Malaysia
Official name: Malaysia. Form of government: federal constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [70]; House of Representatives [219]). Chief of state: Yang di-Pertuan Agong (Paramount Ruler) Tuanku Mizan Zainal Abidin ibni al-Marhum Sultan Mahmud (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Datuk Seri Abdullah Ahmad Badawi (from 2003). Capital: transferring from Kuala Lumpur to Putrajaya between 1999 and 2012. Official language: Malay. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 ringgit, or Malaysian dollar (RM) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = RM 3.27.
Demography
Area: 127,366 sq mi, 329,876 sq km. Population (2007): 26,572,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 208.6, persons per sq km 80.6. Urban (2005): 67.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.75%; female 49.25%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 32.4%; 15-29, 26.2%; 30-44, 20.6%; 45-59, 13.8%; 60-74, 5.6%; 75-84, 1.2%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2005): Malay 50.5%; other indigenous 11.0%; Chinese 23.5%; Indian 7.0%; other citizen 1.2%; noncitizen 6.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 60.4%; Buddhist 19.2%; Christian 9.1%; Hindu 6.3%; Chinese folk religionist 2.6%; ani-mist 0.8%; other 1.6%. Major cities (2000): Kuala Lumpur 1,297,526; Ipoh 566,211; Klang 563,173; Petaling Jaya 438,084; Johor Bahru 384,613; Putra-jaya (2006) 55,000. Location: southeastern Asia, on the Malay Peninsula and the northern third of the island of Borneo, bordering Thailand, the South China Sea, Brunei, and Indonesia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.5 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.07. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 71.8 years; female 76.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: RM 105,856,000,000 (income tax revenue 71.2%, of which corporate taxes 19.4%, taxes on petroleum 15.9%, personal income taxes 9.4%, excises 7.9%; nontax revenue 28.8%). Expenditures: RM 128,755,000,000 (current expenditure 76.3%; developmentexpenditure 23.7%). Population economically active (2004): total 10,353,600; activity rate of total population 40.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2000] 65.5%; female 47.3%; unemployed [April 2006-March 2007] 3.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): oil palm fruit 75,650,000, rice 2,154,000, natural rubber 1,283,600; livestock(num-ber of live animals) 2,168,000 pigs, 185,000,000 chickens; roundwood 28,237,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 11%; fisheries production (2005) 1,390,000 (from aquaculture 13%). Mining and quarrying (2004): iron ore 663,732; tin (metal content) 2,745; gold 4,221 kg. Manufacturing (value added in RM ’000,000; 2004): electrical machinery/electronics 39,790; chemical products 16,468; petroleum and coal products 16,183. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 82,282,000,000 (81,759,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 792,000 ([2004] 13,275,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 250,500,000 ([2004] 200,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 20,450,000 (21,244,000); natural gas (cu m; May 2006-April 2007) 60,360,000,000 ([2004] 30,045,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$141,751,000,000 (US$5,428 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$22,449,000,000. Households. Average household size (2004) 4.6; annual gross income per household (2002) RM 36,132 (US$9,508); expenditure (2003): food and nonalcoholic beverages 26.0%, housing and energy 22.1%, transportation 20.8%, restaurantsand hotels 6.1%.Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 8,846; remittances (2006) 1,492; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,964; official development assistance (2005) 798 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,711; remittances (2006) 5,527; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1,715. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.5%, in permanent crops 17.6%, in pasture 0.9%; overall forest area (2005) 63.6%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): RM 400,076,800,000 (micro-circuits, transistors, and valves 25.7%; computers/office machines 5.9%; petroleum products 5.3%; telecommunications equipment 3.6%). Major import sources (2006): Japan 13.2%; US 12.5%; China 12.1%; Singapore 11.7%; Thailand 5.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): RM 588,965,000,000 (semiconductors/office machines 37.6%; crude and refined petroleum 8.8%; telecommunications equipment 5.9%; natural gas 4.0%; palm oil 3.7%). Major export destinations (2006): US 18.8%; Singapore 15.4%; Japan 8.9%; China 7.2%; Thailand 5.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 1,949 km; passenger-km 1,152,139,000; metric ton-km cargo I,016,730,000. Roads (2004): total length 77,695 km (paved 76%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 5,987,421; trucks and buses 827,215. Airtransport (2006; Malaysia Airlines only): passenger-km 41,100,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,598,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 2,435,000 (93); televisions (2003): 5,480,000 (222); telephone landlines (2006): 4,342,000 (163); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 19,464,000 (731); personal computers (2005): 5,600,000 (218); total Internet users (2006): II,292,000 (424); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 897,000 (34).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling/unknown 8.4%; primary education 28.7%; lower secondary 20.7%; upper secondary 31.1%; higher 11.1%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 94.4%; males literate 95.6%; females literate 93.2%. Health (2004): physicians 18,246 (1 per 1,402 persons); hospital beds 47,822 (1 per 535 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 6.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,035 (vegetable products 84%, animal products 16%); 164% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 109,000 (army 73.4%, navy 12.8%, air force 13.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.4%; per capita expenditure US$119.
Background
Malaya has been inhabited for 6,000-8,000 years, and small kingdoms existed in the 2nd-3rd century ad, when adventurers from India first arrived. Suma-tran exiles founded the city-state of Malacca about 1400, and it flourished as a trading and Islamic religious center until its capture by the Portuguese in 1511. Malacca passed to the Dutch in 1641. The British founded a settlement on Singapore Island in 1819, and by 1867 they had established the Straits Settlements, including Malacca, Singapore, and Penang. During the late 19th century the Chinese began to migrate to Malaya. Japan invaded in 1941. Opposition to British rule led to the creation of the United Malays National Organization (UNMO) in 1946, and in 1948 the peninsula was federated with Penang. Malaya gained independence in 1957, and the Federation of Malaysia was established in 1963. Its economy expanded greatly from the late 1970s, but it suffered from the economic slump that struck the area in the mid-1990s.
Recent Developments
Malaysia’s economy remained robust in 2007, with GDP growth of 6.3% for the year. The country enjoyed a large trade surplus, but with plantations in Johor damaged by flooding, exports of palm oil (Malaysia’s most valuable agricultural export, contributing about 13% of the value of GDP in 2007) dropped by about 10%. One year after its launch in September 2006, Malaysia’s biotechnology initiative had attracted about 40 companies and investments of 1 billion ringgit (about US$300 million). In February Malaysia, Indonesia, and Brunei pledged to protect 200,000 sq km (124,000 sq mi) of rainforest on the island of Borneo, where palm-oil plantations and logging had destroyed vast tracts of rainforest. In June the US added Malaysia to a list of countries that it said were not doing enough to stop human trafficking, a charge the government denied. Free-trade negotiations with the United States broke down and showed no signs of starting again in 2008.
Maldives
Official name: Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa (Republic of Maldives). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Majlis [50]). Head of state and government: President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom (from 1978). Capital: Male. Official language: Divehi. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Maldivian rufiyaa (Rf) = 100 laari; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Rf 12.80.
Demography
Area: 115 sq mi, 298 sq km. Population (2007): 305,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 6,763, persons per sq km 2,611. Urban (2006): 34.7%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.66%; female 49.34%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 31.1%; 15-29, 33.2%; 30-44, 18.3%; 45-59, 9.2%; 60-74, 5.2%; 75-84,1.1%; 85 and over, 0.2%; unknown 1.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Maldivian 98.5%; Sinhalese 0.7%; other 0.8%. Religious affiliation: virtually 100%
Sunni Muslim. Major islets (2006): Male (capital island) 103,693; Hithadhoo 9,465; Fuvammulah 7,636; Kulhudhuffushi 6,998; Thinadhoo 4,442. Location: islands in the Indian Ocean, south of India.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 3.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.72. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.7 years; female 72.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: Rf 6,548,800,000 (nontax revenue 41.3%, of which resort lease rent 19.2%; tax revenue 32.2%, of which import duties 23.2%; grants 25.9%; other 0.6%). Expenditures: Rf 8,644,700,000 (community programs 25.7%; economic services 18.0%; general administration 17.6%; education 13.6%; police/security 10.4%; health 8.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 15,827, bananas 3,930; fisheries production 185,980, of which skipjack 132,100, yellowfin tuna 24,600. Mining and quarrying: coral for construction materials. Manufacturing: major industries include boat building and repairing, coir yarn and mat weaving, coconut and fish processing, lacquerwork, garment manufacturing, and handicrafts. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 160,000,000 (160,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (236,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 287; remittances (2006) 2; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 13; official development assistance (2005) 67. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 70; remittances (2006) 84. Population economically active (2006): total 128,836; activity rate of total population 43.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 65.8%; female 41.3%; unemployed 14.4%). Households (2002-03). Average household size (2006) 6.5; average annual income per household Rf 188,743 (US$14,746); sources of income: self-employment 34.5%, wages and salaries 31.5%, rent 13.4%; expenditure: housing and energy 35.8%, food, beverages, and tobacco 29.9%, transportation and communications 7.8%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 13%, in permanent crops 30%, in pasture 3%; overall forest area (2005) 3%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$870,000,000 (US$2,897 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; December 2006): US$267,300,000.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$644,700,000 (consumer goods 34.2%, of which food products 15.2%; petroleum products 19.6%; construction-related goods 13.1%; transport equipment 8.2%). Major import sources:Singapore 23.9%; UAE 21.1%; India 9.4%; Malaysia 6.6%; Sri Lanka 6.1%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$225,200,000 (domestic exports 60.0%, of which chilled or frozen tuna 44.8%, dried fish 5.6%, canned fish 5.1%; reexports [mostly jet fuel] 40.0%). Major export destinations: Thailand 26.1%; Japan 15.0%; Sri Lanka 12.8%; UK 9.7%; France 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Vehicles: passenger cars (2007) 3,393; trucks and buses (2005) 1,573. Air transport (2005; Male airport only): passenger arrivals 773,845, passenger departures 761,922; cargo unloaded 17,336 metric tons, cargo loaded 10,923 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 8,000 (25); televisions (2003): 41,000 (144); telephone landlines (2006): 33,000 (110); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 263,000 (876); personal computers (2005): 45,000 (152); total Internet users (2005): 20,000 (68); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 4,700 (16).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Population ages 25 and over 71,937, of which percentage with university education 0.4%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 97.4%; males literate 97.4%; females literate 97.3%. Health (2005): physicians 380 (1 per 775 persons); hospital beds 765 (1 per 384 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 12.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,327 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 181% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): n.a.; the national security service (paramilitary police force) includes an air element and coast guard. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 5.5%; per capita expenditure US$169.
Background
The archipelago was settled in the 5th century bc by Buddhists from Sri Lanka and southern India, and Islam was adopted there in 1153. The Portuguese held sway in Male in 1558-73. The islands were a sultanate under the Dutch rulers of ceylon (now Sri Lanka) during the 17th century. After the British gained control of ceylon in 1796, the area became a British protectorate, a status formalized in 1887. The islands won full independence from Britain in 1965, and in 1968 a republic was founded. During the 1990s its economy gradually developed.
Recent Developments
In the wake of the first-ever bomb explosion in Male targeting foreign tourists, the government remained seriously concerned over the growing threat of Islamic extremism. As a countermeasure, it began to crack down on religious groups advocating Islamic fundamentalism and militancy. Among other steps, the government declared that bearded mullahs or clerics were barred from entering the country unless invited by the authorities. The political reform process continued at a snail’s pace in 2007. An August referendum on the nature of the political system resulted in an overwhelming number of voters choosing a presidential system over a parliamentary one. In August 2008, however, a new constitution, providing for multiparty elections, was signed and adopted.
Mali
Official name: Republique du Mali (Republic of Mali). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [147]). Chief of state: President Amadou Toumani Toure (from 2002). Head of government: Prime Minister Modibo Sidibe (from 2007). Capital: Bamako. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60.
Demography
Area: 482,077 sq mi, 1,248,574 sq km. Population (2007): 11,995,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 24.9, persons per sq km 9.6. Urban (2005): 30.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.67%; female 50.33%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 48.1%; 15-29, 27.7%; 30-44,12.9%; 45-59, 6.4%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Bambara 30.6%; Senufo 10.5%; Fula Macina (Niafunke) 9.6%; Soninke 7.4%; Tuareg 7.0%; Maninka 6.6%; Songhai 6.3%; Dogon 4.3%; Bobo 3.5%; other 14.2%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 90%; Christian (mostly Roman Catholic) 5%; traditional beliefs/nonreligious 5%. Major cities (1998): Bamako (2005; urban agglomeration) 1,368,000; Sikasso 113,803; Segou 90,898; Mopti 79,840; Koutiala 74,153. Location: western Africa, bordering Algeria, Niger, Burkina Faso, Cote d’Ivoire, Guinea, Senegal, and Mauritania.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 49.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 33.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 7.42. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 47.2 years; female 51.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:CFAF 694,300,000,000 (tax revenue 66.1%; grants 23.4%; nontax revenue 4.3%; other 6.2%). Expenditures:CFAF 795,100,000,000 (current expenditure 56.8%; capital expenditure 43.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$2,843,000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 148; remittances (2006) 177; foreign direct invest-ment(2001-05 avg.) 152; official development assistance (2005)691. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 77; remittances (2006) 70. Population economically active (2004): total 2,598,200; activity rate of total population 23% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 51.1%; female 42.5%; officially unemployed 8.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): millet 1,157,810, rice 945,823, corn (maize) 634,464; livestock (number of live animals) 12,050,000 goats, 8,370,000 sheep, 7,700,000 cattle, 472,000 camels; roundwood 5,440,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 92%; fisheries production 101,008 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): salt 6,000; gold 44,230 kg. Manufacturing (2001): beef and veal 215,000; mutton and lamb meat 66,000; raw sugar (2003) 34,000. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 455,000,000 (455,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (184,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.0. Gross national income (2006): US$5,704,000,000 (US$477 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3.9%, in permanentcrops, 0.03%, in pasture 28.4%; overall forest area (2005) 10.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 669,000,000,000 (petroleum products 32.5%; machinery and apparatus 24.1%; food products 21.2%). Major import sources (2004): African countries 49.3%, of which Senegal 9.8%, Cote d’Ivoire 7.6%; France 14.5%; Germany 4.0%. Exports (2005): CFAF 598,900,000,000 (gold 65.0%; raw cotton and cotton products 24.2%). Major export destinations (2004): China 31.6%; Thailand 6.9%; Italy 6.9%; Germany 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length (2004) 729 km; passenger-km 196,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 188,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 18,709 km (paved 18%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 18,900; trucks and buses 31,700. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 34,000 (3.1); televisions (2004): 400,000 (36); telephone landlines (2006): 83,000 (5.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,513,000 (129); personal computers (2005): 45,000 (4.1); total Internet users (2006): 70,000 (5.0); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,900 (0.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 82.1%; incomplete primary education 7.7%; complete primary 2.0%; secondary 6.5%; higher 1.7%. Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 29.5%; males literate 40.0%; females literate 19.4%. Health: physicians (2004) 1,053 (1 per 10,566 persons); hospital beds (2001) 1,664 (1 per 6,203 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 107.5.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 7,350 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$10.
Background
Inhabited since prehistoric times, the region was situated on a caravan route across the Sahara. In the 12th century the Malinke empire of Mali was founded on the Upper and Middle Niger. In the 15th century the Songhai empire in the Timbuktu-Gao region gained control. In 1591 Morocco invaded the area, and Timbuktu remained under the Moors for two centuries. In the mid-19th century the French conquered the area, which became a part of French West Africa known as the French Sudan. In 1946 it became an overseas territory of the French Union. It was proclaimed the Sudanese Republic in 1958, briefly joined with Senegal (1959-60) to form the Mali Federation, and became the Republic of Mali in 1960. The government was overthrown by military coups in 1968 and 1991. Elections were held in 1992 and 1997, but political instability continued.
Recent Developments
In late August 2007 members of a dissident Tuareg group, allied with the Niger Movement for Justice, launched two attacks on military targets in northern Mali. The rebels had refused to accept a 2006 peace settlement. At least 35 soldiers were kidnapped, while 11 civilians were reported killed by land mines. In September seven Tuaregs and one soldier died in a skirmish near Tinzaouatene, in northeastern Mali.
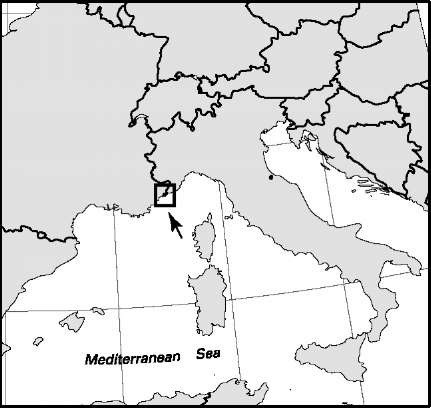
Malta
Official name: Repubblikka ta’ Malta (Maltese); Republic of Malta (English). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (House of Representatives [65]). Chief of state: President Eddie Fenech Adami (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Lawrence Gonzi (from 2004). Capital: Valletta. Official languages: Maltese; English. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 121.9 sq mi, 315.6 sq km. Population (2007): 409,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 3,355, persons per sq km 1,296. Urban (2005): 95.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.59%; female 50.41%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 17.2%; 15-29, 21.7%; 30-44, 19.7%; 45-59, 22.3%; 60-74, 13.5%; 75-84, 4.5%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2005): Maltese 97.0%; other European 23.7%, of which British 1.2%; other 0.7%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 95%; other Christian 0.5%; Muslim 0.7%; nonreligious/atheist 2%; other 1.8%. Major localities (2005): Birkirkara 21,858; Mosta 18,735; Qormi 16,559; Zabbar 14,671; Valletta 6,300 (urban agglomeration 81,047). Location: islands in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Sicily (Italy).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.4 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 80.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 1.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.37. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 77.7 years; female 81.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Lm 1,032,046,000 (social security 21.5%; income tax 19.0%; grants and loans 17.1%; VAT 16.3%). Expenditures: Lm 985,552,000 (recurrent expenditures 76.7%, of which social security 22.4%, education 5.2%; capital expenditure 13.3%; public debt service 9.0%). Public debt (2006): US$731,600,000. Production (metric tons except where noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): potatoes 22,000, melons 17,680, tomatoes 15,910; livestock (number of live animals) 73,025 pigs, 19,742 cattle, 14,642 sheep; fisheries production (2005) 2,171 (from aquaculture 34%). Mining and quarrying (2006): limestone 1,200,000 cu m; small quantities of salt. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): telecommunications equipment and electronics 171; food products 78; printing and publishing 59. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,216,000,000 (2,216,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (799,000). Population economically active (2006): total 164,400; activity rate of total population 40.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 59.1%; female 32.1%; unemployed [March 2007] 6.8%). Households. Average household size (2005) 2.9; average annual income per household (2000) Lm 7,945 (US$18,155); sources of income (1993): wages and salaries 63.8%, professional and unincorporated enterprises 19.3%, rents, dividends, and interest 16.9%; expenditure (2000): food and beverages 36.6%, transportation and communications 23.4%, recreation, entertainment, and education 9.4%. Gross national income (2006): US$5,899,-000,000 (US$14,575 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 754; remittances (2006) 34; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 326. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 268; remittances (2006) 32; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 101. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 31%, in permanent crops 3%; overall forest area (2005) 1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): Lm 1,316,900,000 (machinery and transport equipment 47.4%; food 9.2%; chemicals and chemical products 8.4%; mineral fuels 8.0%). Major import sources: Italy 17.9%; France 17.7%; UK 9.6%; Germany 9.1%; Singapore 6.9%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): Lm 909,300,000 (machinery and transport equipment [mostly electronic microcircuits] 63.9%; basic manufactures 18.8%; refined petroleum 4.4%). Major export destinations: Singapore 15.2%; US 11.6%; France 10.9%; UK 10.0%; Germany 8.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 2,254 km (paved 88%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 207,055; trucks and buses 45,054. Air transport (2006; Air Malta only): passenger-km 2,376,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 11,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 68,000 (169); televisions (2004): 222,000 (553); telephone land-lines (2006): 202,000 (502); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 347,000 (860); personal computers (2005): 67,000 (166); total Internet users (2005): 127,000 (315); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 42,000 (104).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 2.4%; special education for disabled 0.3%; primary education 25.9%; secondary 45.3%; some postsec-ondary 16.5%; undergraduate or professional qualification 7.2%; graduate 2.4%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 10 and over literate 92.8%; males literate 91.7%; females literate 93.9%. Health (2002): physicians 1,084 (1 per 365 persons); hospital beds 1,932 (1 per 205 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 6.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,762 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,237 (armed forces includes air and marine elements). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$101.
Background
Inhabited as early as 3800 bc, Malta was ruled by the Carthaginians from the 6th century bc until it came under Roman control in 218 bc. In ad 60 the apostle Paul converted the inhabitants to Christianity. It was under Byzantine rule until the Arabs seized control in 870. In 1091 the Normans defeated the Arabs, and Malta was ruled by feudal lords until it came under the Knights of Malta in 1530. Napoleon seized control in 1798, the British took it in 1800, and it was returned to the Knights in 1802. The Maltese protested and acknowledged the British as sovereign, an arrangement ratified in 1814. It became self-governing in 1921 but reverted to a colonial regime in 1936. Malta was severely bombed by Germany and Italy during World War II, and in 1942 it received the George Cross, Britain’s highest civilian decoration. In 1964 it gained independence within the Commonwealth and in 1974 became a republic. When its alliance with Britain ended in 1979, Malta proclaimed its neutral status.
Recent Developments
In 2007 patrols run by the EU border agency Frontex turned back from Malta more than 700 would-be illegal immigrants from Africa. In April an agreement to set up a SmartCity in Malta was signed, and in September the master plan and model of the project, the biggest foreign investment Malta had ever seen, was unveiled in Dubai. Tourism to Malta was the best since 2001, while GDP was expected to rise 4%. Malta joined the euro zone on 1 Jan 2008.
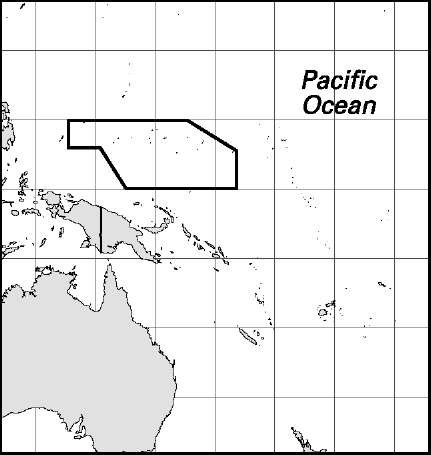
Marshall Islands
Official name: Majol (Marshallese); Republic of the Marshall Islands (English). Form of government: unitary republic with one legislative house (Nitijela [33]). Head of state and government: President Litokwa Tomeing (from 2008). Capital: Majuro (Rita). Official languages: Marshallese (Kajin-Majol); English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 70.05 sq mi, 181.43 sq km. Population (2007): 56,600. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 808.0, persons per sq km 312.0. Urban (2005): 66.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.02%; female 48.98%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 38.1%; 15-29, 30.8%; 30-44, 16.5%; 45-59, 10.3%; 60-74, 3.4%; 75-84, 0.8%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (nationality; 2000): Marshallese 88.5%; US white 6.5%; other Pacific Islander and East Asian 5.0%. Religious affiliation (1999): Protestant 85.0%, of which United Church of Christ 54.8%, Assemblies of God 25.8%; Roman Catholic 8.4%; Mormon 2.1%; nonreli-gious 1.5%; other/unknown 3.0%. Major towns (1999): Majuro (2004) 20,800; Ebeye 9,345; Laura 2,256; Ajeltake 1,170; Enewetak 823. Location: Oceania, group of atolls and reefs in the North Pacific Ocean, halfway between Hawaii (US) and Papua New Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 33.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 28.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.84. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 68.3 years; female 72.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:US$83,900,000 (US government grants 63.9%; tax revenue 26.4%, of which income tax 11.7%, import duties 9.3%; nontax revenue 9.7%). Expenditures: US$86,900,000 (current expenditure 80.2%; capital expenditure 19.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004-05): US$100,800,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2002-03): breadfruit 4,536, coconuts 885, bananas 161; livestock (number of live animals) 12,900 pigs, 86,000 chickens; fisheries production (2005) 56,664, of which skipjack (2004) 36,810. Mining and quarrying: for local construction only. Manufacturing (2005): copra 5,194; coconut oil and chilled or frozen fish are important products; the manufacture of handicrafts and personal items (clothing, mats, boats, etc.) by individuals is also significant. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 81,000,000 (81,000,000). Population economically active (1999): total 14,677; activity rate of total population 28.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 52.1%; female 34.1%; unemployed [2004] 33.6%). Households. Average household size (2006) 7.9; average annual income per household (2005) US$17,482; sources of income (2002): wages and salaries 89.3%, rent and investments 2.4%, social security 2.2%; expenditure (2003): food 35.9%, housing and energy 17.1%, transportation 13.7%, education and communication 6.6%. Gross national income (2006): US$191,000,000 (US$3,295 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004-05) 5.5; remittances (2005) 0.4; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 125; official development assistance (2005) 52 (commitments). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 6%, in permanent crops 44%, in pasture 22%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2000; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$68,200,000 (mineral fuels and lubricants 43.6%; machinery and transport equipment 16.9%; food, beverages, and tobacco 10.9%). Major import sources (2003): US 54.1%; Australia 13.4%; Japan 4.9%; New Zealand 3.4%; Hong Kong 3.3%. Exports (2005): US$16,-400,000 (reexports of diesel fuel 80.9%; crude coconut oil 15.4%). Major export destinations (2000): US 71%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2002): only Majuro and Kwajalein have paved roads (64.5 km). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 1,694; trucks and buses 602. Air transport (2005; Air Marshall Islands only): passenger-km 36,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 327,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Telephone landlines (2004): 4,500 (82); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 600 (12); personal computers (2004): 5,000 (92); total Internet users (2006): 2,200 (36).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 2.1%; elementary education 28.0%; secondary 55.8%; some higher 7.9%; undergraduate degree 5.1%; advanced degree 1.1%. Literacy (2000): total population ages 15 and over literate 92.0%; males literate 92.0%; females literate 92.0%. Health (2004): physicians 33 (1 per 1,744 persons); hospital beds 140 (1 per 411 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 28.3.
Military
The US provides for the defense of the Republic of the Marshall Islands under the 1984 and 2003 compacts of free association (the US Army’s premier ballistic-missile test site is at Kwajalein).
Background
The islands were sighted in 1529 by the Spanish navigator Alvaro Saavedra. Germany purchased them from Spain in 1899, and Japan seized them in 1914. During World War II the US took Kwajalein and Enewe-tak, and the Marshall Islands were made part of a UN trust territory under US jurisdiction in 1947. Bikini and Enewetak atolls served as testing grounds for US nuclear weapons from 1946 to 1958. The country became an internally self-governing republic in 1979. In 1986 it became fully self-governing when it entered into a Compact of Free Association with the US, which was renewed in 2003.
Recent Developments
Tension arose in the Marshall Islands over the Nuclear Claims Tribunal, which awarded US$1 billion to Marshall Islanders exposed to fallout during the 1954 hydrogen bomb test at Bikini Atoll. The award brought an end to an action initiated 15 years earlier, but the plaintiffs were unlikely to receive compensation because the tribunal had virtually no funds.
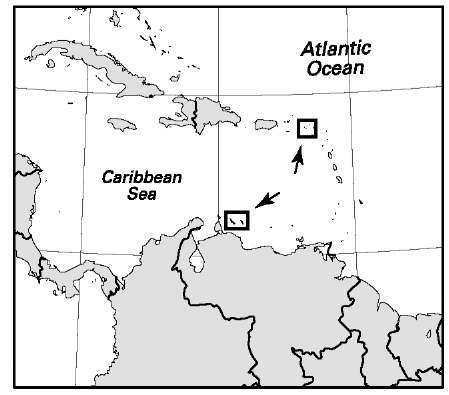
Martinique
Official name: Département de la Martinique (Department of Martinique). Political status: overseas department of France with two legislative houses (General Council [45]; Regional Council [41]). Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007). Head of government: Prefect (for France) Ange Mancini (from 2007); President of the General Council (for Martinique) Claude Lise (from 1992). Capital: Fort-de-France. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 436 sq mi, 1,128 sq km. Population (2007): 401,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 919.7, persons per sq km 355.5. Urban (2005): 98.0%. Sex distribution (2004): male 47.01%; female 52.99%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 21.4%; 15-29, 19.4%; 30-44, 23.7%; 45-59, 18.4%; 60-74, 11.1%; 75-84, 4.3%; 85 and over, 1.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): mixed race (black/white/Asian) 93.4%; French (metropolitan and Martinique white) 3.0%; East Indian 1.9%; other 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 86.0%; Protestant 5.6% (mostly Seventh-day Adventist); other Christian 5.4%; other 3.0%. Major communes (2003): Fort-de-France 96,400; Le Lamentin 36,400; Schrelcher 21,400; Le Robert (1999) 21,201; Sainte-Marie 20,600. Location: island in the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, between Dominica and Saint Lucia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 13.3 (world avg. 20.3); (1997) within marriage 31.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.90. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 75.9 years; female 82.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €599,000,000 (current revenue 75.3%, of which tax revenue 46.1%, aid from France 25.7%; capital revenue 24.7%). Expenditures: €599,000,000 (current expenditure 70.8%, of which transfers 51.1%, wages and salaries 13.2%; capital expenditure 29.2%). Public debt (1994): US$186,-700,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): bananas 300,000, sugarcane 211,000, plantains 18,030; livestock (number of live animals) 25,000 cattle, 20,000 pigs, 18,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 12,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 83%; fisheries production (2005) 5,592 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2005): salt 200,000; pumice 130,000. Manufacturing (2004): cement 224,090; sugar 4,140; rum 81,091 hectolitres. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,190,000,000 (1,190,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (4,400,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 820,000 (605,000). Households. Average household size (2004-05) 2.6; average annual disposable income per household (2001) €32,859 (US$36,720); sources of income (2000): wages and salaries 54.7%, inheritance or endowment 14.0%, self-employment 12.7%; expenditure (1993): food and beverages 32.1%, transportation and communications 20.7%, housing and energy 10.6%, household durable goods 9.4%, clothing and footwear 8.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 280. Population economically active (2003): total 183,000; activity rate of total population 46.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.4%; female 49.7%; unemployed [2005] 21.8%). Gross national income (2003): US$5,780,000,000 (US$14,730 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 9%, in permanent crops 10%, in pasture 10%; overall forest area (2005) 44%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2002; c.i.f.): €1,855,000,000 (products for agricultural industry and food 18.5%; automobiles 12.2%; mineral fuels 9.7%; chemicals and chemical products 7.9%). Major import sources: France 64.5%; Venezuela 5.9%; Netherlands Antilles 3.8%; Germany 3.3%; Italy 2.7%. Exports (2002; f.o.b.): €325,-000,000 (agricultural products [significantly bananas] 42.8%; refined petroleum 20.0%; processed foods and beverages [significantly rum] 19.1%). Major export destinations: France 68.9%; Guadeloupe 19.1%; French Guiana 4.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 2,105 km (paved [1988] 75%). Vehicles (1998): passenger cars 147,589; trucks and buses 35,615. Air transport (2004): passengers 1,614,876; cargo 13,003 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 30,000 (75); televisions (2001): 66,000 (169); telephone landlines (2001): 172,000 (417); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 295,000 (745); personal computers (2004): 82,000 (207); total Internet users (2005): 130,000 (326).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 20 and over having: unknown/no formal education through lower secondary education 63.6%; vocational 16.7%; upper secondary 9.2%; incomplete higher 5.0%; complete higher 5.5%. Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 98.0%; males literate 97.6%; females literate 98.3%. Health (2004): physicians 986 (1 per 403 persons); hospital beds 2,036 (1 per 195 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 7.3.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2005): 1,250 French troops (including troops stationed in Guadeloupe, excluding gendarmerie).
Background
Carib Indians, who had ousted earlier Arawak inhabitants, resided on the island when Christopher Columbus visited it in 1502. In 1635 the French established a colony there. The British captured and held the island in 1762-63 and again during the Napoleonic Wars, but each time it was returned to France. Made a department of France in 1946, Martinique remains under French rule despite a 1970s independence movement.
Recent Developments
Martinique was affected by two natural disasters in 2007. In August Hurricane Dean swept over the island. Though the tourism industry was largely unaffected, the storm destroyed the entire banana crop. In November a 7.4-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Martinique, causing property damage and knocking out power to half of the island.
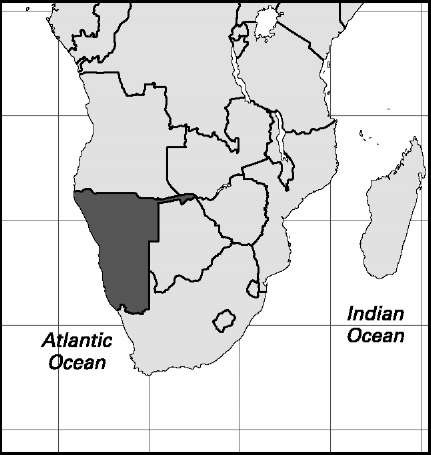
Mauritania
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-Islamiyah al-Muri-taniyah (Islamic Republic of Mauritania). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [56]; National Assembly [95]). Head of state and government: Chairman of the High Council of State Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz (from 2008), assisted by Prime Minister Moulaye Ould Mohamed Laghdaf (from 2008). Capital: Nouakchott. Official language: Arabic (Arabic, Fulani, Soninke, and Wolof are national languages). Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 ouguiya (UM) = 5 khoums; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = UM 235.96.
Demography
Area: 398,000 sq mi, 1,030,700 sq km. Population (2007): 3,124,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 7.8, persons per sq km 3.0. Urban (2006): 65.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.50%; female 50.50%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 45.6%; 15-29, 27.2%; 30-44,15.6%; 45-59, 8.0%; 60-74, 3.1%; 75 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2003): black African-Arab-Berber (Black Moor) 40%; Arab-Berber (White Moor) 30%; black African (mostly Wolof, Tukulor, Soninke, and Fulani) 30%. Religious affiliation (2000): Sunni Muslim 99.1%; traditional beliefs 0.5%; Christian 0.3%; other 0.1%. Major cities (2005): Nouakchott 743,500; Nouadhibou 94,700; Rosso (2000) 48,922; Boghe (2000) 37,531; Adel Bagrou (2000) 36,007. Location: northern Africa, bordering Western Sahara (annexed by Morocco), Algeria, Mali, Senegal, and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 41.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.86. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 50.9 years; female 55.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: UM 131,300,000,000 (tax revenue 57.9%, of which VAT 20.3%, corporate taxes 17.0%, import taxes 8.2%; nontax revenue 34.3%, of which fishing royalties 26.9%; grants 7.8%). Expendi-tures:UM 166,100,000,000 (current expenditure 76.2%, of which goods and services 36.5%, wages and salaries 13.5%, defense 10.7%; capital expenditure 23.8%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.5%, in permanent crops 0.01%, in pasture 38.3%; overall forest area (2005) 0.3%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sorghum 83,800, rice 70,462, dates 22,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2005) 7,363,000 sheep, 5,600,000 goats, I,651,000 camels; roundwood (2005) 1,629,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 99.6%; fisheries production 491,877, of which octopuses 19,023. Mining and quarrying (gross weight; 2006-07): iron ore II,439,000; gypsum (2005) 39,000; copper 5,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1997): food, beverages, and tobacco products 5.2; machinery, transport equipment, and fabricated metals 3.8; bricks, tiles, and cement 1.6. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006-07)404,000,000 (290,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (7,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 9,600,000 ([2004] 8,830,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2006-07) none (431,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11; remittances (2006) 2; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 109; official development assistance (2005) 190. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1999) 55. Population economically active (2006): total 1,238,000; activity rate of total population 39.2% (participation rates: over age 15, 68.8%; female 40.4%; unemployed [2005] 32.5%). Households. Average household size (2004): 5.8; expenditure (2002-03): food and beverages 53.1%, housing and energy 13.7%, transportation and communications 12.1%. Gross national income (2006): US$2,830,-000,000 (US$930 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$2,300,000,000.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$1,167,000,000 (petroleum exploration equipment 37.2%; petroleum products 19.5%). Major import sources: France 11.9%; China 8.2%; US 6.8%; Belgium 6.7%; Italy 5.9%. Exports (2006): US$1,366,600,000 (petroleum 47.0%; iron ore 34.2%; fish 14.7%). Major export destinations: China 26.3%; Italy 11.8%; France 10.2%; Belgium 6.8%; Spain 6.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2005) 697 km; metric ton-km cargo (2000)7,766,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 9,144 km (paved 30%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 12,200; trucks and buses 18,200. Air transport (2002): passenger-km 45,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 123,000 (44); telephone land-lines (2006): 34,000 (11); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,060,000 (348); personal computers (2005): 42,000 (14); total Internet users (2006): 100,000 (33); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 700 (0.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 6 and over having: no formal schooling 43.9%; no formal schooling but literate 2.5%; Islamic schooling 18.4%; primary education 23.2%; lower secondary 5.3%; upper secondary 4.6%; higher technical 0.4%; higher 1.7%. Literacy (2006): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 51.2%; males literate 59.5%; females literate 43.4%. Health (2006): physicians (2005) 477 (1 per 6,212 persons); hospital beds 1,826 (1 per 1,667 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 69.5. Food (2003): daily per capita caloric intake 2,786 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 121% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 15,870 (army 94.5%, navy 3.9%, air force 1.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.6%; per capita expenditure US$24.
Background
Inhabited in ancient times by Sanhadja Berbers, in the 11th and 12th centuries Mauritania was the center of the Berber Almoravid movement, which imposed Islam. Arab tribes arrived in the 15th century and formed powerful confederations; the Portuguese also arrived then. France gained control of the coast in 1817 and in 1903 made the territory a protectorate. In 1904 it was added to French West Africa, and later it became a colony. In 1960 Mauritania achieved independence. Its first president was ousted in a 1978 military coup. After a series of military rulers, in 1991 a new constitution was adopted, and multiparty elections were held in 1992. During the 1990s relations between the government and opposition groups deteriorated, even as there was some success in liberalizing the economy.
Recent Developments
Voters went to the polls in March 2007 to elect a new president for Mauritania. Sidi Mohamed Ould Cheikh Abdallahi took 53% of the vote in the second round of balloting that marked Mauritania’s first truly democratic presidential election since independence in 1960. The African Union indicated its approval by lifting its suspension of Mauritania. However, in August 2008 the government, accused of being soft on terrorism, was overthrown in a military coup.
Mauritius
Official name: Republic of Mauritius. Form of government: republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [70]). Chief of state: President Sir Anerood Jugnauth (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Navin Ramgoolam (from 2005). Capital: Port Louis. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Mauritian rupee (Mau Re; plural Mau Rs) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Mau Rs 27.25.
Demography
Area: 788 sq mi, 2,040 sq km. Population (2007): 1,263,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 1,603, persons per sq km 619.1. Urban (2006): 42.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.43%; female 50.57%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 23.9%; 15-29, 24.9%; 30-44, 23.4%; 45-59, 18.0%; 60-74, 7.2%; 75-84, 2.1%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): Indo-Pakistani 67.0%; Creole (mixed Caucasian, Indo-Pakistani, and African) 27.4%; Chinese 3.0%; other 2.6%. Religious affiliation (2000): Hindu 49.6%; Christian 32.2%, of which Roman Catholic 23.6%; Muslim 16.6%; Buddhist 0.4%; other 1.2%. Major urban areas (2006): Port Louis 148,878; Beau Bassin-Rose Hill 109,182; Vacoas-Phoenix 106,255; Curepipe 83,375; Quatre Bornes 80,325. Location: island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.73. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 68.9 years; female 75.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:Mau Rs 39,220,000,000 (tax revenue 90.2%, of which taxes on goods and services 47.8%, taxes on trade 18.3%, corporate income tax 12.0%; nontax revenue/grants 9.8%). Expenditures: Mau Rs 48,875,000,000 (social security 21.1%; interest on debt 15.0%; education 14.0%; police/defense 8.8%; health 8.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$731,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$6,460,000,000 (US$5,160 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 4,984,000, tomatoes 12,840, potatoes 12,780; livestock (number of live animals) 28,000 cattle; roundwood 12,500 cu m, of which fuelwood 40%; fisheries production 10,448 (from aquaculture 4%). Mining (2005): basalt, n.a.; marine salt 7,900. Manufacturing (value added in Mau Rs ’000,000; 2004): apparel 10,734; food products 3,887; beverages and tobacco 2,224. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,165,000,000 (2,165,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (289,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (791,000). Population economically active (2004): total 549,600; activity rate of total population 44.5% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 59.2%; female 35.0%; unemployed [2006] 8.9%). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.9; annual income per household (2001-02) Mau Rs 170,784 (US$5,780); expenditure (2001-02): food and nonalcoholic beverages 31.9%, transportation 12.7%, housing and energy 9.4%, alcohol and tobacco 9.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 871; remittances (2006) 215; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 21; official development assistance (2005) 47 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 275; remittances (2006) 11; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 17. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 49%, in permanent crops 3%, in pasture 3%; overall forest area (2005) 18%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): Mau Rs 93,282,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 22.9%; food and live animals 14.8%; refined petroleum 14.4%; fabrics and yarn 8.0%; transport equipment 5.1%). Major import sources: China 9.8%; South Africa 8.6%; France 7.5%; India 6.9%; Bahrain 5.5%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): Mau Rs 63,219,000,000 (domestic exports 66.6%, of which clothing 30.9%, sugar 16.7%, fish and fish preparations 5.0%; reexports 26.9%, of which machinery and transport equipment 14.5%).
Major export destinations: UK 29.9%; France 13.3%; US 9.0%; UAE 8.0%; Madagascar 5.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2005): total length 2,020 km (paved 98%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 84,818; trucks and buses 38,596. Air transport (2005; Air Mauritius only): passenger-km 6,274,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 211,716,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 60,000 (48); televisions (2004): 260,000 (209); telephone landlines (2006): 357,000 (285); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 772,000 (615); personal computers (2005): 210,000 (169); total Internet users (2005): 300,000 (241); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 22,000 (17).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education/unknown 12.8%; primary 44.1%; lower secondary 23.2%; upper secondary/some higher 17.3%; complete higher 2.6%. Literacy (2000): percentage of total population ages 12 and over literate 85.1%; males literate 88.7%; females literate 81.6%. Health (2006): physicians 1,400 (1 per 895 persons); hospital beds 3,727 (1 per 336 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 14.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,945 (vegetable products 85%, animal products 15%); 154% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none; a 2,000-person paramilitary force includes a coastguard unit. Paramilitary expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.2%; per capita expenditure US$9.
Background
The island was visited by the Portuguese in the early 16th century. The Dutch took possession in 1598 and made attempts to settle it (1638-58 and 1664-1710) before abandoning it to pirates. The French East India Company occupied Mauritius in 1721 and administered it until the French government took over in 1767. Sugar production allowed the colony to prosper. The British captured the island in 1810 and were granted formal control in 1814. In the late 19th century, competition from beet sugar and the opening of the Suez Canal caused an economic decline. After World War II, Mauritius adopted political and economic reforms, and in 1968 it became an independent state within the Commonwealth. In 1992 it became a republic. It experienced political unrest during the 1990s.
Recent Developments
Prompted by a downturn in two key industries, sugar production and textiles (following price cuts and the imposition of global trade quotas), Mauritius attempted in 2007 to bolster its economy through trade agreements with China and Pakistan. In mid-May the High Court in London rejected an appeal to block the right of exiled Chagos islanders (who had been removed from Diego Garcia, the largest of the islands, to allow the US to build a military base there) to return to the Chagos Archipelago (British-controlled territory claimed by Mauritius).
Mayotte
Official name: Collectivite Departementale de May-otte (Departmental Collectivity of Mayotte); known as Mahore or Maore in Shimaore, the local Swahili-based language. Political status: overseas dependency of France with one legislative house (General Council [19]); claimed by Comoros since 1975. Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007). Head of government: President ofthe General Council Said Omar Oili (from 2004). Capital: Mamoudzou. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 144.1 sq mi, 373.3 sq km. Population (2007): 194,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,346, persons per sq km 519.7. Sex distribution (2006): male 52.27%; female 47.73%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 45.9%; 15-29, 24.6%; 30-44, 18.1%; 45-59, 8.4%; 60-74, 2.5%; 75-84, 0.4%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Comorian 92.3%; Swahili 3.2%; white (French) 1.8%; Makua 1.0%; other 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Sunni Muslim 96.5%; Christian, principally Roman Catholic, 2.2%; other 1.3%. Major communes (2002): Mamoud-zou 45,485; Koungou 15,383; Dzaoudzi 12,308. Location: island in the Indian Ocean, between the northern tip of Madagascar and the African mainland.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 41.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 33.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.79. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 59.6; female 64.0.
National economy
Budget (2005; Mayotte is largely dependent on French aid). Revenue: €269,400,000 (current revenue 81.0%, of which taxes including customs duties 44.8%; development revenue 19.0%). Expenditures: €252,000,000 (current expenditure 78.9%, development expenditure 21.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): ylang-ylang (export production) 8,057 kg; bananas, coconuts, and mangoes are also cultivated; livestock (number of live animals; 2003) 22,800 goats, 17,200 cattle; fisheries production (2005) 2,050 (from aquaculture 8%). Manufacturing: mostly processing of agricultural products, housing construction materials, printing and publishing, and textiles/clothing. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2006) n.a. (151,000,000); petroleum products, none (n.a.). Households. Average household size (2002) 4.3; expenditure (1995): food and beverages 38.8%, transport and communications 13.1%, clothing and footwear 10.7%, household furnishings 9.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 18; official development assistance (2005) 208 (commitments). Population economically active (2002): total 44,558; activity rate of total population 27.8% (participation rates: ages 15-60, 50.0%; female 38.6%; unemployed [2006] 25.6%). Gross national income (2002): US$444,000,000 (US$2,780 per capita). Public debt (1997): US$74,600,000. Land use as % of total land area (2005): overall forest area 14.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): €218,200,000 (food products 25.5%; machinery and apparatus 16.7%; transport equipment 14.0%; chemicals and chemical products 8.9%). Major import sources: France 49.3%; Seychelles 9.0%; China 4.2%; South Africa 2.9%; Brazil 2.8%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): €5,200,000 (transport equipment and parts 27.0%; machinery and apparatus 23.1%; food products 19.4%, of which fish 10.7%; ylang-ylang 8.8%). Major export destinations: France 42.6%; Comoros 36.1%; Reunion 14.9%; Madagascar 3.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2006): total length 232 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 2,279; trucks and buses 1,453. Air transport (2005): passenger arrivals and departures 200,389; cargo unloaded and loaded 1,395 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Telephone landlines (2002): 10,000 (63); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 48,000 (277).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education 37.6%; participating in formal education 17.8%; primary education 20.8%; lower secondary 13.4%; upper secondary 6.3%; higher 4.1%. Literacy (1997): 86.1%. Health (2006): physicians 120 (1 per 1,587 persons); hospital beds 245 (1 per 780 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 61.2.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): n.a.; a detachment of the French Foreign Legion and French naval personnel is stationed at Dzaoudzi.
Background
Originally inhabited by descendants of Bantu and Malayo-Indonesian peoples, Mayotte was converted to Islam by Arab invaders in the 15th century. Taken by a Malagasy tribe from Madagascar at the end of the 18th century, it came under French control in 1843. Together with the other Comoros islands and Madagascar, it became part of a single French overseas territory in the early 20th century. It has been administered separately since 1975, when the three northernmost islands of the Comoros declared independence.
Recent Developments
Illegal immigrants continued to drown while attempting to cross from the Comoros islands to the relatively prosperous island of Mayotte. In one incident in August 2007, at least 17 people were confirmed dead and another 19 were missing after a primitive wooden vessel capsized in rough waters off the coast. In March 2008 Mohamed Bacar, the self-declared rebel president of the Comoran island of An-jouan, was arrested after having fled to Mayotte.
Mexico
Official name: Estados Unidos Mexicanos (United Mexican States). Form of government: federal republic with two legislative houses (Senate [128]; Chamber of Deputies [500]). Head of state and government: President Felipe Calderon Hinojosa (from 2006). Capital: Mexico City. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Mexican peso (Mex$) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Mex$10.41.
Demography
Area: 758,450 sq mi, 1,964,375 sq km. Population (2007): 106,535,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 140.8, persons persq km 54.4. Urban (2005): 76.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.66%; female 51.34%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 30.7%; 15-29, 26.3%; 30-44, 20.4%; 45-59, 11.8%; 60-74, 5.9%; 75-84, 1.7%; 85 and over, 0.5%; unknown 2.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 64.3%; Amerindian 18.0%, of which detribalized 10.5%; Mexican white 15.0%; Arab 1.0%; Mexican black 0.5%; Spaniard 0.3%; US white 0.2%; other 0.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 96.3%, of which Roman Catholic 87.0%, Protestant 3.2%, independent Christian 2.7%, unaffiliated Christian 1.4%, other Christian (mostly Mormon and Jehovah’s Witness) 2.0%; Muslim 0.3%; nonreligious 3.1%; other 0.3%. Major cities (urban agglomerations) (2005): Mexico City 8,463,906 (19,411,000); Ecatepec 1,687,549; Guadalajara 1,600,894 (3,968,000); Puebla 1,399,519 (1,824,000); Juarez 1,301,452 (1,540,000); Tijuana 1,286,187 (1,649,000); Leon 1,137,465 (1,481,000); Ciudad Netzahualcoyotl 1,136,300; Monterrey 1,133,070 (3,596,000); Za-popan 1,026,492. Location: middle America, bordering the US, the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, Belize, Guatemala, and the North Pacific Ocean. Households (2000). Total number of households 21,954,733; distribution by size: 1 person 6.0%, 2 persons 12.3%, 3 persons 17.2%, 4 persons 21.8%, 5 persons 17.7%, 6 persons 10.9%, 7 or more persons 14.1%. Migration. Legal Mexican immigrants entering the US in 2004: 173,664; total number of illegal Mexican immigrants in US (2006) 6,500,000.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 19.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.45. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 72.4 years; female 77.2 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 10.9%; incomplete primary education 14.3%; complete primary 17.6%; incomplete/complete secondary 25.2%; vocational/professional 31.3%; advanced university (masters or doctorate degree) 0.7%. Access to services (2005). Proportion of dwellings having: electricity 96.6%; piped water supply 87.8%; piped sewage 84.8%. Material well-being. Percentage of households possessing (2005): television 91.0%; refrigerator 79.0%; washing machine 62.7%; computer 19.6%. Quality of working life. Average workweek (2004) 43.5 hours. Annual rate per 100,000 insured workers for (2004) injury 2,922; death 11. Labor stoppages (2001) 35, involving 23,234 workers. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last national election (July 2006) 58.6%. Trade union membership in total workforce (2000) less than 20%. Practicing religious population (1995-97): percentage of adult population attending church services at least once per week 46%. Social deviance (2000). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: murder 14.1; rape 13.3; major assault 185.0; automobile theft 162.0. Incidence per 100,000 in general population of: alcoholism 7.6; suicide (2001) 3.1.
National economy
Mex$1,774,200,000,000 (tax revenue 43.4%, of which income tax 19.5%; nontax revenue 28.2%; revenue from PEMEX state oil company 10.9%; other 17.5%). Expenditures: Mex$1,797,500,000,000 (current expenditure 58.3%; capital expenditure 15.2%; extra-budgetary expenditure 26.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$108,786,-000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 50,600,000, corn (maize) 21,760,000, sorghum 5,487,000, oranges 3,980,000, wheat 3,336,000, tomatoes 2,878,000, bananas 2,197,000, guavas and mangoes 2,050,000, lemons and limes 1,866,000, chilies and green peppers 1,681,000, potatoes 1,543,000, dry beans 1,375,000, green onions 1,151,000, avocados 1,137,000, papayas 805,700, blue agave 778,000, pineapples 627,800, grapefruit and pomelos 379,700, coffee (green) 287,600, nuts 176,200, safflower seeds 72,370, vanilla 306; livestock (number of live animals) 28,648,787 cattle, 15,370,386 pigs, 8,897,182 goats, 7,484,118 sheep, 6,540,000 asses, mules, and hinnies, 6,260,000 horses, 289,663,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 44,646,877 cu m, of which fu-elwood 86%; fisheries production (2005) 1,422,344 (from aquaculture 8%). Mining and quarrying (2005): fluorite 876,000 (world rank: 2); bismuth (metal content) 970 (world rank: 2); silver (metal content) 2,894,161 kg (world rank: 2); celestite 110,833 (world rank: 3); lead 134,388 (metal content) (world rank: 5); cadmium (metal content) 1,627 (world rank: 5); gypsum 6,251,969 (world rank: 6); zinc (metal content) 476,307 (world rank: 6); sulfur 1,590,000; copper (metal content) 429,042; iron ore (metal content) 7,012,000; gold 30,356 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2000): motor vehicles and parts 10,718; food products 8,883; paints, soaps, pharmaceuticals 7,044; beverages 5,422; bricks, cement, ceramics 3,580; iron and steel 2,891; paper and paper products 2,243; basic chemicals 1,682; fabricated metal products 1,518. Households. Average household size (2005) 4.2; average annual income per household (2004) Mex$28,177 (US$2,497); sources of income (2004): wages and salaries 53.7%, nonmonetary income 19.0%, self-employment 14.0%, transfers 9.6%; expenditure (2000): food, beverages, and tobacco 29.9%, transportation and communications 17.8%, education 17.3%, housing (includes household furnishings) 16.5%. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 224,077,000,000 (223,118,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 1,735,000 (1,765,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 8,147,000 (11,681,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 1,216,000,000 (743,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 66,539,000 (71,195,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 49,797,000,000 ([2004] 50,450,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 43,575,500; activity rate of total population 41.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 63.0%; female 37.1%; unemployed 3.2%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11,803; remittances (2006) 24,732; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 19,268; official development assistance (2005) 305 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,600; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 3,430. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 13.0%, in permanent crops 1.3%, in pasture 41.9%; overall forest area (2005) 33.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$221,269,800,000 (non-maquiladora sector 66.0%, of which machinery and apparatus 18.7%, transport and communications equipment 11.9%, chemicals and chemical products 5.9%, processed food, beverages, and tobacco 3.6%; maquiladora sector 34.0%, of which electrical machinery, apparatus, and electronics 14.9%, nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 7.7%). Major import sources: US 53.4%; China 8.0%; Japan 5.9%; Germany 3.9%; South Korea 3.0%; Canada 2.8%; Brazil 2.4%. Exports (2005): US$213,711,200,000 (non-maquiladora sector 54.7%, of which road vehicles and parts 14.8%, crude petroleum 13.3%, machinery and apparatus 7.4%; maquiladora sector 45.3%, of which electrical machinery, apparatus, and electronics 19.1%, nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 8.5%). Major export destinations: US 85.7%; Canada 2.0%; Spain 1.4%; Germany 1.1%; Colombia 0.7%; Japan 0.7%; UK 0.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 26,662 km; passenger-km 73,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 55,113,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 355,796 km (paved 34%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 14,713,085; trucks and buses 7,158,105. Airtransport(2005): passenger-km 27,864,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 177,048,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2000): 9,850,000 (98); televisions (2003): 29,400,000 (282); telephone landlines (2006): 19,861,000 (183); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 57,016,000 (526); personal computers (2005): 14,000,000 (131); total Internet users (2005): 18,623,000 (181); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 3,728,000 (36).
Education and health
Literacy (2000): total population ages 15 and over literate (2005) 91.6%; males literate 93.4%; females literate 89.5%. Health (2005): physicians 134,157 (1 per 777 persons); hospital beds 76,420 (1 per 1,364 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 16.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,252 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 171% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 192,770 (army 74.7%, navy 19.2%, air force 6.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.4%; per capita expenditure US$29.
Background
Inhabited for more than 20,000 years, Mexico produced great civilizations in ad 100-900, including the Olmec, Toltec, Mayan, and Aztec. The Aztec were conquered in 1521 by Spanish explorer Hernan Cortes, who established Mexico City on the site of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. Francisco de Montejo conquered the remnants of Maya civilization in the mid-16th century, and Mexico became part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. In 1821 rebels negotiated a status quo independence from Spain, and in 1823 a new congress declared Mexico a republic. In 1845 the US voted to annex Texas, initiating the Mexican War. Under the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, Mexico ceded a vast territory in what is now the western and southwestern US. The Mexican government endured several rebellions and civil wars in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. During World War II it declared war on the Axis powers (1942), and in the postwar era it was a founding member of the UN (1945) and the Organization of American States (1948). In 1993 it ratified the North American Free Trade Agreement. The election of Vicente Fox to the presidency in 2000 ended 71 years of rule by the Institutional Revolutionary Party.
Recent Developments
Mexican Pres. Felipe Calderon began his term with a high-visibility militarized offensive against drug-trafficking cartels. By early 2007 he had deployed 30,000 army troops and federal police in such operations in nine different states. Human rights advocates voiced concerns about the extensive use of the armed forces for this purpose because military operations of this kind had often produced serious human rights violations. On balance, though, public opinion polls indicated strong public support for Calderon’s actions. The fact that Mexico experienced an unprecedented surge in drug-related killings, kidnappings, and gruesome violence (including beheadings) did suggest, however, that any progress against drug cartels would be slow, and this was confirmed in May 2008 when gunmen assassinated the acting chief of federal police in Mexico. Between the start of Calderon’s offensive and mid-2008 more than 200 policemen were killed. In foreign affairs the Calderon administration worked hard to repair diplomatic relations with Cuba and Venezuela, which had been severely strained during the previous administration. Within North America the Mexican government pursued discussions with Canada and the United States concerning a “Security and Prosperity Partnership” designed to deepen cooperation between the three countries. Mexico demonstrated its commitment to cooperation with the US government in the battle against organized drug trafficking by extraditing several major traffickers to the US. It also conducted extensive negotiations with the US over greatly expanded US financial and technical assistance to combat drug-related organized crime. However, the US government’s failure to enact a progressive immigration-reform bill and continuing US efforts to tighten border security to block Mexican migrants remained significant irritants in bilateral relations. Mexico’s GDP rose by 3.0% during 2007. The annual rate of inflation was 4.0%. The US economic slowdown, especially in industries such as home construction, also affected the volume of cash remittances that emigrants sent back to Mexico (US$24 billion in 2007). Remittances in January 2008 fell at the fastest pace in 13 years.
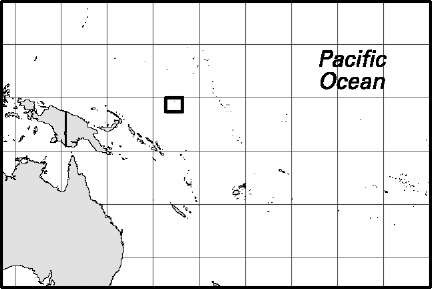
Federated States of Micronesia
Official name: Federated States of Micronesia. Form of government: federal nonparty republic in free association with the US with one legislative house (Congress [14]). Head of state and government: President Emanuel Mori (from 2007). Capital: Palikir. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 270.8 sq mi, 701.4 sq km. Population (2007): 111,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 409.9, persons per sq km 158.3. Urban (2005): 22.5%. Sex distribution (2007): male 50.37%; female 49.63%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.1%; 15-29, 29.6%; 30-44, 17.2%; 45-59, 11.7%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): Chuukese/Mortlockese 33.6%; Pohnpeian 24.9%; Yapese 10.6%; Kosraean 5.2%; US white 4.5%; Asian 1.3%; other 19.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 50%; Protestant 47%; other 3%. Major towns (2000): Weno 13,802; Palikir 6,444; Nett 6,158; Kolonia 5,681; Colonia 3,216. Location Oceania, island group in the North Pacific Ocean, northeast of New Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 27.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2003) within marriage 78.9%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 21.6 (world avg. 11.7). Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.3 years; female 68.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue:US$134,100,000 (external grants 63.0%; tax revenue 21.7%; nontax revenue 15.3%, of which fishing access revenue 9.8%). Expenditures: US$146,900,000 (current expenditures 90.8%; capital expenditure 9.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$60,800,000. Population economically active (2000): total 37,414; activity rate of total population 35.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 60.7%; female 42.9%; unemployed 22.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 40,000, cassava 11,800, sweet potatoes 3,000; livestock (number of live animals) 32,000 pigs, 13,900 cattle; fisheries production 29,336, of which (2004) skipjack tuna 22,998. Mining and quarrying: quarrying of sand and aggregate for local construction only. Manufacturing: n.a.; however, copra and coconut oil, traditionally important products, are being displaced by garment production; the manufacture of handicrafts and personal items (clothing, mats, boats, etc.) by individuals is also important. Energy production (consumption): electricity(kW-hr; 2005)74,400,000(n.a.); petroleum products, none (n.a.). Households (2004). Average household size 7.0; annual income per household (2000) US$8,944 (median income: US$4,618); sources of income (1994): wages and salaries 51.8%, operating surplus 23.0%, social security 2.1%; expenditure (1998): food 45.5%, services (includes taxi fares) 16.5%, alcohol, tobacco, kava (sakau), and betel nut 8.5%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$256,000,000 (US$2,317 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 17; remittances (2005) 6.0. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5.7. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 6%, in permanent crops 46%, in pasture 16%; overall forest area 91%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$137,993,000 (food and beverages 32.1%; mineral fuels 22.4%; machinery and apparatus 10.6%; transport equipment 6.0%). Major import sources: US 39.7%; Japan 8.8%; South Korea 5.8%; Singapore 4.6%; Philippines 4.4%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$14,003,000 (marine products [mostly fish] 73.5%; garment products 20.7%; betel nuts 2.5%; copra 1.2%; kava [sakau] 0.9%). Major export destinations: Japan 21.4%; US 20.9%; Guam 3.4%; Northern Marianas 1.0%; unspecified 53.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 240 km (paved 18%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 4,601; trucks and buses 3,770. Air transport (2004): passengers 17,473; freight 1,713,086 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 2,800 (26); telephone landlines (2005): 12,000 (109); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 14,000 (127); personal computers (2005): 6,000 (55); total Internet users (2006): 16,000 (144).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 12.3%; primary education 37.0%; some secondary 18.3%; secondary 12.9%; some college 18.4%. Literacy (2000): total population ages 10 and over literate 92.4%; males literate 92.9%; females literate 91.9%. Health (2005): physicians 62 (1 per 1,774 persons); hospital beds 365 (1 per 301 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 36.0.
Background
The islands of Micronesia were probably settled by people from eastern Melanesia some 3,500 years ago. Europeans first landed on the islands in the 16th century. Spain took control of the islands in 1886 and then sold them to Germany in 1899. The islands came under Japanese rule after World War I. They were captured by US forces during World War II, and in 1947 they became a UN trust territory administered by the US. The group of islands centered on the Caroline Islands became an internally self-governing federation in 1979. In 1986 Micronesia entered into a Compact of Free Association with the US, which was amended in 2003. In the late 1990s the republic was struggling to solve its economic difficulties.
Recent Developments
Some of the weaknesses of the loose federal structure of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) became apparent in 2007. Some US$100 million in funds from the US Compact of Free Association, along with an additional US$36 million in grants, flowed annually through the FSM government to the governments of the four semiautonomous states, yet two states, Chuuk and Kosrae, found themselves in serious budgetary difficulties. Of serious concern also was the threat of rising sea levels inundating the low-lying islands.
Moldova
Official name: Republica Moldova (Republic of Moldova). Form of government: unitary parliamentary republic with a single legislative body (Parliament [101]). Head of state: President Vladimir Voronin (from 2001). Head of government: Prime Minister Zi-naida Greceanii (from 2008). Capital: Chisinau. Official language: Romanian (constitutionally designated as Moldovan). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Moldovan leu (plural lei) = 100 bani; valuation (1 Jul 2008) free rate, US$1 = 9.83 Moldovan lei.
Demography
Area: 13,067 sq mi, 33,843 sq km. Population (2007): 3,794,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 290.3, persons per sq km 112.1. Urban (2006): 40.9%. Sex distribution (2006): male 47.89%; female 52.11%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 19.1%; 15-29, 26.3%; 30-44, 20.9%; 45-59, 19.1%; 60 and over, 14.3%; unknown 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2004): Moldovan 75.8%; Ukrainian 8.4%; Russian 5.9%; Gagauz 4.4%; Rom (Gypsy) 2.2%; Bulgarian 1.9%; other 1.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Moldovan Orthodox 31.8%; Bessarabian Orthodox 16.1%; Russian Orthodox 15.4%; Sunni Muslim 5.5%; Protestant 1.7%; Jewish 0.6%; nonreligious 19.9%; other 9.0%. Major cities (2006): Chisinau 593,800; Tiraspol 159,163; Balti 122,700; Tighina (2004) 97,027; Rabnita (2004) 53,648. Location: eastern Europe, bordering Ukraine and Romania.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.5 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 76.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.81. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 64.6 years; female 72.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:11,324,000,000 Moldovan lei (tax revenue 84.3%, of which VAT 30.3%, social fund contributions 22.0%, excise taxes 8.0%, personal income tax 7.0%; nontax and extra budgetary revenue 14.6%; grants 1.1%). Expenditures: 11,092,000,000 Moldovan lei (currentexpenditures95.5%, of which social fund expenditures 25.0%, education 15.2%, health 10.4%%; capital expenditure 4.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; end of 2006): US$718,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2006): corn (maize) 1,322,000, sugar beets 1,177,000, wheat 691,500; livestock (number of live animals) 818,300 sheep, 460,678 pigs, 310,476 cattle; roundwood (2005) 56,800 cu m, of which fuelwood 52%; fisheries production (2005) 5,001 (from aquaculture 89%). Mining and quarrying (2004): gypsum 491,000. Manufacturing (value of production in ’000,000 Moldovan lei; 2004): alcoholic beverages 4,013, of which wine 3,098; food products 3,461, of which dairy products 624; nonmetallic mineral products 1,273. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 3,617,000,000 (6,554,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (186,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (621,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (2,773,000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 1,422,300; activity rate of total de facto population 39.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 53.2%; female 51.5%; unemployed [2006] 7.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$3,356,000,000 (US$876 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.2; annual average income per household (2002) US$1,200; sources of income (1994): wages and salaries 41.2%, social benefits 15.3%, agricultural income 10.4%; expenditure (2001): food and drink 40.4%, housing 13.5%, utilities 10.5%, transportation 8.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 128; remittances (2006) 1,182; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 138; official development assistance (2005) 172 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 167; remittances (2006) 85. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 56.4%, in permanent crops 9.1%, in pasture 11.5%; overall forestarea (2005) 10.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$1,774,000,000 (mineral fuels 21.7%; machinery and apparatus 13.5%; chemicals and chemical products 9.1%; textiles and wearing apparel 8.6%). Major import sources (2005): Ukraine 23.3%; Romania 15.8%; Russia 13.2%; Germany 7.6%; Italy 5.4%. Exports (2004): US$986,000,000 (processed food, beverages [significantly wine], and tobacco products 35.1%; textiles and wearing apparel 17.3%; vegetables, fruits, seeds, and nuts 12.2%). Major export destinations (2005): Russia 31.9%; Italy 12.2%; Romania 10.2%; Ukraine 9.1%; Belarus 6.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 1,154 km; pas-senger-km 471,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,673,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 9,467 km (paved 94%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 252,490; trucks and buses 77,534. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 481,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,300,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 75,000 (18); televisions (2003): 1,300,000 (327); telephone landlines (2006): 1,018,000 (243); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,358,000 (324); personal computers (2005): 348,000 (83); total Internet users (2006): 728,000 (174); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 22,000(5.2).
Education and health
Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 99.1%; males literate 99.6%; females literate 98.7%. Health (2006): physicians 12,674 (1 per 283 persons); hospital beds 22,471 (1 per 160 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 12.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,295 (vegetable products 84%, animal products 16%); 167% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 6,750 (army 84.6%, air force 15.4%); opposition forces (excluding Russian troops) in Transdniestria (2006) 7,500; Russian troops in Transdniestria (2006) 500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.3%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Background
Moldova, once part of the principality of Moldavia, was founded by the Vlachs in the 14th century. In the mid-16th century it was under Ottoman rule. In 1774 it came under Russian control and lost portions of its territory. In 1859 it joined with the principality of Walachia to form the state of Romania, and in 1918 some of the territory it had ceded earlier also joined Romania. Romania was compelled to cede some of the Moldavian area to Russia in 1940, and that area combined with what Russia already controlled to become the Moldavian SSR. In 1991 Moldavia declared independence from the Soviet Union. It adopted the Romanian spelling of Moldova after having legitimized (1989) the use of the Roman rather than the Cyrillic alphabet. During the 1990s the country struggled to find economic equilibrium.
Recent Developments
In July 2007 Moldovan Pres. Vladimir Voronin confirmed that he had been negotiating with the Kremlin in an effort to secure an end to the secession of Transdniestria, where much of the country’s industry was located. In recent years Voronin had engaged in a balancing game between the West and Russia, and this move suggested that he was tilting toward Russia. He had been especially shaken in 2006 by the imposition of an embargo on Moldovan wine by Russia, a major consumer. However, a poll in Mayshowed that 72% of Moldovans would vote to join the European Union. Igor Smirnov, the leader of Transdnies-tria, cracked down sharply on opposition after his parliament in January annulled a decision that left open the prospect of a confederation between the pro-Russian breakaway territory and Moldova.
Monaco
Official name: Principaute de Monaco (Principality of Monaco). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative body (National Council [24]). Chief of state: Prince Albert II (from 2005). Head of government: Minister of State Jean-Paul Proust (from 2005). Capital: no separate area is distinguished as such. Official language: French. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 0.76 sq mi, 1.97 sq km. Population (2007): 34,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 44,737, persons persq km 17,259. Urban (2005): 100%. Sex distribution (2005): male 47.65%; female 52.35%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 15.4%; 15-29, 13.9%; 30-44, 20.2%; 45-59, 21.3%; 60-74, 17.3%; 75-84, 8.7%; 85 and over, 3.2%. Ethnic composition (2007): French 47%; Italian 16%; Mone-gasque 16%; other 21%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 93.2%, of which Roman Catholic 89.3%; Jewish 1.7%; nonreligious and other 5.1%. Location: western Europe, bordering the Mediterranean Sea and France.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 26.8 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 61.4%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.70. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 74.7 years; female 83.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: €727,936,000 (taxes on commerce 51.8%; state-run monopolies 11.4%; property taxes 8.7%). Expenditures: €789,132,000 (current expenditure 65.8%; capital expenditure 34.2%). Production. Agriculture, forestry, fishing: some horticulture and greenhouse cultivation; fisheries production (metric tons; 2005) 2. Manufacturing (value of sales in €’000; 2006): chemicals, cosmetics, perfumery, and pharmaceuticals 361,392; plastic products 265,783; light electronics and precision instruments 83,612. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2001) n.a. (475,000,000 [imported from France]). Gross national income (2006): US$1,165,000,000 (US$35,725 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 40,289; activity rate of total population 58.4% (participation rates: ages 17-64 [2000] 61.1%; female 41.4%; unemployed [2000] 3.6%). Households. Average household size (2004) 2.3. Selected balance of payments data (2006): tourism: 2,555 hotel rooms, 313,070 overnight visitors. Land use as % of total land area (2000): public gardens 20%.
Foreign trade
Imports (excluding trade with France; 2006): €752,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 36.0%; consumer goods 15.9%; food products 9.8%; automobiles 6.5%). Major import sources: China 27.3%; Italy 19.1%; Japan 10.2%; Belgium 6.7%; Germany 5.4%. Exports (excluding trade with France; 2006): €679,000,000 (rubber and plastic products, glass, construction materials, organic chemicals, and paper and paper products 35.9%; products of automobile industry 13.6%; pharmaceuticals, perfumes, clothing, and publishing 12.2%). Major export destinations: Germany 17.2%; Italy 10.3%; Spain 10.1%; UK 9.1%; Japan 4.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): length 1.7 km; passengers 2,171,100; cargo 3,357 tons. Roads (2001): total length 50 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (1997): passenger cars 21,120; trucks and buses 2,770. Air transport (2004; charter service of Monacair) pas-senger-km 414,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 25,000 (758); telephone landlines (2005): 34,000 (1,019); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 17,000 (510); total Internet users (2006): 20,000 (593); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 9,400 (282).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 17 and over having: primary/lower secondary education 24.7%; upper secondary 27.6%; vocational 12.7%; university 35.0%. Literacy: virtually 100%. Health (2002): physicians 156 (1 per 207 persons); hospital beds 521 (1 per 62 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 5.4.
Military
Defense responsibility lies with France according to the terms of the Versailles Treaty of 1919.
Background
Inhabited since prehistoric times, Monaco was known to the Phoenicians, Greeks, Carthaginians, and Romans. In 1191 the Genoese took possession of it; in 1297 the reign of the Grimaldi family began. The Grimaldis allied themselves with France except for the period 1524-1641, when they were under the protection of Spain. France annexed Monaco in 1793, and it remained under French control until the fall of Napoleon, when the Grimaldis returned. In 1815 it was put under the protection of Sardinia. A treaty in 1861 called for the sale of the towns of Men-ton and Roquebrune to France and the establishment of Monaco’s independence. Monaco is one of Europe’s most luxurious resorts. In 1997 the 700-year rule of the Grimaldis, then under Prince Rainier III, was celebrated.
Recent Developments
Planning continued in 2007 on Monaco’s expansion of its territory into the Mediterranean. The new district would be built on the surface of the water in order to avoid disturbing the marine life below and would increase Monaco’s current land surface by about 5%.
Mongolia
Official name: Mongol Uls (Mongolia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (State Great Hural [76]). Chief of state: President Nambaryn Enkhbayar (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Sanj Bayar(from 2007). Capital: Ulaanbaatar (Ulan Bator). Official language: Khalkha Mongolian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 tugrik (Tug) = 100 mongo; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Tug 1,158.25.00.
Demography
Area: 603,930 sq mi, 1,564,160 sq km. Population (2007): 2,609,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 4.3, persons per sq km 1.7. Urban (2006): 60.9%. Sex distribution (2004): male 49.60%; female 50.40%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 28.9%; 15-29, 32.3%; 30-44, 22.6%; 45-59, 10.3%; 60-74, 4.5%; 75-84, 1.1%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Khalkha Mongol 81.5%; Kazakh 4.3%; Dorbed Mongol 2.8%; Bayad 2.1%; Buryat Mongol 1.7%; Dariganga Mongol 1.3%; Zakh-chin 1.3%; Tuvan (Uriankhai) 1.1%; other 3.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs (shamanism) 32%; Buddhist (Lamaism) 23%; Muslim 5%; Christian 1%; nonreligious 30%; atheist/other 9%. Major cities (2000): Ulaanbaatar (Ulan Bator [2004]) 942,747; Erdenet 68,310; Darhan 65,791; Choybal-san 41,714; Ulaangom 26,319. Location: north-central Asia, bordering Russia and China.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.3 (world avg. 20.3); (2001) within marriage 82.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.97. Life expectancy at birth (2004): male 61.6 years; female 67.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: Tug 1,360,400,000,000 (tax revenue 83.0%, of which income taxes 35.0%, taxes on goods and services 25.9%; nontax revenue 16.6%; other 0.4%). Expenditures: Tug 1,237,000,000,000 (economic services 26.1%; social security 20.8%; general administration 19.6%; education 15.6%; health 8.0%). Population economically active (2004): total 986,100; activity rate of total population 39.3% (participation rates: ages 16-59, 63.7%; female 51.0%; unemployed [2006] 3.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): hay (2005) 830,700, wheat 127,757, potatoes 109,070; livestock (number of live animals) 13,267,000 goats, 12,884,500 sheep, 2,029,100 horses, 254,200 camels; roundwood (2005) 631,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 29%; fisheries production (2005) 366. Mining and quarrying (2005): fluorspar 367,000; copper (metal content) 126,547; molybdenum (metal content) 1,188. Manufacturing (value of production in Tug ’000,000; 2006): textiles 93,475; base metals 74,879; food products 71,428.
Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 3,303,000,000 (3,466,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 1,120,000 (1,120,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 5,745,000 (4,185,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 201,000 (n.a.); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (562,000). Gross national income (2006): US$2,916,000,000 (US$1,120 per capita). Public debt (external; 2005): US$1,267,000,000. Households: Average household size (2004) 4.2; annual income per household (2005) Tug 1,629,600 (US$1,350); sources of income (2005): wages 35.2%, self-employment 31.3%, transfer payments 10.6%; expenditure (2005): food and nonalcoholic beverages 42.2%, housing and energy 10.5%, clothing and footwear 10.1%, transportation 9.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 201; remittances (2006) 177; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 106; official development assistance (2005) 133 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 205; remittances (2006) 40. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.8%, in pasture 82.5%; overall forest area (2005) 6.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$1,489,200,000 (mineral fuels 30.0%; machinery and apparatus 18.2%; food and agricultural products 12.4%; transportation equipment 10.3%). Major import sources: Russia 36.6%; China 27.5%; Japan 6.8%; South Korea 5.6%; Kazakhstan 3.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$1,528,800,000 (copper concentrate 42.7%; gold 18.1%; refined copper 7.2%; combed goat down 5.3%; raw [greasy] cashmere 4.2%). Major export destinations: China 68.1%; Canada 11.2%; US 7.8%; Russia 2.9%; UK 2.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 1,810 km; passenger-km 1,287,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 10,513,000,000. Roads (2002): total length 49,250 km (paved 4%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 95,115; trucks and buses 41,234. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 835,800,000; metric ton-km cargo 86,400,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 50,000 (20); televisions (2003): 220,000 (88); telephone landlines (2005): 156,000 (59); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 557,000 (211); personal computers (2005): 340,000 (133); total Internet users (2005): 268,000 (105); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 1,800 (0.7).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal education 11.6%; primary education 23.5%; secondary 46.1%; vocational secondary 11.2%; higher 7.6%. Literacy (2004): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 97.8%; males literate 98.0%; females literate 97.5%. Health (2004): physicians 6,590 (1 per 384 persons); hospital beds 18,400 (1 per 138 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 19.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,954 (vegetable products 65%, animal products 35%); 105% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 8,600 (army 87.2%, air force 9.3%, unspecified 3.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$12.
Background
In Neolithic times Mongolia was inhabited by small groups of nomads. During the 3rd century bc it became the center of the Xiongnu empire. Turkic-speaking peoples held sway in the 4th-10th centuries ad. In the early 13th century Genghis Khan united the Mongol tribes and conquered central Asia. His successor, Ogodei, conquered the Chin dynasty of China in 1234. Kublai Khan established the Yuan, or Mongol, dynasty in China in 1279. After the 14th century the Ming dynasty of China confined the Mongols to their homeland in the steppes; later they became part of the Chinese Ch’ing dynasty. Inner Mongolia was incorporated into China in 1644. After the fall of the Ch’ing dynasty in 1911, Mongol princes declared Mongolia’s independence from China, and in 1921 Russian forces helped drive off the Chinese. The Mongolian People’s Republic was established in 1924 and recognized by China in 1946. The nation adopted a new constitution in 1992 and shortened its name to Mongolia.
Recent Developments
The renegotiation of a contract with Ivanhoe Mines (Rio Tinto) for exploitation of Mongolia’s prime gold and copper deposit at Oyuu Tolgoy was delayed into 2008 following public protests and government indecision. Several regions suffered problems that were caused by gangs of unlicensed miners, pollution, and environmental damage. Mongolia’s GDP grew 9.9% in 2007 and was projected to grow significantly in 2008. Although minerals such as copper and gold made up two-thirds of exports in 2007, the value of total reported gold production dropped for the year, suggesting a rise in smuggling.
Montenegro
Official name: Republika Crna Gora (Republic of Montenegro). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [81]). Chief of state: President Filip Vujanovic (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Milo Djukanovic (from 2008). Capital: Cetinje. Administrative center: Podgorica. Official language: Montenegrin. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63; Montenegro uses the euro as its official currency, even though it is not a member of the EU.
Demography
Area: 5,333 sq mi, 13,812 sq km. Population (2007): 624,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 117.0, persons per sq km 45.2. Urban (2005): 52.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.23%; female 50.77%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 19.6%; 15-29, 23.6%; 30-44, 19.8%; 45-59, 19.1%; 60-74, 12.8%; 75-84, 4.3%; 85 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2003): Montenegrin 43.2%; Serb 32.0%; Bosniac/Muslim 11.8%; Albanian 5.0%; undeclared 4.0%; other 4.0%. Religious affiliation (2003): Orthodox 70%; Muslim 21%; Roman Catholic 4%; other 5%. Major cities (2005): Podgorica 173,000; Niksic 75,000; Bijelo Polje 50,000; Bar 41,000; Berane 35,000. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Kosovo, Albania, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 11.8 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 79.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.4 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.60. Life expectancy at birth (2004): male 71 years; female 75 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: €582,258,287 (tax revenue 85.8%, of which VAT 44.5%, income tax 12.5%, excise tax 12.4%, taxes on international trade 9.7%; nontax revenue 14.2%). Expenditures: €579,780,129 (wages and salaries 27.4%; transfers 20.7%; debtser-vice 20.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; January 2007): US$655,056,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): potatoes 126,000, grapes 50,000, tomatoes 21,600; livestock (number of live animals) 254,898 sheep, 117,842 cattle, 10,697 pigs; roundwood (2005; state forests only) 279,228 cu m, of which fuelwood 13%; fisheries production (2005) 1,236. Mining and quarrying (2006): bauxite 659,370; sea salt 5,000. Manufacturing (gross value added in €’000; 2004): base and fabricated metal products (mostly of aluminum) 58,718; food products, beverages, and tobacco 56,846; paper products, publishing, and printing 6,647. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 2,952,000,000 ([2004] 19,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2005) n.a. (66,900); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 1,500,000 ([2005] 1,230,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) n.a. (164,000). Land use as % of total land area (2005): in temporary crops 3.3%, in permanent crops 1.1%, in pasture 32.8%; overall forest area 44.7%. Population economically active (2005): total 256,569; activity rate 40.4% (participation rates: ages 16 and over, 49.9%; female 44.2%; unemployed 30.3%). Gross national income (2006): US$2,251,000,000 (US$3,745 per capita). Households (2006). Average household size 3.5; average annual income per household €5,328 (US$6,684); sources of income: wages and salaries 62.5%, transfer payments 19.7%, agriculture 9.0%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 42.5%, housingand energy 12.5%, transportation 8.7%, clothing and footwear 7.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 340; remittances (2006) 100; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2002-05 avg.) 139. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): FDI (2006) 223.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): €940,344,000 (machinery and transportation equipment 22.3%, of which motor vehicles 6.1%; mineral fuels and lubricants 15.6%; food and live animals 15.6%; household equipment 15.1%; chemicals and chemical products 8.7%). Major import sources:Serbia and Kosovo 34.8%; Italy 9.2%; Slovenia 7.1%; Croatia 7.0%; Greece 5.6%. Exports (2005): €434,458,000 (aluminum 42.9%; machinery and transportation equipment 11.7%; food and live animals 8.3%; beverages and tobacco 7.1%; wood and wood products 4.1%). Major export destinations: Serbia and Kosovo 36.8%; Italy 27.3%; Greece 9.1%; Slovenia 6.8%; Bosnia and Herzegovina 5.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 250 km; passen-ger-km 131,500,000; metric ton-km cargo 182,163,000. Roads (2006): total length 7,368 km (paved [2005] 58%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 118,930. Airtransport (2006): passengers 833,715. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 73,000 (118); telephone landlines (2006): 176,000 (282); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 703,000 (1,126); personal computers (2004): 389,000 (359); total Internet users (2006): 266,000 (426); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 26,000 (42).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education 3.2%; incomplete primary education 6.8%; complete primary 22.5%; secondary 55.0%; higher 12.5%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 20 and over literate 97.3%; males literate 99.2%; females literate 95.5%. Health (2005): physicians 1,257 (1 per 496 persons); hospital beds 4,065 (1 per 153 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 9.5.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 7,300 (army 54.8%, navy 45.2%).
Background
The Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes was created after the collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I. The country signed treaties with Czechoslovakia and Romania in 1920-21, marking the beginningofthe Little Entente. In 1929 an absolute monarchy was established, the country’s name was changed to Yugoslavia, and it was divided into regions without regard to ethnic boundaries. Axis powers invaded Yugoslavia in 1941, and German, Italian, Hungarian, and Bulgarian troops occupied it for the rest of World War II. In 1945 the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was established; it included the republics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. Its independent form of communism under Josip Broz Tito’s leadership provoked the USSR. Internal ethnic tensions flared up in the 1980s, causing the country’s ultimate collapse. In 1991-92 independence was declared by Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina; the new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (containing roughly 45% of the population and 40% of the area of its predecessor) was proclaimed by Serbia and Montenegro. Still fueled by long-standing ethnic tensions, hostilities continued into the 1990s. Despite the approval of the Dayton Peace Agreement (1995), sporadic fighting continued and was followed in 1998-99 by Serbian repression and expulsion of ethnic populations in the province of Kosovo. In September-October 2000, the battered nation ofYugoslavia ended the autocratic rule of Pres. Slobodan Milosevic. In April 2001 he was arrested and in June extradited to The Hague to stand trial for war crimes, genocide, and crimes against humanity committed during the fighting in Kosovo. In February 2003 both houses of the Yugoslav federal legislature voted to accept a new state charter and change the name of the country from Yugoslavia to Serbia and Montenegro. Henceforth, defense, international political and economic relations, and human rights matters would be handled centrally, while all other functions would be run from the republican capitals, Belgrade and Podgorica, respectively. A provision was included for both states to vote on independence after three years, and in June 2006 Montenegro’s parliament declared the republic’s independence, severing some 88 years of union with Serbia.
Recent Developments
In October 2007 Montenegro’s parliament adopted the country’s first constitution after gaining independence from Serbia in June 2006. The country took steps toward EU membership by joining the Council of Europe and by signing the Stabilization and Association Agreement with NATO. The governing coalition unveiled a judiciary-reform program to combat corruption, pledged to cooperate with the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia on any war crimes committed in Montenegro, prepared draft laws on national security, and began the planned reduction of its armed forces. Montenegro agreed to bolster ties with Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina and underscored the country’s neutral stance regarding the final status of Kosovo. Foreign direct investment topped €1 billion (almost US$1.5 billion) for the year, a 56% increase from 2006. The budget showed a surplus and inflation was under 10%. Real wages rose 15.0% in 2007, while the cost of living increased only 4.2%. Unemployment was estimated at 19.3% for the year, however.
Morocco
Official name: Al-Mamlakah al-Maghribiyah (Kingdom of Morocco). Form of government: constitutional
monarchy with two legislative houses (House of Councillors [270]; House of Representatives [325]). Chief of state and head of government: King Muhammad VI (from 1999), assisted by Prime Minister Abbas El Fassi (from 2007). Capital: Rabat. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Moroccan dirham (DH) = 100 Moroccan francs; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = DH 7.28.
Demography
Area (includes Western Sahara): 274,461 sq mi, 710,850 sq km. Population (includes Western Sahara; 2007): 31,704,000. Density (includes Western Sahara; 2007): persons per sq mi 115.5, persons per sq km 44.6. Urban (2004): 55.1%. Sex distribution (2004): male 49.33%; female 50.67%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 31.2%; 15-29, 28.9%; 30-44, 20.1%; 45-59, 11.7%; 60-74, 6.0%; 75 and over, 2.0%; unknown 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Amazigh (Berber)45%, of which Arabized 24%; Arab 44%; Moors originally from Mauritania 10%; other 1%. Religious affiliation (2004): Muslim, more than 99%, of which Sunni 97%, Shi’i 2%; other, less than 1%. Major cities (2004): Casablanca 2,933,684; Rabat 1,622,860; Fes946,815; Marrakech 823,154; Agadir 678,596;Tangier 669,685. Location: northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla, Algeria, Mauritania, and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.73. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.4 years; female 73.1 years.
National economy
Budget. Revenue (2005): DH 131,436,000,000 (VAT 24.8%; income tax 17.3%; corporate taxes 14.7%; excises 11.9%). Expenditures (2005): DH 151,693,000,000 (current expenditure 83.6%; capital expenditure 13.2%; other 3.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$13,113,000,000. Households. Average household size (2004) 5.3; expenditure (2001): food 41.3%, housing and energy 22.1%, health 7.6%. Population economically active (2006): total 10,990,000; activity rate 36.0% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 51.3%; female [2005] 27.5%; unemployed 9.7%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 6,300,000, sugar beets 2,252,000, potatoes 1,569,000; livestock (number of live animals) 16,872,000 sheep, 5,331,600 goats, 2,721,700 cattle; roundwood (2005) 957,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 40%; fisheries production (2005) 934,961, of which sardines 629,496 (roughly 60% of Morocco’s fisheries production comes from Atlantic waters off of Western Sahara). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock 27,254,000; barite 475,700; zinc (metal content) 77,100. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food products 1,130; wearing apparel 733; tobacco products 595. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 18,701,000,000 (16,968,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none ([2005] 5,938,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 246,000 (47,204,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 6,352,000 (7,454,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 50,665,000 ([2005] 40,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 19.0%, in permanent crops 2.0%, in pasture 47.1%; overall forest area (2005) 9.8%. Gross national income (2006): US$64,066,000,000 (US$2,046 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,610; remittances (2006) 5,048; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,968. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 612; remittances (2006) 40.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): DH 180,294,000,000 (mineral fuels 21.8%, of which crude petroleum 13.3%, refined petroleum products 6.4%; machinery and apparatus 19.7%; food, beverages, and tobacco 8.6%). Major import sources: France 18.2%; Spain 11.0%; Saudi Arabia 6.8%; Italy 6.1%; China 5.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): DH 94,358,000,000 (food, beverages, and tobacco products 19.8%, of which fisheries products 9.8%; garments 18.7%; phosphoric acid 8.1%; knitwear 7.2%; cannabis is an important illegal export; estimated production [2004] 88,900 metric tons). Major export destinations: France 31.3%; Spain 16.3%; UK 7.1%; Italy 4.3%; US 3.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 1,907 km; passenger-km 2,645,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,563,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 56,987 km (paved 61%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2002) 1,326,108; trucks and buses (2000) 415,700. Air transport (2006; Royal Air Maroc only): passenger-km 8,643,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 72,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 411,000 (14); televisions (2004): 5,010,000 (164); telephone landlines (2006): 1,266,000 (41); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 16,005,000 (521); personal computers (2005): 740,000 (24); total Internet users (2006): 6,100,000 (199); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 391,000 (13).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal education through incomplete primary education 45.5%; complete primary 40.8%; secondary 8.7%; higher 5.0%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 16 and over literate 53.5%; males literate 65.5%; females literate 41.5%. Health (2004): physicians 16,775 (1 per 1,778 persons); hospital beds (public hospitals only) 26,136 (1 per 1,141 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 41.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,492 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 187% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 200,800 (army 89.6%, navy 3.9%, air force 6.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.5%; per capita expenditure US$77.
Background
The Berbers entered Morocco near the end of the 2nd millennium bc. Phoenicians established trading posts along the Mediterranean during the 12th century bc, and Carthage had settlements along the Atlantic in the 5th century bc. After the fall of Carthage, Morocco became a loyal ally of Rome, and in ad 42 it was annexed by Rome as part of the province of Mau-retania. It was invaded by Muslims in the 7th century. Beginning in the mid-11th century, the Almoravids, Al-mohads, and Marinids ruled successively. After the fall of the Marinids in the mid-15th century, the Sa’dis ruled for a century after 1550. The French fought Morocco over the Algerian boundary in the 1840s, and the Spanish seized part of Moroccan territory in 1859. It was a French protectorate from 1912 until its independence in 1956. In the mid-1970s it reasserted claim to the Western Sahara, and in 1976 Spanish troops left there. Conflicts with Mauritania and Algeria over the region continued into the 1990s. As the decade wore on, the UN tried to solve the dispute. King Hassan II died in July 1999 after 38 years on the throne and was succeeded by his eldest son, Sidi Muhammad, who took the name Muhammad VI.
Recent Developments
Marrakech is the chief city of central Morocco. The first of Morocco’s four imperial cities, it lies in the center of the fertile, irrigated Haouz Plain, south of the Wadi Tennsift. The ancient section of the city, known as the medinah, was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1985. Cafe after an altercation with the owner, and in April three suicide bombers blew themselves up in Casablanca and a fourth was shot by police. Days later the US consulate and a US cultural center came under attack when two suicide bombers detonated their explosives near the buildings. Police later apprehended three suspected accomplices and were able to connect all the perpetrators in the March-April bombings.
Mozambique
Official name: Republica de Mogambique (Republic of Mozambique). Form of government: multiparty republic with a single legislative house (Assembly of the Republic [250]). Head of state and government: President Armando Guebuza (from 2005), assisted by Prime Minister Luisa Diogo (from 2004). Capital: Maputo. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 (new) metical (MTn; plural meticais) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = MTn 23.99 (the [new] metical replaced the [old] metical [MT] on 1 Jul 2006, at the rate of 1 MTn = MT 1,000).
Demography
Area: 308,642 sq mi, 799,379 sq km. Population (2007): 20,906,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 67.7, persons per sq km 26.2. Urban (2006): 39.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.05%; female 50.95%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 43.1%; 15-29, 26.8%; 30-44, 16.5%; 45-59, 9.0%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Makuana 15.3%; Makua 14.5%; Tsonga 8.6%; Sena 8.0%; Lomwe 7.1%; Tswa 5.7%; Chwabo 5.5%; other 35.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs 46%; Christian 37%, of which Roman Catholic 19%, Protestant 11%; Muslim 9%; other 8%. Major cities (2004): Maputo 1,140,400; Matola 520,500; Beira 487,100; Nampula 371,800; Chi-moio 209,700. Location: southern Africa, bordering Tanzania, the Indian Ocean, South Africa, Swaziland, Zimbabwe, Zambia, and Malawi.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 39.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.35. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 41.2 years; female 40.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:MT 26,891,000,000,000 (tax revenue 58.0%, of which VAT 23.9%, personal income tax 9.0%, taxes on international trade 8.5%; grants 37.4%; nontax revenue 4.6%). Expenditures: MT 32,602,000,000,000 (current expenditures 58.3%; capital expenditures 38.5%; net lending 3.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,727,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): cassava 11,460,000, sugarcane 2,650,000, corn (maize) 1,300,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,320,000 cattle, 392,000 goats, 28,000,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 18,028,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 93%; fisheries production (2005) 43,695 (from aquaculture 3%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 654,179; bauxite 9,518; tantalite 281,212 kg. Manufacturing (value added in MT ’000,000,000; 2003): aluminum 19,067; beverages 4,773; food products 2,577. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 11,714,000,000 (10,579,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 38,000 (23,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (624,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) I,341,000,000 (3,152,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.2; source of income (1992-93): wages and salaries 51.6%, self-employment 12.5%, barter 11.5%; expenditure (1998): food, beverages, and tobacco 63.5%, firewood and furniture 17.0%, transportation and communications 4.6%, clothing and footwear 4.6%. Population economically active (2003): total 8,981,000; activity rate of total population 47.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 84.4%; female 53.8%). Gross national income (2006): US$6,790,000,000 (US$324 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 130; remittances (2006) 80; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 258; official development assistance (2005) 1,286. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 176; remittances (2006) 26. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.5%, in permanent crops 0.3%, in pasture 56.1%; overall forest area (2005) 24.6%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. for commodities and trading partners): US$1,753,-000,000 (mineral fuels 16.5%; machinery and apparatus 16.2%; food products 12.3%, of which cereals 7.2%; transport equipment 9.0%). Major import sources (2004): South Africa 41.4%; The Netherlands II.0%; Portugal 3.3%; US 2.4%. Exports (2003): US$1,044,000,000 (aluminum 54.4%; electricity 10.9%; prawns 7.3%; cotton 3.1%). Major export destinations (2004): The Netherlands 60.9%; South Africa 12.9%; Malawi 3.3%; Portugal 2.8%; Spain 2.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): route length (2002) 3,123 km; passenger-km 167,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,362,000,000. Roads (1999): total length 30,400 km (paved 19%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 81,600; trucks and buses 76,000. Air transport (2006; LAM [Linhas Aereas de Mogambique] only): passenger-km 462,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 16,000 (0.8); televisions (2003): 391,000 (20); telephone landlines (2006): 67,000 (3.3); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,339,000 (116); personal computers (2005): 283,000 (14); total Internet users (2005): 178,000 (9).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1997). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 79.0%; primary education 18.4%; secondary 2.0%; technical 0.4%; higher 0.2%. Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 50.4%; males literate 65.7%; females literate 35.6%. Health: physicians (2003) 635 (1 per 30,525 persons); hospital beds (2003) 16,493 (1 per 1,175 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 112.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,287 (vegetable products 98%, animal products 2%); 121% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 11,200 (army 89%, navy 2%, air force 9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.9%; per capita expenditure US$3.
Background
Inhabited in prehistoric times, Mozambique was settled by Bantu peoples about the 3rd century ad. Arab traders occupied the coastal region from the 14th century, and the Portuguese controlled the area from the early 16th century. The slave trade later became an important part of the economy. In the late 19th century private trading companies began to administer parts of the inland areas. It became an overseas province of Portugal in 1951. After years of war beginning in the 1960s, the country was granted independence in 1975. It was wracked by civil war in the 1970s and ’80s. In 1990 a new constitution was promulgated, and a peace treaty was signed with the rebels in 1992.
Recent Developments
Mozambique’s stability and security, together with the government’s efforts to wipe out corruption and to increase food production, continued to impress foreign donors in 2007. In May donors and funding agencies announced their support for the 2008 budget by offering US$385.8 million, while the US Millennium Challenge Cooperation promised an additional US$506.9 million over the next five years. Two oil refineries were planned as well, costing over US$12 billion and with output capacities of 650,000 bbl per day.
Myanmar (Burma)
Official name: Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (Union of Myanmar). Form of government: military regime. Head of state and government: Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council Gen. Than Shwe (from 1997), assisted by Prime Minister Thein Sein (from 2007). Capital: Naypyidaw. Official language: Burmese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Myanmar kyat (K) = 100 pyas; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = K 6.42.
Demography
Area: 261,228 sq mi, 676,577 sq km. Population (2007): 47,374,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 181.4, persons per sq km 70.0. Urban (2005): 30.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.48%; female 50.52%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 26.5%; 15-29, 29.2%; 30-44, 23.1%; 45-59, 13.5%; 60-74, 6.1%; 75-84, 1.4%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Burman 55.9%; Karen 9.5%; Shan 6.5%; Han Chinese 2.5%; Mon 2.3%; Yangbye 2.2%; Kachin 1.5%; other 19.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Buddhist 74%; Protestant 6%; Muslim 3%; Hindu 2%; traditional beliefs 11%; other 4%. Major cities (2004): Yangon (Rangoon; 2005) 4,107,000; Mandalay (2005) 924,000; Moulmein (Mawlamyine) 405,800; Bassein (Pathein) 215,600; Pegu (Bago) 200,900. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering China, Laos, Thailand, the Andaman Sea, the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh, and India.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.98. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 59.9 years; female 64.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2002-03). Revenue: K 279,377,000,000 (nontax revenue 59.6%; tax revenue 40.3%, of which taxes on goods and services 22.1%, taxes on individual income 16.3%; foreign grants 0.1%). Expenditures: K 353,389,000,000 (economic affairs 31.4%, of which transport 18.4%; public services 23.4%; defense 21.5%; education 14.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,196,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 25,364,000, sugarcane 7,187,000, dry beans (2006) 1,700,000; livestock (number of live animals) 12,123,000 cattle, 5,677,000 pigs, 81,518,000 chickens; roundwood 42,548,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 90%; fisheries production 1,743,000 (from aquaculture 27%). Mining and quarrying (2006): copper (metal content; 2005) 34,500; jade 20,647,000 kg; rubies 1,685,000 carats. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): tobacco products (2002) 1,320; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 728; transportation equipment 483. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 6,437,000,000 (6,437,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 831,000 (117,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 182,000 (68,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 7,675,000 ([2004] 7,509,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 917,000 (1,808,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 12,502,000,000 ([2004] 1,650,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 84; remittances (2006) 117; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 245; official development assistance (2005) 145. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 29; remittances (2006) 25. Households. Average household size (2004) 5.0; expenditure (1997): food and nonalcoholic beverages 70.4%, fuel and lighting 6.6%, transportation 3.3%. Gross national income (2006): US$13,611,000,000 (US$280 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 26,361,000; activity rate of total population 53.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 78.7%; female 44.9%; unemployed [2006] 10.2%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 15.3%, in permanent crops 1.4%, in pasture 0.5%; overall forest area (2005) 49.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006-07; c.i.f.): K 15,440,000,000 (mineral fuels 24.8%; nonelectrical machinery and transport equipment 15.9%; base and fabricated metals 7.0%; synthetic fabrics 6.5%). Major import sources: Singapore 36.5%; China 24.4%; Thailand 10.3%; India 5.3%; Japan 4.9%. Exports (2006-07; f.o.b.): K 27,381,000,000 (natural gas 42.6%; pulses [mostly beans] 11.1%; hardwood 10.0%, of which teak 6.0%; garments 5.3%). Major export destinations: Thailand 48.9%; India 13.7%; Hong Kong 8.2%; China 7.9%; Singapore 3.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length (2004) 3,955 km; passenger-km 5,263,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 829,000,000. Roads (1999): total length 27,966 km (paved 11%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 203,441; trucks and buses 74,037. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 124,697,000; metric ton-km cargo 245,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 501,000 (11); televisions (2004): 373,000 (8.1); telephone landlines (2005): 504,000 (9.3); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 214,000 (4.2); personal computers (2005): 400,000 (8.6); total Internet users (2006): 94,000 (1.8); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 800.
Education and health
Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 89.7%; males literate 93.7%; females literate 86.2%. Health (2004-05): physicians 17,564 (1 per 2,660 persons); hospital beds 34,654 (1 per 1,350 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 52.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,620 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 199% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 482,750 (army 72.5%, navy 2.8%, air force 2.5%, paramilitary [people's militia and people's police] 22.2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 7.6%.
Background
Myanmar, until 1989 known as Burma, has long been inhabited, with the Mon and Pyu states dominant between the 1st century bc and the 9th century ad. It was united in the 11th century under a Burmese dynasty that was overthrown by the Mongols in the 13th century. The Portuguese, Dutch, and English traded there in the 16th-17th centuries. The modern Burmese state was founded in the 18th century. It fell to the British in 1885 and became a province of India. It was occupied by Japan in World War II and became independent in 1948. A military coup took power in 1962 and nationalized major economic sectors. Civilian unrest in the 1980s led to antigovernment rioting. In 1990 opposition parties won in national elections, but the army remained in control. Trying to negotiate for a freer government amid the unrest, Aung San Suu Kyi, the National League for Democracy leader, was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1991. She spent extended periods of the 1990s under house arrest.
Recent Developments
In May 2008 Myanmar was struck by Cyclone Nargis. Billions of dollars of damage was done by the winds and accompanying sea surge. As many as 2.5 million people were in need of food and shelter, and officials feared that the death toll would top 100,000. Thousands of livestock were lost and much of the country’s rice crop was wiped out. The ruling junta was criticized for delaying the distribution of humanitarian aid, and there were reports of continuing exports of the country’s rice and the distribution of rotting food to storm survivors.
Namibia
Official name: Republic of Namibia. Form of government: republic with two legislative houses (National Council [26]; National Assembly [72]). Head of state and government: President Hifikepunye Pohamba (from 2005), assisted by Prime Minister Nahas An-gula (from 2005). Capital: Windhoek. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Namibian dollar (N$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = N$7.92.
Demography
Area: 318,193 sq mi, 824,116 sq km. Population (2007): 2,074,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 6.5, persons per sq km 2.5. Urban (2006): 34.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.13%; female 49.87%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 38.2%; 15-29, 31.3%; 30-44, 15.6%; 45-59, 9.2%; 60-74, 4.5%; 75 and over, 1.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Ovambo 34.4%; mixed race (black/white) 14.5%; Kavango 9.1%; Afrikaner 8.1%; San (Bushmen) and Bergdama 7.0%; Herero 5.5%; Nama 4.4%; Kwambi 3.7%; German 2.8%; other 10.5%. Religious affiliation (2000): Protestant (mostly Lutheran) 49.3%; Roman Catholic 17.7%; unaffiliated Christian 14.1%; independent Christian 10.8%; traditional beliefs 6.0%; other 2.1%. Major urban localities (2001): Windhoek 233,529; Rundu 44,413; Walvis Bay 42,015; Oshakati 28,255; Katima Mulilo 22,694. Location: southwestern Africa, bordering Angola, Zambia, Botswana, South Africa, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 24.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.06. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 44.5 years; female 42.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2006-07). Revenue:N$16,209,000,000 (tax revenue 90.0%, of which customs duties and excises 39.9%, income tax 28.9%, VAT 19.7%; nontax revenue and grants 10.0%). Expenditures: N$15,287,800,000 (current expenditure 82.0%, of which wages and salaries 40.2%; capital expenditure 18.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): roots and tubers 295,000, corn (maize) 60,853, millet 49,000; livestock (number of live animals) 2,660,252 sheep, 2,383,960 cattle, 2,061,403 goats; fisheries production (2005) 552,745. Mining and quarrying (2005): salt 573,248; fluorspar 84,211; zinc (metal content) 68,000. Manufacturing (value added in N$’000,000; 2006): food and food products 2,633 (of which fish processing 620, meat processing 101); other manufactures include fur products (from Karakul sheep), textiles, carved wood products, and refined metals. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,397,000,000(2,819,000,000). Households (2003-04). Average household size 4.9; average annual income per household N$43,520 (US$6,554); sources of income: wages and salaries 46.4%, farming 29.6%, transfer payments 10.2%, self-employment 7.1%; expenditure (2001): food and nonalcoholic beverages 29.6%, housing and energy 20.6%, transportation 14.8%, education 7.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 348; remittances (2006) 16; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 254; official development assistance (2005) 119 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 108; remittances (2006) 17; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -12. Population economically active (2006): total 656,000; activity rate of total population 32.0% (participation rates: over age 15, 54.0%; female 43.4%; officially unemployed 5.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004-05): US$317,015,000. Gross national income (2006): US$6,428,000,000 (US$3,141 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.0%, in permanent crops 0.01%, in pasture 46.2%; overall forest area (2005) 9.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f. for commodities and trading partners): N$21,719,000,000 (refined petroleum products 18.3%; transport equipment 16.0%; chemicals, rubber, and plastics 12.1%; food, beverages, and tobacco 11.5%; machinery and apparatus 9.8%). Major import sources (2004): South Africa 85.4%; UK 2.6%; Germany 1.9%; China 1.2%; Zimbabwe 0.8%. Exports (2006): N$20,605,000,000 (diamonds 33.0%; fish 18.2%; other minerals [mainly gold, zinc, copper, lead, and silver] 12.4%; refined zinc 12.2%; meat preparations [mostly beef] 7.8%). Major export destinations (2004): South Africa 27.8%; UK 14.9%; Angola 13.8%; US 11.0%; Spain 9.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2006) 2,382 km; passenger-km (1995-96) 48,300,000; metric ton-km (2003-04) 1,247,400. Roads (2004): total length 42,237 km (paved 13%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 82,580; trucks and buses 81,002. Air transport (2005; Air Namibia only): passenger-km 1,012,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 60,429,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 47,000 (23); televisions (2003): 509,000 (259); telephone landlines (2005): 139,000 (69); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 495,000 (245); personal computers (2004): 220,000 (109); total Internet users (2005): 81,000 (40).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 26.5%; incomplete primary education 25.5%; complete primary 8.0%; incomplete secondary 24.9%; complete secondary 11.4%; higher 3.7%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 85.0%; males literate 86.8%; females literate 83.5%. Health: physicians (2004) 598 (1 per 3,201 persons); hospital beds (2004-05; public sector only) 6,811 (1 per 283 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 48.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,996 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 109% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 9,200 (army 97.8%, navy 2.2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.2%; per capita expenditure US$92.
Background
Long inhabited by indigenous peoples, Namibia was explored by the Portuguese in the late 15th century. In 1884 it was annexed by Germany as German South West Africa. It was captured in World War I by South Africa, which received it as a mandate from the League of Nations in 1920 and refused to give it up after World War II. A UN resolution in 1966 ending the mandate was challenged by South Africa in the 1970s and ’80s. Through long negotiations involving many factions and interests, Namibia achieved independence in 1990.
Recent Developments
Namibia’s international standing suffered somewhat in 2007. By September six senior police officers were facing charges or were under investigation for alleged corruption. Namibia also continued to support the regime of Pres. Robert Mugabe in Zimbabwe and invited him to make a state visit. The government was, however, able to persuade the De Beers diamond-mining company to sell it a larger share of its seafloor mining and to establish the Namibia Diamond Trading Company as a joint venture to sell some of Namibia’s diamonds to local cutting and polishing companies. As a result of the increase in the price of uranium oxide, the Rossing uranium mine announced plans for large-scale expansion.
Nauru
Official name: Naoero (Republic of Nauru). Form of government: republic with one legislative house (Parliament [18]). Head of state and government: President Marcus Stephen (from 2007). Capital: government offices are located in Yaren district. Official language: none; Nauruan is the national language; English is the language of business and government. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Nauruan dollar ($N) = 1 Australian dollar ($A) = 100 Nauruan and Australian cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = $A 1.05.
Demography
Area: 8.2 sq mi, 21.2 sq km. Population (2007): 10,200. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,244, persons per sq km 481.1. Urban (2005): 100%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.11%; female 49.89%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.5%; 15-29, 29.5%; 30-44, 17.8%; 45-59, 11.8%; 60-74, 3.1%; 75 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Nau-ruan 48.0%; Kiribertese (Gilbertese) 19.3%; Chinese 13.0%; Tuvaluan 6.9%; Australian white 6.2%; other 6.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 49%, of which Congregational 29%; Roman Catholic 24%; Chinese folk-religionist 10%; other 17%. Major cities: none; population of Yaren urban area (2007) 4,616. Location: western Pacific Ocean, near the equator east of Papua New Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 25.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.19. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 59.2 years; female 66.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: $A 27,000,000 (largely from fishing license fees). Expenditures: $A 26,400,000. Public debt (2005): US$33,300,000. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$79,000,000 (US$7,840 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): coconuts 1,600, tropical fruit (including mangoes) 275; coffee, almonds, figs, and pandanus (screw pine) are also cultivated; livestock (number of live animals) 2,800 pigs, 5,000 chickens; fisheries production (2005) 39. Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock (gross weight including basic slagand guano) 11,000. Manufacturing: none. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 32,000,000 (32,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (46,000). Population economically active (2002): 3,280; activity rate of total population 32.6% (participation rates: over age 15, 76.7%; female 45.5%; unemployed 22.7%). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.1. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1.0; official development assistance (2005) 16 (commitments).
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; f.o.b. in trading partners and c.i.f. in commodities): US$20,000,000 (agricultural products 8.0%, of which food 6.5%). Major import sources (2005): Australia 57.4%; US 9.6%; Germany 8.0%; Indonesia 7.4%; Fiji 3.7%. Exports (1999): US$40,000,000 (phosphate, virtually 100%). Major export destinations (2005): South Africa 56.9%; India 15.7%; Canada 5.9%; South Korea 3.3%; Germany 2.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): length 5 km. Roads (2004): total length 40 km (paved 73%). Vehicles (1989): passenger cars, trucks, and buses 1,448. Air transport (2001): passenger-km 287,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 29,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2002): 800 (77); telephone landlines (2003): 1,600 (160); cellular telephone subscribers (2003): 1,300 (130).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1992). Percentage of population ages 5 and over having: primary education or less 77.4%; secondary education 12.9%; higher 4.1%; not stated 5.6%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 97%. Health (2004): physicians 5 (1 per 2,012 persons); hospital beds 60 (1 per 168 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 10.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): Nauru does not have any military establishment. The defense is assured by Australia, though no formal agreement exists.
Background
Nauru was inhabited by Pacific islanders when British explorers arrived in 1798 and named it Pleasant Island for the friendly welcome they received. Annexed by Germany in 1888, it was occupied by Australia at the start of World War I, and in 1919 it was placed under a joint mandate of Britain, Australia, and New Zealand. During World War II it was occupied by the Japanese. Made a UN trust territory under Australian administration in 1947, it gained independence in 1968. During the mid-1990s Nauru suffered political unrest.
Recent Developments
In March 2008 the detention center on Nauru set up to hold people seeking asylum in Australia was closed, dealing a severe blow to the island’s economy (as much as 10% of the population was estimated to have been supported by the center in some capacity). A positive economic note, however, was that the country’s flagging phosphate industry, once the mainstay of the economy and a source of great riches, was revived, with new mining methods and new deposits that some thought could last 30 more years.
Nepal
Official name: Nepal (Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal). Form of government: multiparty republic with interim legislature (Constituent Assembly [statutory number, 601]). Chief of state and government: Prime Minister Pushpa Kamal Dahal (from 2008). Capital: Kathmandu. Official language: Nepali. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Nepalese rupee (NR; plural NRs) = 100 paisa (pice); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = NRs 68.30.
Demography
Area: 56,827 sq mi, 147,181 sq km. Population (2007): 28,196,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 496.2, persons per sq km 191.6. Urban (2005): 15.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.56%; female 50.44%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 39.0%; 15-29, 27.9%; 30-44, 17.2%; 45-59, 10.2%; 60-74, 4.7%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Nepalese 55.8%; Maithili 10.8%; Bhojpuri 7.9%; Tharu 4.4%; Tamang 3.6%; Newar 3.0%; Awadhi 2.7%; Magar 2.5%; Gurkha 1.7%; other 7.6%. Religious affiliation (2001): Hindu 80.6%; Buddhist 10.7%; Muslim 4.2%; Kirat (local traditional belief) 3.6%; Christian 0.5%; other 0.4%. Major cities (2001): Kathmandu 671,846; Biratnagar 166,674; Lalitpur 162,991; Pokhara 156,312; Birganj 112,484. Location: south-central Asia, bordering China and India.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 29.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 8.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.48. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 62.1 years; female 62.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:NRs 86,800,000,000 (tax revenue 69.1%; grants 15.9%; nontax revenue 15.0%). Expenditures: NRs 97,900,000,000 (economic services 24.1%; education 19.5%; general public services 14.9%; defense 11.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,217,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 4,290,000, sugarcane 2,376,103, potatoes 1,738,840; livestock (number of live animals) 7,154,000 goats, 6,994,000 cattle, 4,081,000 buffalo; roundwood 13,952,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production 42,463 (from aquaculture 53%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 263,701; marble 23,850 sq m; talc 5,832. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): food products 83; textiles and wearing apparel 73; tobacco products 55. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 2,401,000,000 (1,964,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 9,298 (257,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (685,000). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$7,476,000,000 (US$270 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 9,981,000; activity rate of total population 38.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 66.3%; female 41.0%; unofficially unemployed [2004] 42%). Households (2003-04). Average household size 5.3; income per household NRs 80,111 (US$1,084); sources of income: self-employment 47%, wages and salaries 28%; expenditure: food and beverages 59.0%, housing 9.5%, education 2.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 131; remittances (2006) 1,211; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 7.0; official development assistance (2005) 428. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 163; remittances (2006) 65. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 16.5%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 12.1%; overall forest area (2005) 25.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; c.i.f.): NRs 175,108,000,000 (basic manufactures [including fabrics, yarns, and made-up articles] 24.3%; mineral fuels [mostly refined petroleum] 20.8%; machinery and transport equipment 15.0%; chemicals and chemical products 14.2%). Major import sources (2006): India 48%; China 13%; UAE 12%; Saudi Arabia 5%; Kuwait 4%. Exports (2005-06; f.o.b.): NRs 61,167,000,000 (agricultural products 14.5%, of which vegetable ghee 6.6%; ready-made garments 12.2%; carpets 9.7%; jute goods 4.4%; pashminas 3.0%). Major export destinations (2006): India 58%; US 14%; Germany 6%; UK 3%; France 2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 53 km; passengers carried (2002) 1,600,000; freight handled 22,000 metric tons. Roads (2004): total length 17,281 km (paved 31%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 66,395; trucks and buses 40,267. Air transport (2003): passenger-km 652,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 486,000 (18); televisions (2003): 249,000 (9.6); telephone landlines (2006): 596,000 (22); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,042,000 (38); personal computers (2005): 132,000 (4.9); total Internet users (2006): 249,000 (9).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 6 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 9.9%; primary education 41.9%; incomplete secondary 30.6%; complete secondary and higher 17.6%. Literacy (2003-04): total population ages 15 and over literate 48.0%; males literate 64.5%; females literate 33.8%. Health (2005-06): physicians 1,259 (1 per 21,737 persons); hospital beds 6,796 (1 per 4,027 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 59.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,503 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 138% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 69,000 (army 100.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.1%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Background
Nepal developed under early Buddhist influence, and dynastic rule dates from about the 4th century ad. It was formed into a single kingdom in 1769 and fought border wars with China, Tibet, and British India in the 18th-19th centuries. Its independence was recognized by Britain in 1923. A new constitution in 1990 restricted royal authority and accepted a democratically elected parliamentary government. The Maoist Communist Party of Nepal began an armed insurgency in 1996. Nepal signed trade agreements with India in 1997. On 1 Jun 2001, King Birendra, the queen, and seven other members of the royal family were fatally shot by Crown Prince Dipendra, who then turned the gun on himself.
Recent Developments
With the signing of a comprehensive peace accord between the government and Maoist rebels in November 2006, Nepal’s 11-year-long Maoist insurgency came to an end. With the promulgation of an interim constitution in January 2007, Nepal turned from a Hindu kingdom into a secular state, with the role of the monarchy suspended. In December 2007 the legislature agreed to Maoist demands and voted to end the monarchy, and the Maoists, who had left the government over the issue, rejoined it. In April 2008 legislative elections the Maoists won the largest number of seats, and in late May the monarchy was abolished.
The Netherlands
Official name: Koninkrijk der Nederlanden (Kingdom of The Netherlands). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with a parliament (States General) comprising two legislative houses (Senate [75]; House of Representatives [150]). Chief of state: Queen Beatrix (from 1980). Head of government: Prime Minister Jan Peter Balkenende (from 2002). Seat of government: The Hague. Capital: Amsterdam. Official language: Dutch. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 16,034 sq mi, 41,528 sq km. Population (2007): 16,371,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,255, persons per sq km 484.6. Urban (2005): 80.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.45%; female 50.55%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 18.3%; 15-29, 18.1%; 30-44, 23.0%; 45-59, 21.3%; 60-74, 12.9%; 75-84, 4.9%; 85 and over, 1.5%. Ethnic composition (by place of origin [including 2nd generation]; 2005): Netherlander 80.7%; Indonesian 2.4%; Turkish 2.2%; Surinamese 2.0%; Moroccan 2.0%; other 10.7%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 30%; Reformed/Lutheran tradition 20%; Muslim 6%; nonreligious/atheist 40%; other 4%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Amsterdam 1,465,405; Rotterdam 1,176,869; The Hague 990,463; Utrecht 577,389; Haarlem 405,430. Location: northwestern Europe, bordering the North Sea, Germany, and Belgium.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.3 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 62.9%. Death rate per I,000 population (2006): 8.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.72. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 77.6 years; female 81.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €192,220,000,000 (social security contributions 35.7%; VAT 19.8%; income tax 15.3%; corporate taxes 7.8%; nontax revenue 7.5%). Expenditures: €200,270,000,000 (social security and welfare 41.9%; education 11.1%; health 10.4%; economic affairs 6.6%; defense 3.6%). National debt (2006): US$322,400,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): potatoes 6,240,000, sugar beets 5,414,000, wheat 1,184,000, flowering bulbs and tubers 79,000 acres (32,000 hectares), of which tulips 24,700 acres (10,000 hectares), cut flowers/plants under glass 12,400 acres (5,000 hectares); livestock (number of live animals) II,356,000 pigs, 3,749,000 cattle, 1,376,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 1,110,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 26%; fisheries production (2005) 617,383 (from aquaculture 11%). Manufacturing (value added in €’000,000; 2002): food, beverages, and tobacco 12,936; chemicals and chemical products 7,542; printing and publishing 5,743; electric/electronic machinery 5,050. Energy production (con-sumption,):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 96,366,000,000 (95,556,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) negligible (13,551,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 15,500,000 ([2004] 361,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 65,801,000 (28,801,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 82,920,000,000 ([2004] 54,010,000,000). Households (2005). Average household size (2006) 2.3; disposable income per household €34,321 (US$42,683); sources of income (1996): wages 48.4%, transfers 28.5%, self-employment 11.3%; expenditure: housing and energy 22.2%, transportation and communications 15.9%, food and beverages 13.6%, recreation and culture 10.1%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 26.7%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 29.1%; overall forest area (2005) 10.8%. Gross national income (2006): US$670,483,000,000 (US$40,940 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 8,308,000; activity rate of total population 51% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 75.1%; female 45.1%; unemployed [April 2005-March 2006] 6.3%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 10,383; remittances (2006) 2,424; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 28,556. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 16,082; remittances (2006) 6,662; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 52,706.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): €248,827,000,000 (mineral fuels 14.7%, of which crude petroleum 7.5%; chemicals and chemical products 13.1%; computers and related equipment 11.7%; food 7.6%; road vehicles 5.7%). Major import sources:Germany 19.0%; Belgium/Luxembourg 10.7%; US 8.0%; China 7.7%; UK 6.3%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): €280,743,000,000 (chemicals and chemical products 17.0%; food 11.6%; mineral fuels 11.0%; computers and related equipment 10.6%). Major export destinations: Germany 23.6%; Belgium/Luxembourg 11.9%; UK 9.3%; France 9.2%; Italy 5.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: length (2006) 2,797 km; pas-senger-km (2004) 14,097,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 4,293,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 134,981 km (paved 90%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 7,230,178; trucks and buses 1,064,846. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 68,316,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,650,500,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 4,712,000 (289); televisions (2003): 10,514,000 (648); telephone landlines (2005): 7,600,000 (466); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 15,834,000 (971); personal computers (2005): 12,060,000 (740); total Internet users (2006): 14,544,000 (889); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 5,192,000 (318).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 15-64 having: primary education 9.5%; lower secondary 9.6%; upper secondary 10.7%; vocational 44.0%; higher 25.4%, of which university 9.2%; unknown 0.8%. Health: physicians (2003) 50,854 (1 per 319 persons); hospital beds (2003) 81,125 (1 per 200 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 4.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,479 (vegetable products 70%, animal products 30%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 53,130 (army 43.6%, navy 22.8%, air force 20.8%, paramilitary 12.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$523.
Background
Celtic and Germanic tribes inhabited The Netherlands at the time of the Roman conquest. Under the Romans, trade and industry flourished, but by the mid-3rd century AD Roman power had waned, eroded by resurgent German tribes and the encroachment of the sea. A Germanic invasion (406-07) ended Roman control. The Merovingian dynasty followed the Romans but was supplanted in the 7th century by the Carolingian dynasty, which converted the area to Christianity. After Charlemagne’s death in 814, the area was increasingly the target of Viking attacks. It became part of the kingdom of Lotharingia, which established an Imperial Church. In the 12th-14th centuries dike building occurred on a large scale. The dukes of Burgundy gained control in the late 14th century. By the early 16th century the Low Countries were ruled by the Spanish Habsburgs. In 1581 the seven northern provinces, led by Calvinists, declared their independence from Spain, and in 1648, following the Thirty Years’ War, Spain recognized Dutch independence. The 17th century was the golden age of Dutch civilization. The Dutch East India Company secured Asian colonies, and the country’s standard of living soared. In the 18th century the region was conquered by the French and became the kingdom of Holland under Napoleon (1806). It remained neutral in World War I and declared neutrality in World War II but was occupied by Germany. It joined NATO in 1949, was a founding member of what is now the European Community, and is part of the EU.
Recent Developments
Immigration and integration remained important topics of discussion in The Netherlands in 2007. Ayaan Hirsi Ali, a Somali-born former MP and controversial opponent of radical Islam, returned to The Netherlands in October from her work at the American Enterprise Institute in Washington DC when the Dutch government ended funding for her security detail abroad. There were political discussions about the presumed loyalty of dual citizens, as well as lively debate in response to a speech by Argentine-born Dutch Crown Princess Maxima, champion of integration in The Netherlands, in which she described Dutch identity as not “static” but rather multidimensional and fluid. The Dutch economy grew 4.7% in 2007. The government, which anticipated a budget surplus in 2008, announced plans to reemploy many of the long-term unemployed. It also reported its goal of giving priority to improvements in energy, water quality and water control, health care for citizens, and education. In an effort to continue to attract international business and innovative research, the government formulated plans to improve access to the country in order to admit talented foreigners to work in The Netherlands and to study at Dutch universities. In November the government extended the mandate to 2010 for some 1,700 Dutch soldiers stationed in southern Afghanistan.
Netherlands Antilles
Official name: Nederlandse Antillen (Netherlands Antilles). Political status: nonmetropolitan territory of The Netherlands with one legislative house (Island Council of Curasao [21]). Chief of state: Dutch Queen Beatrix (from 1980), represented by Governor Frits Goedgedrag (from 2002). Head of government: Prime Minister Emily de Jongh-Elhage (from 2006). Capital: Willemstad. Official language: Dutch. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Netherlands Antil-lean guilder (NAf.)= 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = NAf. 1.79.
Demography
Area: 308 sq mi, 800 sq km. Population (2007): 192,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 623.4, persons per sq km 240.0. Urban (2003): 70.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 46.53%; female 53.47%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 22.7%; 15-29, 18.6%; 30-44, 23.9%; 45-59, 20.8%; 60-74, 10.3%; 75-84, 2.8%; 85 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): local black-other (Antillean Creole) 81.1%; Dutch 5.3%; Surinamese 2.9%; other (significantly West Indian black) 10.7%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 72.0%; Protestant 16.0%; Spiritist 0.9%; Buddhist 0.5%; Jewish 0.4%; Baha’i 0.3%; Hindu 0.2%; Muslim 0.2%; other/unknown 9.5%. Major locales (2001): Willemstad 93,599; Kralendijk 3,179; Philipsburg 1,227; Oranjestad 1,003; The Bottom 462. Location: two separate island groups in the Caribbean Sea, one just north of Venezuela, the other east of Puerto Rico.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.99. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 73.8 years; female 78.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:NAf. 822,600,000 (tax revenue 78.9%, of which sales tax 40.0%, import duties 17.4%; grants 10.9%; nontax revenue 10.2%). Expenditures: NAf. 910,600,000 (current expenditures 99.8%, of which transfers 38.2%, wages 32.5%, interest payments 16.1%; development expenditures 0.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): mostly tomatoes, beans, cucumbers, gherkins, melons, and lettuce grown on hydroponic farms; livestock (number of live animals) 13,500 goats, 9,000 sheep, 2,600 asses; fisheries production 2,422. Mining and quarrying (2003): salt 500,000; sulfur byproduct (2002) 30,000. Manufacturing (2002): residual fuel oil 5,200,000; gas-diesel oils 2,620,000; asphalt 1,030,000; other manufactures include electronic parts, cigarettes, textiles, rum, and Curagao liqueur. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 1,248,000,000 ([2004] 1,065,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (79,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 9,081,000 (2,176,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 988; remittances (2005) 5; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -11. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 109; remittances (2004) 52; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 5.0. Households. Average household size (2005) 2.8; expenditure (1996): housing 26.5%, transportation and communications 19.9%, food 14.7%, household furnishings 8.8%, recreation and education 8.2%. Population economically active (2006): total 91,178; activity rate of total population 48.5% (participation rates [2001]: ages 15-64, 68.7%; female 49.0%; unemployed [2006] 13.2%). Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$3,341,000,000 (US$17,691 per capita). Public debt (external outstanding; 2006): US$459,200,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.0%; overall forest area (2005) 1.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2002; c.i.f.): US$2,268,500,000 (crude petroleum 59.7%; refined petroleum 8.7%; food 6.4%). Major import sources (2004): Venezuela 51.1%; US 21.9%; The Netherlands 5.0%. Exports (2002; f.o.b.): US$1,699,200,000 (refined petroleum 94.7%; food 1.2%). Major export destinations (2004): US 20.4%; Panama 11.2%; Guatemala 8.8%; Haiti 7.1%; The Bahamas 5.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2003): total length 600 km (paved 50%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 64,947; trucks and buses 15,335. Airtransport (2001; Curagaoand Sint Maarten airports only): passenger arrivals and departures 2,131,000; freight loaded and unloaded 18,900 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 66,000 (349); televisions (1999): 71,000 (390); telephone landlines (2004): 80,000 (437); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 200,000(1,092); total Internet users (1999): 2,000 (11).
Education and health
Secondary 42.8%; upper secondary 16.8%; higher 11.4%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 96.9%; males literate 96.9%; females literate 97.0%. Health: physicians (2001) 333 (1 per 520 persons); hospital beds (2002) 1,264 (1 per 138 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 9.9. Food (2004): daily per capita caloric intake 2,464 (vegetable products 85%, animal products 15%); 128% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2005): more than 1,000 Dutch naval personnel are stationed in the Netherlands Antilles and Aruba.
Background
The islands of the Netherlands Antilles were sighted by Christopher Columbus in 1493 and claimed for Spain. In the 17th century the Dutch gained control, and in 1845 the islands became the Netherlands Antilles. In 1954 they became an integral part of The Netherlands, with full autonomy in domestic affairs. Aruba seceded from the group in 1986.
Recent Developments
The Netherlands Antillean islands of Bonaire, Sint Eu-statius, and Saba were due to achieve the status of Dutch local authorities in January 2010 following agreement on a new constitution (which also conferred local autonomy on Curasao and Sint Maarten). In December 2007 The Netherlands agreed to write off some >2.5 billion (about US$3.7 billion) of the islands’ debt, a key development that the local governments had desired.
New Caledonia
Official name: Nouvelle-Caledonie (New Caledonia). Political status: overseas collectivity of France with one legislative house (Congress [54]). Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007), represented by High Commissioner Yves Dassonville (from 2007). Head of government: President Harold Martin (from 2007). Capital: Noumea. Official language: none; Kanak languages and French have special recognition per the Noumea Accord. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 franc de la Comptoirs fransais du Pacifique franc (CFPF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFPF 75.59.
Demography
Area: 7,172 sq mi, 18,575 sq km. Population (2007): 242,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 33.7, persons persq km 13.0. Urban (2005): 63.7%. Sex distribution (2004): male 50.47%; female 49.53%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 28.0%; 15-29, 24.3%; 30-44, 23.4%; 45-59, 14.9%; 60-74, 7.2%; 75-84, 1.7%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (1996): Melanesian 45.3%, of which local (Kanak) 44.1%, Vanuatuan 1.2%; European 34.1%; Wallisian or Futunan 9.0%; Indonesian 2.6%; Tahitian 2.6%; Vietnamese 1.4%; other 5.0%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 54.2%; Protestant 14.0%; unaffiliated/other Christian 18.8%; Muslim 2.7%; nonreligious 5.8%; other 4.5%. Major communes (2004): Noumea 91,386 (urban agglomeration 146,245); Mont-Dore 24,195; Dum-bea 18,602; Paita 12,062; Poindimie 4,824. Location: South Pacific Ocean, east of Australia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.7 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 32.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.20. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.9 years; female 78.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFPF 116,323,000,000 (tax revenue 71.4%, of which indirect taxes 35.8%, direct taxes 35.6%; nontax revenue 28.6%). Expenditures: CFPF 108,085,000,000 (current expenditure 95.8%; development expenditure 4.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 1998): US$79,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 16,350, yams 11,080, corn (maize) 5,669; livestock (number of live animals) 111,000 cattle, 27,000 pigs, 600,000 chickens; roundwood 4,800 cu m; fisheries production 5,848, of which tuna 2,450, shrimp 2,440 (from aquaculture 43%). Mining and quarrying (2006): nickel ore 6,150,000, of which nickel content 105,000; cobalt 1,100 (recovered). Manufacturing (2006): cement (2004) 114,762; ferronickel (metal content) 48,723; nickel matte (metal content) 13,655; other manufactures include beer, copra cake, and soap. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 1,873,000,000 ([2005] 1,826,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (281,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (580,000). Population economically active (2004): total 96,406; activity rate of total population 41.8% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 57.1%; female [1996] 39.7%; registered unemployed [2005] 15.8%). Gross national income (2006): US$4,743,000,000 (US$19,935 per capita). Households (1991). Average household size (2004) 3.6; average annual income per household: cFpF 3,361,233 (US$32,879); sources of income: wages and salaries 68.2%, transfer payments 13.7%; expenditure: food and beverages 25.9%, housing 20.4%, transportation and communications 16.1%, recreation 4.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 253; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 65. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 171; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 8.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.3%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 13.1%; overall forest area (2005) 39.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): CFPF 170,692,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 20.4%; mineral products [mostly coal and refined petroleum] 16.4%; transportation equipment 14.8%; food 13.4%; chemicals and chemical products 7.7%). Major import sources: EU 47.2%, of which France 32.3%; Singapore 15.0%; Australia 9.2%; New Zealand 5.5%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): CFPF 104,047,000,000 (ferronickel 62.1%; nickel ore 15.3%; nickel matte 13.1%; shrimp 2.3%). Major export destinations: EU 34.5%, of which France 16.0%; Japan 18.8%; South Korea 13.5%; Taiwan 12.2%; China 5.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 5,432 km (paved [1993] 52%). Vehicles:passenger cars (2005) 105,159; trucks and buses (1997) 23,000. Airtransport (2006; Air Caledonie only): passenger-km 1,432,076,000; metric ton-km cargo 20,181,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 19,000 (79); televisions (2004): 115,000 (498); telephone landlines (2005): 55,000 (236); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 134,000 (573); personal computers (2005): 6,000 (25); total Internet users (2006): 80,000 (332); broadband Internetsubscribers (2005): 9,600 (41).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling through some primary education 38.1%; primary 9.5%; lower secondary 6.4%; upper secondary 11.8%; vocational 19.8%; higher 14.4%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 91.0%; males literate 92.0%; females literate 90.0%. Health: physicians (2004) 485 (1 per 476 persons); hospital beds (2004) 727 (1 per 317 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 5.7.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,540 French troops.
Between July 1772 and July 1775 James Cook made what ranks as one of the greatest sailing ship voyages, with a small former Whitby ship, the Resolution, and a consort ship, the Adventure. He found no trace of Terra Aus-tralis, though he sailed beyond latitude 70 deg S in the Antarctic, but he successfully completed the first west-east circumnavigation in high latitudes, charted Tonga and Easter Island during the winters, and discovered New Caledonia in the Pacific and the South Sandwich Islands and South Georgia Island in the Atlantic Ocean.
Background
Excavations indicate an Austronesian presence in New Caledonia about 2000-1000 bc. The islands were visited by James Cook in 1774 and by various navigators and traders in the 18th-19th centuries. They were occupied by France in 1853 and were a penal colony from 1864 to 1897. During World War II the islands were the site of Allied bases. They became a French overseas territory in 1946. In 1987 residents voted by referendum to remain part of France.
Recent Developments
After temporary setbacks, two nickel-mining plants in New Caledonia were scheduled to go ahead. The US$3.2 billion Goro nickel-cobalt project, which was stalled after cost blowouts of 72%, was due to commence production by the end of 2008. Construction of the US$3.8 billion Koniambo project in the Northern Province was scheduled to begin in 2010.
New Zealand
Official name: New Zealand (English); Aotearoa (Maori). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (House of Representatives [121]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Anand Satyanand (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Helen Clark (from 1999). Capital: Wellington. Official languages: English; Maori. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 New Zealand dollar (NZ$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = NZ$ 1.32.
Demography
Area: 104,515 sq mi, 270,692 sq km. Population (2007): 4,184,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 40.0, persons per sq km 15.5. Urban (2005): 86.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.22%; female 50.78%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 21.1%; 15-29, 20.5%; 30-44, 22.0%; 45-59, 19.4%; 60-74, 11.4%; 75-84, 4.3%; 85 and over, 1.3%. Ethnic composition (2006): European 67.6%, of which NZ European 59.1%; Maori (local Polynesian) 14.6%; Asian 9.2%, of which Chinese 3.7%; other Pacific peoples (mostly other Polynesian) 6.9%; other 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2006): Christian 51.1%, of which Anglican 13.3%, Roman Catholic 12.2%, Presbyterian 9.2%, Methodist 2.9%, Maori (indigenous) Christian 1.6%; Hindu 1.6%; Buddhist 1.3%; Muslim 1.0%; nonreligious 31.1%; unknown 12.9%; other 1.0%. Major urban agglomerations (2006): Auckland 1,208,091; Wellington 397,974; Christchurch 360,768; Hamilton 184,838; Napier 118,404. Location: between the South Pacific Ocean and the Tasman Sea, southeast of Australia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006-07): 14.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 54.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006-07): 6.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006-07): 2.14. Life expectancy at birth (2004-06): male 77.9 years; female 81.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue:NZ$51,489,000,000 (tax revenue 91.8%, of which individual income taxes 45.7%, taxes on goods and services 26.7%; nontax revenue 8.0%; grants 0.2%). Expenditures: NZ$44,099,000,000 (social protection 35.0%; health 20.0%; education 17.9%; defense 3.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): apples 524,000, potatoes 500,000, kiwifruit 318,000, greasy wool 209,250; livestock (number of live animals) 39,928,000 sheep, 9,501,000 cattle; roundwood 19,143,000 cu m, of which fuelwood, none; fisheries production 640,695 (from aquaculture 16%). Mining and quarrying (2004): limestone/marl 5,226,000; silver 43,003 kg; gold 10,583 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2005): food products 4,175; fabricated metals 1,350; printing and publishing 1,250. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 40,034,000,000 ([2004] 41,813,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 2,527,000 (198,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 2,629,000 (3,576,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 5,900,000 ([2004] 37,856,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 5,067,000 (6,214,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 3,773,000,000 ([2004] 3,766, 000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 2,152,200; activity rate of total population 52.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 77.0%; female 46.2%; unemployed [2006] 3.8%). Households (2003-04). Average household size (2004) 2.6; annual gross income per household (2006) NZ$68,500 (US$41,500); sources of income: wages and salaries 69.9%, transfer payments 12.8%, self-employment 9.1%; expenditure: housing 24.4%, food 16.1%, transportation 16.0%, household goods 12.6%. Gross national income (2006): US$98,383,000,000 (US$23,780 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,984; remittances (2006) 650; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 2,091. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,657; remittances (2006) 865; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -475. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.6%, in permanent crops 7.0%, in pasture 51.7%; overall forest area (2005) 31.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): NZ$40,774,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 21.4%; mineral fuels 14.9%; vehicles 11.7%; aircraft 4.2%; plastics 3.8%). Major import sources: Australia 20.1%; China 12.2%; US 12.1%; Japan 9.1%; Germany 4.4%. Exports (2006): NZ$34,619,000,000 (dairy products 20.6%; beef and sheep meat 12.1%; wood and paper [all forms] 9.4%; machinery and apparatus 8.6%; aluminum 4.3%; fish 3.7%). Major export destinations: Australia 20.5%; US 13.1%; Japan 10.3%; China 5.4%; UK 4.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2003) 3,898 km; metric ton-km cargo (1999-2000) 4,040,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 92,931 km (paved 64%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 2,402,207; trucks and buses 444,909. Air transport (2005; Air New Zealand only): passenger-km 26,093,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 781,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 746,000 (182); televisions (2004): 2,338,000 (576); telephone landlines (2005): 1,729,000 (422); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 3,530,000 (876); personal computers (2005): 2,077,000 (507); total Internet users (2006): 3,200,000 (788); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 576,000 (139).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling to incomplete secondary 24.5%; completed secondary 57.4%; completed undergraduate 18.1%. Literacy: virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2003) 8,790 (1 per 455 persons); hospital beds (2002) 23,825 (1 per 165 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006-07) 5.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,394 (vegetable products 70%, animal products 30%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 8,660 (army 51.1%, air force 26.0%, navy 22.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$269.
Background
Polynesian occupation of New Zealand dates to about ad 1000. First sighted by Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman in 1642, the main islands were charted by Capt. James Cook in 1769. Named a British crown colony in 1840, the area was the scene of warfare between colonists and native Maori through the 1860s. In 1907 the colony became the Dominion of New Zealand. It administered Western Samoa during 1919-62 and participated in both world wars. When Britain joined what is now the European Union in the early 1970s, its influence led New Zealand to expand its export markets and diversify its economy.
Recent Developments
In her formal address to the House of Representatives in February 2007, New Zealand Prime Minister Helen Clark declared plans for a carbon-neutral public service from 2012, a single government procurement policy for sustainably produced goods and services, a low-emission state vehicle fleet, improved waste management, and a program that would enable businesses to label themselves as carbon neutral. A guaranteed minimum wage for disabled workers was enacted in March, along with sick pay and leave entitlements. Free part-time preschool education for three- and four-year-olds was introduced in July, in addition to subsidized medical consultations and prescription medicines for those aged 25-44. Permits authorizing oil and gas exploration in the Great South Basin of the Southern Ocean over the next five years were granted in July to two international consortia. Bottom trawling and dredging was banned over 30% of the seabed in New Zealand’s 200-nautical-mile exclusive economic zone. Government officials signed a free-trade agreement with China in April 2008 and began talks for similar agreements with Japan and South Korea in May.
Nicaragua
Official name: Republica de Nicaragua (Republic of Nicaragua). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [92]). Head of state and government: President Daniel Ortega (from 2007). Capital: Managua. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 cordoba oro (C$) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = C$19.37.
Demography
Area: 50,337 sq mi, 130,373 sq km; land area alone equals 46,464 sq mi, 120,340 sq km. Population (2007): 5,602,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 120.6, persons per sq km 46.6. Urban (2005): 55.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.29%; female 50.71%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.6%; 15-29, 29.9%; 30-44, 17.1%; 45-59, 9.3%; 60-74, 4.3%; 75-84, 1.3%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo (Spanish/Indian) 63.1%; white 14.0%; black 8.0%; multiple ethnicities 5.0%; other 9.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 58.5%; Protestant/independent Christian 23.2%, of which Evangelical 21.6%, Moravian 1.6%; nonreligious 15.7%; other 2.6%. Major cities (2005; populations of urban areas of municip-ios): Managua 908,892; Leon 139,433; Chinandega 95,614; Masaya 92,598; Estelf 90,294. Location: Central America, bordering Honduras, the Caribbean Sea, Costa Rica, and the North Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.94. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.3 years; female 74.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:C$12,250,700,000 (tax revenue 96.3%, of which sales tax 38.2%, import duties 27.8%, tax on income and profits 25.9%; nontax revenue 3.7%). Expenditures: C$16,697,800,000 (current expenditure 58.4%; development expenditure 41.6%). Production (metric tons exceptas noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 4,682,000, corn (maize) 504,100, rice 312,100; livestock (number of live animals) 3,500,000 cattle, 268,000 horses; roundwood (2005) 6,042,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 98%; fisheries production (2005) 29,500, of which lobster 8,800 (from aquaculture 29%). Mining and quarrying (2004-05): gold 123,600 troy oz. Manufacturing (value added in C$’000,000 at prices of 1994; 2003): food 1,917; textiles and wearing apparel 969; beverages 713. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,822,000,000 (2,823,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (6,443,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 820,000 (1,308,000). Households. Average household size (2005) 4.9; expenditure (1999): food and beverages 41.8%, education 9.8%, housing 9.8%, transportation 8.5%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 15.9%, in permanent crops 1.9%, in pasture 39.7%; overall forest area (2005) 42.7%. Population economically active (2006): total 2,204,300; activity rate of total population 39.9% (participation rates: ages 10 and over [2005] 55.0%; female [2005] 35.2%; officially unemployed 5.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$5,233,000,000 (US$946 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,113,-000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 207; remittances (2006) 656; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 209; official development assistance (2005) 741 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 90; FDI (2001-03 avg.) 12.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$2,595,100,000 (nondurable consumer goods 24.4%; mineral fuels 20.8%; capital goods for industry 11.0%; transport equipment 7.3%). Major import sources: US 20.1%; Venezuela 11.9%; Costa Rica 8.9%; Mexico 8.3%; Guatemala 7.0%. Exports (2005): US$857,900,000 (coffee 14.5%; meat 13.9%; sugar 7.0%; shrimp 5.6%; gold 5.0%; chemical products 4.2%; lobster 3.9%). Major export destinations: US 32.1%; El Salvador 14.3%; Honduras 7.9%; Costa Rica 6.1%; Mexico 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 18,669 km (paved [2002] 11%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 94,998; trucks and buses 152,813. Air transport (2000): passenger-km 72,200,000; metric ton-km cargo (2003) 200,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 91,000 (18); televisions (2003): 648,000 (123); telephone landlines (2006): 248,000 (44); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,830,000(327); personal computers (2005): 220,000 (43); total Internet users (2006): 155,000 (28); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 19,000 (3.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 20.5%; 1-3 years 16.6%; 4-6 years 27.0%; 7-9 years 16.1%; 10-12 years 10.5%; vocational 2.3%; incomplete university 2.6%; complete university 4.4%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 78.0%; males literate 78.1%; females literate 77.9%. Health (2003): physicians 2,076(1 per 2,538 persons); hospital beds 5,030 (1 per 1,047 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 26.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,542 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 140% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 14,000 (army 85.7%, navy 5.7%, air force 8.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Background
Nicaragua has been inhabited for thousands of years, most notably by the Maya. Christopher Columbus arrived in 1502, and Spanish explorers discovered Lake Nicaragua soon thereafter. Nicaragua was governed by Spain until 1821, when it declared its independence. It was part of Mexico and then the United Provinces of Central America until 1838, when full independence was achieved. The US intervened in political affairs by maintaining troops there in 1912-33. Ruled by the dictatorial Somoza dynasty from 1936 to 1979, it was taken over by the Sandinistas after a popular revolt. They were opposed by armed insurgents, the US-backed contras, from 1981. The Sandinista government nationalized several sectors of the economy but lost the national elections in 1990. The new government returned many economic activities to private control, but unrest continued through the 1990s.
Recent Developments
The government signed cooperation agreements with Venezuela, Brazil, and Iran. Venezuela agreed to fund social programs, provide low-cost fuel, and build an oil refinery. Sweden, however, announced that it would soon withdraw all development assistance. Nicaraguan police seized ExxonMobil storage tanks by court order in August, citing unpaid customs duties. Although a settlement was later reached that allowed temporary usage of the tanks to store Venezuelan fuel, barriers to distribution caused prices to rise. Nicaragua’s projected economic growth rate was 3.9%, with a 10% inflation rate. On 4 September Hurricane Felix struck north of Puerto Cabezas as a Category 5 storm, killing more than 100 people and leaving about 150 missing. (See Disasters.)