8%; New Zealand 5.0%; Fiji 4.2%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$120,393,000 (timber 70.2%; fish products 15.9%; palm oil 3.3%; cacao beans 3.3%). Major export destinations: China 45.7%; South Korea 14.0%; Japan 8.5%; Thailand 4.4%; Philippines 4.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2007): total length 1,500 km (paved 2.7%). Vehicles (1993): passenger cars 2,052; trucks and buses 2,574. Airtransport (2004; Solomon Airlines only): passenger-km 76,733,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,259,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2006): 4,000 (8.3); televisions (2004): 5,300 (11); telephone landlines (2005): 7,400 (16); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 6,000 (13); personal computers (2005): 22,000 (47); total Internet users (2006): 8,000 (17); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 400 (0.8).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005-06). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no schooling/unknown 15.6%; primary education 46.7%; secondary 32.8%; vocational 4.0%; higher 0.9%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 76.6%. Health (2005): physicians 89 (1 per 5,293 persons); hospital beds 691 (1 per 682 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 20.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,056 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 116% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2007): none; 200-300 military troops and police in an Australian-led multinational regional intervention force (from mid-2003) maintain civil and political order.
Background
The Solomon Islands were probably settled c. 2000 bc by Austronesian people. Visited by the Spanish in 1568, the islands were subsequently explored and charted by the Dutch, French, and British. They came under British protection in 1893 and became the British Solomon Islands. During World War II, the Japanese invasion of 1942 ignited three years of the most bitter fighting in the Pacific, particularly on Guadalcanal. The protectorate became self-governing in 1975 and fully independent in 1978. (Another island group named Solomon Islands, which includes Bougainville, is part of Papua New Guinea.)
Recent Developments
In 2007 there was continuing tension between Prime Minister Manasseh Sogavare and the Australian-led Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI), which had been invited to the Solomons in 2003 to restore order and to rebuild government institutions. The economy was growing very quickly, but it was heavily dependent on unsustainable levels of logging, which had been growing at 6-12% annually. Natural forests were likely to be depleted in six years.
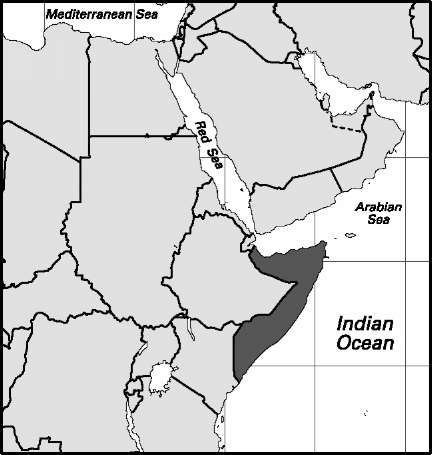
Somalia
Somaliland had not received international recognition as of early 2008. This entity represented about a quarter of Somalia’s territory. Official name: Soomaaliya (Somali); Al-Sumal (Arabic) (Somalia). Form of government: transitional regime (the “new transitional government” from October 2004 lacked effective control in early 2008) with one legislative body (Transitional Federal Parliament [275]). At present Somalia is divided into three autonomous regions: Somaliland in the northwest, Puntland in the northeast, and Somalia in the south. Head of state and government: President Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed (from 2004), assisted by Prime Minister Nur Hassan Hussein (from 2007). Capital: Mogadishu. Official languages: Somali; Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Somali shilling (So.Sh.) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = So.Sh. 1,392.00(in early 2007 the black-market value was about 23,000 So.Sh. = US$1).
Demography
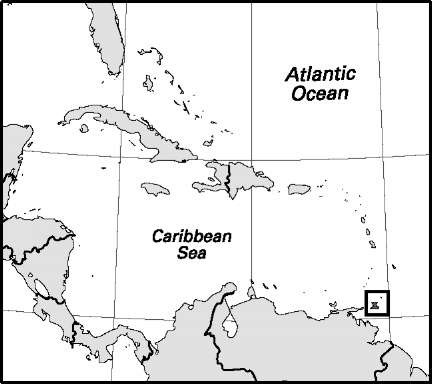
Area: 246,000 sq mi, 637,000 sq km. Population (2007): 8,699,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 35.4, persons per sq km 13.7. Urban (2006): 36.5%. Sex distribution (2002): male 51.47%; female 48.53%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 44.1%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44, 16.1%; 45-59, 8.5%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75-84, 0.6%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Somali 92.4%; Arab 2.2%; Afar 1.3%; other 4.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 99%; other 1%. Major cities (1990): Mogadishu (urban agglomeration; 2005) 1,320,000; Hargeysa (1997) 300,000; Kismaayo 90,000; Berbera 70,000; Marka 62,000. Location: eastern Africa, bordering Djibouti, the Gulf of Aden, the Indian Ocean, Kenya, and Ethiopia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 45.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 28.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 6.84. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 46.4 years; female 49.9 years.
National economy
Budget (1991). Revenue:So.Sh. 151,453,000,000 (domestic revenue sources [principally indirect taxes and import duties] 60.4%; external grants and transfers 39.6%). Expenditures:So.Sh. 141,141,000,000 (general services 46.9%; economic and social services 31.2%; debt service 7.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,882,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 200,000, corn (maize) 190,000, sorghum 150,000, other tree/bush products include khat, frankincense, and myrrh; livestock (number of live animals) 13,100,000 sheep, 12,700,000 goats, 7,000,000 camels; roundwood 10,912,897 cu m, of which fuelwood 99%; fisheries production 30,000. Mining and quarrying (2004): gypsum 1,500; salt 1,000; garnet and opal are mined in Somaliland. Manufacturing (value added in So.Sh. ’000,000; 1988): food 794; cigarettes and matches 562; hides and skins 420. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 286,000,000 (286,000,000). Population economically active (2001-02): total 3,906,000; activity rate of total population 52.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 56.4%; unemployed 47.4%). Households (2001-02). Average household size 5.8; income per household US$226; sources of income: self-employment 50%, remittances 22.5%, wages 14%, rent/aid 13.5%. Gross national income (2006): US$2,313,000,000 (US$274 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): remittances (2005) 1,000; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 8.8; official development assistance (2005) 236. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.7%, in permanent crops 0.04%, in pasture 68.5%; overall forest area (2005) 11.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$397,000,000 (agricultural products 26.5%, of which sugar 13.5%, cereals 6.4%; unspecified 73.5%). Major import sources (2004): Djibouti 31%; Kenya 14%; India 10%; Brazil 6%; Oman 5%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): US$95,000,000 (agricultural products 45.1%, of which goats and sheep 25.6%, bovines 7.8%; unspecified 54.9%). Major export destinations (2004): Thailand 29%; UAE 24%; Yemen 15%; India 8%; Oman 6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2003): total length 22,000 km (paved 12%). Airtransport (2003; four Somaliland airports only): passenger arrivals 50,096, passenger departures 41,979; cargo unloaded 3,817 metric tons, cargo loaded 152 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 4,500 (0.5); televisions (2003): 108,000 (14); telephone landlines (2005): 100,000 (12); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 500,000 (61); personal computers (2005): 75,000 (9.1); total Internet users (2006): 94,000 (11).
Education and health
Literacy (2002): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 19.2%; males literate 25.1%; females literate 13.1%. Health (1997): physicians 265 (1 per 25,032 persons); hospital beds 2,786 (1 per 2,381 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 116.7.
Military
Total active duty personnel: no national army from 1991. African Union peacekeeping troops (September 2007) 1,600 (of planned 7,000).
Background
Muslim Arabs and Persians first established trading posts along the coasts of Somalia in the 7th-10th centuries. By the 10th century Somali nomads occupied the area inland from the Gulf of Aden, and the south and west were inhabited by various groups of pastoral Oromo peoples. Intensive European exploration began after the British occupation of Aden in 1839, and in the late 19th century Britain and Italy set up protectorates in the region. During World War II the Italians invaded British Somaliland (1940); a year later British troops retook the area, and Britain administered the region until 1950, when Italian Somaliland became a UN trust territory. In 1960 it was united with the former British Somaliland, and the two became the independent Republic of Somalia. Since then it has suffered political and civil strife, including military dictatorship, civil war, drought, and famine. In the 1990s no effective central government existed. In 1991 a proclamation of a Republic of So-maliland, on territory corresponding to the former British Somaliland, was issued by a breakaway group, but it did not receive international recognition. A multinational force intervened from 1992 to 1994 in an unsuccessful attempt to stabilize the region. The country remained in turmoil.
Recent Developments
Fierce fighting continued between forces from Ethiopia and from Somalia’s Transitional Federal Government and soldiers of the Islamic Courts Union (ICU), an Islamic fundamentalist movement that had controlled most of the country in 2006. In January 2007, as fleeing ICU fighters became sandwiched between Ethiopian forces, the Kenyan border, and the Somali coastline, US gunships mounted a pair of air raids that were reportedly aimed at three high-ranking al-Qaeda operatives. Ethiopian troops in Mogadishu were joined by a contingent of some 1,500 African Union peacekeepers from Uganda. In March violence there reached its worst levels in more than a decade, with battles so intense that bodies were left lying in the streets for days, and fighting continued in 2008. The number of internally displaced people in Somalia approached one million, and more than 400,000 were refugees in neighboring countries.
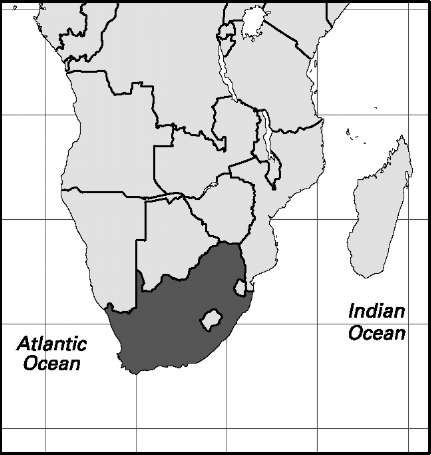
South Africa
Official name: Republic of South Africa. Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (National Council of Provinces [90]; National Assembly [400]). Head of state and government: President Thabo Mbeki (from 1999). Capitals (de facto): Pretoria/Tshwane (executive); Bloem-fontein/Mangaung (judicial); Cape Town (legislative).
Official languages: Afrikaans; English; Ndebele; Pedi; Sotho; Swazi; Tsonga; Tswana; Venda; Xhosa; Zulu. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 rand (R) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = R 7.92.
Demography
Area: 470,693 sq mi, 1,219,090 sq km. Population (2007): 47,851,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 101.6, persons per sq km 39.2. Urban (2005): 59.3%. Sex distribution (2007): male 49.24%; female 50.76%. Age breakdown (2007): under 15, 31.9%; 15-29, 29.2%; 30-44, 19.3%; 45-59, 11.7%; 60-74, 6.3%; 75 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic composition (2001): black 78.4%, of which Zulu 23.8%, Xhosa 17.6%, Pedi 9.4%, Tswana 8.2%, Sotho 7.9%, Tsonga 4.4%, Swazi 2.7%, other black 4.4%; white 9.6%; mixed white/black 8.9%; Asian 2.5%; other 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): independent Christian 37.1%, of which Zion Christian 9.5%; Protestant 26.1%; traditional beliefs 8.9%; Roman Catholic 6.7%; Muslim 2.5%; Hindu 2.4%; nonreli-gious 3.0%; other/unknown 13.3%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Johannesburg 3,288,000; Cape Town 3,103,000; Ekurhuleni (East Rand) 3,043,000; Ethekwini (Durban) 2,643,000; Tshwane (Pretoria) 1,282,000. Location: southern Africa, bordering Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland, and the southern Atlantic and western Indian oceans; wholly contained within South Africa is the country of Lesotho.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 21.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2007): 2.69. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 49.0 years; female 52.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:R 411,085,100,000 (personal income taxes 30.6%; VAT 28.0%; company income taxes 23.5%). Expenditures: R 417,819,200,000 (transfer to provinces 36.0%; debt payments 12.7%; police and prisons 9.0%; defense 5.4%; education 3.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$11,662,000,000. Production (in metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 20,275,400, corn (maize) 6,935,000, wheat 2,105,000; livestock (number of live animals) 24,983,000 sheep, 13,790,000 cattle; roundwood (2005) 33,071,100 cu m, of which fuel-wood 36%; fisheries production (2005) 820,750; aquatic plants production (2005) 9,619 (from aqua-culture 30%). Mining and quarrying (value of sales in R ’000,000,000; 2005): platinum-group metals 38.4; coal 35.6; gold 24.6. Manufacturing (value of sales in R ’000,000; 2005): food products and beverages 153,496; transport equipment 137,870; chemicals 81,240. Energy production (consumption; 2004 data include Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, and Swaziland): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 244,920,000,000 (223,257,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 244,500,000 ([2004] 180,287,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 4,800,000 (206,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 23,825,000 (19,750,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 1,978,000,000 (1,978,000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 16,788,000; activity rate of total population 35.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 56.5%; female 45.7%; unemployed 26.7%). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.0; expenditure (2005): food, beverages, and tobacco 25.8%, transportation and communications 16.9%, household furnishings 9.7%, housing 9.6%. Gross national income (2006): US$241,635,000,000 (US$5,005 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,335; remittances (2006) 735. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,374; remittances (2006) 1,067. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.1%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 69.1%; overall forest area (2005) 7.6%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$34,543,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery 13.8%; chemical products 10.7%; crude petroleum 10.4%; road vehicles 7.1%; telecommunications equipment 5.0%). Major import sources (2005): Germany 14.9%; US 7.0%; China 6.9%; UK 6.8%; Saudi Arabia 6.5%. Exports (2003): US$36,230,000,000 (gold 12.7%; iron and steel 10.7%; platinum-group metals 8.8%; road vehicles 8.6%; food 6.6%; nonelectrical machinery 6.5%). Major export destinations (2005): UK 11.1%; US 9.1%; Japan 8.3%; Germany 6.3%; China 5.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): route length (2005) 20,872 km; passenger-km 3,930,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 106,786,000,000. Roads (2002): length 362,099 km (paved 20%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 4,574,972; trucks and buses 2,112,601. Air transport (2006; SAA only): passen-ger-km 25,501,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,228,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,408,000 (30); televisions (2003): 9,134,000 (199); telephone landlines (2005): 4,729,000 (101); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 33,960,000 (724); personal computers (2005): 3,966,000 (85); total Internet users (2005): 5,100,000 (109); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 165,000 (3.5).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Percentage of population ages 20 and over having: no formal schooling 10.4%; some primary education 21.1%; complete primary/some secondary 34.0%; complete secondary 24.9%; higher 9.1%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 87.1%. Health: physicians (2006) 33,220 (1 per 1,427 persons); hospital beds (2004) 153,465 (1 per 303 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2007) 45.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,933 (vegetable products 87%, animal products 13%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 62,334 (army 66.3%, navy 9.3%, air force 14.7%, military health service 9.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$76.
Background
San and Khoikhoi peoples roamed southern Africa as hunters and gatherers in the Stone Age, and the latter had developed a pastoralist culture by the time of European contact. By the 14th century, Bantu-speaking peoples had settled in the area and developed gold and copper mining and an active East African trade. In 1652 the Dutch established a colony at the Cape of Good Hope; the Dutch settlers became known as Boers and later as Afrikaners, after their Afrikaans language. In 1795 British forces captured the Cape, and in the 1830s, to escape British rule, Dutch settlers began the Great Trek northward and established the independent Boer republics of Orange Free State and the South African Republic(latertheTransvaal region), which the British annexed as colonies by 1902 after the 30-month-long Boer War. In 1910 the British colonies of Cape Colony, Transvaal, Natal, and Orange River were unified into the new Union of South Africa. It became independent and withdrew from the Commonwealth in 1961. Throughout the 20th century South African politics were dominated by the issue of maintaining white supremacy over the country’s black majority, and in 1948 South Africa formally instituted apartheid. Faced by increasing worldwide condemnation, it began dismantling the policy in the 1980s and ended it in 1990. In free elections in 1994, Nelson Mandela became the country’s first black president. South Africa also rejoined the Commonwealth in 1994.
Recent Developments
A one-month public-service strike in June 2007 in South Africa involving up to one million workers was settled with a 7.5% pay increase. That strike and numerous others by midyear had accounted for more than 11 million lost working days, the highest ever recorded. GDP growth in 2007 was recorded at 14.5%. Inflation remained below the reserve bank’s target of 6% for much of the year, but by year’s end it had reached 7.1%. Growth boosted the current-account deficit in 2006 to 6.4% of GDP; the deficit for 2007 was estimated at 7.1%. Though unemployment had dropped somewhat during the year, by September 2007 it was still at 23.0%. In the 2006-07 financial year, there was an unprecedented budgetsur-plus of 5 billion rand (about US$700 million).
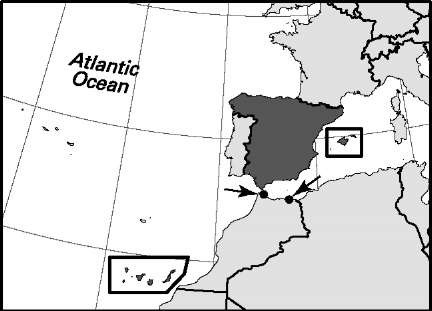
Spain
Official name: Reino de Espana (Kingdom of Spain). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [259]; Congress of Deputies [350]). Chief of state: King Juan Carlos I (from 1975). Head of government: Prime Minister Jose Luis Rodriguez Zapatero (from 2004). Capital: Madrid. Official language: CastilianSpanish; perconstitution, Euskera (Basque), Catalan, Galician, and all otherSpanish languages are also official in their autonomous communities). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
76.7%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.42%; female 50.58%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 14.3%; 15-29, 19.7%; 30-44, 25.3%; 45-59, 18.9%; 60-74, 13.6%; 75-84, 6.2%; 85 and over, 2.0%. Ethnic composition (2000): Spaniard 44.9%; Catalonian 28.0%; Galician 8.2%; Basque 5.5%; Aragonese 5.0%; Rom (Gypsy) 2.0%; other 6.4%. Religious affiliation (2006): Roman Catholic 77%; Muslim 2.5%; Protestant 1%; other (mostly nonreligious) 19.5%. Major cities (2006): Madrid 3,128,600 (urban agglomeration 6,008,183); Barcelona I,605,602 (urban agglomeration 5,309,404); Valencia 805,304; Seville 704,414; Zaragoza 649,181. Location: southwestern Europe, bordering France, Andorra, the Mediterranean Sea, Gibraltar, the Atlantic Ocean, and Portugal; the North African exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla border Morocco.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.7 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 73.4%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.35. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 80.0 years; female 83.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:€129,546,000,000 (direct taxes 55.6%; indirect taxes 34.8%; transfers 4.3%; other 5.3%). Expenditures: €174,976,000,000 (current expenditures 64.9%, of which wages and salaries 12.6%, debt service 10.0%; capital expenditures 10.0%, of which transfers 4.6%; other 25.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$1,208,184,000,000 (US$27,530 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 27.3%, in permanent crops 9.9%, in pasture 21.2%; overall forest area (2005) 35.9%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): alfalfa II,000,000, barley 8,318,400, grapes 6,401,500; livestock (number of live animals) 25,131,000 pigs, 22,513,970 sheep, 6,464,000 cattle; roundwood 15,531,798 cu m, of which fuelwood 14%; fisheries production (2005) 1,070,730 (fromaquaculture 21%). Mining and quarrying (2005): slate 1,200,000; sepio-lite 800,000; fluorspar 133,495. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): food products 13,909; chemicals and chemical products 10,881; motor vehicles and parts 10,009. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 275,575,-000,000 (256,120,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2006) 11,572,000 (37,552,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 6,820,000 (6,820,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 863,190,000 (457,438,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2006-07) 56,376,000 ([2004] 58,547,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 80,376,000 (35,739,000,000). Public debt (December 2005): US$355,341,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 21,584,800; activity rate of total population 49.2% (participation rates: ages 16-64, 71.9%; female 41.9%; unemployed 8.5%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006-07) 54,435; remittances (2006) 8,863; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 28,246. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2006-07) 18,043; remittances (2006) 11,004; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 38,531. Households (2005). Average household size 2.9; average annual net income per household (2004) €21,551 (US$26,758); expenditure: housing 26.5%, food 17.8%, household expenses 7.5%, clothing/footwear 6.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): €208,410,703,600 (road vehicles 17.0%; nonelectrical machinery 12.0%; mineral fuels 11.2%; chemicals and chemical products 9.8%; electrical machinery 8.9%). Major import sources: Germany 16.0%; France 15.3%; Italy 9.1%; UK 6.1%; China 4.1%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): €146,924,-722,500 (road vehicles 23.3%; food 11.8%, of which fruits and vegetables 6.0%; chemicals and chemical products 8.5%; nonelectrical machinery 8.1%). Major export destinations: France 19.4%; Germany 11.6%; Portugal 9.8%; Italy 9.0%; UK9.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 15,212 km; passenger-km 22,105,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 11,599,000,000. Roads (2003): length 677,646 km (paved 99%). Vehicles (2006): cars 20,909,000; trucks, vans, and buses 4,945,000. Air transport (2006-07): passenger-km 78,501,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,124,499. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 4,240,000 (97); televisions (2003): 24,228,000 (564); telephone landlines (2006): 18,385,000 (409); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 46,152,000 (1,028); personal computers (2005): 12,000,000 (269); total Internet users (2006): 18,578,000 (414); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 6,655,000 (148).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 16 and over having: no formal schooling 12.2%; primary education 26.1%; secondary 47.8%; undergraduate degree 6.5%; graduate degree 7.4%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 97.9%; males literate 98.7%; females literate 97.2%. Health (2005): physicians 199,123 (1 per 223 persons); hospital beds 159,215 (1 per 282 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 3.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,169 (vegetable products 67%, animal products 33%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 147,255 (army 64.9%, navy 13.2%, air force 15.5%, other 6.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$268.
Background
Remains of Stone Age populations dating back some 35,000 years have been found in Spain. Celtic peoples arrived in the 9th century bc, followed by the Romans, who dominated Spain from c. 200 bc until the Visigoth invasion in the early 5th century. In the early 8th century most of the peninsula fell to Muslims (Moors) from North Africa and remained under their control until it was gradually reconquered by the Christian kingdoms of Castile, Aragon, and Portugal. Spain was reunited in 1479 following the marriage of Ferdinand II (of Aragon) and Isabella I (of Castile). The last Muslim kingdom, Granada, was reconquered in 1492, and around this time Spain also established a colonial empire in the Americas. In 1516 the throne passed to the Habsburgs, whose rule ended in 1700 when Philip V became the first Bourbon king of Spain. His ascendancy caused the War of the Spanish Succession, which resulted in the loss of numerous European possessions and sparked revolution in most of Spain’s American colonies. Spain lost its remaining overseas possessions to the US in the Spanish-American War (1898). It became a republic in 1931. The Spanish Civil War (1936-39) ended in victory for the Nationalists under Gen. Francisco Franco, who ruled as dictator until his death in 1975. His successor as head ofstate, King Juan Carlos I, restored the monarchy; a new constitution in 1978 established a parliamentary monarchy. Spain joined NATO in 1982 and the European Community in 1986.
Recent Developments
In economic terms Spain continued to outperform most of its European Union partners, with growth of 7.0% in GDP in 2007. In the second half of the year, however, the slowdown in the all-important construction industry was accompanied by evidence of reduced consumer spending and export growth as well as a worrying rise in inflation. In December 2007 the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development cut its prediction for 2008 growth to 2.5%, and by March 2008 the unemployment rate stood at 9.6%. The most worrying development for the Socialist government of Prime Minister Jose Luis Rodriguez Zapatero came in June 2007, when the Basque separatist organization Euskadi Ta Askatasuna (ETA) broke off its 15-month cease-fire, dashing hopes of an end to the organization’s 40-year armed struggle. In March hundreds of thousands of flag-waving demonstrators protested the early release of an ETA hunger striker who was allowed to serve out his sentence under house arrest. On 1 December two Civil Guard officers were shot and killed after a chance encounter with three ETA members. In March 2008 ETA was blamed for the murder of a former Socialist party official. At the NATO summit in Bucharest, Romania, in April 2008, Spain agreed to add a few hundred extra troops to its contingent in Afghanistan, which at the beginning of the month was 770 strong.
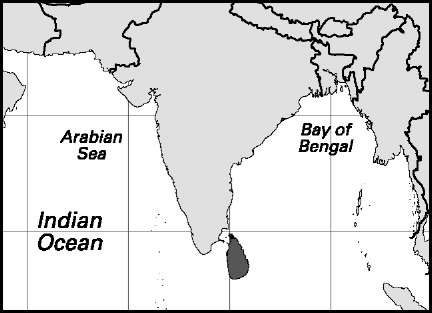
Sri Lanka
Official name: Sri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Ja-narajaya (Sinhala); Ilangai Jananayaka Socialisa Ku-diarasu (Tamil) (Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [225]). Head of state and government: President Mahinda Rajapakse (from 2005), assisted by Prime Minister Ratnasiri Wickremanayake (from 2005). Capitals: Colombo (executive and judicial); Sri Jayewar-denepura Kotte (Colombo suburb; legislative). Official languages: Sinhala; Tamil. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Sri Lanka rupee (LKR) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = LKR 107.69.
Demography
Area: 25,332 sq mi, 65,610 sq km. Population (2007): 20,102,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 793.5, persons per sq km 306.4. Urban (2005): 15.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.82%; female 49.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 24.1%; 15-29, 26.6%; 30-44, 22.6%; 45-59, 16.0%; 60-74, 8.0%; 75-84, 2.3%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): Sinhalese 72.4%; Tamil 17.8%; Sri Lankan Moor 7.4%; other 2.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Buddhist 70%; Hindu 15%; Christian (mostly Roman Catholic) 8%; Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 7%. Major cities (2004): Colombo 669,700 (greater Colombo 2,490,300); Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia 218,800; Moratuwa 184,800; Jaffna 172,300; Negombo 127,200. Location: island in the northern Indian Ocean, southeast of India.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.11. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 72.5 years; female 76.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:LKR 584,783,000,000 (tax revenue 57.6%, of which VAT 23.7%, excises 13.2%; domestic borrowings 21.2%; foreign loans/grants 13.8%; nontax revenue 7.4%). Expenditures: LKR 584,783,000,000 (interest payments 20.5%; welfare 15.9%; education 10.9%; defense 10.5%; health 7.7%; tsunami expenditure 4.1%). Households (2002). Average household size (2003-04) 4.3; average annual income per household: LKR 153,636 (US$1,606); sources of income: wages 42.0%, non-monetary income 18.9%, agriculture 7.8%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 44.5%, housing 12.6%, transportation and communication 7.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 429; remittances (2005) 1,908; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 221; official development assistance (2005) 1,378 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 315; remittances (2006) 257; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 16. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 3,342,000, sugarcane 1,136,600, coconuts 913,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,214,650 cattle, 314,080 buffalo; roundwood (2005) 6,277,917 cu m, of which fuel-wood 89%; fisheries production (2005) 163,684 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2006): kaolin 9,500; graphite 3,200; sapphires 790,000 carats; diamonds, n.a. Manufacturing (value added in LKR ’000,000; 2004): textiles and apparel 91,308; food, beverages, and tobacco 72,636; petrochemicals 26,179. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 8,766,000,000 (7,254,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (95,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (16,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 2,085,000 (3,550,000). Gross national income (2006): US$27,026,000,000 (US$1,407 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$9,812,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 7,602,000; activity rate 38.2% (participation rates: ages 15-59 [2000] 60.6%; female 36.3%; unemployed 6.5%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 14.2%, in permanent crops 15.5%, in pasture 6.8%; overall forest area (2005) 29.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): LKR 891,359,000,000 (petroleum 18.7%; textiles [mostly yarns and fabrics] 17.3%; machinery and equipment 9.7%; food and beverages 8.5%; building materials 5.7%). Major import sources (2004): India 18.0%; Singapore 8.7%; Hong Kong 7.7%; China 5.7%; Iran 5.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): LKR 638,276,000,000 (textiles, clothing, and accessories 45.6%; tea 12.8%; sapphires, other precious and semiprecious stones, and jewelry 6.3%). Major export destinations (2004): US 32.4%; UK 13.5%; India 6.8%; Belgium/Luxembourg 5.1%; Germany 4.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 1,449 km; passenger-km 4,684,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 134,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 97,286 km (paved 81%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 293,747; trucks and buses 453,610. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 8,796,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 325,416,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily news paper circulation (2005): 591,000 (30); televisions (2003): 2,400,000 (117); telephone landlines (2006): 1,884,000 (90); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,413,000 (259); personal computers (2005): 734,000 (35); total Internet users (2006): 428,000 (21); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 29,000 (1.5).
Education and health
Literacy (2003-04): total population ages 5 and over literate 93.0%; males literate 94.9%; females literate 91.3%. Health (2004): physicians 8,749 (1 per 2,351 persons); hospital beds 60,328 (1 per 341 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2003) 11.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,559 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 138% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 150,900 (army 78.1%, navy 9.9%, air force 12.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.6%; per capita expenditure US$30.
Background
The Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka (Ceylon) probably originated with the blending of aboriginal inhabitants and migrating Indo-Aryans from India c. the 5th century bc. The Tamils were later immigrants from Dravidian India, migrating over a period from the early centuries ad to c. 1200. Buddhism was introduced during the 3rd century bc. As Buddhism spread, the Sinhalese kingdom extended its political control over Ceylon but lost it to invaders from southern India in the 10th century ad. Between 1200 and 1505 Sinhalese power gravitated to southwestern Ceylon, while a southern Indian dynasty seized power in the north and established the Tamil kingdom in the 14th century. Foreign invasions from India, China, and Malaya occurred in the 13th-15th centuries. In 1505 the Portuguese arrived, and by 1619 they controlled most of the island. The Sinhalese enlisted the Dutch to help oust the Portuguese and eventually came under the control of the Dutch East India Co., which relinquished power in 1796 to the British. In 1802 Ceylon became a crown colony, gaining independence in 1948. It became the Republic of Sri Lanka in 1972 and was renamed the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka in 1978. Civil strife between Tamil and Sinhalese groups has beset the country in recent years, with the Tamils demanding a separate autonomous state in northern Sri Lanka.
Recent Developments
The civil war between the government of Sri Lanka and the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) that had continued at varying levels of intensity since 1983 flared up again in the form of fighting, suicide bombings, assassinations, and abductions. In November 2007 the government killed S.P. Thamilsel-van, the leader of the LTTE’s political wing. Reportedly, 350,000 people had been displaced and 5,000 had died in the latest fighting, bringing cumulative deaths since 1983 to more than 67,000. In addition, more than 1,000 individuals were abducted in 2007. Economic growth slowed to approximately 6% in 2007, though the garment sector continued to thrive and worker remittances provided valuable foreign exchange.
The Sudan
Official name: Jumhuriyat al-Sudan (Republic of the Sudan). Form of government: military-backed interim regime with two legislative houses (Council of States [50]; National Assembly [450]). Head of state and government: President Omar Hassan Ahmad al-Bashir (from 1989). Capitals: Khartoum (executive); Omdurman (legislative). Official language: Arabic; English has been designated the “principal” language in southern Sudan. Official religion: Islamic law and custom are sources of national law per 1998 constitution. Monetary unit: 1 Sudanese pound (SDG); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SDG 2.06 (the Sudanese pound replaced the Sudanese dinar [SDD] 10 Jan 2007, at the rate of 1 SDG = 100 SDD).
Demography
Area: 967,499 sq mi, 2,505,810 sq km. Population (2007): 39,379,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 40.7, persons per sq km 15.7. Urban (2006): 37.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.69%; female 49.31%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 42.1%; 15-29, 28.4%; 30-44, 16.9%; 45-59, 8.4%; 60-74, 3.6%; 75-84, 0.5%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2003): black 52%; Arab 39%; Beja 6%; other 3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Sunni Muslim 68.4%; traditional beliefs 10.8%; Roman Catholic 9.5%; Protestant 8.8%, of which Anglican 5.4%; other 2.5%. Major cities (1993): Omdurman 1,271,403; Khartoum 947,483 (urban agglomeration [2006] 6,700,000, including 2,000,000 internally displaced persons); Khartoum North 700,887; Port Sudan 308,195; Kassala 234,622. Location: northeastern Africa, bordering Egypt, the Red Sea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Chad, and Libya.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 35.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.79. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 47.1 years; female 48.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: SDD 1,507,500,000,000 (nontax revenue 61.0%, of which government receipts for crude petroleum 50.3%; tax revenue 39.0%, of which customs and excise duties 20.9%). Expenditures: SDD 1,825,300,000,000 (federal government 64.1%; transfers to: northern states 19.7%; southern Sudan 16.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$11,163,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$33,882,000,000 (US$900 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 7,186,000, sorghum 4,275,000, millet 745,000; livestock (number of live animals) 49,797,000 sheep, 42,526,000 goats, 40,468,000 cattle, 3,908,000 camels; round-wood 19,871,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 89%; fisheries production 63,600 (from aquaculture 3%). Mining and quarrying (2006): marble 11,470 cu m; gold 3,246 kg. Manufacturing (2006): diesel 1,817,000; flour 1,200,000; benzene 1,139,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 4,521,000,000 (3,458,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 132,700,000 (34,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2006)3,912,000(3,623,000). Population economically active (2000): total 12,207,000; activity rate of total population 37.8% (participation rate: female 29.9%). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.2. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 189; remittances (2006) 1,016; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,290; official development assistance (2005) 1,829. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 668; remittances (2006) 2. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.2%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 49.3%; overall forest area (2005) 28.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$8,074,000,000 (machinery and equipment 34.8%; manufactured goods 20.3%; transport equipment 18.5%; foodstuffs 9.4%, of which wheat and wheat flour 5.1%). Major import sources:China 20.8%; EU 17.2%; Saudi Arabia 8.0%; Japan 7.4%; India 6.6%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$5,657,000,000 (crude petroleum 83.2%; benzene 6.3%; sesame seeds 3.0%; livestock [mainly sheep and camels] 2.2%; cotton 1.5%). Major export destinations: China 75.0%; Japan 9.2%; UAE 4.0%; Saudi Arabia 2.2%; Egypt 1.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 4,578 km; passenger-km 49,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 893,000,000. Roads (2000): total length 11,900 km (paved 36%). Vehicles (2002): passengercars 47,300; trucks and buses 62,500. Airtransport: passenger-km (2003) 659,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 54,542,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 12,886,000 (352); telephone landlines (2006): 637,000 (17); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,683,000 (121); total Internet users (2006): 3,500,000 (91); broadband Internetsubscribers (2006): 2,100(0.05).
Education and health
50.4%. Health (2006): physicians 8,799 (1 per 4,384 persons); hospital beds 26,577 (1 per 1,451 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 96.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,351 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 128% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 104,800 (army 95.4%, navy 1.7%, air force 2.9%); foreign troops (September 2007): southern Sudan-UN peacekeeping 8,800; Darfur-African Union/UN peacekeeping 9,500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$13.
Background
From the end of the 4th millennium bc Nubia (now the northern Sudan) periodically came under Egyptian rule, and it was part of the kingdom of Cush from the 11th century bc to the 4th century ad. Christian missionaries converted The Sudan’s three principal kingdoms during the 6th century ad; these black Christian kingdoms coexisted with their Muslim Arab neighbors in Egypt for centuries, until the influx of Arab immigrants brought about their collapse in the 13th-15th centuries. Egypt had conquered all of The Sudan by 1874 and encouraged British interference in the region; this aroused Muslim opposition and led to the revolt of al-Mahdi, who captured Khartoum in 1885 and established a Muslim theocracy in The Sudan that lasted until 1898, when his forces were defeated by the British. The British ruled the country, generally in partnership with Egypt, until The Sudan achieved independence in 1956. Since then the country has fluctuated between ineffective parliamentary government and unstable military rule. The non-Muslim population of the south has engaged in ongoing rebellion against the Muslim-controlled government of the north, leading to famines and the displacement of some four million people. Arab militias known as Janjaweed responded by killing as many as 400,000 people beginning in 2003 and causing a massive humanitarian disaster.
Recent Developments
Benefiting from high oil prices, The Sudan in 2007 recorded one of Africa’s fastest-growing economies, estimated at nearly 10%. Foreign investment, spurred mainly by China, had quadrupled over the past decade. In October the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement, the ruling party in southern Sudan, suspended its participation in the Government of National Unity, claiming that its northern counterpart (the National Congress Party) was causing delays in the compilation of a census, general elections, and the distribution of oil revenues from the disputed border region. Meanwhile, the rebellion in the western province of Darfur remained the focus of international attention. The UN Security Council in June declared that it had secured an unconditional agreement with the Sudanese govern-menttodeployajointAfrican Union-UN peacekeeping force for Darfur, which would consist of nearly 20,000 troops and more than 6,000 police. Almost immediately the chief of the AU commission, reflecting the concerns of other African countries, stated that non-African troops would not be necessary because African countries had offered adequate reinforcements, but by April 2008 the force in country numbered 7,300 troops and 1,700 police from around the world.
Suriname
Official name: Republiek Suriname (Republic of Suri-name). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [51]). Head of state and government: President Ronald Veneti-aan (from 2000), assisted by Vice President Ram Sardjoe (from 2005). Capital: Paramaribo. Official language: Dutch. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Suriname dollar (SRD) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SRD 2.75 (the Suriname dollar replaced the Suriname guilder [SRG] 1 Jan 2004, at the rate of 1 SRD = SRG 1,000).
Demography
Area: 63,251 sq mi, 163,820 sq km. Population (2007): 510,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 8.1, persons per sq km 3.1. Urban (2005): 73.9%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.71%; female 50.29%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 28.5%; 15-29, 26.8%; 30-44, 24.3%; 45-59, 12.0%; 60-74, 6.2%; 75 and over, 2.2%. Ethnic composition (2004): Indo-Pakistani (“Hindustani”) 27.4%; Suri-name Creole (“Afro-Surinamese”) 17.7%; Maroon (descendants of runaway slaves living in the interior) 14.7%; Javanese (“Indonesian”) 14.6%; mixed race 12.5%; Amerindian 1.5%; other/unknown 11.6%. Religious affiliation (2004): Christian (mostly Roman Catholic and Moravian) 40.7%; Hindu 19.9%; Muslim 13.5%; nonreligious 4.4%; traditional beliefs 3.3%; other 2.5%; unknown 15.7%. Major cities (1996/97): Paramaribo 222,800; Lelydorp 15,600; Nieuw Nick-erie 11,100; Mungo (Moengo) 6,800; Meerzorg 6,600. Location: northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, French Guiana, Brazil, and Guyana.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.5 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.05. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.3 years; female 75.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: SRD 1,665,800,000 (tax revenue 77.1%, of which taxes on international trade 23.3%, corporate taxes 18.3%, income tax 16.2%; nontax revenue 18.0%; grants 4.9%). Expenditures: SRD 1,660,500,000 (current expenditures 87.4%, of which wages and salaries 36.6%; capital expenditures 11.9%; other 0.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$504,300,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 195,000, sugarcane 120,000, bananas 17,488; livestock (number of live animals) 137,000 cattle, 24,500 pigs, 3,800,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 226,846 cu m, of which fuelwood 20%; fisheries production (2005) 40,191 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2006): bauxite 4,945,000; alumina 2,133,000; gold (2005) 10,619 kg (recorded production). Manufacturing (value of production at factor cost in SRG; 1993): food products 992,000,000; beverages 558,000,000; tobacco 369,000,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 805,800,000 ([2004] 1,509,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 4,800,000 ([2004] 3,248,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 374,000 (583,000). Population economically active (2004): total 173,130; activity rate of total population 35.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 56.0%; female 36.7%; unemployed 9.5%). Gross national income (2006): US$2,039,000,000 (US$4,478 per capita). Households (2004). Average household size 4.0; average disposable income per household SRD 32,150 (US$11,760); expenditure (2000): food and beverages 40.0%, housing, energy, and household furnishings 23.6%, clothing and footwear 11.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 45; remittances (2006) 4.0; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -35; official development assistance (2005) 51 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 17; remittances (2006) 9.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.4%, in permanent crops 0.06%, in pasture 0.1%; overall forest area (2005)94.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$1,099,900,000 (machinery and transport equipment 26.8%, mineral fuels 15.6%, food products 9.1%, chemical products 6.9%). Major import sources: US 24.4%; The Netherlands 14.5%; Trinidad and Tobago 10.5%; China 5.4%; Japan 4.3%. Exports (2005): US$929,100,000 (alumina 48.1%; gold 36.4%; shrimp and fish 6.1%; crude petroleum 5.8%). Major export destinations: Norway 23.9%; US 16.8%; Canada 16.4%; France 8.1%; Iceland 2.9%.
Transport and communications
23,220. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 1,745,800,000; metric ton-km cargo 27,100,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 118,000 (243); telephone landlines (2006): 82,000 (162); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 320,000 (634); personal computers (2001): 20,000 (45); total Internet users (2005): 32,000 (64); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,700 (5.3).
Education and health
Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 89.6%; males literate 92.0%; females literate 87.2%. Health: physicians (2001) 236 (1 per 2,000 persons); hospital beds (2005) 1,797 (1 per 278 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 20.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,973 (vegetable products 88%, animal products 12%); 156% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,840 (all personnel are technically part of the army; army 76.1%, navy 13.0%, air force 10.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$43.
Background
Suriname was inhabited by various native peoples prior to European settlement. Spanish explorers claimed it in 1593, but the Dutch began to settle there in 1602, followed by the English in 1651. It was ceded to the Dutch in 1667, and in 1682 the Dutch West India Co. introduced coffee and sugarcane plantations and African slaves to cultivate them. Slavery was abolished in 1863, and indentured servants were brought from China, Java, and India to work the plantations, adding to the population mix. Except for brief interludes of British rule (1799-1802, 1804-15), it remained a Dutch colony. It gained internal autonomy in 1954 and independence in 1975. A military coup in 1980 ended civilian control until the electorate approved a new constitution in 1987. Military control resumed after a coup in 1990. Elections were held in 1991, followed by a resumption of democratic government.
Recent Developments
In September 2007 Suriname received the verdict of the UN International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea with dismay, as it awarded neighboring Guyana 65% of the contested maritime area, containing potentially valuable oil and natural gas deposits. Otherwise, Suriname enjoyed progress on several fronts, with improvements in its credit rating, tax revenue, and trade surplus and GDP growth of just above 5%.
Swaziland
Official name: Umbuso weSwatini (Swazi); Kingdom of Swaziland (English). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [30]; House of Assembly [65]). Head of state and government: KingMswati III(from 1986), assisted by Prime Minister Absalom Themba Dlamini (from 2003). Capitals: Mbabane (administrative and judicial); Lozitha and Ludzidzini (royal); Lobamba (legislative). Official languages: Swati (Swazi); English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 lilangeni (plural emalangeni [E])= 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 =E 7.92.
Demography
Area: 6,704sq mi, 17,364sq km. Population (2007): 1,141,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 170.2, persons per sq km 65.7. Urban (2006): 24.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.26%; female 51.74%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 41.0%; 15-29, 33.7%; 30-44, 11.6%; 45-59, 8.3%; 60-74, 4.4%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Swazi 82.3%; Zulu 9.6%; Tsonga 2.3%; Afrikaner 1.4%; mixed (black-white) 1.0%; other 3.4%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 87%, of which African indigenous 43%, unaffiliated Christian 19%, Protestant 18%, Roman Catholic 5%; traditional beliefs 11%; Muslim 1%; nonreligious 1%. Major cities (1997): Mbabane 57,992; Manzini 25,571 (urban agglomeration 78,734); Big Bend 9,374; Mhlume 7,661; Malkerns 7,400. Location: southern Africa, bordering South Africa and Mozambique.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 27.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 28.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): -0.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.62. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 32.5 years; female 34.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue: E 4,842,000,000 (receipts from Customs Union of Southern Africa 57.3%; individual income taxes 14.6%; sales taxes 11.3%; taxes on companies 8.4%). Expenditures: E 5,554,500,000 (general administration 26.2%; education 20.1%; police/defense 15.2%; transportation and communications 10.6%; health 8.0%). Gross national income (2006): US$2,775,000,000 (US$2,448 per capita). Population economically active (2001): total 392,000; activity rate of total population 39.3% (unemployed [2004] 31%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$451,000,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.3%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 69.8%; overall for-estarea (2005)31.5%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 5,000,000, oranges 35,900, grapefruit and pomelo 34,040; livestock (number of live animals) 580,000 cattle, 3,200,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 890,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 63%; fisheries production 70. Mining and quarrying (2005): fer-rovanadium 345; crushed stone 566,771 cu m. Manufacturing (value of exports in US$’000; 2002): apparel and clothing accessories 173,500; unbleached wood pulp 56,100; preserved fruit (significantly pineapples) 17,400. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 156,300,000 (1,123,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 221,700 ([2003] 372,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.4; average annual income per household (2002) US$1,540; expenditure (1996): food 24.5%, housing 15.9%, household furnishings and operation 13.2%, clothing and footwear 11.0%, transportation and communications 8.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 69; remittances (2006) 81; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 25; official development assistance (2005) 53 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 15; remittances (2006) 11; foreign di-rectdisinvestment(2001-05 avg.)-1.4.
Foreign trade
Imports (2002; c.i.f.): US$879,400,000 (food and live animals 15.0%; machinery and apparatus 14.5%; chemicals and chemical products 10.8%; refined petroleum 10.6%; textile yarn, fabrics, and made-up articles 8.6%; road vehicles 8.4%). Major import sources (2004): South Africa 95.6%; EU 0.9%; Japan 0.9%. Exports (2003): US$1,484,000,000 (soft drink [including sugar and fruit juice] concentrates 51.3%; cottonseed and lint 14.8%; wood pulp 12.0%; sugar 8.0%; reexports 6.7%). Major export destinations (2004): South Africa 59.7%; US 8.8%; EU 8.8%; Mozambique 6.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 301 km; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 746,000,000. Roads (2002): total length 3,594 km (paved 30%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 44,113; trucks and buses 47,761. Air transport: (2000) passenger-km 68,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 29,000 (28); televisions (2003): 38,000 (34); telephone landlines (2006): 44,000 (43); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 250,000 (243); personal computers (2005): 42,000 (41); total Internet users (2005): 42,000 (40).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 79.6%; males literate 80.9%; females literate 78.3%. Health: physicians (2004) 171 (1 per 6,047 persons); hospital beds (2000) 1,570 (1 per 665 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 71.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,664 (vegetable products 86%, animal products 14%); 90% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 3,000 troops. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$39.
Background
Stone tools and rock paintings indicate prehistoric habitation in the region, but it was not settled until the Bantu-speaking Swazi people migrated there in the 18th century and established the nucleus of the Swazi nation. The British gained control in the 19th century after the Swazi king sought their aid against the Zulus. Following the South African War, the British governor of Transvaal administered Swaziland; his powers were transferred to the British high commissioner in 1906. In 1949 the British rejected the Union of South Africa’s request to control Swaziland. The country gained limited self-government in 1963 and achieved independence in 1968. In the 1970s new constitutions were framed based on the supreme authority of the king and traditional tribal government. During the 1990s forces demanding democracy arose, but the kingdom remained in place. In 2005 a new constitution was signed that contained a bill of rights, but it retained the ban on opposition political parties.
Recent Developments
The economic and social uncertainty that had dominated Swaziland during the previous year remained in 2007, though the budget showed a 2.8% surplus and GDP stood at US$2.3 billion. Corruption continued to be a problem in both government and the private sector, and in February the Prevention of Corruption Act was promulgated. The number of those living below the poverty line rose to 70%, from 69% in 2006. The prevalence of HIV/AIDS dropped sharply from 39.2% to 26% among those sexually active and to 19% overall.
Sweden
Official name: Konungariket Sverige (Kingdom of Sweden). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Parliament [349]). Chief of state: King Carl XVI Gustaf (from 1973). Head of government: Prime Minister Fredrik Reinfeldt (from 2006). Capital: Stockholm. Official language: Swedish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Swedish krona (SEK) = 100 ore; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SEK 5.98.
Demography
84.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.64%; female 50.36%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 17.0%; 15-29, 18.8%; 30-44, 20.7%; 45-59, 19.5%; 60-74, 15.2%; 75-84, 6.2%; 85 and over, 2.6%. Ethnic composition (2005): Swedish 83.8%; other European 10.1%, of which Finnish 2.9%, pre-1991 Yugoslav 2.2%; Asian 4.1%; other 2.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Church of Sweden 77%; other Protestant 4.5%; Muslim 4%; Roman Catholic 1.6%; Orthodox 1.1%; other 11.8%. Major cities (2006): Stockholm 782,885; Goteborg 489,757; Malmo 276,244; Uppsala 185,187; Linkoping 138,580. Location: northern Europe, bordering Finland, the Gulf of Bothnia, the Baltic Sea, and Norway.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.6 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 44.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.77. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 78.7 years; female 82.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:SEK 718,249,000,000 (taxes on goods and services 45.6%; statutory social security fees 37.9%; income/profits/capital gains taxes 9.5%). Expenditures:SEK 750,965,000,000 (social insurance 40.0%; defense 5.9%; education 5.8%; health 5.1%; debt service 4.7%). Public debt (September 2007): US$175,055,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugar beets 2,189,000, wheat 2,001,400, barley 1,112,400; livestock (number of live animals) 1,681,000 pigs, 1,590,000 cattle, 480,000 sheep, (2004) 250,500 reindeer; round-wood (2005) 98,700,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 7%; fisheries production (2005) 262,239 (from aquaculture 2%). Miningand quarrying(2005): iron ore (metal content) 15,300,000; zinc (metal content) 214,600; copper (metal content) 97,800. Manufacturing (value added in SEK ’000,000 at constant prices of 2000; 2005): electrical machinery, telecommunications equipment, and electronics 108,909; road vehicles/parts 65,211; chemicals and chemical products 62,320. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 154,981,000,000 (147,587,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (3,329,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (150,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 18,360,000 (11,691,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (1,054,000,000). Households. Average household size (2005) 2.1; average annual disposable income per household (2004) SEK 258,900 (US$35,230); sources of gross income (2004): wages and salaries 60.2%, transfer payments 30.7%, self-employment 2.8%; expenditure (2005): housing and energy 20.7%, transportation 16.6%, recreation and culture 15.5%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 13.3%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 6.5%, in permanent crops 0.01%, in pasture 12.0%; overall forest area (2005) 66.9%. Gross national income (2006): US$381,786,000,000 (US$42,030 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 4,586,000; activity rate of total population 50.5% (participation rates: ages 16-64, 78.7%; female 47.6%; unemployed [July 2006-June 2007] 4.9%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,361; remittances (2006) 630; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 10,812. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 10,776; remittances (2006) 611; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 17,187.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.):SEK 724,200,000,000 (road vehicles 10.9%; crude and refined petroleum 10.8%; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 10.1%; office machines/telecommunications equipment 9.9%; base metals 6.8%). Major import sources: Germany 17.9%; Denmark 9.4%; Norway 8.7%; The Netherlands 6.3%; UK 6.2%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): SEK 851,200,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 14.4%; road vehicles 13.6%; telecommunications equipment 8.5%; paper and paper products 6.8%; medicines and pharmaceuticals 6.0%; iron and steel 5.7%). Major export destinations: Germany 9.9%; US 9.4%; Norway 9.3%; UK 7.2%; Denmark 7.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length 11,050 km; pas-senger-km (2005) 8,922,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 21,675,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 425,383 km (paved 31%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 4,154,000; trucks and buses 474,000. Air transport (2006; includes SAS international and domestic traffic applicable to Sweden only): passenger-km 4,404,000,000; (2005) metric ton-km cargo 2,784,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 4,312,000 (480); televisions (2003): 8,645,000 (965); telephone landlines (2006): 5,399,000 (594); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 9,607,000 (1,058); personal computers (2005): 7,548,000 (836); total Internet users (2006): 6,981,000 (769); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,346,000 (258).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15-74 having: incomplete or complete primary education 24.1%; incomplete or complete secondary 50.4%; incomplete or complete higher 23.9%; unknown 1.6%. Health (2005): physicians 27,600 (1 per 327 persons); hospital beds 26,540 (1 per 340 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 2.4.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 27,600 (army 50.0%, navy 28.6%, air force 21.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$612.
Background
The first inhabitants of Sweden were apparently hunters who crossed the land bridge from Europe c. 9000 bc. During the Viking era (9th-10th centuries) the Swedes controlled river trade in eastern Europe between the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea and also raided western European lands. Sweden was loosely united and Christianized in the 11th-12th centuries. It conquered the Finns in the 12th century and in the 14th united with Norway and Denmark under a single monarchy. It broke away in 1523 under Gustav I Vasa. In the 17th century it emerged as a great European power in the Baltic region, but its dominance declined after its defeat in the Second Northern War (1700-21). Sweden became a constitutional monarchy in 1809 and united with Norway 1814-1905; it acknowledged Norwegian independence in 1905. It maintained its neutrality during both world wars. It was a charter member of the UN but abstained from membership in the European Union until the 1990s and in NATO altogether. A new constitution drafted in 1975 reduced the monarch’s role to that of ceremonial head of state. In 1997 it decided to begin the controversial shutdown of its nuclear power industry.
Recent Developments
The Swedish economy in 2007 grew 6.6%. Economic development included a rapid drop in the percentage of unemployed (from 4.9% in September 2006 to 4.2% a year later, though by March 2008 it had risen to 6.3%) and a sizable increase in the active workforce (which added 131,000 more jobs in the same period), though there was also a drop in productivity. Combined with generous wage agreements in the private sector, however, this situation was expected to have inflationary effects in the years to come.
Switzerland
Official name: Confederation Suisse (French); Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft (German); Confederazione Svizzera (Italian); Confederaziun Svizra (Romansh) (Swiss Confederation). Form of government: federal state with two legislative houses (Council of States [46]; National Council [200]). Head of state and government: President Pascal Couchepin (from 2008). Capitals: Bern (administrative); Lausanne (judicial). Official languages: French; German; Italian; Romansh (locally). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Swiss franc (CHF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CHF 1.02.
Demography
Area: 15,940 sq mi, 41,284 sq km. Population (2007): 7,607,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 477.2, persons per sq km 184.3. Urban (2005): 75.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.97%; female 51.03%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 16.0%; 15-29, 18.1%; 30-44, 23.6%; 45-59, 20.6%; 60-74, 13.9%; 75-84, 5.7%; 85 and over, 2.1%. National composition (2004): Swiss 79.4%; pre-1991 Yugoslav 4.7%; Italian 4.1%; Portuguese 2.2%; German 2.0%; Turkish 1.0%; other 6.6%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 41.8%; Protestant 33.0%; Muslim 4.3%; Orthodox 1.8%; Jewish 0.2%; other Christian 2.7%; nonreli-gious 11.1%; other 0.8%; unknown 4.3%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Zurich 1,101,710; Geneva 493,445; Basel 486,146; Bern 343,789; Lausanne 310,028. Location: central Europe, bordering Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Italy, and France.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.7 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 86.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 1.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.42. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 78.7 years; female 83.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:CHF 165,097,000,000 (tax revenue 59.1%, of which taxes on income and wealth 39.6%; nontax revenue 22.2%; social security obligations 18.7%). Expenditures:CHF 170,738,000,000 (social security 19.0%; social welfare 16.2%; education 16.2%; health 11.3%; transportation 8.4%; defense 2.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugar beets 1,243,000, wheat 540,700, potatoes 392,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,652,000 pigs, 1,554,700 cattle; roundwood (2005)5,044,061 cum, of which fuelwood 21%; fisheries production (2005) 2,689 (from aquaculture 45%). Mining (2006): salt 560,000 (polished diamond exports [2006]: US$661,000,000). Manufacturing (value added in CHF ’000,000; 2002): chemicals and chemical products 14,771; professional and scientific equipment 10,892; food products, beverages, and tobacco 8,907. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 65,299,000,000(64,596,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (177,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (37,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 5,034,000 (10,527,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) none (3,058,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 4,220,000; activity rate of total population 55.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 81.2%; female 45.7%; unemployed 4.0%). Households (2004). Average household size 2.3; average gross income per household CHF 102,072 (US$82,084); sources of income: wages and salaries 64.7%, transfers 24.0%; expenditure: housing and energy 27.5%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 12.9%, transportation 12.0%, recreation 10.8%, restaurants and hotels 10.2%. Gross national income (2006): US$394,522,000,000 (US$52,922 per capita). Public debt (end of year; 2004): US$111,952,100,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11,063; remittances (2006) 1,946; foreign direct investment (FDI)(2001-05 avg.) 7,636. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 9,262; remittances (2006) 13,871; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 22,332. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.2%, in permanent crops 0.6%, in pasture 27.3%; overall forestarea (2005) 30.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): CHF 149,094,300,000 (chemicals 22.0%; machinery 20.1%; vehicles 9.6%; precision instruments, watches, and jewelry 7.2%). Major import sources (2006): Germany 33.3%; Italy 11.2%; France 10.3%; The Netherlands 5.0%; US 5.0%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): CHF 156,977,300,000 (chemicals 34.9%; machinery 22.4%; watches 7.9%; fabricated metals 7.4%; precision instruments 7.3%). Major export destinations (2006): Germany 20.2%; US 10.3%; Italy 8.9%; France 8.6%; UK 4.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length (2004) 5,024 km; passenger-km 15,400,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,534,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 71,296 km. Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 3,863,807; trucks and buses 307,264. Airtransport (2006): passenger-km 22,788,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,039,032,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,486,000 (333); televisions (2004): 4,300,000 (576); telephone landlines (2006): 5,040,000 (694); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 7,418,000 (1,021); personal computers (2005): 6,430,000 (857); total Internet users (2006): 4,360,000 (600); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,140,000 (283).
Education and health
Health (2005): physicians 28,251 (1 per 266 persons); hospital beds (2004) 42,417 (1 per 176 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 4.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,085 (vegetable products 63%, animal products 37%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 4,200. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$464.
Background
The original inhabitants of Switzerland were the Helvetians, who were conquered by the Romans in the 1st century bc. Germanic tribes penetrated the region from the 3rd to the 6th century ad, and Muslim and Magyar raiders ventured in during the 10th century. It came under the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. In 1291 three cantons formed an anti-Habsburg league that became the nucleus of the Swiss Confederation. It was a center of the Reformation, which divided the confederation and led to a period of political and religious conflict. The French organized Switzerland as the Helvetic Republic in 1798. In 1815 the Congress of Vienna recognized Swiss independence and guaranteed its neutrality. A new federal state was formed in 1848 with Bern as the capital. It remained neutral in both world wars and continued to guard this stance. With the formation of the European Union, it took steps toward provisional association with the European economic area.
Recent Developments
Switzerland showed no sign of wanting to join the EU, but its role as a transport hub at the heart of Europe was cemented with the opening in June 2007 of the transalpine Lotschberg Base Tunnel. The world’s longest overland tunnel—a 34.6-km (21.5-mi) rail link—took eight years to build, and when full rail service began in December, it slashed the train journey between Germany and Italy from less than four hours to less than two. An even more ambitious project—the 57-km (35-mi) Gotthard Base Tunnel—was scheduled for completion by 2017 in a bid to move heavy trucks off the road and onto the rails. Swiss economic growth was forecast at a better-than-expected 2.6%. Unemployment fell for the third straight year, to 2.8%, and the government budget showed a surplus for the second year in a row. A government expert panel, however, warned that prospects for 2008 were highly uncertain. The crisis in the subprime mortgage sector in the US and the rising cost of foodstuffs and commodities were factors contributing to the dampening of expectations.
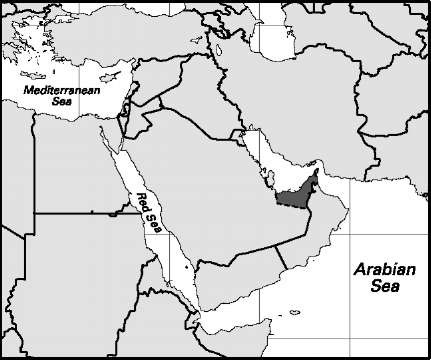
Syria
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-’Arabiyah al-Suriyah (Syrian Arab Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (People’s Assembly [250]). Head of state and government: President Bashar al-Assad (from 2000), assisted by Prime Minister Muhammad Naji al-Otari (from 2003). Capital: Damascus. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: none, although Islam is the required religion of the head of state and is the basis of the legal system. Monetary unit: 1 Syrian pound (S.P) = 100 piastres; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = S.P 50.95.
Demography
Area: 71,498 sq mi, 185,180 sq km. Population (2007): 19,048,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 266.4, persons per sq km 102.9. Urban (2005): 50.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.21%; female 48.79%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 37.0%; 15-29, 31.1%; 30-44, 18.7%; 45-59, 8.4%; 60-74, 3.7%; 75 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Syrian Arab 74.9%; Bedouin Arab 7.4%; Kurd 7.3%; Palestinian Arab 3.9%; Armenian 2.7%; other 3.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 86%, of which Sunni 74%, Alawite (Shi’i) 11%; Christian 8%, of which Orthodox 5%, Roman Catholic 2%; Druze 3%; nonreligious/atheist 3%. Major cities (2004): Aleppo 1,975,200; Damascus 1,614,500; Homs (Hims) 800,400; Latakia 468,700; Hamah 366,800. Location: the Middle East, bordering Turkey, Iraq, Jordan, Israel, Lebanon, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 27.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.40. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.0 years; female 71.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: S.P 377,100,000,000 (petroleum royalties and taxes 33.2%; nonpetroleum nontax revenues 27.0%; nonpetroleum tax on income and profits 13.5%; taxes on international trade 6.7%). Expenditures: S.P 436,500,000,000 (current expenditures 61.4%, capital expenditures 38.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,640,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$28,697,000,000 (US$1,479 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 4,668,750, sugar beets 1,096,291, seed cotton 1,021,996; livestock (number of live animals) 19,651,051 sheep, 1,295,725 goats, 1,082,623 cattle; roundwood (2005) 58,100 cu m, of which fuel-wood 31%; fisheries production (2005) 16,980 (from aquaculture 50%). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock 3,850,000; gypsum 440,000. Manufacturing (value added in S.P ’000,000; 2002): food, beverages, and tobacco 23,788; textiles and clothing 20,344; fabricated metals 15,462. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 34,900,000,000 (34,000,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 147,825,000 (83,950,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 10,756,000 (10,651,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 8,500,000,000 (5,100,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 7,880,000; activity rate of total population 40.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 66.8%; female 30.9%; unemployed 8.5%). Households. Average household size (2004): 5.2; sources of income (2003-04): wages 49.2%, self-employment 39.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,175; remittances (2006) 823; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 236; official development assistance (2005) 78. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 550; remittances (2006) 40. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 25.4%, in permanent crops 4.5%, in pasture 45.4%; overall forest area (2005) 2.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): S.P 481,406,000,000 (mineral fuels 25.7%; base and fabricated metals 13.2%; machinery and equipment 12.7%; foodstuffs 12.4%; transport equipment 8.0%). Major import sources (2004): Turkey 9.4%; Ukraine 8.7%; China 7.8%; Russia 5.4%; Saudi Arabia 5.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): S.P 307,750,000,000 (crude petroleum 58.1%; textiles 5.8%; live animals and meat 3.4%; cotton fiber 2.7%). Major export destinations (2004): Italy 22.7%; France 18.0%; Turkey 12.9%; Iraq 9.0%; Saudi Arabia 6.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 2,711 km; passenger-km (2004) 691,916,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,922,829,000. Roads (2004): total length 48,767 km (paved 20%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 227,639; trucks and buses 441,579. Airtransport (2006; SyrianAir only): passenger-km 2,340,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 16,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2006): 175,000 (9.4); televisions (2003): 3,093,000 (178); telephone landlines (2006): 3,243,000 (175); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,675,000 (252); personal computers (2005): 800,000 (44); total Internet users (2006): 1,500,000 (81); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 5,600 (0.03).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003-04). Percentage of population having: no formal education (illiterate) 14.3%; no formal education (literate) 9.9%; primary education 45.8%; secondary 22.5%; incomplete higher 3.9%; higher 3.6%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 78.4%; males literate 90.6%; females literate 66.1%. Health (2004): physicians 25,890 (1 per 685 persons); hospital beds 22,282 (1 per 760 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 28.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,058 (vegetable products 86%, animal products 14%); 166% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 307,600 (army 65.0%, navy 2.5%, air force 13.0%, air defense 19.5%); UN peacekeeping troops in Golan Heights (September 2007) 1,043. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 7.2%; per capita expenditure US$80.
Background
Syria has been inhabited for several thousand years. From the 3rd millennium bc it was under the control variously of Sumerians, Akkadians, Amorites, Egyptians, Hittites, Assyrians, and Babylonians. In the 6th century bc it became part of the Persian Achaemenian dynasty, which fell to Alexander the Great in 330 bc. Seleucid rulers governed it from 301 bc to c. 164 bc; then Parthians and Nabataean Arabs divided the region. It flourished as a Roman province (64 bc-ad 300) and as part of the Byzantine Empire (300-634) until Muslims invaded and established control. It came under the Ottoman Empire in 1516, which held it, except for brief rules by Egypt, until the British invaded in World War I. After the war it became a French mandate; it achieved independence in 1945. It united with Egypt in the United Arab Republic (1958-61). During the Six-Day War (1967), it lost the Golan Heights to Israel. Syrian troops frequently clashed with Israeli troops in Lebanon during the 1980s and ’90s. Hafez al-Assad’s long and harsh regime was marked also by antagonism toward Syria’s neighbors Turkey and Iraq.
Recent Developments
Syria’s relations with Israel were the most newsworthy in 2007. In February an elite Israeli unit carried out exercises in the Golan Heights for the first time in five years, and the commander of the UN Disengagement Observer Force warned in late September that Israel was engaged in a dangerous troop buildup along the Golan front. Syrian officials told Egyptian journalists that “Syria wants the Golan back, whether peacefully or through a war.” In September Israeli warplanes bombed a remote site outside Dair al-Zur. Some observers claimed that the strike destroyed a secret facility for the production or storage of chemical agents or nuclear material. Suspicions that the site was an illicit nuclear-weapons facility were strengthened by the lack of vigorous response from Syria or its allies, though the government did complain to the UN a week later. In April 2008 the US government released video evidence that it claimed showed that the facility was indeed to be a nuclear reactor for non-peaceful use, and that North Korea had assisted in its construction. However, that same month Turkey’s government confirmed that it had been an intermediary between Israel and Syria in secret peace talks since April 2007.
Taiwan
Official name: Chung-hua Min-kuo (Republic of China) Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative body (Legislative Yuan [113]). Chief of state: President Ma Ying-jeou (from 2008). Head of government: Premier Liu Chao-shiuan (from 2008). Administrative center: Taipei. Official language: Mandarin Chinese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 New Taiwan dollar (NT$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = NT$30.37.
Demography
Area: 13,972 sq mi, 36,188 sq km. Population (2007): 22,902,000. Density (2006): persons per sq mi 1,639, persons per sq km 632.9. Urban (2000): 80.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.67%; female 49.33%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 18.1%; 15-29, 23.5%; 30-44, 24.6%; 45-59, 20.5%; 60-74, 9.1%; 75-84, 3.4%; 85 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2003): Taiwanese 84.0%; mainland Chinese 14.0%; indigenous tribal peoples 2.0%, of which Ami 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2002): Buddhism 23.8%; Taoism 19.7%; Christian 4.5%, of which Protestant 2.6%, Roman Catholic 1.3%; I-kuan Tao 3.7% (syncretistic religion); Muslim 0.6%; other (mostly Chinese folk-religionist or nonreligious) 47.7%. Major cities (2006): Taipei 2,632,242; Kao-hsiung 1,514,706; T’ai-chung 1,044,392; T’ai-nan 760,037; Pan-ch-’iao 544,292. Location: island between the East China Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the South China Sea, north of the Philippines and southeast of mainland China.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.9 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 95.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.11. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 74.5 years; female 80.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:NT$2,115,227,000,000 (tax revenue 72.4%, of which income taxes 30.6%, corporate tax 11.2%, customs tax 3.8%). Expenditures: NT$2,309,564,000,000 (social security 27.4%; education, science, and culture 20.4%; economic development 20.2%). Population economically active (2006): total 10,522,000; activity rate of total population 46.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 57.9%; female 42.4%; unemployed 3.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 1,262,000, sugarcane 651,000, citrus fruits 548,991; livestock (number of live animals) 7,068,621 pigs, 134,793cattle; timber 30,372 cu m; fisheries production 1,282,279 (from aquaculture 25%). Mining and quarrying (2006): marble 25,493,000. Manufacturing (value added in NT$’000,000,000; 2003): electronic parts and components 452; computers, telecommunications, video electronics 232; refined petroleum products 223. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 181,245,000,000 (167,478,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2002) none (50,600,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 280,000 ([2003] 327,000,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 796,000,000 ([2002] 8,127,000,000). Gross national income (2005): US$354,900,000,000 (US$16,630 per capita). Households (2004). Average household size (2006) 3.1; average annual disposable income per household NT$891,249 (US$26,673); sources of income: wages and salaries 55.3%, transfers 15.2%, self-employment 15.1%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 23.7%, housing and energy 23.1%, education, recreation, and culture 13.3%, health care 12.9%, transportation and communication 12.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,040; remittances (2005) 323; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 1,906. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 8,682; remittances(2005) 1,342; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 5,844. Land use as % of total land area (2001): in temporary crops 16.1%, in permanent crops 6.6%, in pasture 0.3%; overall forestarea 58.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$202,698,135,000 (minerals 19.1%; electronic machinery 18.1%; metals and metal products 11.4%; chemicals 11.1%; nonelectrical machinery 8.8%). Major import sources: Japan 22.8%; China 12.2%; US 11.2%; South Korea 7.4%; Saudi Arabia 4.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$224,017,271,000(nonelectrical machinery, electrical machinery, and electronics 49.8%; metal products 10.7%; clocks, precision instruments, watches, and musical instruments 8.2%; plastic articles 7.1%). Major export destinations: China 23.1%; Hong Kong 16.7%; US 14.4%; Japan 7.3%; Singapore 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006; Taiwan Railway Administration only): route length 1,118 km; passenger-km 12,352,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 997,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 39,286 km. Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 5,698,000; trucks and buses 1,000,000. Air transport (2006; China Airlines, EVA, and Far Eastern Air transport only): passenger-km 59,108,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 11,470,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 6,530,000 (289); televisions (1999): 9,200,000 (418); telephone landlines (2006): 14,497,000 (636); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 23,249,000 (1,020); personal computers (2005): 13,098,000 (575); total Internet users (2006): 14,520,000 (637); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 4,506,000 (197).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 4.6%; primary 19.8%; vocational 23.7%; secondary 26.8%; some college 12.0%; higher 13.1%. Literacy (1999): total population ages 15 and over literate 94.6%; males literate 97.6%; females literate 91.4%. Health (2006): physicians 34,899 (1 per 654 persons); hospital beds 148,962 (1 per 153 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 5.9.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 290,000 (army 69.0%, navy 15.5%, air force 15.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.2%; per capita expenditure US$324.
Background
Known to the Chinese as early as the 7th century, Taiwan was widely settled by them early in the 17th century. In 1646 the Dutch seized control of the island, only to be ousted in 1661 by a large influx of Chinese refugees from the Ming dynasty. Taiwan fell to the Manchus in 1683 and was not open to Europeans again until 1858. In 1895 it was ceded to Japan following the Sino-Japanese War. A Japanese military center in World War II, it was frequently bombed by US planes. After Japan’s defeat it was returned to China, which was then governed by the Nationalists. When the Communists took over mainland China in 1949, the Nationalist government fled to Taiwan and made it their seat of government, with Gen. Chiang Kai-shek as president. In 1954 he and the US signed a mutual defense treaty, and Taiwan received US support for almost three decades, developing its economy in spectacular fashion. It was recognized by many noncommunist countries as the representative of all China until 1971, when it was replaced in the UN by the People’s Republic of China. Martial law was lifted in Taiwan in 1987 and travel restrictions with mainland China in 1988. In 1989 opposition parties were legalized. The relationship with the mainland became increasingly close in the 1990s.
Recent Developments
Taiwan’s politics were focused on the presidential elections scheduled for March 2008. The Kuom-intang (KMT), or Nationalist Party, and the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) were locked in an ideological struggle over the status of Taiwan—the DPP regarded Taiwan as an already independent country, while the KMT wanted to see Taiwan more closely integrated with China economically over the short term and ultimately united. The DPP’s Frank Hsieh won his party’s presidential nomination in May 2007 and called for a new constitution and name for the country. Hsieh’s KMT opponent, Ma Ying-jeou, attempted to focus his campaign on the state of Taiwan’s economy, promising that if elected he would restore economic growth by opening direct air and shipping links with China and by dropping a restriction on Taiwanese companies that capped their Chinese investments at 40% of their net assets. Both candidates proposed referenda to join the UN, increasingly straining relations with the US, which saw them as steps toward formal independence. The refusal to drop the proposals led senior US diplomat Thomas Christensen to abandon the US’s policy of strategic ambiguity on the status of Taiwan by saying that the US does “not recognize Taiwan as an independent state.” In March 2008 Ma won the election and both referenda were rejected, leading many to hope that Taiwan’s ties with China, and the US, would improve.
Tajikistan
Official name: Jumhurii Tojikiston (Republic of Tajikistan). Form of government: parliamentary republic with two legislative houses (National Assembly [34]; House of Representatives [63]). Chief of state: President Imomalii Rakhmon (from 1994). Head of government: Prime Minister Akil Akilov(from 1999). Capital: Dushanbe. Official language: Tajik (Tojik). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 somoni (TJS) = 100 dirams; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = TJS 3.43.
Demography
Area: 55,300 sq mi, 143,100 sq km Population (2007): 6,736,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 121.8, persons per sq km 47.1. Urban (2006): 26.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.74%; female 50.26%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 35.6%; 15-29, 31.2%; 30-44, 18.8%; 45-59, 9.2%; 60-74, 4.0%; 75 and over, 1.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Tajik 80.0%; Uzbek 15.3%; Russian 1.1%; Tatar 0.3%; other 3.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Sunni Muslim 78%; Shi’i Muslim 6%; nonreligious 12%; other (mostly Christian) 4%. Major cities (2001): Dushanbe 575,900; Khujand 147,400; Kulyab 79,500; Kurgan-Tyube 61,200; Ura-Tyube 51,700.
Location: central Asia, bordering Kyrgyzstan, China, Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 27.4 (world avg. 20.3); (1994) within marriage 90.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.14. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 61.2 years; female 67.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: TJS 1,566,000,000 (tax revenue 87.7%, of which taxes on goods and services 46.5%, customs duties 16.1%, payroll tax 11.0%; nontax revenue 9.8%; grants 2.3%). Expenditures: TJS 1,944,000,000 (education 17.3%; defense 12.3%; social security and welfare 12.2%; general administrative services 9.5%; health 5.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$785,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): potatoes 573,700, wheat 570,850, raw seed cotton 440,245; livestock (number of live animals) 1,893,000 sheep, 1,377,000 cattle, 1,160,000 goats, 42,000 camels; fisheries production (2005) 210 (from aquaculture 12%). Mining and quarrying (2004): antimony (metal content) 2,000; silver 5,000 kg; gold 3,000 kg. Manufacturing (value of production in TJS ’000,000, at 1998 constant prices; 2001): nonferrous metals (nearly all aluminum) 442,000; food 138,000; textiles 104,000. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006-07) 19,198,800,000 ([2005] 17,321,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2006) 102,000 ([2004] 138,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 15,000 (15,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 161,000 ([2004] 110,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (1,283,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 20,000,000 ([2004] 563,500,000). Population economically active (2003): total 1,932,000; activity rate of total population 29.1% (participation rates: ages 15-62 [male], 15-57 [female] 51.7%; female [1996] 46.5%; officially unemployed [September 2006-August 2007] 2.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$3,478,-000,000 (US$524 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 6.6%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 22.8%; overall forest area (2005) 2.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 1.0; remittances (2006) 1,019; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 77; official development assistance (2005) 189 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 3.0; remittances (2006) 393. Households (2005). Average household size (2004) 5.2; average disposable income per household TJS 3,462 (US$1,111); sources of income: wages and salaries 45.5%, self-employment 28.9%, transfers 7.0%; expenditure: food 72.1%, clothing 8.2%, transportation and communications 4.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$1,247,000,000 (alumina 26.8%; petroleum products 8.2%; electricity 5.3%; grain and flour 4.3%; natural gas 2.7%). Major import sources (2005): Russia 19.3%; Kazakhstan 12.7%; Uzbekistan 11.5%; Azerbaijan 8.6%; China 7.0%. Exports (2004): US$915,000,000 (aluminum 62.6%; cotton fiber 17.7%; electricity 6.6%). Major export destinations (2005): The Netherlands 46.6%; Turkey 15.8%; Russia 9.1%; Uzbekistan 7.3%; Latvia 4.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length (2006) 482 km; passenger-km 50,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,087,000,000. Roads (2000): total length 27,767 km (paved [1996] 83%). Air transport (2005; Tajikistan Airlines only): passenger-km 1,030,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 7,031,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 2,350,000 (357); telephone landlines (2005): 280,000 (43); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 265,000 (40); total Internet users (2005): 20,000 (3.1); broadband Internet subscribers (2003): 10,000 (1.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1989). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: primary education or no formal schooling 16.3%; some secondary 21.1%; completed secondary and some postsecondary 55.1%; higher 7.5%. Literacy (2006): virtually 100%. Health (2006): physicians 13,300 (1 per 506 persons); hospital beds 40,300 (1 per 167 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 45.0. Food (2004): daily per capita caloric intake 1,963 (vegetable products 89%, animal products 11%); 77% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 7,600 (army 100%); Russian troops (2007) 7,000. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 2.2%; per capita expenditure US$7.
Background
Settled by the Persians c. the 6th century bc, Tajikistan was part of the empires of the Persians and of Alexander the Great and his successors. In the 7th-8th centuries ad it was conquered by the Arabs, who introduced Islam. The Uzbeks controlled the region in the 15th-18th centuries. In the 1860s Russia took over much of Tajikistan. In 1924 it became an autonomous republic under the administration of the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, and it gained republic status in 1929. It achieved independence with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. Civil war raged through much of the 1990s between government forces and an opposition of mostly Islamic forces. Peace was reached in 1997.
Recent Developments
The drift toward authoritarianism in Tajikistan continued in 2007 as Pres. Imomalii Rakhmon’s extended family and personal clique made up most of the appointees to high government posts. He announced in March that he was dropping the Russian suffix (-ov) from his surname and urged his countrymen to join in “Tajikization” of their names. The year began with Tajikistan in the midst of a severe power shortage caused by extremely low water levels in the reservoirs behind the country’s power dams and Uzbekistan failing to fulfill its commitment to supply Tajikistan with power in winter. The disastrous winter intensified the Tajik government’s efforts to find foreign investors to develop the country’s hydroelectric potential.
Tanzania
Official name: Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania (Swahili); United Republic of Tanzania (English). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [274]). Head of state and government: President Jakaya Kikwete (from 2005), assisted by Prime Minister Mizengo Pinda (from 2008). Capital: Dar es Salaam (Dodoma is the capital designate). Official languages: Swahili; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Tanzania shilling (TZS) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = TZS 1,169.50.
Demography
Area: 364,901 sq mi, 945,090 sq km. Population (2007): 39,384,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 107.9, persons per sq km 41.7. Urban (2006): 38.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.46%; female 50.54%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 44.3%; 15-29, 29.1%; 30-44, 14.6%; 45-59, 7.6%; 60-74, 3.6%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Eth-nolinguistic composition (2000): 130 different Bantu tribes 95%, of which Sukuma 9.5%, Hehe and Bena 4.5%, Gogo 4.4%, Haya 4.2%, Nyamwezi 3.6%, Makonde 3.3%, Chagga 3.0%, Ha 2.9%; other 5%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 35%, of which Sunni 30%, Shi’i 5%; Christian 35%; other (significantly traditional beliefs) 30%; Zanzibar only is 99% Muslim. Major urban areas (2002): Dar es Salaam 2,339,910; Arusha 270,485; Mbeya 232,596; Mwanza 209,806; Morogoro 209,058. Location: eastern Africa, bordering Kenya, the Indian Ocean, Mozambique, Malawi, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, Rwanda, and Uganda.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 36.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.93. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 48.5 years; female 50.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2003-04). Revenue:TZS 1,447,500,000,000 (VAT 34.2%; income tax 24.9%; excise tax 15.0%; import duties 9.0%). Expenditures: TZS 2,531,500,000,000 (current expenditure 74.5%, of which wages 18.3%, education 17.7%, health 8.4%; capital expenditure 25.5%). Gross national income (2006): US$12,743,000,000 (US$332 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$6,183,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): cassava 6,500,000, corn (maize) 3,373,000, sweet potatoes 1,056,000; livestock (number of live animals) 17,719,091 cattle, 12,550,000 goats, 3,521,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 24,025,852 cu m, of which fuelwood 90%; fisheries production (2005) 347,811. Mining and quarrying (2005): gold 52,236 kg; garnets 7,400 kg; rubies 3,400 kg. Manufacturing (2005): cement 1,281,000; wheat flour 347,296; sugar 202,200; konyagi (a Tanzan-ian liquor) 41,050 hectoliters. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,478,000,000 (2,591, 000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 65,000 (65,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (1,074,000). Population economically active (2002): total 14,841,000; activity rate of total population 43.1% (participation rates: ages 10 and over 64.9%; female 48.0%; officially unemployed 3.7%). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.0; annual income per household (2000-01) TZS 1,055,000 (US$1,310); sources of income (2000-01): agricultural income 51.4%, self-employment 20.6%, wages and salaries 12.0%; expenditure (2001): food 55.9%, transportation 9.7%, energy 8.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 824; remittances (2006) 16; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 473; official development assistance (2005) 1,505. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 554; remittances (2006) 41. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.5%, in permanent crops 1.2%, in pasture 48.7%; overall forest area (2005) 39.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): TZS 3,125,000,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 22.5%; transport equipment 12.1%; crude and refined petroleum 11.5%; construction materials 10.5%; food and beverages 7.5%). Major import sources (2006): South Africa 12.7%; UAE 11.6%; China 7.2%; Saudi Arabia 5.9%; Japan 5.8%. Exports (2005): TZS 1,608,000,000 (gold 40.7%; cotton 7.9%; coffee 5.2%; cashews 3.4%; diamonds 1.8%; cloves 0.6%). Major export destinations (2006): UK 18.1%; Switzerland 13.9%; South Africa 9.2%; China 6.9%; Germany 5.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length (2001) 3,690 km; passenger-km 1,305,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,461,000,000. Roads (2006): length 85,000 km (paved 5%). Vehicles:passenger cars (2000) 36,000; trucks and buses (1999) 98,800. Air transport (2005; Air Tanzania only): passenger-km 246,000,000; metric ton-km 2,364,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 105,000 (2.9); televisions (2003): 1,500,000 (41); telephone landlines (2006): 157,000 (4); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,767,000 (148); personal computers (2005): 356,000 (9.3); total Internet users (2005): 384,000 (10).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 49.6%; incomplete/complete primary education 44.0%; incomplete/complete secondary 5.5%; postsecondary 0.9%, of which university 0.4%. Literacy (2006): total percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 69.4%; males literate 77.5%; females literate 62.2%. Health (2002): physicians 822 (1 per 42,085 persons); hospital beds 36,853 (1 per 939 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 73.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,230 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 123% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 27,000 (army 85.2%, navy 3.7%, air force 11.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$4.
Background
Inhabited from the 1st millennium bc, Tanzania was occupied by Arab and Indian traders and Bantu-speaking peoples by the 10th century ad. The Portuguese gained control of the coastline in the late 15th century, but they were driven out by the Arabs of Oman and Zanzibar in the late 18th century. German colonists entered the area in the 1880s, and in 1891 the Germans declared the region a protectorate as German East Africa. In World War I Britain captured the German holdings, which became a British mandate (1920) under the name Tanganyika. Britain retained control of the region after World War II when it became a UN trust territory (1947). Tanganyika gained independence in 1961 and became a republic in 1962. In 1964 it united with Zanzibar under the name Tanzania.
Recent Developments
In 2007 the government of Tanzania announced a number of measures that were aimed at encouraging both foreign and local investors. These included a plan with Kuwait to create a deep-water harbor at Tanga to provide an alternative port to handle heavy goods. In May the Nile Basin Initiative launched a project to construct a US$200 million hydroelectric plant on the Kagera River on Tanzania’s northwestern border with Uganda. A US$2.6 billion contract to build an oil refinery was controversially awarded to an international consortium in which a company owned by the ruling Chama Cha Mapinduzi party had a share. On a visit to Burundi in June, Pres. Jakaya Mrisho Kikwete announced that with peace restored in Burundi, the refugee camps in the northwest—long-standing drains on the country’s resources—would close by year’s end.
Thailand
Official name: Ratcha Anachak Thai (Kingdom of Thailand). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [150]; House of Representatives [480]). Chief of state: King Bhu-mibol Adulyadej (from 1946). Head of government: Prime Minister Samak Sundaravej (from 2008). Capital: Bangkok. Official language: Thai. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1Thai baht(THB) = 100stangs; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = THB 33.49.
Demography
Area: 198,117 sq mi, 513,120 sq km. Population (2007): 63,884,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 322.5, persons per sq km 124.5. Urban (2006): 29.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.79%; female 51.21%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 21.7%; 15-29, 24.1%; 30-44, 24.1%; 45-59, 18.8%; 60-74, 8.6%; 75-84, 2.2%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): Tai peoples 81.4%, of which Thai (Siamese) 34.9%, Lao 26.5%; Han Chinese 10.6%; Malay 3.7%; Khmer 1.9%; other 2.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Buddhist 83%; Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 9%; traditional beliefs 2.5%; nonre-ligious 2%; other (significantly Christian) 3.5%. Major cities (2000): Bangkok 6,355,144; Samut Prakan 378,741; Nonthaburi 291,555; Udon Thani 222,425; Nakhon Ratchasima 204,641. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering Laos, Cambodia, the Gulf of Thailand, Malaysia, and Myanmar (Burma).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.84. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.9 years; female 74.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: THB 1,490,900,000,000 (tax revenue 81.8%, of which taxes on goods and services 40.0%, corporate taxes 23.7%, income tax9.3%; nontax revenue 13.4%; social contributions 4.8%). Expenditures: THB 1,316,800,000,000 (economic affairs 30.3%; education 20.0%; general public services 17.6%; health 8.4%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$13,483,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005):sugarcane 49,586,000, rice 30,292,000, cassava 16,938,000; livestock (number of live animals) 8,023,000 pigs, 5,610,000 cattle, 187,400,000 chickens; roundwood 28,566,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 70%; fisheries production 3,743,000 (from aquaculture 31%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gypsum 6,920,000; feldspar 1,000,000; dolomite 950,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2000): textiles and wearing apparel 1,905; electronics 1,817; food products 1,311. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 136,767,000,000 (133,572,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) negligible (7,536,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 18,991,000 ([2004] 20,547,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 69,900,000 ([2004] 315,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 44,725,000 (39,643,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 24,807,000,000 ([2004] 27,295,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 27.7%, in permanent crops 7.0%, in pasture 1.6%; overall forest area (2005) 28.4%. Population economically active (2006): total 36,867,200; activity rate of total population 56.4% (participation rates: ages 15-59, 78.5%; female 46.0%; unemployed 1.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$202,098,000,000 (US$3,190 per capita). Households (2006). Average household size (2004) 3.5; average annual income per household THB 213,444 (US$5,634); sources of income: wages and salaries 39.9%, self-employment 32.6%, nonmonetary income 16.2%, transfers 9.4%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 33.2%, housing, energy, and household furnishings 24.6%, transportation and communications 24.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 10,104; remittances (2006) 1,333; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,377; official development assistance (2005) 607 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,995; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 262.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): THB 4,871,000,000,000 (electrical machinery 19.6%, of which electronic integrated circuits 4.2%; crude petroleum 15.6%; nonelectrical machinery and parts 14.1%; base and fabricated metals 13.4%, of which iron and steel 8.2%). Major import sources:Japan 20.1%; China 10.6%; US 6.7%; Malaysia 6.6%; Singapore 4.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): THB 4,931,500,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery 18.3%; electrical machinery 17.8%, of which electronic integrated circuits 4.9%; food products 11.0%; road vehicles 7.7%; rubber [all forms] 6.7%; plastics [all forms] 5.0%). Major export destinations: US 15.0%; Japan 12.7%; China 9.0%; Singapore 6.4%; Hong Kong 5.5%; Malaysia 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): route length (2006) 4,071 km; passenger-km 10,251,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,987,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 57,403 km (paved 99%). Vehicles (2006): pas-sengercars 3,312,941; trucks and buses 4,568,895. Air transport (2006; Thai Airways and Bangkok Airways only): passenger-km 56,891,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,107,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 3,957,000 (63); televisions (2003): 17,971,000 (289); telephone landlines (2006): 7,073,000 (111); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 40,816,000 (643); personal computers (2005): 4,408,000 (70); total Internet users (2006): 8,466,000 (133).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Percentage of employed population having: no formal schooling/unknown 4.1%; incomplete primary education 33.9%; complete primary 21.5%; lower secondary 14.4%; upper secondary 12.0%; some to complete higher 14.1%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 92.5%; males literate 94.9%; females literate 90.5%. Health (2005): physicians (2004) 18,918 (1 per 3,307 persons); hospital beds 134,016 (1 per 470 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 11.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,042 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 163% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 306,600 (army 62.0%, navy 23.0%, air force 15.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$31.
Background
The region of Thailand has been occupied continuously for 20,000 years. It was part of the Mon and Khmer kingdoms from the 9th century ad. Thai-speaking peoples emigrated from China c. the 10th century. During the 13th century two Thai states emerged: the Sukhothai kingdom, founded c. 1220 after a successful revolt against the Khmer, and Chiang Mai, founded in 1296 after the defeat of the Mon. In 1350 the Thai kingdom of Ayutthaya succeeded Sukhothai. The Burmese were its most powerful rivals, occupying it briefly in the 16th century and destroying the kingdom in 1767. The Chakri dynasty came to power in 1782, moving the capital to Bangkok and extending the empire along the Malay Peninsula and into Laos and Cambodia. The country was named Siam in 1856. Though Western influence increased during the 19th century, Siam’s rulers avoided colonization by granting concessions to European countries; it was the only Southeast Asian nation able to do so. In 1917 it entered World War I on the side of the Allies. It became a constitutional monarchy following a military coup in 1932 and was officially renamed Thailand in 1939. It was occupied by Japan in World War II. It participated in the Korean War as a UN forces member and was allied with South Vietnam in the Vietnam War. Along with other Southeast Asian nations, it suffered from the 1990s regional financial crisis.
Recent Developments
In May 2007 the military junta in Thailand—in power since ousting then prime ministerThaksin Shinawatra in a September 2006 coup—dissolved Thaksin’s Thai Rak Thai (TRT) party and barred Thaksin and more than 100 top-ranking TRT members from politics for five years. Other TRT members formed or joined new parties, including the People Power Party (PPP). In August a referendum was held on a new constitution drafted by the junta’s appointees. Approved by nearly 58% of referendum voters, the charter contained several undemocratic clauses that allowed the government to appoint half of the members of the Senate and to pardon the junta for its unconstitutional usurpation of power in 2006. Many Thais voted for the referendum because the junta threatened to postpone the general election if the referendum was rejected. Held on 23 December, the electionsawthe pro-Thaksin PPP gain the most parliamentary seats and Samak Sun-daravej, a Thaksin ally, named the first democratically elected prime minister since the 2006 coup.
Togo
Official name: Republique Togolaise (Togolese Republic). Form of government: republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [81]). Chief of state: President Faure Gnassingbe (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Komlan Mally(from 2007). Capital: Lome. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60.
Demography
Area: 21,925 sq mi, 56,785 sq km. Population (2007): 6,585,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 300.3, persons per sq km 116.0. Urban (2005): 40.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.07%; female 50.93%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 42.3%; 15-29, 29.9%; 30-44, 15.6%; 45-59, 8.0%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Ewe 22.2%; Kabre 13.4%; Wachi 10.0%; Mina 5.6%; Kotokoli 5.6%; Bimoba 5.2%; Losso4.0%; Gurma 3.4%; Lamba 3.2%; Adja 3.0%; other 24.4%. Religious affiliation (2004): Christian 47.2%, of which Roman Catholic 27.8%, Protestant 9.5%, independent and other Christian 9.9%; traditional beliefs 33.0%; Muslim 13.7%; nonreligious 4.9%; other 1.2%. Major cities (2003): Lome 676,400 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,337,000); Sokode 84,200; Kpalime 75,200; Atakpame 64,300; Kara 49,800. Location: western Africa, bordering Burkina Faso, Benin, the Atlantic Ocean, and Ghana.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 37.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 5.01. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 55.0 years; female 59.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 175,600,000,000 (tax revenue 87.0%, of which taxes on international trade 41.5%; nontax revenue 7.0%; grants 6.0%). Ex-penditures:CFAF 168,400,000,000 (current expenditure 80.0%; capital expenditure 20.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): cassava 767,400, yams 621,100, corn (maize) 543,300; livestock (number of live animals) 1,850,000 sheep, 1,480,000 goats; round-wood (2005) 5,927,873 cu m, of which fuelwood 97%; fisheries production (2005) 29,267 (from aqua-culture 5%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 2,400,000; phosphate rock 1,020,870; diamonds 41,000 carats. Manufacturing (value added in CFAF ’000,000; 2006): food products, beverages, and tobacco products 33,800; bricks, cement, and ceramics 19,300; base and fabricated metals 10,800. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 262,000,000 (610,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (622,000). Households (2004). Average household size 6.0; expenditure: food products 36.1%, hotels and restaurants 12.9%, housing and energy 12.4%, transportation 8.5%, clothing and footwear 6.0%. Population economically active (2003): total 2,295,000; activity rate of total population 38.9% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 70.2%; female 37.0%; unemployed [2004] 32%). Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$2,254,000,000 (US$352 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,469,000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 19; remittances (2006) 179; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 52; official development assistance (2005) 87. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 8; remittances (2006) 34. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 46.1%, in permanent crops 2.2%, in pasture 18.4%; overall forest area (2005) 7.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.; trade data breakdown is estimated): US$548,100,000 (mineral fuels 23.0%; food products 9.7%; iron and steel 8.1%; construction materials 7.4%; machinery and apparatus 6.9%; road vehicles 6.4%). Major import sources: France 19.5%; China 8.3%; Cote d’Ivoire 6.1%; Belgium 4.8%; Italy 3.7%. Exports (2004; trade data breakdown is estimated): US$384,400,000 (food products 19.1%, of which cocoa beans 6.4%; portland cement17.3%; cotton 15.3%; phosphates 13.6%; iron and steel 11.7%). Major export destinations: Burkina Faso 13.1%; Benin 12.2%; Ghana 11.9%; Mali 11.2%; China 4.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): route length (2004) 568 km; passenger-km 44,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 440,000,000. Roads (2001): total length 7,500 km (paved 24%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 51,400; trucks and buses 24,500. Air transport: pas-senger-km (2001) 130,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2003) 7,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 8,000 (1.5); televisions (2004): 650,000 (107); telephone landlines (2006): 82,000 (13); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 708,000 (112); personal computers (2005): 185,000 (34); total Internet users (2006): 320,000 (51).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1998). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education 56.3%; primary education 24.5%; secondary and higher 18.3%; unknown 0.9%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 53.2%; males literate 68.7%; females literate 38.5%. Health: physicians (2004) 225 (1 per 23,357 persons); hospital beds (2002) 4,991 (1 per 997 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 62.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,123 (vegetable products 97%, animal products 3%); 116% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 8,550 (army 94.7%, navy 2.3%, air force 3.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$5.
Background
Until 1884 what is now Togo was an intermediate zone between the black African military states of Ashanti and Dahomey, and its various ethnic groups lived in general isolation from each other. In 1884 it became part of the Togoland German protectorate, which was occupied by British and French forces in 1914. In 1922 the League of Nations assigned eastern Togoland to France and the western portion to Britain. In 1946 the British and French governments placed the territories under UN trusteeship. Ten years later British Togoland was incorporated into the Gold Coast, and French Togoland became an autonomous republic within the French Union. Togo gained independence in 1960. It suspended its constitution in 1967-80. A multiparty constitution was approved in 1992, but the political situation remained unstable.
Recent Developments
The UNHCR advised the refugees to return home, but the extent to which they were doing so was unclear. In August the severe floods that hit much of West Africa left more than 20,000 homeless in Togo. As a result, the opening of the school year was postponed for several weeks because many of the classrooms were requisitioned as shelters. The European Union pledged >2 million (about US$2.7 million) to assist flood victims in Togo, Ghana, and Burkina Faso.
Tonga
Official name: Pule’anga Fakatu’i ‘o Tonga (Tongan); Kingdom of Tonga (English). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Legislative Assembly [34]). Head of state and government: King Siaosi (George) Tupou V (from 2006), assisted by Prime Minister of the Privy Council Feleti Sevele (from 2006). Capital: Nuku’alofa. Official languages: Tongan; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 pa’anga (T$) = 100 seniti; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = T$1.80.
Demography
Area: 289.5 sq mi, 749.9 sq km. Population (2007): 101,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 363.2, persons per sq km 140.2. Urban (2005): 23.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.62%; female 49.38%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 37.4%; 15-29, 29.8%; 30-44, 14.6%; 45-59, 9.4%; 60-74, 6.7%; 75 and over, 2.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Ton-gan 95.2%; mixed-race (Euronesian) 0.7%; British or Australian expatriates 0.5%; other 3.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Mormon 35%; Protestant 30%, of which Methodist 25%; independent Christian (mostly local Methodist) 16%; Roman Catholic 12%; Baha’i 5%; other 2%. Major towns (2006): Nuku’alofa 23,438 (urban agglomeration 34,058); Neiafu 4,108; Haveloloto 3,384; Tofoa-Koloua 3,193; Pan-gai 2,523. Location: archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean between Hawaii (US) and New Zealand.
Vital statistics
5.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.30. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 71.0 years; female 74.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:T$172,446,000 (tax revenue 72.9%; grants 15.1%; nontax revenue 12.0%). Expenditures: T$166,031,000 (current expenditure 93.0%; development expenditure 7.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 58,000, pumpkins, squash, and gourds 20,000, cassava 9,000; livestock (number of live animals) 81,000 pigs, 12,500 goats, 11,400 horses; roundwood 2,100 cu m, of which fuelwood, none; fisheries production (2005) 1,901; aquatic plants production (2005) 887 (from aquaculture 9%). Mining and quarrying: coral and sand for local use. Manufacturing (value of production in T$’000; 2005): food products and beverages 19,722; bricks, cement, and ceramics 4,109; chemicals and chemical products 2,044. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 54,000,000 (47,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (38,000). Gross national income (2006): US$230,000,000 (US$2,304 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 36,450; activity rate of total population 34.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [1996] 60.4%; female 41.9%; unemployed 5.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$83,200,000. Households (2000-01). Average household size (2006) 5.7; cash income per household T$12,871 (US$6,511); sources of cash income: wages and salaries 35.6%, remittances 19.7%, sales of own produce 16.1%; cash expenditure (2002): food and nonalcoholic beverages 44.4%, transportation 14.2%, alcoholic beverages, kava, and tobacco 12.3%, household furnishings and operation 12.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006-07) 13; remittances (2006) 66; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 4.0; official development assistance (2005) 16 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2002) 3.0; remittances (2006) 16. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 21%, in permanent crops 15%, in pasture 6%; overall forest area (2005) 5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; c.i.f.): US$113,075,000 (mineral fuels and chemical products 31.7%; food and beverages 28.0%; machinery and transport equipment 12.9%). Major import sources: New Zealand 35.0%; Fiji 27.0%; Australia 10.7%; US 9.1%; Japan 3.6%. Exports (2005-06): US$9,225,000 (squash 43.7%; fish 34.7%; root crops 7.9%; manufactured goods 6.8%; kava 3.2%). Major export destinations: Japan 53.7%; New Zealand 11.6%; US 10.5%; Australia 2.1%; Fiji 1.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 680 km (paved 27%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 7,705; trucks and buses 5,297. Airtransport (2002): passenger-km 14,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 7,100 (70); telephone landlines (2005): 14,000 (139); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 30,000 (298); personal computers (2005): 5,000 (50); total Internet users (2006): 3,100 (31); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 600 (0.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1996). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: primary education 26%; lower secondary 58%; upper secondary 8%; higher 6%; unknown 2%. Literacy (2006): 99%. Health (2004): physicians 41 (1 per 2,447 persons); hospital beds 296 (1 per 332 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 20.0. Food (1992): daily per capita caloric intake 2,946 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 129% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2007): 450-member force includes air and coast guard elements. Tonga has defense cooperation agreements with both Australia and New Zealand. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$23.
Background
Tonga was inhabited at least 3,000 years ago by people of the Lapita culture. The Tongans developed a stratified social system headed by a paramount ruler whose dominion by the 13th century extended as far as the Hawaiian Islands. The Dutch visited the islands in the 17th century; in 1773 Capt. James Cook arrived and named the archipelago the Friendly Islands. The modern kingdom was established during the reign (1845-93) of King George Tupou I. It became a British protectorate in 1900. This was dissolved in 1970, when Tonga, the only ancient kingdom surviving from the pre-European period in Polynesia, achieved complete independence within the Commonwealth.
Recent Developments
In 2007 Tonga still suffered from the aftermath of the November 2006 rioting that had caused some US$200 million in damages and destroyed about 80% of the capital’s central business district. The parliament convened in May 2007, but little progress was made on political reform, and popular discontent was rising. Although international aid donors, including Australia and New Zealand, contributed to the reconstruction in Nuku’alofa, civil servants were told by the government that anticipated salary increases could not be afforded.
Trinidad and Tobago
Official name: Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [31]; House of Representatives [41]). Chief of state: President George Maxwell Richards (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Patrick Manning (from 2001). Capital: Port of Spain. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Trinidad and Tobago dollar (TT$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = TT$6.19.
Demography
Area: 1,990 sq mi, 5,155 sq km. Population (2007): 1,303,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 654.8, persons per sq km 252.8. Urban (2005): 12.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.17%; female 50.83%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 22.3%; 15-29, 30.2%; 30-44, 22.6%; 45-59, 15.4%; 60-74, 7.0%; 75-84, 2.0%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 39.2%; East Indian 38.6%; mixed 16.3%; Chinese 1.6%; white 1.0%; other/not stated 3.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 29%; Hindu 24%; Protestant 19%; independent and other Christian 7%; Muslim 7%; nonreligious 2%; other/unknown 12%. Major cities/built-up areas (2000): Chaguanas 67,433; San Fernando 55,149; Port of Spain 49,031 (greater Port of Spain [2004] 264,000); Arima 32,278; Point Fortin 19,056. Location: islands northeast of Venezuela, between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.63. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.3 years; female 71.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:TT$38,489,000,000 (taxes on oil/natural gas corporations 45.7%; VAT 10.6%; nonoil corporate taxes 10.4%; other oil revenue 9.8%). Expenditures: TT$31,062,000,000 (current expenditures 85.4%; development expenditures and net lending 14.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 503,000, fruits 68,685, coconuts 10,560; livestock (number of live animals) 59,300 goats, 43,000 pigs, 28,200,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 99,467 cu m, of which fuelwood 35%; fisheries production (2005) 13,414. Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 850,000; natural asphalt 16,200.
Manufacturing (2006): methanol 6,015,600; anhydrous ammonia 5,110,500; cement 883,000. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 6,430,000,000 (6,430,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006)52,100,000 ([2004] 47,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 7,013,000 (601,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 37,973,000,000 ([2004] 12,528,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.8; average income per household (2002): TT$53,015 (US$8,484); expenditure (2003): housing 20.4%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 18.0%, transportation 16.7%, recreation and culture 8.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 453; remittances (2006)87; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 907. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 222; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 108. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 14.6%, in permanent crops 9.2%, in pasture 2.1%; overall forest area (2005)44.1%. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$17,542,000,000 (US$13,520 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 623,700; activity rate of total population 48.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.1%; female 41.9%; unemployed [2006] 6.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,197,000,000.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): TT$40,934,000,000 (mineral fuels 35.0%; machinery 19.7%; chemicals and chemical products 8.1%; transport equipment 7.0%). Major import sources (2005): US 27.2%; Venezuela 13.1%; Brazil 13.1%; Japan 5.4%; Canada 4.1%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): TT$89,298,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 39.8%; natural gas [all forms] 34.4%; chemicals [including ammonia, methanol, and urea] 15.1%). Major export destinations (2005): US 68.6%; Jamaica 5.4%; Barbados 2.9%; Mexico 2.4%; France 2.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 8,320 km (paved 51%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 261,087; trucks and buses 54,843. Airtransport (2005; BWIA only): passenger-km 3,101,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 47,883,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 159,000 (123); televisions (2003): 461,000 (359); telephone landlines (2006): 325,000(250); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,655,000 (1,275); personal computers (2005): 129,000 (100); total Internet users (2005): 163,000 (126); broadband Internetsubscribers (2006): 21,000 (16).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 8.0%; primary education 35.4%; secondary 52.0%; university 4.6%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.5%; males literate 99.0%; females literate 97.9%. Health (2004): physicians 1,293 (1 per 998 persons); hospital beds 4,553 (1 per 283 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 13.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,946 (vegetable products 83%, animal products 17%); 151% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,700 (army 74.1%, coast guard 25.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GNP (2005): 0.2%; per capita expenditure US$25.
Background
When Christopher Columbus visited Trinidad in 1498, it was inhabited by the Arawak Indians; Caribs inhabited Tobago. The islands were settled by the Spanish in the 16th century. In the 17th and 18th centuries African slaves were imported for plantation labor to replace the original Indian population, which had been worked to death by the Spanish. Trinidad was surrendered to the British in 1797. The British attempted to settle Tobago in 1721, but the French captured the island in 1781 and transformed it into a sugar-producing colony; the British acquired it in 1802. After slavery ended in the islands in 1834-38, immigrants from India were brought in to work the plantations. The islands of Trinidad and Tobago were administratively combined in 1889. Granted limited self-government in 1925, the islands became an independent state within the Commonwealth in 1962 and a republic in 1976. Political unrest was followed in 1990 by an attempted Muslim fundamentalist coup against the government.
Recent Developments
The Ministry of Energy and Energy Industries confirmed in May 2007 that cross-border natural gas in reservoirs straddling blocks located in Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela could amount to about 283 billion cu m (10 trillion cu ft), 27% of which was on the Trinidad and Tobago side—the commercialization of natural gas had led to the country’s rapid industrial development in recent years.
Tunisia
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-Tunisiyah (Tunisian Republic). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Chamber of Councilors [126]; Chamber of Deputies [189]). Chief of state: President Zine al-Abidine Ben Ali (from 1987). Head of government: Prime Minister Mohamed Ghan-nouchi (from 1999). Capital: Tunis. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 dinar (TND) = 1,000 millimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1= TND 1.16.
Demography
Area: 63,170 sq mi, 163,610 sq km. Population (2007): 10,226,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 161.9, persons per sq km 62.5. Urban (2005): 65.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.39%; female 49.61%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 25.9%; 15-29, 30.1%; 30-44, 22.1%; 45-59, 13.2%; 60-74, 6.6%; 75-84, 1.8%; 85 and over,0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Tunisian Arab 67.2%; Bedouin Arab 26.6%; Algerian Arab 2.4%; Amazigh (Berber) 1.4%; other 2.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 99%, of which Sunni 97%, Shi’i 2%; other 1%. Major cities (2004): Tunis 728,453 (urban agglomeration [2003] 1,996,000); Safaqis 265,131; Al-Arianah 240,749; Susah 173,047; Et-tadhamen 118,487. Location: northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Libya, and Algeria.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.04. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.6 years; female 75.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:TND 12,279,600,000 (tax revenue 64.5%, of which VAT 18.7%, income tax 12.4%, social security 11.1%; grants and loans 24.3%; nontax revenue 11.2%). Expenditures:TND 13,024,500,000 (current expenditure 78.7%; development expenditure 21.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$12,982,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 1,251,000, olives 1,000,000, tomatoes 850,000; livestock (live animals) 7,213,390 sheep, 1,426,640 goats, 686,320 cattle, 231,000 camels; roundwood (2005) 2,366,704 cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production (2005) 111,782 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock 8,204,000; iron ore 206,000; zinc (metal content) 29,200. Manufacturing (value added in TND ’000,000; 2005): textiles, leather, and wearing apparel 1,948; refined petroleum and petroleum products 1,478; food products 1,210. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 13,006,000,000 (11,239,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2002) none (1,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 26,200,000 ([2004] 11,964,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 1,811,000 (3,922,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 2,344,000,000 (3,642,000,000). Households (2000). Average household size (2004) 4.5; income per household TND 6,450 (US$4,640); expenditure: food and beverages 38.0%, housing and energy 21.5%, household durables 11.1%, health and personal care 10.0%, transportation 9.7%. Gross national income (2006): US$28,905,000,000 (US$2,830 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 3,503,400; activity rate of total population 34.6% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 46.6%; female 25.0%; unemployed 14.3%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,124; remittances (2006) 1,499; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 662. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 365; remittances (2006) 15; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 7.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 18.0%, in permanent crops 13.8%, in pasture 31.2%; overall forest area (2005) 6.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): TND 17,101,500,000 (textiles 17.3%; crude and refined petroleum 12.5%; machinery and apparatus 10.8%; electrical machinery 10.7%; motor vehicles 6.7%; food products 5.5%). Major import sources:France 23.5%; Italy 20.9%; Germany 8.2%; Spain 5.1%; Libya 3.9%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): TND 13,607,700,000 (textiles 32.7%; electrical machinery 14.5%; crude and refined petroleum 12.9%; leather products 5.0%; phosphates and phosphate derivatives 4.4%; olive oil 3.5%). Major export destinations: France 32.9%; Italy 24.0%; Germany 8.4%; Spain 5.5%; Libya 4.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 2,153 km; passenger-km 1,317,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,068,200,000. Roads (2004): total length 19,232 km (paved 66%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 825,990; trucks and buses 119,064. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 2,976,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 17,916,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 272,000 (27); televisions (2004): 2,150,000 (217); telephone landlines (2006): 1,269,000 (124); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 7,339,000 (719); personal computers (2005): 568,000 (56); total Internet users (2006): 1,295,000 (127); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 16,000(1.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling 22.0%; primary education 36.5%; secondary 33.1%; higher8.4%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 10 and over literate 74.3%; males literate 83.4%; females literate 65.3%. Health: physicians (2005)9,422 (1 per 1,036 persons); hospital beds (2004) 17,269 (1 per 576 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 20.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,408 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 180%of FAO recommended minimum.
Background
From the 12th century bc the Phoenicians had a series oftrading posts on the northern African coast. By the 6th century bc the Carthaginian kingdom encompassed most of present-day Tunisia. The Romans ruled from 146 bc until the Muslim Arab invasions in the mid-7th century ad. The area was fought over, won, and lost by many, including the Abbasids, the Al-mohads, the Spanish, and the Ottoman Turks, who finally conquered it in 1574 and held it until the late 19th century. For a time it maintained autonomy as the French, British, and Italians contended for the region. In 1881 Tunisia became a French protectorate. In World War II US and British forces captured it (1943) to end a brief German occupation. In 1956 France granted it full independence; Habib Bourguiba assumed power and remained in office until 1987.
Recent Developments
The Tunisian cereal harvest in 2007 reached two million tons and, despite both budget and current-account deficits, GDP growth reached 8.9% for the year. The country was still coping with corruption, however, and was tied for 61st out of 179 countries in Transparency International’s annual Corruption Perceptions Index. The regime continued its repressive policies and targeted persons whom the government suspected of havingsympathies for political Islam, as well as others, particularly journalists and human rights organizations that sought to create awareness of human rights abuses. In January 2007 about two dozen Islamic extremists who had apparently intended to attack US consular facilities inTuniswere intercepted by security forces in Grombalia, south of the capital. At least 12 people were killed, and 15 others were arrested.
Turkey
Official name: Turkiye Cumhuriyeti (Republic of Turkey). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Grand National Assembly of Turkey [550]). Chief of state: President Abdullah Gul (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan (from 2003). Capital: Ankara. Official language: Turkish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 new Turkish lira (YTL) = 100 kurush; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = YTL 1.25 (the new Turkish lira replaced the [old] Turkish lira [TL] 1 Jan 2005, at the rate of 1 YTL = TL 1,000,000).
Demography
Area: 302,535 sq mi, 783,562 sq km. Population (2007): 73,884,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 244.2, persons per sq km 94.3. Urban (2006): 62.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.44%; female 49.56%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 28.3%; 15-29, 27.7%; 30-44, 22.4%; 45-59, 13.4%; 60-74, 6.5%; 75-84, 1.5%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Turk 65.1%; Kurd 18.9%; Crimean Tatar 7.2%; Arab 1.8%; Azerbaijani 1.0%; Yoruk 1.0%; other 5.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 97.5%, of which Sunni 82.5%, Shi’i (mostly nonorthodox Alevi) 15.0%; nonreligious 2.0%; other (mostly Christian) 0.5%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Istanbul 9,712,000; Ankara 3,573,000; Izmir 2,487,000; Bursa 1,414,000; Adana 1,245,000; Gaziantep 992,000. Location: southwestern Asia and southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, the Mediterranean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.18. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.1 years; female 74.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: YTL 134,819,231,000 (tax revenue 79.3%, of which income tax 22.5%; nontax revenue 17.2%; grants and other revenue 3.5%). Expenditures: YTL 141,020,860,000 (finances 51.8%; education 10.5%; labor and social security 10.2%; defense 7.2%). Production (in ’000 metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 20,010, sugar beets 14,452, tomatoes 9,855, barley 9,551, potatoes 4,397; livestock (number of live animals) 25,304,000 sheep, 10,526,000 cattle, 317,000,000 chickens, (2004) 230,037 angora goats; roundwood (2005) 16,185,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 31%; fisheries production (2005) 546 (from aquaculture 22%). Mining (2005): magnesite 3,400; refined borates 800; chromite 700. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2005): food products 8,800; telecommunications equipment and electronics 7,450; chemicals and chemical products 7,400; base metals 7,000; motor vehicles and parts 6,500. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 161,983,000,000 (118,768,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2005) 3,010,000 ([2004] 18,900,000); lignite (metric tons; 2005) 55,600,000 ([2004] 45,500,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 15,900,000 ([2004] 185,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 23,724,000 ([2004] 24,972,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 708,000,000 (23,372,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 24,775,000; activity rate of total population 34.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 51.1%; female 26.1%; unemployed [May 2006-April 2007] 9.7%). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.1; average annual income per household (2003) TL 10,767,998,904 (US$7,174); sources of income (2004): wages and salaries 38.7%, self-employment 31.8%, transfers 21.2%; expenditure (2005): housing 25.9%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 24.9%, transportation 12.6%; household furnishings 6.8%. Gross national income (2006): US$397,699,000,000 (US$5,380 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; June 2007): US$65,310,000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 18,152; remittances (2006) 851; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 3,752; official development assistance (2005) 1,668 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,872; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 622. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 30.4%, in permanent crops 3.4%, in pasture 19.0%; overall forest area (2005) 13.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$137,449,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 21.5%; mineral fuels 21.5%; base and fabricated metals 13.7%; transport equipment 9.1%; chemicals and chemical products 9.0%). Major import sources: EU 42.5%, of which Germany 10.6%, Italy 6.2%, France 5.2%; Russia 12.8%; China 6.9%; US 4.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$85,309,000,000 (textiles and wearing apparel 23.1%; transport equipment 15.9%; machinery and apparatus 15.0%; base and fabricated metals 14.2%; mineral fuels 6.1%). Major export destinations: EU 56.0%, of which Germany 11.3%, UK 8.0%, Italy 7.9%, France 5.4%; US 5.9%; Russia 3.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 8,697 km; pas-senger-km 5,036,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,152,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 347,553 km (paved 45%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 5,730,320; trucks and buses 2,624,259. Air transport (2006; Atlasjet, Turkish, Pegasus, and Sun Express airlines only): passenger-km 37,512,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 391,831,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 4,948,000 (70); televisions (2002): 29,440,000 (424); telephone landlines (2006): 18,832,000 (258); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 52,663,000 (722); personal computers (2005): 4,073,000 (57); total Internet users (2006): 12,283,000 (168); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,774,000 (38).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through primary education 64%; lower secondary 10%; upper secondary/higher vocational 17%; university 9%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 88.1%; males literate 96.0%; females literate 80.4%. Health: physicians (2004) 104,226 (1 per 683 persons); hospital beds (2006) 180,767 (1 per 404 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 22.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,416 (vegetable products 88%, animal products 12%); 173% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 514,850 (army 78.1%, navy 10.2%, air force 11.7%); US troops in Turkey (June 2007) 1,650. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.8%; per capita expenditure US$143.
Background
Turkey’s early history corresponds to that of Asia Minor, the Byzantine Empire, and the Ottoman Empire. Byzantine rule emerged when Constantine the Great made Constantinople (now Istanbul) his capital. The Ottoman Empire, begun in the 12th century, dominated for more than 600 years; it ended in 1918 after the Young Turk revolt precipitated its demise. Under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, a republic was proclaimed in 1923, and the caliphate was abolished in 1924. Turkey remained neutral throughout most of World War II, siding with the Allies in 1945. Since the war it has alternated between civil and military governments and has had several conflicts with Greece over Cyprus. The 1990s saw political and civic turmoil between fundamentalist Muslims and secularists.
Recent Developments
Militants of the radical nationalist Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK), which had its chief operational base in northern Iraq, mounted hit-and-run raids on Turkish security forces in 2007, while other PKK terrorists set off bombs in metropolitan areas. These attacks cost the lives of some 150 people during the year. A convention on the prevention of terrorism signed with Iraq in September had little effect. Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan asked the parliament to authorize the deployment of Turkish forces outside the country’s boundaries. Attempts by the US administration to dissuade Turkey from an incursion into northern Iraq were hampered by a vote in October by the Foreign Affairs Committee of the US House of Representatives to recognize the massacres that attended the deportation of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire in 1915 as an act of genocide. US-Turkish relations improved, however, after Erdogan visited Pres. George W. Bush in Washington in early November. Following an agreement to share intelligence on the PKK, the US opened Iraqi airspace prior to a series of Turkish raids on PKK camps in December, and attacks by both sides continued in 2008. Progress on EU membership for Turkey, meanwhile, was stalled.
Turkmenistan
Official name: Turkmenistan. Form of government: unitary single-party republic with one legislative body (Majlis [Parliament; 50]). Head of state and government: President Gurbanguly Berdymukhammedov (from 2006). Capital: Ashgabat. Official language: Turkmen. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: manat (m); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = m 14,250.00 (in mid-2006 the black market value was about m 24,000 = US$1).
Demography
Area: 188,500 sq mi, 488,100 sq km. Population (2007): 5,097,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 27.0, persons per sq km 10.4. Urban (2005): 46.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.24%; female 50.76%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 31.8%; 15-29, 30.0%; 30-44, 20.6%; 45-59, 11.4%; 60-74, 4.6%; 75-84, 1.4%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Turkmen 79.2%; Uzbek 9.0%; Russian 3.0%; Kazakh 2.5%; Tatar 1.1%; other 5.2%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (mostly Sunni) 87.2%; Russian Orthodox 1.7%; nonreligious 9.0%; other 2.1%. Major cities (1999): Ashgabat (2002) 743,000; Turkmenabat 203,000; Dasoguz 165,000; Mary 123,000; Balkanabat 108,000. Location: central Asia, bordering Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Iran, and the Caspian Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 25.6 (world avg. 20.3); (1998) within marriage 96.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.19. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 64.9 years; female 71.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: m 14,262,000,000,000 (tax revenue 94.3%; nontax revenue 5.7%). Expenditures: m 14,251,000,000,000 (current expenditure 94.8%; development expenditure 5.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$912,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 3,260,000, seed cotton 700,000, tomatoes 282,000; livestock(number of live animals) 15,694,000 sheep, 2,065,000 cattle, 904,000 goats; roundwood (2005) 3,400 cu m, of which fuelwood 100%; fisheries production (2005) 15,016. Mining and quarrying (2004): iodine 250,000, salt 215,000, gypsum 100,000. Manufacturing (2001): residual fuel oils 2,681,000; distillate fuel (gas-diesel oil; 2003) 1,750,000; motor spirits 1,283,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 11,470,000,000 (9,816,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 69,600,000 ([2004] 46,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 6,230,000 (3,407,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 63,000,000,000 ([2004] 13,691,000,000). Households. Average household size (2002) 5.7; sources of income (1998): wages and salaries 70.6%, pensions and grants 20.9%, self-employment (mainly agricultural income) 2.3%; expenditure (1998): food 45.2%, clothingand footwear 16.8%, furniture 13.3%, transportation 7.6%, health 7.0%. Population economically active (2003): total 2,073,000; activity rate of total population 44.1%(par-ticipation rates: ages 15-64, 70.7%; female 46.8%; unofficially unemployed [2004] 60%). Gross national income (2006): US$6,047,000,000 (US$1,234 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 192; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 83; official develop-mentassistance (2005) 24 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1997) 125. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.7%, in permanent crops 0.1%, in pasture 65.3%; overall forest area (2005)8.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$2,450,000,000(machinery and transport equipment 45.9%; basic manufactures 19.9%; chemicals and chemical products 11.1%; food products 5.3%). Major import sources (2006): UAE 13.9%; Azerbaijan 11.3%; Turkey 9.9%; Russia 8.0%; Ukraine 7.8%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): US$3,720,-000,000 (natural gas 49.7%; petrochemicals 18.3%; crude petroleum 8.9%; cotton fiber 3.2%). Major export destinations (2006): Ukraine 46.3%; Iran 16.8%; Azerbaijan 4.2%; UAE 3.2%; Italy 3.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (1999): length (2005) 2,440 km; passenger-km 701,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 7,337,000,000. Roads (2001): total length 22,000 km (paved 82%). Vehicles (1995): passenger cars 220,000; trucks and buses 58,200. Air transport (2005; Turkmenistan Airlines only): passenger-km 1,913,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 25,997,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 57,000 (12); televisions (2003): 855,000 (182); telephone landlines (2005): 398,000 (82); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 105,000 (22); personal computers (2005): 348,000 (72); total Internet users (2006): 65,000 (13).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 3.2%; incomplete primary to complete standard secondary education 60.1%; vocational secondary 23.5%; higher 13.2%. Literacy (1995): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.8%; males literate 99.3%; females literate 98.3%. Health: physicians (2002) 20,032 (1 per 231 persons); hospital beds (1997) 33,000 (1 per 131 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 55.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,217 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 167% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 26,000 (army 80.8%, navy 2.7%, air force 16.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.7%; per capita expenditure US$93.
Background
The earliest traces of human settlement in central Asia, dating back to Paleolithic times, have been found in Turkmenistan. The nomadic, tribal Turkmen probably entered the area in the 11th century ad. They were conquered by the Russians in the early 1880s, and the region became part of Russian Turk-istan. It was organized as the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic in 1924 and became a constituent republic of the USSR in 1925. The country gained full independence from the USSR in 1991 under the name Turkmenistan. From 1990 to 2006 the country was ruled by the ever more autocratic and mercurial strongman Saparmurad Niyazov.
Recent Developments
Following his election in February 2007, Gurbanguly Berdymukhammedov carried out a reform of the educational system, restoring the 10th year of basic education and the 5th year of university, and restored pensions that his predecessor had canceled. He promised to make Internet access available to all, and Internet cafes began to open early in the year, but access to sites outside the country was restricted. In June the Turkmen government granted permission to the American oil firm Chevron and to British Petroleum to open offices in Ashgabat, and the projected gas pipeline supplying Turkmen natural gas to Pakistan via Afghanistan came closer to realization in August when the American firm International Oil announced its decision to undertake the construction. In early October Indian Ambassador Mohammad Afzal informed Berdymukhammedov that India also wanted to take part in the trans-Afghan pipeline project. In return Berdymukhammedov raised the possibility of cooperation with India’s information-technology sector.
Tuvalu
Official name: Tuvalu. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Parliament [15]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Filoimea Telito (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Apisai Ielemia (from 2006). Capital: government offices are at Vaiaku, on Funafuti atoll. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary units: 1 Tuvaluan dollar ($T) = 1 Australian dollar ($A) = 100 Tuvaluan and Australian cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = $A 1.05.
Demography
Area: 9.90 sq mi, 25.63 sq km. Population (2007): 9,700. Density(2007): persons persq mi 979.8, persons persq km 378.5. Urban (2004): 55.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.79%; female 51.21%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 30.3%; 15-29, 27.5%; 30-44, 20.7%; 45-59, 14.1%; 60-74, 5.8%; 75 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic composition (2002): Tuvaluan (Polynesian) 93.6%; mixed (Tuvaluan/other) 4.6%; other Pacific 1.5%; other 0.3%. Religious affiliation (2002): Christian 97.0%, of which Church of Tuvalu (Congregational) 91.0%, Seventh-day Adventist 2.0%, Roman Catholic 1.0%; Baha’i 1.9%; other 1.1%. Major locality (2002): Fongafale islet of Funafuti atoll 4,492. Location: western Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea near the Equator.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 22.2 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 92.7%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.1 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.98. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 66.1 years; female 70.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: $A 25,539,000 (tax revenue 23.9%; nontax revenue [includes remittances from phosphate miners in Nauru and seafarers on German ships; rentals of fishing resources to Japan, Taiwan, and the US; and the leasingof the country's Internetdo-main, ".tv"] 38.0%; grants 38.1%). Expenditures:$A 22,323,000 (current expenditure 95.4%; development expenditure 4.6%). Public debt (external; 2002): US$5,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$26,000,000 (US$2,441 per capita). Production (metric tons exceptas noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): coconuts (2005) 1,139, fruits 749, bananas (2005) 284, other agricultural products include breadfruit, pulaka (taro), pandanus fruit, sweet potatoes, and pawpaws; livestock (number of live animals; 2005) 13,500 pigs, 15,000 ducks, 45,000 chickens; fisheries production (2005) 2,561. Manufacturing (value added in $A ’000; 2002): cigarettes 755, cottage industries (including handicrafts and garments) 158. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) n.a. (4,200,000); petroleum products, none (none). Population economically active (2002): total 3,463; activity rate of total population 36.2% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 58.2%; female 43.4%; unemployed 6.5%). Households (2004-05). Average household size 5.3; average annual net income per household $A 13,007 (US$9,746); sources of income: wages and salaries 47.0%, rents, interest, bonuses, and other 28.7%, self-employment 12.1%, overseas remittances 9.1%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 48.9%, housing 18.8%, household furnishings and energy 12.2%, education, health, and recreation 9.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 0.2; remittances (2006) 3.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 6.8; official development assistance (2005) 9.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in permanentcrops 67%; overall forestarea (2005) 33%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): $A 16,908,333 (food products [including live animals] 33.4%; mineral fuels 21.7%; machinery and apparatus 13.7%; transport equipment 5.2%; textiles 4.5%). Major import sources:Australia 33.7%; Fiji 19.7%; Singapore 17.5%; New Zealand 9.9%; China 5.1%. Exports (2005): $A 80,403 (precision instruments 18.6%; machinery and apparatus 17.4%; base and fabricated metals 15.4%; wood and wood products 12.5%; transportation equipment 11.6%). Major export destinations: Germany 60.5%; Italy 20.2%; Fiji 6.8%; Australia 2.7%; Ghana 1.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2002): total length 8 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 102; trucks and buses 33. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Telephone landlines (2005): 900 (93); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 1,300 (135); total Internet users (2005): 1,700 (177).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004-05). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education/unknown 8.8%; primary education 52.4%; secondary 29.8%; higher 9.0%. Literacy (2004): total population literate 95%. Health: physicians (2003) 4 (1 per 2,393 persons); hospital beds (2001) 56 (1 per 170 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 19.5.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none; Tuvalu has nonformal security arrangements with Australia and New Zealand.
Background
The original Polynesian settlers of Tuvalu probably came mainly from Samoa or Tonga. The islands were sighted by the Spanish in the 16th century. Europeans settled there in the 19th centuryand intermarried with Tuvaluans. During this period Peruvian slave traders, known as “blackbirders,” decimated the population. In 1856 the US claimed the four southern islands for guano mining. Missionaries from Europe arrived in 1865 and rapidly converted the islanders to Christianity. In 1892 Tuvalu joined the British Gilbert Islands, a protectorate that became the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony in 1916. Tuvaluans voted in 1974forseparation from the Gilberts (now Kiribati), whose people are Mi-cronesian. Tuvalu gained independence in 1978, and in 1979 the US relinquished its claims. Elections were held in 1981, and a revised constitution was adopted in 1986. In recent decades, the government has tried to find overseas job opportunities for its citizens.
Recent Developments
Tuvalu’s well-managed Tuvalu Trust Fund, which invested in major economies and funded a significant part of the government budget, suffered from global credit problems that emerged late in the year. Sea levels around Tuvalu were rising at a rate of almost an inch annually, as well, causing accelerated coastal degradation, and underground water supplies were deteriorating. The prospect that Tuvalu’s nine atolls might be submerged by as early as 2040 had already raised questions concerning where the population might be relocated.
Uganda
Official name: Republic of Uganda. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [333]). Head of state and government: President Yoweri Museveni (from 1986), assisted by Prime Minister Apolo Nsibambi (from 1999). Capital: Kampala. Official language: English; Swahili. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Uganda shilling (UGX) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = UGX 1,600.00.
Demography
Area: 93,263 sq mi, 241,551 sq km. Population (2007): 30,263,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 396.7, persons per sq km 153.2. Urban (2006): 13.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.08%; female 49.92%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 50.3%; 15-29, 27.7%; 30-44, 12.9%; 45-59, 5.7%; 60-74, 2.7%; 75-84, 0.6%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Eth-nolinguistic composition (2002): Ganda 17.3%; Nkole 9.8%; Soga 8.6%; Kiga 7.0%; Teso 6.6%; Lango 6.2%; Acholi 4.8%; Gisu 4.7%. Religious affiliation (2002): Christian 85.3%, of which Roman Catholic 41.9%, Anglican 35.9%, Pentecostal 4.6%, Seventh-day Adventist 1.5%; Muslim 12.1%; traditional beliefs 1.0%; nonreligious 0.9%; other 0.7%. Major cities (2002): Kampala (urban agglomeration) 1,208,544; Gulu 119,430; Lira 80,879; Jinja 71,213; Mbale 71,130. Location: eastern Africa, bordering The Sudan, Kenya, Lake Victoria, Tanzania, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 48.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 35.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.88. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 50.2 years; female 51.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2003-04). Revenue:UGX 2,939,000,000,000 (tax revenue 52.7%, of which VAT 18.1%, petroleum taxes 9.2%, income tax 6.8%, tax on international trade 4.6%; grants 43.2%; nontax revenue 4.1%). Expenditures: UGX 3,170,000,000,000 (current expenditures 58.8%, of which education 13.8%, public administration 11.0%, defense 10.3%; capital expenditures 41.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): plantains 9,054,000, cassava 4,926,000, sweet potatoes 2,628,000; livestock (number of live animals) 8,034,000 goats, 6,973,000 cattle, 2,000,000 pigs; roundwood (2005) 39,972,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 92%; fisheries production (2005) 427,575 (from aquaculture 3%). Miningand quarrying(2005): cobalt 638; columbite-tantalite(ore and concentrate) 273 kg. Manufacturing (2005): cement 692,709; sugar 182,906; soap 127,589. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 1,858,000,000 ([2004] 1,726,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (504,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): intemporarycrops 26.4%, in perma-nentcrops 10.9%, in pasture 25.9%; overall forestarea (2005) 18.4%. Gross national income (2006): US$9,702,000,000 (US$324 per capita). Population economically active (2002-03): total 9,773,000; activity rate of total population 37.7% (participation rates [2001]: ages 15-64, 78.9%; female 35.2%; officially unemployed 3.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,250,000,000. Households. Average household size (2004) 4.7; income per household (1999-2000) UGX 141,000 (US$91); sources of income (1999-2000): wages and self-employment 78.0%, transfers 13.0%, rent 9.0%; expenditure (2002-03): food and nonalcoholic beverages 41.3%, rent, energy, and services 19.9%, education 8.0%, transportation 6.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 355; remittances (2006) 845; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 204; official development assistance (2005) 1,198. Disbursements for (US$’000,-000): tourism (2005) 133; remittances (2006) 360.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$2,054,137,000 (petroleum products 16.7%; chemicals and chemical products 13.1%; food, beverages, and tobacco products 11.4%, of which cereals 6.9%; transport equipment 9.8%; base and fabricated metals 8.2%). Major import sources:Kenya 25.3%; Japan 7.1%; South Africa 7.0%; UAE 6.7%; India 6.4%. Exports (2005): US$812,-857,000 (coffee 21.3%; fish and fish products 17.6%; gold 9.0%; tea 4.2%; petroleum products 3.9%; tobacco 3.9%; cotton 3.5%; in 2005 the estimated value of the unreported illegal export trade in diamonds from the Democratic Republic of the Congo via Uganda was US$200,000,000). Major export destinations: The Netherlands 10.5%; UAE 10.4%; Switzerland 9.2%; Kenya 8.9%; Democratic Republic of the Congo 7.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 1,244 km; metric ton-km cargo 185,559,000. Roads (2003): total length 70,746 km (paved 23%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 65,472; trucks and buses 100,323. Air transport: passenger-km (2003) 237,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 27,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 89,000 (3.4); televisions (2003): 450,000 (17); telephone landlines (2006): 108,000 (3.6); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,009,000 (67); personal computers (2005): 300,000 (10); total Internet users (2006): 750,000 (25).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 34.4%; incomplete primary education 36.0%; complete primary 11.1%; incomplete secondary 12.0%; complete secondary (some higher) 1.8%; complete higher (including vocational) 4.7%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 66.8%; males literate 76.8%; females literate 57.7%. Health (2004): physicians 2,209 (1 per 11,947 persons); hospital beds 26,772 (1 per 986 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 68.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,333 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 132% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 45,000 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$7.
Background
By the 19th century the region around Uganda comprised several separate kingdoms inhabited by various peoples, including Bantu- and Nilotic-speaking tribes. Arab traders reached the area in the 1840s. The native kingdom of Buganda was visited by the first European explorers in 1862. Protestant and Roman Catholic missionaries arrived in the 1870s, and the development of religious factions led to persecution and civil strife. In 1894 Buganda was formally proclaimed a British protectorate. As Uganda, itgained its independence in 1962, and in 1967 it adopted a republican constitution. The civilian government was overthrown in 1971 and replaced by a military regime under Idi Amin. His invasion of Tanzania in late 1978 resulted in the collapse of his regime. In 1985 the civilian government was again deposed by the military, which in turn was overthrown in 1986. A constituent assembly enacted a new constitution in 1995.
Recent Developments
At the end of 2007 there were more than 1,250,000 internally displaced persons in Uganda, many displaced by the Lord’s Resistance Army’s (LRA’s) rebellion. A precarious cease-fire prevailed, and intermittent negotiations took place into 2008 between the government and the LRA under rebel leader Joseph Kony. In Karamoja district, in the northeast, there was an acute shortage of food throughout the year, and cattle rustling remained endemic. In the less-turbulent central region, continuous heavy rains starting in July led to serious flooding, which displaced thousands of people. Along the western border, news of oil reserves remained good, but in August there was a dispute with the Democratic Republic of the Congo over a joint border. Even the more prosperous south had its problems. Aventure there to build a third dam on the Nile River north of two existing dams located where the river leaves Lake Victoria proved contentious. The aim was to remedy Uganda’s chronic need for more electricity, but critics pointed out that the dangerously low water level in Lake Victoria was already due as much to the excessive demands of the existing generators as to the persistent drought.
Ukraine
Official name: Ukrayina (Ukraine). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (Parliament [450]). Head of state: President Viktor Yushchenko (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Yuliya Tymoshenko (from 2007). Capital: Kiev(Kyyiv). Official language: Ukrainian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: hryvnya (UAH); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = UAH 4.51.
Demography
Area: 233,062 sq mi, 603,628 sq km. Population (2007): 46,457,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 199.3, persons per sq km 77.0. Urban (2006): 68.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 45.97%; female 54.03%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 14.3%; 15-29, 23.0%; 30-44, 21.1%; 45-59, 21.2%; 60-74, 14.1%; 75-84, 5.5%; 85 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2001): Ukrainian 77.8%; Russian 17.3%; Belarusian 0.6%; Moldovan 0.5%; Crimean Tatar 0.5%; other 3.3%. Religious affiliation (2004): Ukrainian Orthodox, of which “Kiev patriarchy” 19%, “no particular patriarchy” 16%, “Moscow patriarchy” 9%, Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox 2%; Ukrainian Catholic 6%; Protestant 2%; Latin Catholic 2%; Muslim 1%; Jewish 0.5%; nonreli-gious/atheist/other 42.5%. Major cities (2005): Kiev 2,718,000; Kharkiv 1,461,000; Dnipropetrovsk 1,039,000; Odesa (Odessa) 1,001,000; Donetsk (2005) 999,975. Location: eastern Europe, bordering Belarus, Russia, the Black Sea, Romania, Moldova, Hungary, Slovakia, and Poland.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 78.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.21. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 62.1 years; female 73.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:UAH 133,464,000,000 (tax revenue 71.0%, of which VAT 37.8%, corporate taxes 19.4%, excise tax 6.4%; nontax revenue 26.8%; other 2.2%). Expenditures: UAH 137,063,000,000 (social security 22.1%; education and health 12.8%; transportation and communications 4.9%; agriculture 4.8%; energy and construction 4.1%). Public debt (external; April 2007): US$12,400,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugar beets 22,421,000, potatoes 19,467,000, wheat 14,000,000, sour cherries 120,000; livestock (number of live animals) 7,053,000 pigs, 6,514,000 cattle, 140,500,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 14,606,300 cu m, of which fuelwood 56%; fisheries production (2005) 273,688 (from aquaculture 11%). Mining and quarrying (2005): iron ore (metal content) 37,700,000; manganese (metal content) 770,000; ilmenite concentrate (2004) 370,000. Manufacturing (value of production in UAH ’000,000,000; 2005): base and fabricated metals 103.4; food and beverages 76.3; machinery and apparatus 59.7. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 192,204,000,000 ([2004] 76,831,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2006) 61,200,000 ([2004] 64,500,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 278,000 ([2004] 634,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 32,200,000 ([2004] 177,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 20,576,000 (11,938,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 17,733,000,000 ([2004] 78,531,000,000). Households (2005). Average household size 2.6; average annual disposable income per household UAH 16,527 (US$3,225); sources of income: wages and salaries 46.0%, transfers 30.9%, self-employment 4.9%; expenditure: food 61.0%. Population economically active (2005): total 22,280,800; activity rate of total population 47% (participation rates [2003]: ages 15-64, 65.8%; female 48.9%; unemployed [2006] 7.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$105,253,000,000 (US$2,260 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,125; remittances (2006) 595; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 2,486; official development assistance (2005) 608 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,805; remittances (2006) 34. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 56.1%, in permanent crops 1.6%, in pasture 13.8%; overall forest area (2005) 16.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$45,039,000,000 (mineral fuels 28.2%, of which natural gas 10.6%, crude petroleum 9.8%; machinery and apparatus 17.5%; road vehicles 10.9%; base and fabricated metals 7.4%). Major import sources (2005): Russia 35.5%; Germany 9.4%; Turkmenistan 7.4%; China 5.0%. Exports (2006): US$38,368,000,000 (base and fabricated metals 42.8%, of which iron and steel 34.0%; agricultural products 12.3%; chemical products 8.8%; machinery 8.7%). Major export destinations (2005): Russia 22.1%; Turkey 6.0%; Italy 5.6%; Germany 3.8%; Poland 3.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 21,870 km; pas-senger-km 52,400,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 223,400,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 169,104 km (paved 98%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2005) 5,538,972; trucks and buses (2004) 1,093,372. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 4,393,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 40,692,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,466,000 (52); telephone landlines (2006): 12,341,000 (264); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 49,076,000 (1,049); personal computers (2005): 1,810,000 (38); total Internet users (2006): 5,545,000 (119).
Education and health
Literacy (2004): virtually 100%. Health (2006): physicians 225,000 (1 per 208 persons); hospital beds 444,000 (1 per 105 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 9.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,289 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 167% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 272,500 (army 45.9%, air force/air defense 18.0%, navy 5.0%, paramilitary 31.1%); Russian naval forces (2006) 1,100. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.4%; per capita expenditure US$42.
Background
The area around Ukraine was invaded and occupied in the first millennium bc by the Cimmerians, Scythians, and Sarmatians and in the first millennium ad by the Goths, Huns, Bulgars, Avars, Khazars, and Magyars. Slavic tribes settled there after the 4th century. Kiev was the chief town of Kievan Rus. The Mongol conquest in the mid-13th century decisively ended Kievan power. Ruled by Lithuania in the 14th century and Poland in the 16th century, it fell to Russian rule in the 18th century. The Ukrainian National Republic, established in 1917, declared its independence from Soviet Russia in 1918 but was reconquered in 1919; it was made the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic of the USSR in 1922. The northwestern region was held by Poland from 1919 to 1939. Ukraine suffered a severe famine in 1932-33 under Soviet leader Joseph Stalin; over five million Ukrainians died of starvation in an unprecedented peacetime catastrophe. Overrun by Axis armies in 1941 in World War II, it was further devastated before being retaken by the Soviets in 1944. It was the site of the 1986 accident in Chernobyl, at a Soviet-built nuclear power plant. Ukraine declared independence in 1991. In recent years it has struggled economically as well as politically.
Recent Developments
Ukraine in 2007 was dominated by early parliamentary elections, which were held on 30 September. The election was notable for the sweeping gains made by the opposition party led by former prime minister Yuliya Tymoshenko. On 18 December she returned to the prime ministership after having gained the 226-vote majority needed for approval in the 450-member assembly by a single vote. According to government figures, GDP grew 32.6% in 2007, and industrial output increased by 10.2%, though agricultural output fell by 5.6% and consumer prices increased 16.6%. In April 2008 official unemployment stood at only 2.3%. In June 2007 Ukraine and Russia signed a new protocol on regulations for gas whereby Russia agreed to raise the volume of gas transported through Ukraine by 30 billion cu m by 2030. In 2007 Ukraine paid US$130 per 1,000 cu m of Russian gas, compared with US$95 in 2006. In October Ukraine’s energy minister, Yury Boyko, signed an agreement with the head of the Russian energy company Gazprom to clear an outstanding debt of more than US$1.3 billion by cash payments and through the return of US$1.2 billion in gas owned by the Ukrainian energy company RosUkrEnergo to Gazprom Eksport. Though the EU did not accept Ukraine’s request for membership, it had earlier promised US$647 million in aid to the country over the next four years. It also lifted visa restrictions, allowing free travel from Ukraine to the EU for those Ukrainians under the age of 18 or of retirement age.
United Arab Emirates
Official name: Al-Imarat al-’Arabiyah al-Muttahidah (United Arab Emirates). Form of government: federation of seven emirates with one advisory body (Federal National Council [40]). Chief of state: President Sheikh Khalifah ibn Zayid al-Nahyan (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Sheikh Muhammad ibn Rashid al-Maktum (from 2006). Capital: Abu Dhabi. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 UAE dirham (AED) = 100 fils; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = AED 3.67.
Demography
Area: 32,280 sq mi, 83,600 sq km. Population (2007): 4,444,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 137.7, persons per sq km 53.2. Urban (2005): 76.7%. Sex distribution (2006): male 68.61%; female 31.39%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 20.8%; 15-29, 29.3%; 30-44, 36.9%; 45-59, 11.3%; 60-74, 1.5%; 75-84, 0.2%; 85 and over, negligible. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 48.1%, of which UAE Arab 12.2%, UAE Bedouin 9.4%, Egyptian Arab 6.2%, Omani Arab 4.1%, Saudi Arab 4.0%; South Asian 35.7%, of which Pashtun 7.1%, Balochi 7.1%, Malayali 7.1%; Persian 5.0%; Filipino 3.4%; white 2.4%; other 5.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 62% (mostly Sunni); Hindu 21%; Christian 9%; Buddhist 4%; other 4%. Major cities (2007): Dubai 1,225,137; Abu Dhabi 633,136; Sharjah 584,286; Al-’Ayn 444,331; ‘Ajman 250,808 Location: the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, Oman, and Saudi Arabia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.44. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 73.0 years; female 78.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: AED 200,704,000,000 (royalties on hydrocarbons 80.5%; tax revenue 4.2%; other 15.3%). Expenditures: AED 128,238,000,000 (current expenditures 78.5%; development expenditure 13.1%; loans, net equity, and foreign grants 8.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$174,536,-000,000 (US$41,082 per capita). Public debt (2005): US$20,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): dates 760,000, tomatoes 240,000, eggplants 20,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,520,000 goats, 580,000 sheep, 250,000 camels; fisheries production 90,570 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gypsum 100,000; lime 50,000. Manufacturing (value added in AED ’000,000; 2002): chemical products (including refined petroleum) 18,467; textiles and wearing apparel 4,281; fabricated metal products and machinery 3,695. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 60,698,000,000 (53,874,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 942,585,000 ([2005] 153,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 22,655,000 (9,667,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 47,000,000,000 ([2004] 38,753,000,000). Population economically active (2004): total 2,459,145; activity rate of total population 56.9% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 76.2%; female [2001] 11.7%; unemployed [2001] 2.4%). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.4; expenditure (2000): housing and energy 36.1%, transportation and communications 14.9%, food 14.4%, education, recreation, and entertainment 10.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,233; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 5,421. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005)5,300; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1,853. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.8%, in permanent crops 2.3%, in pasture 3.6%; overall forest area (2005) 3.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): AED 316,280,000,000 (emirate imports 78.7%; free zone imports 21.3%). Major import sources: US 11.4%; China 11.0%; India 9.8%; Germany 6.2%; Japan 5.8%. Exports (2006): AED 523,350,000,000 (crude petroleum 40.8%; reexports 32.3%; free zone exports 14.4%; natural gas 5.0%). Major export destinations: Japan 25.9%; South Korea 10.3%; Thailand 5.9%; India 4.5%; Iran 3.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2003): total length, n.a. (paved roads only, 4,030 km). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 684,092; trucks and buses 92,965. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 73,893,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,027,339,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2006): 706,000 (165); televisions (2004): 843,000 (216); telephone landlines (2006): 1,310,000 (307); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,519,000 (1,294); personal computers (2005): 850,000 (208); total Internet users (2006): 1,709,000 (401); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 241,000 (56).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling (illiterate) 9.1%, (literate) 13.3%; primary education 14.5%; incomplete/complete secondary 42.0%; post-secondary 4.2%; undergraduate 15.1%; graduate 1.8%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 10 and over literate 90.9%; males literate 90.4%; females literate 92.2%. Health (2004): physicians 4,864 (public sector only; 1 per 779 persons); hospital beds 7,775 (1 per 487 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 13.9. Food (2004): daily per capita caloric intake 3,280 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%); 162%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 50,500 (army 87.1%, navy 5.0%, air force 7.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.0%; per capita expenditure US$546.
Background
The Persian Gulf was the location of important trading centers as early as Sumerian times. Its people converted to Islam in Muhammad’s lifetime. The Portuguese entered the region in the early 16th century, and the British East India Company arrived about 100 years later. In 1820 the British exacted a peace treaty with local rulers along the coast of the eastern Arabian Peninsula. The area formerly called the Pirate Coast became known as the Trucial Coast. In 1892 the rulers agreed to restrict foreign relations to Britain. Though the British administered the region from 1853, they never assumed sovereignty; each state maintained full internal control. The states formed the Trucial States Council in 1960. In 1971 the sheikhs terminated defense treaties with Britain and established the six-member federation. Ras al-Khaymah joined it in 1972. The UAE aided coalition forces against Iraq in the Persian Gulf War (1991).
Recent Developments
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) unveiled its National Development Strategy in 2007, recognizing the need to develop an infrastructure that was not based on oil revenues. In September Dubai became the largest shareholder in the London Stock Exchange, with 28% ownership, and acquired a 20% stake in the Nasdaq stock market index. Dubai also announced an initial public offering (IPO) of its port-operating company DP World, which at US$4.96 billion was the largest IPO in the Middle East. Abu Dhabi struck a deal with Boeing to become a major supplier of high-tech aerospace components.
United Kingdom
Official name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (House of Lords [750]; House of Commons [646]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952). Head of government: Prime Minister Gordon Brown (from 2007). Capital: London. Official language: English. Official religion: Churches of England and Scotland “established” (protected by the state but not “official”) in their respective countries; no established church in Northern Ireland or Wales. Monetary unit: 1 pound sterling (£) = 100 new pence; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = £0.50.
Demography
Area: 93,628 sq mi, 242,495 sq km, of which England 50,301 sq mi, 130,279 sq km; Wales 8,005 sq mi, 20,733 sq km; Scotland 30,080 sq mi, 77,907 sq km; Northern Ireland 5,242 sq mi, 13,576 sq km. Population (2007): 60,863,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 650.1, persons per sq km 251.0. Urban (2005): 89.7%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 17.9%; 15-29, 19.3%; 30-44, 22.3%; 45-59, 19.3%; 60-74, 13.6%; 75-84, 5.7%; 85 and over, 1.9%. Ethnic composition (2002-03): white 89.2%; black 2.0%, of which Caribbean origin 1.0%, African origin 0.9%; Asian Indian 1.7%; Pakistani 1.2%; Bangladeshi 0.5%; Chinese 0.3%; other and not stated 5.1%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 71.8%, of which Anglican-identified 29%, other Protestant-identified (significantly Presbyterian) 14%, Roman Catholic-identified 10%; Muslim 2.8%; Hindu 1.0%; Sikh 0.6%; Jewish 0.5%; nonreligious 15.0%; other 0.5%; unknown 7.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.96%; female 51.04%. Major cities (urban agglomeration) (2005): London 7,518,000 (8,505,000); Birmingham 1,001,000 (2,280,000); Manchester 441,000 (2,228,000); Leeds 723,000 (1,519,000); Glasgow 579,000 (1,159,000); Newcastle 276,000 (879,000); Liverpool 448,000 (810,000); Sheffield 521,000; Bradford 485,000; Edinburgh 458,000; Bristol 398,000; Wakefield 321,000; Cardiff 320,000; Coventry 304,000; Don-caster 290,000; Sunderland 284,000; Belfast 268,000. Location: western Europe, bordering the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, the Irish Sea, and Ireland. Mobility (2001). Population living in the same residence as 2000: 88.6%; different residence, same country/region (of the UK) 8.6%; different residence, different country/region (of the UK) 2.1%; from outside the UK 0.7%. Households (2003-04). Average household size 2.4; 1 person 28%, couple 22%, couple with 1-2 children 16%, couple with 3 or more children 3%, single parent with children 6%, other 25%. Immigration (2004): permanent residents 518,000; from Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka 10.6%; South Africa 5.6%; Australia 5.0%; Pakistan 4.1%; US 2.7%; New Zealand 1.5%; Canada 1.0%; other 69.5%, of which EU 20.8%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.4 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 56.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.79. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 75.9 years; female 81.0 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: up to lower secondary education only 16%; upper secondary 56%; higher 28%, of which at least some university 19%. Quality of working life (2004). Average full-time workweek (hours): male 40.8, female 37.5. Annual rate per 100,000 workers (2005; England, Scotland, and Wales only) for: injury or accident 562; death 0.6. Proportion of labor force (employed persons) insured for damages or income loss resultingfrom: injury 100%; permanent disability 100%; death 100%. Average days lost to labor stoppages per 1,000 employee workdays 34. Social participation. Population ages 16 and over participating in voluntary work (2001; England, Scotland, and Wales only) 39%. Trade union membership in total workforce (2003) 27%. Percentage of population attending weekly church services (2001) 8%. Social deviance (2004-05; England and Wales only). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: theft and handling stolen goods 3,822.1; criminal damage 2,234.7; violence against the person 1,951.1; burglary 1,281.9; fraud and forgery 525.8; drug offenses 268.3; robbery 167.2. Material well-being (2005-06). Households possessing: automobile 74%; telephone 92%; refrigerator/freezer 97%; washing machine 95%; central heating 94%; video recorder 86%; digital, cable, or satellite television receiver 65%.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:£485,400,000,000 (income tax 26.9%; production and import taxes 24.9%; social security contributions 17.6%). Expenditures: £500,700,000,000 (social protection 34.2%; health 17.7%; education 13.9%; defense 6.1%; public order 6.0%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$2,425,690,000,000 (US$40,086 per capita). Public debt (2005): US$960,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 14,735,000, sugar beets 7,150,000, potatoes 5,684,000, barley 5,239,000, rapeseed 1,870,000, carrots 832,600, oats 728,000, onions 383,400, cabbages 308,200, apples 218,500; livestock (number of live animals) 34,722,000 sheep, 10,159,910 cattle, 4,933,000 pigs; roundwood (2005)8,589,000 cu m, of which fu-elwood 4%; fisheries production (2005) 842,271 (from aquaculture 21%). Mining and quarrying (2005): sand and gravel 90,000,000; dolomite 13,000,000; chalk 8,000,000; china clay (kaolin) 2,148,000. Manufacturing (value added in £’000,000; 2004): food, beverages, and tobacco 22,570; paper products, printing, and publishing 20,020; transport equipment 18,864; electrical and optical equipment 16,881; chemicals and chemical products 15,645; base metals and fabricated metal products 15,644; machinery and equipment 11,962; rubber and plastic products 8,003. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 395,853,000,000 (403,343,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2005-06) 20,600,000 ([2005] 61,800,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005-06) 565,400,000 ([2005] 598,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 86,003,000 (80,977,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005-06) 99,037,000,000 ([2004] 115,230,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 30,613,000; activity rate of total population 50.6% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 60.1%; female 45.9%; unemployed [June 2007-August 2007] 5.4%). Households. Average household size (2003-04) 2.4; average annual disposable income per household (2004-05) £25,360 (US$46,447); sources of income (2005-06): wages and salaries 67.3%, social security benefits 12.7%, self-employment 8.2%, transfers 7.4%; expenditure (2005-06): food and beverages 18.7%, recreation and culture 18.7%, housing 18.3%, transportation 14.5%, household furnishings 7.6%, clothing and footwear 5.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 25,959; remittances (2006) 7,339; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 62,835. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 58,617; remittances (2006) 3,425; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 73,461. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 23.4%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 46.5%; overall forest area (2005) 11.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): £274,828,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 27.2%, of which electrical machinery 19.3%, nonelectrical machinery 7.9%; transport equipment 14.3%, of which motor vehicles and parts 11.4%, aircraft and other transport equipment 2.9%; chemicals and chemical products 10.6%; petroleum and petroleum products 7.4%; food products 6.7%). Major import sources: Germany 13.9%; US 7.9%; France 7.9%; The Netherlands 7.3%; Belgium/Luxembourg 5.4%; China 4.7%; Italy 4.5%; Norway 4.4%; Spain 3.8%; Ireland 3.7%; Japan 3.1%. Exports(2005; f.o.b.): £209,308,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 29.4%, of which electrical machinery 17.2%, nonelectrical machinery 12.2%; chemicals and chemical products 15.8%, of which pharmaceuticals 5.8%; transport equipment 12.6%, of which motor vehicles and parts 9.2%, aircraft and other transport equipment 3.4%; crude petroleum and petroleum products 9.5%; food products 3.1%). Major export destinations: US 14.7%; Germany 11.0%; France 9.4%; Ireland 7.8%; The Netherlands 5.9%; Belgium/Luxembourg 5.3%; Spain 4.8%; Italy 4.1%; Switzerland 2.4%; Sweden 2.2%; Japan 1.9%; Canada 1.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005-06): length (2005) 17,156 km; passenger-km (England, Scotland, and Wales only) 43,211,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (England, Scotland, and Wales only) 22,000,000,000. Roads (2005; England, Scotland, and Wales only): total length 388,008 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 27,765,100, trucks and buses 3,522,424. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 231,515,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 6,215,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 17,485,000 (292); televisions (2003): 56,576,000 (950); telephone landlines (2006): 33,603,000 (562); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 69,657,000 (1,164); personal computers (2005): 45,659,000 (765); total Internet users (2006): 33,534,000 (560); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 12,995,000 (215).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 122,345 (1 per 492 persons); hospital beds (2004) 233,223 (1 per 257 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 5.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,449 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 191,030 (army 55.0%, navy 21.4%, air force 23.6%); UK troops deployed abroad (2006) 42,900; US troops in the UK (2006) 10,300. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.7%; per capita expenditure US$1,000.
Background
The early pre-Roman inhabitants of Britain were Celtic-speaking peoples, including the Brythonic people of Wales, the Picts of Scotland, and the Britons of Britain. Celts also settled in Ireland c. 500 bc. Julius Caesar invaded and took control of the area in 55-54 bc. The Roman province of Britannia endured until the 5th century and included present-day England and Wales. In the 5th century Nordic tribes of Angles, Saxons, and Jutes invaded Britain. The invasions had little effect on the Celtic peoples of Wales and Scotland.
Christianity began to flourish in the 6th century. During the 8th-9th centuries, Vikings, particularly Danes, raided the coasts of Britain. In the late 9th century Alfred the Great repelled a Danish invasion, which helped bring about the unification of England under Athelstan. The Scots attained dominance in Scotland, which was finally unified under Malcolm II (1005-34).
William of Normandy took England in 1066. The Norman kings established a strong central government and feudal state. The French language of the Norman rulers eventually merged with the Anglo-Saxon of the common people to form the English language. From the 11th century, Scotland came under the influence of the English throne. Henry II conquered Ireland in the late 12th century. His sons, kings Richard I and John, had conflicts with the clergy and nobles, and eventually John was forced to grant the nobles concessions in Magna Carta (1215). The concept of community of the realm developed during the 13th century, providing the foundation for parliamentary government. During the reign of Edward I, statute law developed to supplement English common law, and the first Parliament was convened. In 1314 Robert Bruce won independence for Scotland.
The Tudors became the ruling family of England following the Wars of the Roses (1455-85). Henry VIII established the Church of England and made Wales part of his realm. The reign of Elizabeth I began a period of colonial expansion; 1588 brought the defeat of the Spanish Armada. In 1603 James VI of Scotland ascended to the English throne, becoming James I, and established a personal union of the two kingdoms.
The English Civil Wars erupted in 1642 between Royalists and Parliamentarians, ending in the execution of Charles I (1649). After 11 years of Puritan rule under Oliver Cromwell and his son (1649-60), the monarchy was restored with Charles II. In 1707 England and Scotland assented to the Act of Union, forming the kingdom of Great Britain. The Hanoverians ascended to the English throne in 1714, when George Louis, elector of Hanover, became George I of Great Britain. During the reign of George III, Great Britain’s American colonies won independence (1783). This was followed by a period of war with revolutionary France and later with the empire of Napoleon (1789-1815).
In 1801 legislation united Great Britain with Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Britain was the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century, and it remained the world’s foremost economic power until the late 19th century. During the reign of Queen Victoria, Britain’s colonial expansion reached its zenith, though the older dominions, including Canada and Australia, were granted independence (1867 and 1901, respectively).
The UK entered World War I allied with France and Russia in 1914. Following the war, revolutionary disorder erupted in Ireland, and in 1921 the Irish Free State was granted dominion status. The six counties of Ulster, however, remained in the UK as Northern Ireland. The UK entered World War II in 1939. Following the war the Irish Free State became the Irish Republic and left the Commonwealth. India gained independence from the UK in 1947.
Throughout the postwar period and into the 1970s, the UK continued to grant independence to its overseas colonies and dependencies. With UN forces, it participated in the Korean War (1950-53). In 1956 it intervened militarily in Egypt during the Suez Crisis. In 1982 it defeated Argentina in the Falkland Islands War. As a result of continuing social strife in Northern Ireland, itjoined with Ireland in several peace initiatives, which eventuallyresulted inanagreementto establish an assembly in Northern Ireland. In 1997 referenda approved in Scotland and Wales devolved power to both countries, though both remained part of the UK.
Recent Developments
After 10 years as prime minister of the UK, Tony Blair stepped down on 27 June 2007. He was succeeded by Gordon Brown, who had served as chancellor of the Exchequer under him. Barely 48 hours after Brown became prime minister two car bombs were discovered and defused in central London and a third vehicle was driven into Glasgow (Scotland) Airport, where it caught fire. A series of floods that had started earlier became more intense in the days immediately after he was sworn in—an estimated one million people were directly affected. He subsequently announced £46 million (about US$92 million) in aid and a £500 million (about US$1 billion) annual increase in spending on flood defenses. One month after becoming prime minister, Brown flew to the US for talks with Pres. George W. Bush. Although both men publicly appeared to be in agreement, the encounter was more strained than previous visits from Blair had been. Brown insisted that decisions about British troops in Iraq would be taken on the advice of the UK’s military leaders only. This was evident in September when British troops withdrew from central Basra to Basra Airport, handing over day-to-day control of the city to Iraqi forces and ending the UK’s role in patrolling southern Iraq. In October Brown announced that half of the remaining British force would be withdrawn from Iraq by the spring of 2008, leaving 2,500 troops in the country, but in April 2008 this decision was reversed after a spike in violence in Iraq.
Northern Ireland’s Assembly was reconvened on 8 May, following almost five years of inactivity, after Sinn Fein, the Roman Catholic nationalist party that had historically been associated with the militant Irish Republican Army, ended its long-standing policy of noncooperation with the province’s police service. Ian Paisley, leader of the Protestant Democratic Unionist Party, was sworn in as first minister, with Sinn Fein’s Martin McGuinness as his deputy.
The UK’s economy grew by 3% in 2007, continuing the steady progress that had begun in the early 1990s. Inflation remained subdued, though in April it was announced that the consumer price index had risen by 3.1% over the previous 12 months. Since this exceeded the 2% target set for the Bank of England (BOE), the bank raised the benchmark repo interest rate. Among other things, this had the effect of cooling the housing market. According to figures released by the Halifax bank (the UK’s largest mortgage lender), house prices that had been rising at an annual rate of more than 11% during the first half of 2007 peaked in August and fell in every month after that for the rest of the year. Amid fears that these falls would be accompanied by slower economic growth in 2008, the BOE reduced interest rates again in December.
United States
Official name: United States of America. Form of government: federal republic with two legislative houses (Senate [100]; House of Representatives [435, excluding 4 nonvoting delegates from the District of Columbia, the US Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and Guam; a nonvoting resident commissioner from Puerto Rico; and a nonvoting resident representative from the Northern Mariana Islands]). Head of state and government: President George W. Bush (from 2001). Capital: Washington DC. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 3,676,486 sq mi, 9,522,055 sq km; inland water area equals 78,797 sq mi [204,083 sq km], and Great Lakes water area equals 60,251 sq mi [156,049 sq km]). Population (2007): 302,633,000. Density (2006): persons per sq mi 85.6, persons per sq km 33.0. Urban (2005): 80.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.26%; female 50.74%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 20.5%; 15-29, 20.9%; 30-44, 21.6%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74, 10.7%; 75-84, 4.4%; 85 and over, 1.7%. Population by race and Hispanic origin (persons of Hispanic origin maybe of any race) (2005): non-Hispanic white 66.9%; Hispanic 14.4%; non-Hispanic black 12.8%; Asian and Pacific Islander 4.5%; American Indian and Eskimo 1.0%; other 0.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Christian 83.3%, of which independent Christian 23.2%, Roman Catholic 19.6%, Protestant (including Anglican) 18.9%, unaffiliated Christian 16.5%, Orthodox 1.8%, other Christian (primarily Mormon and Jehovah’s Witness) 3.3%; Jewish 1.9%; Muslim 1.6%; Buddhist 0.9%; New Religionists 0.5%; Hindu 0.4%; traditional beliefs 0.4%; Baha’i 0.3%; Sikh 0.1%; nonreligious 9.8%; atheist 0.5%; other 0.3%. Mobility (2005). Reported gross percentage of population living in the same residence as in 2004:86%; different residence, same county 8%; different county, same state 3%; different state 3%; moved from abroad 1%. Households (2006). Total households 116,011,000 (married-couple families 58,945,000 [50.8%]). Average household size 2.6; 1 person 26.6%, 2 persons 33.0%, 3 persons 16.5%, 4 persons 14.0%, 5 or more persons 9.9%. Family households: 78,425,000 (67.6%); nonfamily 37,587,000(32.4%), of which 1-person 83.1%. Place of birth (2005): native-born 255,999,000 (87.9%); foreign-born 35,157,000 (12.1%), of which (2004) Mexico 10,011,000, Philippines 1,222,000, China/Hong Kong 1,067,000, India 1,007,000, Cuba 952,000, Vietnam 863,000, El Salvador 765,000, South Korea 701,000. Major cities (2006): New York 8,214,426; Los Angeles 3,849,378; Chicago 2,833,321; Houston 2,144,491; Phoenix 1,512,986; Philadelphia 1,448,394; San Antonio 1,296,682; San Diego 1,256,951; Dallas 1,232,940; San Jose 929,936. Location: North America, bordering Canada, the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, Mexico, and the Pacific Ocean; the outlying state of Alaska nearly touches eastern Russia and borders the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean; Hawaii is an island group in the Pacific Ocean. Dependencies: American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and Virgin Islands (of the US). Immigration (2005): permanent immigrants admitted 1,122,400, from Mexico 14.4%, India 7.6%, Africa 7.6%, China 6.2%, Philippines5.4%, Cuba 3.2%, Vietnam 2.9%, Dominican Republic 2.5%, South Korea 2.4%, Ukraine 2.0%, El Salvador 1.9%, Jamaica 1.6%, Poland 1.4%, Haiti 1.3%, Bosnia and Herzegovina 1.3%, other 38.3%. Refugees (2005) 380,000. Asylum seekers (2000) 386,330.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.3 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 64.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.09. Life expectancy at birth (2004): male 75.2 years, of which white male 75.7 years, black male 69.8 years; female 80.4 years, of which white female 80.8 years, black female 76.5 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: primary through incomplete secondary 14.8%; secondary 32.2%; some postsecondary 25.4%; 4-year higher degree 18.1%; advanced degree 9.5%. Number of earned degrees (2004): bachelor’s degree 1,399,542; master’s degree 558,940; doctor’s degree 48,378; first-professional degrees (in fields such as medicine, theology, and law) 63,796. Quality of working life (2007). Average workweek 41.3 hours. Annual death rate per 100,000 workers (2004) 3.5; leading causes of occupational deaths (2004): transportation incidents 24%, falls 14%, assaults/violent acts 14%, struck by object 10%. Annual occupational injury rate per 100,000 workers (2004) 4.8. Average duration of journey to work (2006) 25.0 minutes (private automobile 86.7%, of which drive alone 76.0%, carpool 10.7%; take public transportation 4.8%; walk 2.5%; work at home 4.0%; other 2.0%). Rate per 1,000 employed workers of discouraged workers (unemployed no longer seeking work; 2005) 3.1. Access to services (2005). Proportion of occupied dwellings having access to: electricity 100%; safe public water supply 100%; public sewage collection (1995) 77.0%; septic tanks (1995) 22.8%. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last presidential election (2004) 60.7%. Population ages 16 and over volunteering for an organization (2005): 28.8%; median annual hours 50. Trade-union membership in total workforce (2005) 13.7%. Social deviance (2005). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: murder 5.6; rape 31.7; robbery 140.7; aggravated assault 291.1; motor-vehicle theft416.7; burglaryand housebreaking 726.7; larceny-theft 2,286.3; drug-abuse violation 560.1; drunkenness (2003) 149.1. Estimated drugand substance users (population ages 12 and over; 2004): cigarettes 24.9%; binge alcohol 22.8%; marijuana and hashish 6.1%. Rate per 100,000 population of suicide (2005) 10.7. Leisure (2002). Favorite leisure activities (percentage of total population ages 18 and over that undertook activity at least once in the previous year): movie 60.0%, exercise program 55.0%, gardening47.0%, home improvement 42.0%, amusement park 42.0%, sports events 35.0%, charity work 29.0%. Material well-being (2003). Occupied dwellings with householder possessing: automobiles, trucks, or vans 91.4%, 1 car with or without trucks or vans 48.1%, 2 cars 23.8%, only trucks and vans 12.1%, no cars, trucks, or vans 8.6%, 3 or more cars 7.4%; telephone 95.5%; television receiver 99.0%; video and DVD players (2002) 91.2%; washing machine (2002) 80.1%; clothes dryer (2002) 75.9%; air conditioner (2002) 75.6%; cable television 77.2%; personal computers 61.8%; Internet connections 54.6%; broadband Internet 19.9%. Recreational expenditures (2003): US$660,700,000,000 (television and radio receivers, computers, and video equipment 18.4%; golfing, bowling, and other participatory activities 13.5%; sports supplies 10.3%; nondurable toys and sports equipment 9.1%; books and maps 5.8%; magazines and newspapers 5.5%; spectator amusements 5.4%, of which theater and opera 1.7%, spectator sports 2.1%, movies 1.5%; flowers,seeds, and potted plants 2.8%; other 29.2%).
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:US$2,285,491,000,000(in-come tax 43.6%; social-insurance taxes and contributions 36.8%; corporate taxes 12.1%; excise taxes 3.2%; other 4.3%). Expenditures: US$2,708,677,-000,000 (social security and medicare 33.1%; defense 18.9%; health 9.9%; interest on debt 8.1%; other 30.0%). Total outstanding national debt (September 2007): US$9,027,000,000,000, of which debt held by the public US$5,385,500,000,000, intragovernment holdings US$3,641,500,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$13,150,600,000,000 (US$43,424 per capita). Production. Agriculture, forestry, fishing (value of production in US$’000,000 except as noted; 2005): corn (maize) 21,859, soybeans 16,928, alfalfa hay 7,320, wheat 7,140, cotton 5,574, grapes 3,013, potatoes 2,903, almonds 2,725, tomatoes 2,260, lettuce 1,982, rice 1,789, apples 1,787, lemons 1,498, strawberries 1,383, sugar beets (2004) 1,107, tobacco 1,053, beans 950, onions 922, mushrooms 908, peanuts (groundnuts) 846, sugarcane (2004) 821, cottonseed 809, sorghum 715, peppers 598, carrots 587, pistachios 574, broccoli 564, cherries 549, peaches 510, barley 506, sunflowers 472, walnuts (2004) 452, watermelons 410, pecans 400, oranges 398, cucumbers 383, blueberries 359, grapefruit 352, cabbage 325, pears 315, sweet potatoes 309, cantaloupe 300, avocados (2004) 293; livestock (number of live animals) 95,838,000 cattle, 61,197,000 pigs, 9,200,000 horses, 6,135,000 sheep, 1,950,000,000 chickens; roundwood 471,862,000 cu m (coniferous 312,700,000 cu m, non-coniferous 159,162,000 cu m), of which fuelwood 9%; fisheries production 5,360,579 metric tons (from aquaculture 9%); aquatic plants production 35,922 (from aquaculture, none). Metals mining (metal content in metric tons unless otherwise noted; 2005): molybdenum 56,900 (world rank: 1); beryllium 90 (world rank: 1); copper 1,150,000(world rank: 2); lead 440,000 (world rank: 3); gold 250,000 kg (world rank: 3); palladium 14,200 kg (world rank: 3); platinum 4,200 kg (world rank: 4); zinc 760,000 (world rank: 5); iron 55,000,000 (world rank: 7); silver 1,300,000 kg (world rank: 7). Nonmetals mining (metric tons; 2005): diatomite 635,000 (world rank: 1); bromine 212,000 (world rank: 1); boron 1,230,000 (world rank: 2); perlite 506,000 (world rank: 2); vermiculite 105,000 (world rank: 2); kyanite 90,000 (world rank: 2); barite 500,000 (world rank: 3); feldspar 760,000 (world rank: 4); silicon 276,000 (world rank: 4). Quarrying (metric tons; 2005): salt 45,900,000 (world rank: 1); phosphate rock 38,300,000 (world rank: 1); gypsum 17,500,000 (world rank: 1); lime 20,000,000 (world rank: 2). Manufacturing (value added inUS$’000,000; 2004): chemicals and chemical products 295,328, of which pharmaceuticals and medicine 120,870; transportation equipment 255,974, of which motor vehicle parts 70,796, motorvehicles 84,807, aerospace products and parts 67,594; food and food products 223,433; electronic products 214,650, of which navigational, measuring, medical, and scientific equipment 66,470, communications equipment 30,347, computers and related components 32,344; fabricated metal products 143,899; nonelectrical machinery 133,826; plastic and rubber products 91,517; paper and paper products 74,016; beverages and tobacco products 71,700; refined petroleum and coke 61,830; nonferrous metals 58,800; printing and publishing 57,250; general electrical equipment 52,723; furniture 45,441; wood and wood products 43,662; textiles 32,226; iron and steel 31,445. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 4,174,481,000,000 (4,185,793,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 510,918,000 (502,548,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 497,961,000 (497,934,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 1,965,000,000 (5,869,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 814,664,000 (829,104,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 529,874,000,000 (622,400,000,000). Domestic production of energy by source (2005): coal 33.3%, natural gas 27.2%, crude petroleum 15.7%, nuclear power 11.8%, renewable energy 8.8%, other 3.2%. Energy consumption by source (2006): petroleum and petroleum products 40.3%, natural gas 22.4%, coal 22.5%, nuclear electric power 8.2%, hydroelectric and thermal 2.9%, other renewable energy 3.7%; by end use (2006): industrial 32.3%, residential and commercial 39.2%, transportation 28.5%. Households. Average household size (2006) 2.6; median annual income per household (2006) US$48,201, of which median Asian (including Hispanic) household US$64,238, median white (including Hispanic) household US$50,673, median non-Hispanic household US$52,423, median Hispanic household US$37,781, median black (including Hispanic) household US$31,969; sources of personal income (2004): wages and salaries 68.6%, transfer payments 14.5%, self-employment 9.3%; consumption expenditure (2005): housing 19.0%, transportation 18.0%, insurance and pension 11.2%, food at home 7.1%, fuel and utilities 6.9%, health 5.7%, food away from home 5.7%, recreation 5.1%, wearing apparel 4.1%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco products 1.6%. Average annual expenditure of “consumer units” (households, plus individuals sharing households or budgets; 2005): total US$46,409, of which housing US$15,167, transportation US$8,344, food US$5,931, pensions and social security US$5,204, health care US$2,664, clothing US$1,886, other US$7,213. Selected household characteristics (2006): total number of households 116,011,000, of which (family households by race) white including Hispanic 82.6%, black including Hispanic 12.1%, other 5.3%; Hispanic of any race 14.9%; (by tenure) owned 79,266,000 (68.3%), rented 35,129,000 (30.3%), other 1,616,000 (1.4%); family households 78,425,000, of which married couple 75.2%, female householder 18.4%, male householder 6.4%; nonfamily households 37,587,000, of which female living alone 46.8%, male living alone 36.0%, other 17.2%. Population economically active (2007): total 153,231,000 (civilian population only); activity rate of total population 50.6% (participation rates [2004]: ages 16-64, 74.0%; female 46.5%; unemployed [August 2007] 4.6%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 102,611; remittances (2006)2,935; foreigndi-rect investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 101,785. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 95,730; remittances (2006) 42,794; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 119,779. Number of foreign visitors (2007) 56,716,277 (17,735,000 from Canada, 15,089,000 from Mexico, 11,406,486from Europe); numberof nationals traveling abroad (2006) 63,662,000 (19,659,000 to Mexico, 13,855,000 to Canada). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 19.3%, in permanent crops 0.3%, in pasture 25.9%; overall forestarea (2005) 33.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$1,855,400,000,000 ([2005]; motor vehicles and parts 11.7%; crude petroleum 10.9%; chemicals and chemical products 7.7%; computers and office equipment 6.2%; electrical machinery 5.9%; industrial machinery 5.1%; wearing apparel 4.5%; food and beverages 4.1%; iron and steel 1.5%; footwear 1.1%). Majorimport sources: Canada 16.4%; China 15.5%; Mexico 10.7%; Japan 8.0%; Germany 4.8%; UK 2.9%; South Korea 2.5%; Taiwan 2.1%; France 2.0%; Venezuela 2.0%; Malaysia 2.0%; Italy 1.8%; Ireland 1.5%; Nigeria 1.5%. Exports (2006): US$1,037,300,000,000(chemicals and related products 13.3%; electrical machinery8.2%; motorvehicles 7.9%; agricultural commodities 7.0%; airplanes and parts 5.2%; power-generating machinery 4.6%; general industrial machinery 4.3%; telecommunications equipment 4.2%; computers and office equipment 3.9%; scientific and precision equipment 3.8%; specialized industrial machinery 3.7%). Major export destinations: Canada 22.2%; Mexico 12.9%; Japan 5.8%; China 5.3%; UK 4.4%; Germany 4.0%; South Korea 3.1%; The Netherlands 3.0%; Singapore 2.4%; France 2.3%; Taiwan 2.2%; Belgium 2.1%; Brazil 1.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 156,300 km, of which Amtrak operates 35,610 km; passen-ger-km 41,574,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2006) 2,835,000,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 6,370,400 km (paved 91%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 136,431,000; trucks and buses 100,811,000. Navigable channels (2004) 41,843 km; oil pipeline length (2003) 258,892 km; gas pipeline length (2004) 2,353,300 km. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 1,275,875,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 46,853,000,000. Certified route passenger/cargo air carriers (2005) 80; operating revenue (US$’000,000; 2006) 163,824; operating expenses 156,279. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 53,300,000 (180); televisions (2003): 260,000,000 (893); telephone landlines (2006): 172,032,000 (572); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 233,000,000 (774); personal computers (2005): 223,810,000 (755); total Internet users (2006): 197,800,000 (663); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 49,391,000 (167).
Education and health
Literacy (2003): percentage of population ages 16 and over: “illiterate” (able to perform no more than the most simple literacy skills) 14%; “basically literate” (able to perform simple and everyday literacy activities) 29%; “intermediately and proficiently literate” (able to perform moderately challenging to complex literacy activities) 57%. Health: doctors of medicine (2004) 885,000 (1 per 337 persons), of which office-based practice 538,500; male 74.5%; female 25.5% (includingspecialties in internal medicine 18.9%, general and family practice 13.6%, pediatrics 9.4%, obstetrics and gynecology 6.3%, anesthesiology 5.6%, psychiatry 4.8%, general surgery 4.7%, emergency medicine 3.5%, orthopedic surgery 3.5%, cardiovascular diseases 3.2%, diagnostic radiology 3.1%, ophthalmology 3.0%, pathology 2.0%); doctors of osteopathy 54,100; nurses 2,421,000 (1 per 824 persons); dentists 167,000 (1 per 1,760 persons); hospital beds (2004) 956,000 (1 per 313 persons), of which nonfederal 95.0%(community hospitals84.5%, psychiatric 9.0%, long-term general and special 1.6%), federal 5.0%; infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 6.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,754(vegetable products 72.2%, animal products 27.8%); 143% of FAO recommended minimum. Per capita consumption of major food groups (kilograms annually; 2005): milk 256.4; fresh vegetables 125.5; cereal products 177.2; fresh fruits 122.7; red meat 62.7; potatoes 54.7; poultry products 55.8; fats and oil 31.6; sugar 30.2; fish and shellfish 23.4.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,547,257 (army 38.5%, navy 24.3%, air force 22.5%, marines 12.1%, coast guard 2.6%). Total reserve duty personnel (2006): national guard 464,830 (army 75.6%, air force 24.4%); ready reserves 973,675 (army 55.4%, navy 16.0%, air force 18.3%, marines 9.4%, coast guard 0.9%). Total special operations forces (2006): active 31,496; reserve 11,247. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.1%; per capita expenditure US$1,700. Foreign military sales to the world (2006): US$18,163,000,000, of which to Pakistan 19.2%, to Australia 13.4%, to Greece 11.7%, to Israel 5.8%, to Japan 5.7%, to Turkey 5.4%.
Background
The territory that is now the US was originally inhabited for several thousand years by numerous American Indian peoples who had probably emigrated from Asia. European exploration and settlement from the 16th century began displacement of the Indians. The first permanent European settlement, by the Spanish, was at St. Augustine FL, in 1565; the British settled Jamestown VA (1607), Plymouth MA (1620), Maryland (1632), and Pennsylvania (1681). They took New York, New Jersey, and Delaware from the Dutch in 1664, a year after the Carolinas had been granted to British noblemen. The British defeat of the French in 1763 ensured British political control over the 13 colonies.
Political unrest caused by British colonial policy culminated in the American Revolution (1775-83)and the Declaration of Independence (1776). The US was first organized under the Articles of Confederation (1781) and then finally under the Constitution (1787) as a federal republic. Boundaries extended west to the Mississippi River, excluding Spanish Florida. Land acquired from France by the Louisiana Purchase (1803) nearly doubled the country’s territory. The US fought the War of 1812 with the British and acquired Florida from Spain in 1819. In 1830 it legalized removal of American Indians to lands west of the Mississippi River. Settlement expanded to the West Coast in the mid-19th century, especially after the discovery of gold in California in 1848. Victory in the Mexican War (1846-48) brought the territory of seven more future states (including California and Texas) into US hands. The northwestern boundary was established by treaty with Great Britain in 1846. The US acquired southern Arizona by the Gadsden Purchase (1853). It suffered disunity during the conflict between the slavery-based plantation economy in the South and the free industrial and agricultural economy in the North, culminating in the American Civil War and the abolition of slavery under the 13th Amendment.
After Reconstruction (1865-77), the US experienced rapid growth, urbanization, industrial development, and European immigration. In 1877 it authorized allotment of Indian reservation land to individual tribesmen, resulting in widespread loss of land to whites. By the beginning of the 20th century, it had acquired outlying territories, including Alaska, the Midway Islands, the Hawaiian Islands, the Philippines, Puerto Rico, Guam, Wake Island, American Samoa, the Panama Canal Zone, and the Virgin Islands.
The US participated in World War I during 1917-18. It granted suffrage to women in 1920 and citizenship to American Indians in 1924. The stock market crash of 1929 led to the Great Depression. The US entered World War II after the Japanese bombing of Pearl Harbor (7 Dec 1941). The explosion of the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima, Japan (6 Aug 1945), brought about the end of the war and set the US apart as a military power. After the war the US was involved in the reconstruction of Europe and Japan and embroiled in a rivalry with the Soviet Union that became known as the Cold War. It participated in the Korean War. In 1952 it granted autonomous commonwealth status to Puerto Rico.
Racial segregation in schools was declared unconstitutional in 1954. Alaska and Hawaii were made states in 1959, bringing the total to 50. In 1964 Congress passed the Civil Rights Act and authorized full-scale intervention in the Vietnam War. The mid- to late 1960s were marked by widespread civil disorder, including race riots and antiwar demonstrations. The US accomplished the first manned lunar landing in 1969. All US troops were withdrawn from Vietnam by 1973. The US led a coalition of forces against Iraq in the Persian Gulf War (1991), sent troops to Somalia (1992) to aid starving populations, and participated in NATO air strikes against Serb forces in the former Yugoslavia in 1995 and 1999. Administration of the Panama Canal was turned over to Panama in 1999. The US led another coalition invading Iraq in March 2003 to end the rule of Saddam Hussein.
Recent Developments
Pres. George W. Bush decided in 2007 to increase the US military presence in Iraq with a “surge” of some 30,000 reinforcements. The plan ran counter to majority opinion—from Congress, the Iraq Study Group, and US public-opinion polls. At the surge’s peak, some 160,000 US troops were on Iraqi deployment. By year’s end it had become obvious that the insurgency had lost some momentum—violent incidents were down by two-thirds and Iraqis had taken over security in many areas. Even so, US military deaths in Iraq reached 899 for the year, the highest number since the 2003 US-led incursion.
Islamic radicals, sheltered in sanctuaries in lawless areas of western Pakistan and financed in part by opium production, escalated armed clashes in Afghanistan, and for the first time, US troop deaths there topped 100. At a NATO summit in Bucharest, Romania, in April 2008, France, the Czech Republic, and Romania, among others, pledged to substantially increase their troop commitments in Afghanistan.
Democrats took control of Congress from Republicans in January 2007, promising major changes. However, Bush and the Republican minority, utilizingvetos and procedural rules, managedtoalterorhaltmanyini-tiatives. In the spring Democrats attached an amend-mentsetting a timeline for withdrawal of US forces to a US$90 billion supplemental Iraq War appropriation. Bush rejected the measure—only his second veto in more than six years in office. Amid GOP warnings that US troops needed resupply, Democrats were forced to pass the appropriation without timeline amendments, part of the US$200 billion that Bush was able to obtain for the war in 2007 with no strings attached. President Bush vetoed five additional bills during the year, including ones thatexpanded federal fundingfor embryonic-stem-cell research and doubled expenditures for the State Children’s Health Insurance Program, and threatened rejection of some 50 more. Republicans stymied a plan to force pharmaceutical companies to negotiate with the government over Medicare drug prices and a US$50 billion expansion for the Alternative Minimum Tax, a law originally written to ensure that the wealthy paid at least minimal taxes. A threatened veto forced removal of provisions rolling back tax breaks to oil and gas companies. Numerous investigations of past administration actions were launched; one, regardingthe firing of eight US attorneys in 2006, led to the resignation of Attorney General Alberto Gonzales. Former vice presidential chief of staff I. Lewis (“Scooter”) Libby was convicted in March 2007 of having lied about his involvement in the leak of a covert CIA officer’s identity, but Bush quickly commuted his prison sentence. Congress was able to override only one Bush veto in 2007— an appropriations measure that included funding for rebuilding the hurricane-devastated Gulf coast. Congress also succeeded in raising the minimum wage for the first time in a decade, from US$5.15 to US$7.25 per hour by 2009, and passing a law to reduce interest rates on student loans. Congress provided a record funding increase for veterans’ health care programs and significantly tightened Washington lobbying and ethics rules. Congress also passed new legislation to expand the use of alternative energy, increase vehicle mileage standards by 40% by 2020, and phase out incandescent light bulbs in favor of fluorescent lighting.
The US economy expanded by almost 3% for the year, though the unemployment rate rose from 4.4% to 5.0%. Of major concern was an overheated real-estate market that brokers had fueled by offering adjustable-rate mortgages at low initial interest rates. By mid-2007, however, a substantial minority of homeowners could not make their payments when their interest rates were adjusted upward, leading to rising delinquency rates and foreclosures. An estimated US$500 billion worth of “subprime” mortgage securities were devalued, reducingthe lending capacity of financial institutions. The federal budget deficit declined to US$163 billion by the end of the 2007 fiscal year, but the trade deficit continued at a historic level, and the US dollar lost 10% of its value to the euro in 2007 alone.
An apparent foreign-relations success involved North Korea, which for four years had resisted calls to dismantle its fledgling nuclear-weapons capacity. In September 2007 negotiators announced that North Korea had agreed to catalog and dismantle its nuclear-testing sites in return for a US$300 million aid package. At year’s end North Korea failed to honor a disclosure deadline, but in May 2008 the country turned over a large, if incomplete, file of documents relating to its nuclear programs.
US relations with Russia deteriorated during the year. US officials were openly critical of Vladimir Putin’s centralization of control over the Russian government, suggesting democracy was being undermined, and this notion was strengthened when Putin, barred from seeking a third consecutive term as president in 2008, accepted the role of prime minister from his hand-picked successor in May 2008. As the US pushed toward installing missile defense shields in Poland and the Czech Republic, Russia suspended its participation in the 1990 Conventional Forces in Europe Treaty, an arms-control agreement, and threatened to aim nuclear missiles at European targets.