Bosnia and Herzegovina
Official name: Bosna i Hercegovina (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Form of government: federal multiparty republic with bicameral legislature (House of Peoples [15]; House of Representatives [42]). Chiefs of state: Tripartite presidency with 8-month-long rotating chairmanship (final authority rests with International High Representative Christian Schwarz-Schilling [from 2008]). Head of government: Prime Minister Nikola Spiric (from 2007). Capital: Sarajevo. Official language: Bosnian (Serbo-Croatian). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 marka (KM) = 100 fenning; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = KM 1.24 (pegged to the euro from 1 Jan 2002; the euro also circulates as semiofficial legal tender).
Demography
Area: 19,772 sq mi, 51,209 sq km. Population (2007): 3,855,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 195.0, persons per sq km 75.3. Urban (2005): 45.7%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.63%; female 51.37%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 17.6%; 15-29, 21.6%; 30-44, 22.8%; 45-59, 18.9%; 60-74, 15.5%; 75-84, 3.3%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (1999): Bosniac 44.0%; Serb 31.0%; Croat 17.0%; other 8.0%. Religious affiliation (2002): Sunni Muslim 40%; Serbian Orthodox 31%; Roman Catholic 15%; Protestant 4%; nonreli-gious/other 10%. Major cities (2005): Sarajevo 380,000 (urban agglomeration [2004] 602,500); Banja Luka 165,100; Zenica 84,300; Tuzla 84,100; Mostar 63,500. Location: southeastern Europe, bordered by Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, and the Adriatic Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.0 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 88.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 8.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 0.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.19. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71 years; female 77 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: KM 6,191,000,000 (indirect taxes 42.1%; social security contributions 30.1%; taxes on trade 8.1%; other 19.7%). Expenditures: KM 6,601,000,000 (current expenditures 87.3%; development expenditures 12.3%). Gross national income (2006): US$11,566,000,000 (US$2,946 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): corn (maize) 1,004,000, potatoes 458,600, wheat 248,300; livestock (number of live animals) 902,700 sheep, 653,300 pigs, 459,800 cattle (in addition, 259,600 beehives); roundwood 3,806,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 36%; fisheries production (2004) 8,394 (from aquaculture 76%). Mining (2004): bauxite 480,000; lime 81,000; iron ore (metal content) 64,000. Manufacturing (value of exports in KM ’000,000; 2003): base metals and fabricated metal products 498.3; wood and wood products 398.9; machinery and apparatus 286.1. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 12,599,000,000 (10,517,000,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 8,578,000 (8,953,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (1,088,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (366,000,000). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$2,560,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 1,177,000; activity rate of total population 30.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 51.3%; female 36%; unemployed 31.1%). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.6; sources of income (1990): wages 53.2%, transfers 18.2%, self-employment 12.0%, other 16.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 565; remittances (2005) 1,844; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 334; official development assistance (2005) 384 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 123; remittances (2005) 26. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 19.6%, in permanent crops 1.9%, in pasture 20.4%; overall forest area (2005) 43.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): KM 10,990,000,000 (food products 18.0%; machineryand apparatus 16.2%; mineral fuels 14.5%; base metals and fabricated metal products 9.7%). Major import sources: Croatia 16.1%; Germany 12.1%; Serbia and Montenegro 10.0%; Italy 8.7%; Slovenia 6.0%. Exports (2005): KM 3,533,000,000 (base metals and fabricated metal products 26.4%; mineral fuels 14.2%; wood products 10.7%; machinery and apparatus 9.2%). Major export destinations: Croatia 21.7%; Serbia and Montenegro 16.5%; Italy 14.0%; Slovenia 10.3%; Germany 9.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length (2004) 1,021 km; passenger-km 51,396,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,159,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 22,419 km (paved [2001] 64%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 96,182; trucks and buses 10,919. Air transport (2001): passenger-km 44,000,000; metric ton-km (2003) 1,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 106,000 (28); televisions (2002): 950,000 (248); telephone landlines (2006): 989,000 (253); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,888,000 (483); total Internet users (2006): 950,000 (243); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 40,000 (3.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004; Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina only). Percentage of population ages 18 and over having: no formal schooling 8.0%; some to complete primary education 31.9%; lower secondary 24.4%; upper secondary 26.6%; higher 4.9%; advanced 4.2%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 94.6%; males literate 98.4%; females literate 91.1%. Health: physicians (2004)5,004 (1 per 769 persons); hospital beds (2003) 11,981 (1 per 322 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 6.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,068 (vegetable products 87%, animal products 13%); 153% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 11,865 (army virtually 100%); EU-sponsored peacekeeping troops (EUFOR) (November 2007) 2,450. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.9%; per capita expenditure US$46.
Background
Habitation long predates the era of Roman rule, when much of the country was included in the province of Dalmatia. Slav settlement began in the 6th century ad. For the next several centuries, parts of the region fell under the rule of Serbs, Croats, Hungarians, Venetians, and Byzantines. The Ottoman Turks invaded Bosnia in the 14th century, and after many battles it became a Turkish province in 1463. Herzegovina, then known as Hum, was taken in 1482. In the 16th-17th century the area was an important Turkish outpost, constantly at war with the Habsburgs and Venice. During this period much of the native population converted to Islam. At the Congress of Berlin after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78, Bosnia and Herzegovina was assigned toAustria-Hun-gary, and it was fully annexed in 1908. Growing Serb nationalism resulted in the 1914 assassination of the Austrian archduke Francis Ferdinand at Sarajevo by a Bosnian Serb, an event that precipitated World War I. After the war the area was annexed to Serbia. Following World War II the twin territory became a republic of communist Yugoslavia. With the collapse of communist regimes in Eastern Europe, Bosnia and Herzegovina declared its independence in 1992; its Serb population objected, and conflict ensued among Serbs, Croats, and Muslims. The 1995 peace accord established a loosely federated government roughly divided between a Muslim-Croat Federation and a Serb Republic (Republika Srpska). In 1996 a NATO peacekeeping force was installed there.
Recent Developments
In April 2008 the parliament of Bosnia and Herzegovina adopted reforms of the country’s police forces required by the European Union enlargement commissioner, and in June a stabilization and association agreement was signed, paving the way for eventual membership in the EU. However, local media and government watchdog activists criticized the government for widespread corruption, extensive waste, and poor economic conditions—at least 29% of labor force was unemployed, and nearly half of the population lived at or below the poverty level.
Botswana
Official name: Republic of Botswana. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [63]). Head of state and government: President Festus Mogae (from 1998). Capital: Gaborone. Official language: English (Tswana is the national language). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 pula (P) = 100 thebe; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = P 6.53.
Demography
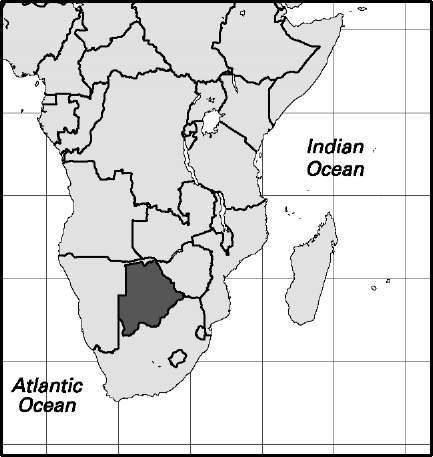
Area: 224,848 sq mi, 582,356 sq km. Population (2007): 1,882,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 8.4, persons per sq km 3.2. Urban (2005): 53.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.12%; female 50.88%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.6%; 15-29, 32.8%; 30-44, 14.9%; 45-59, 9.6%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Tswana 66.8%; Kalanga 14.8%; Ndebele 1.7%; Herero 1.4%; San (Bushman) 1.3%; Afrikaner 1.3%; other 12.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): independent Christian 41.7%; traditional beliefs 35.0%; Protestant 12.8%; Muslim 0.3%; Hindu 0.2%; other 10.0%. Major cities (2004): Gaborone 199,600; Francistown 89,100; Molepolole 58,600; Selebi-Pikwe 53,500; Maun 47,000. Location: southern Africa, bordered by Namibia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa.
Vital statistics
15.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.04. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 48.1 years; female 49.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:P 21,697,300,000 (tax revenue 88.2%, of which mineral royalties 50.2%, customs duties and excise tax 16.1%, general sales tax 8.9%; nontax revenue 10.8%, of which property income 2.6%; grants 1.0%). Expenditures: P 20,122,200,000 (general government services including defense 27.7%, education 24.5%, economic services 15.4%, health 12.4%, transfers 9.0%). Population economically active (2001): total 587,882; activity rate of total population 35.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 57.6%; female 43.8%; unemployed [2004] more than 20%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): roots and tubers 93,000, sorghum 32,000, pulses 17,500; livestock (number of live animals) 3,100,000 cattle, 1,950,000 goats, 300,000 sheep; roundwood 765,750 cu m, of which fuelwood 86%; fisheries production (2004) 161. Mining and quarrying (2005): soda ash 279,085; nickel ore (metal content) 39,305; copper ore (metal content) 31,300; diamonds 31,890,000 carats (Botswana is the world’s leading producer of diamonds by value). Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): beverages 50; motor vehicles (1997) 33; textiles 12. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 891,000,000 (2,641,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 916,000 (916,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.7%, in permanent crops 0.01%, in pasture 45.2%; overall forest area (2005) 21.1%. Gross national income (2006): US$8,153,000,000 (US$4,387 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$438,000,000. Households (2002-03). Average household size (2004) 4.3; average annual disposable income per household P 29,095 (US$5,320), of which cash income P 25,519 (US$4,670); expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 23.7%, transportation 15.6%, housing and energy 12.9%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco 9.6%, household furnishings 8.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 562; remittances (2005) 125; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 318; official development assistance (2005) 117 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 282; remittances (2005) 123; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 129.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$3,247,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 16.3%; food, beverages, and tobacco 13.7%; mineral fuels 13.3%; transport equipment 12.5%; chemical and rubber products 11.9%). Major import sources: Customs Union of Southern Africa (CUSA) 85.1%; Europe 6.5%, of which UK 1.3%; Zimbabwe 1.5%; US 1.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$4,395,000,000 (diamonds 75.1%; copper-nickel matte 10.3%; textiles 5.0%; meat products 1.7%). Major export destinations: Europe 77.0%, of which UK 75.7%; CUSA 9.0%; Zimbabwe 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length 888 km; (2001) passenger-km 106,000,000; (2001) metric ton-km cargo 747,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 25,233 km (paved 35%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 82,056; trucks and buses 74,387. Air transport (2002; Air Botswana only): passenger-km 96,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 300,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 80,000 (45); televisions (2003): 78,000 (44); telephone landlines (2006): 137,000 (78); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 980,000 (557); personal computers (2005): 86,000 (49); total Internet users (2005): 60,000 (34); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 1,600.
Education and health
Educational attainment (1993). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 34.7%; primary education 44.1%; some secondary 19.8%; postsecondary 1.4%. Literacy (2005): total population over age 15 literate 81.4%; males literate 78.6%; females literate 84.1%. Health (2006): physicians 526 (1 per 3,346 persons); hospital beds 3,911 (1 per 450 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 52.7. Food (2004): daily per capita caloric intake 2,084 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 112% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 9,000 (army 94.4%, air force 5.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.0%; per capita expenditure US$177.
Background
The region’s earliest inhabitants were the Khoekhoe and San (Bushmen). Sites were settled as early as AD 190 during the southerly migration of Bantu-speaking farmers. Tswana dynasties, which developed in the western Transvaal in the 13th-14th century, moved into Botswana in the 18th century and established several powerful states. European missionaries arrived in the early 19th century, but it was the discovery of gold in 1867 that excited European interest. In 1885 the area became the British Bechuanaland Protectorate. The next year the region south of the Molopo River became a crown colony, and it was annexed by the Cape Colony 10 years later. Bechuana-land itself continued as a British protectorate until the 1960s. In 1966 the Republic of Bechuanaland (later Botswana) was proclaimed an independent member of the British Commonwealth. Independent Botswana tried to maintain a delicate balance between its economic dependence on South Africa and its relations with the surrounding black countries; the independence of Namibia in 1990 and South Africa’s rejection of apartheid eased tensions.
Recent Developments
Controversy in Botswana continued in 2007 over the eviction of Bushmen from the Central Kalahari Game Reserve and the transfer of sales and distribution of Botswana’s diamonds from London to Gaborone. The De Beers Group’s Diamond Trading Co. neared completion of a US$450 million sorting center near Gaborone’s international airport. New foreign-owned diamond-cutting and polishing workshops, however, came into conflict with local unions over issues related to minimum wages.
Brazil
Official name: Republica Federativa do Brasil (Federative Republic of Brazil). Form of government: multiparty federal republic with two legislative houses (Federal Senate [81]; Chamber of Deputies [513]). Chief of state and government: President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva (from 2003). Capital: Brasflia. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 real (R$) = 100centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 1.61 reais.
Demography
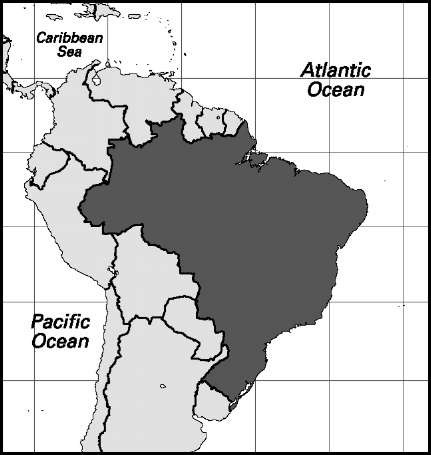
Area: 3,287,612 sq mi, 8,514,877 sq km. Population (2007): 189,335,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 57.6, persons per sq km 22.2. Urban (2005): 82.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.34%; female 50.66%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 27.8%; 15-29, 27.6%; 30-44, 21.7%; 45-59, 14.1%; 60-74, 6.5%; 75-84, 1.8%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Racial composition (2000): white 53.7%; mulatto and mestizo 39.1%; black and black/Amerindian 6.2%; Asian 0.5%; Amerindian 0.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 65.1%; Protestant 12.7%, of which Assemblies of God 9.2%; independent Christian 10.7%, of which Universal Church of the Kingdom of God 2.2%; Spiritist (Kardecist) 1.3%; Jehovah’s Witness 0.7%; African and syncretic religions 0.4%; Muslim 0.4%; nonreligious/other 8.7%. Major cities (metropolitan areas) (2005): Sao Paulo 10,277,500 (19,037,487); Rio de Janeiro 6,094,200 (11,570,524); Belo Hori-zonte 2,375,300 (5,391,284); Porto Alegre 1,386,900 (3,978,263); Recife 1,501,000 (3,599,181); Brasilia 2,231,100 (3,454,961); Salvador 2,672,500 (3,350,523); Fortaleza 2,374,900 (3,349,826); Curitiba 1,757,900 (3,141,366); Campinas 1,028,300 (2,633,938); Belem 1,396,800 (2,042,530); Goiania 1,193,100 (1,897,961); Man-aus 1,634,100 (1,644,690); Santos 416,100 (1,637,565). Location: eastern South America, bordered by Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Uruguay, Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, and Colombia. Families. Average family size (2005) 3.2; 1-2 persons (1996) 25.2%, 3 persons 20.3%, 4 persons 22.2%, 5-6 persons 23.3%, 7 or more persons 9.0%. Emigration (2000): Brazilian emigrants living abroad 1,887,895; in the US 42.3%, in Paraguay 23.4%, in Japan 12.0%. Immigration (2000): foreign-born immigrants living in Brazil 683,830; from Europe 56.3%, of which Portugal 31.2%; South/Central America 21.0%; Asia 17.8%, of which Japan 10.4%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.4 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.30. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.1 years; female 75.8 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling through less than one year of primary education 15.0%; 1 to 3 years of primary education 13.7%; complete primary/incomplete secondary 40.2%; complete secondary 18.8%; 1 to 3 years of higher education 3.8%; 4 years or more of higher education 8.0%; unknown 0.5%. Quality of working life. Proportion of employed population receiving minimum wage (2002) 53.5%. Number and percentage of children (age 5-17) working 5,400,000 (12.6% of age group). Access to services (1999). Proportion of households having access to: electricity (2002) 96.0%, of which urban households having access 98.8%, rural households having access 73.2%; safe public (piped) water supply 79.8%, of which urban households having access 92.3%, rural households having access 24.9%; public (piped) sewage system 43.6%, of which urban households having access 52.5%, rural households having access 4.5%; no sewage disposal 8.5%, of which urban households having no disposal 2.9%, rural households having no disposal 32.9%. Social participation. Voter turnout at last (October 2006) national legislative election 83.3%. Trade union membership in total workforce (2001) 19,500,000. Practicing Roman Catholic population in total affiliated Roman Catholic population (2000): large cities 10-15%; towns and rural areas 60-70%. Social deviance. Annual murder rate per 100,000 population (2002): 28; Rio de Janeiro only, 56; Sao Paulo only, 54. Material well-being (2003). Households possessing: television receiver 89.9%, of which urban 94.5%, rural 69.4%; refrigerator 86.7%, of which urban 91.7%, rural 60.0%; washing machine 34.0%, of which urban 38.1%, rural 10.0%.
National economy
Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$1,041,609,000,000 (US$5,502 per capita). Budget (2004). Revenue: R$422,450,-000,000 (tax revenue 76.4%, of which income tax 24.3%, social security contributions 18.2%, VAT 5.4%; social welfare contributions 22.2%; other 1.4%). Expenditures: R$372,730,000,000 (social security and welfare 33.8%; personnel 23.5%; transfers to state and local governments 18.1%; other 24.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$94,-497,000,000. Production (’000 metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): sugarcane 420,121, soybeans 50,195, corn (maize) 34,860, cassava 26,645, oranges 17,805, rice 13,141, bananas 6,703, wheat 5,201, seed cotton 3,727, tomatoes 3,304, dry beans 3,076, coconuts 3,034, potatoes 2,950, coffee 2,179, papayas 1,650, cashew apples 1,610, sorghum 1,530, pineapples 1,418, grapes 1,209, dry onions 1,059, lemons and limes 1,000, tobacco 879, mangoes 850, apples 844, mate 560, oil palm fruit 550, peanuts (groundnuts) 292, cashews 251, cacao beans 214, sisal 213, natural rubber 97, garlic 88, Brazil nuts 29; livestock (number of live animals) 207,000,000 cattle, 33,200,000 pigs, 15,200,000 sheep, 5,700,000 horses; roundwood (2004) 255,880,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 54%; fisheries production (2004) 1,015,916 (from aquacul-ture 27%). Mining and quarrying (metric tons; 2004): iron ore (metal content) 169,300,000 (world rank: 1); columbium (niobium) 39,741 of pyrochlore in concentrates (world rank: 1); bauxite 19,700,000 (world rank: 2); manganese (metal content in concentrate) 3,143,000 (world rank: 2); tantalum 277 (world rank: 2); asbestos fibre 231,115 (world rank: 4); tin (mine output; metal content) 12,468 (world rank: 5); kaolin (marketable product) 2,148,000; copper (metal content) 103,153; nickel (metal content in ore) 51,886; gold 47,596 kg; diamonds 300,000 carats. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 383,200,000,000 (391,700,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 6,000,000 (21,300,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 603,700,000 ([2004] 624,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 78,984,000 (72,211,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 9,600,000,000 (17,300,000,000); ethanol production (barrels; 2005) 102,900,000, of which exported to US 2,600,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.0%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 23.3%; overall forest area (2005) 57.2%. Population economically active (2004): total 92,860,100; activity rate of total population 51.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 73.2%; female 43.1%; unemployed [February 2006-January 2007] 10.0%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,861; remittances (2006) 7,373; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05) 16,481. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,720; remittances (2005) 498; FDI (2001-05) 2,559. Households. Average household size (2005) 3.5. Family/household in-comeand expenditure. Average family size (2000) 3.5; average annual income per household (2000) R$14,065 (US$7,686), median annual income per household (2000) R$6,744 (US$3,685); expenditure (1995-96; urban areas only): housing, energy, and household furnishings 28.8%, food and beverages 23.4%, transportation and communications 13.8%, health care 9.2%, education and recreation 8.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$73,500,000,000 (mineral fuels 18.3%; mechanical equipment 15.8%; electrical equipment 14.2%; chemicals and chemical products 7.3%; motor vehicles 5.8%). Major import sources (2006): US 16.2%; African countries 8.9%; Argentina 8.8%; China 8.7%; Germany 7.1%; Japan 4.2%; South Korea 3.4%; Chile 3.2%; France 3.1%. Exports (2005): US$118,300,000,000 (food products 22.1%, of which soy 8.6%, meat 6.8%, sugar 4.0%, coffee 2.4%; transportation equipment 16.2%; metal products 10.7%; mineral metals 6.8%; chemicals and chemical products 6.3%; machinery and apparatus 5.9%). Major export destinations (2006): US 18.0%; Argentina 8.5%; China 6.1%; African countries 5.4%; The Netherlands 4.2%; Germany 4.1%; Mexico 3.2%; Japan 2.8%; Italy 2.8%; Chile 2.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 29,605 km; passenger-km 5,852,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 154,870,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 1,751,868 km (paved [2000] 6%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 24,936,541; trucks and buses 6,294,502. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 50,689,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,530,700,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 6,522,000 (36); televisions (2003): 65,949,000 (369); telephone landlines (2006): 38,800,000 (205); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 99,919,000 (529); personal computers (2005): 32,130,000 (174); total Internet users (2006): 42,600,000 (226); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 3,304,000 (18).
Education and health
Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate/functionally literate 89.0%/76.5%; males literate/functionally literate 88.7%/75.9%; females literate/functionally literate 89.2%/77.0%. Health: physicians (2001) 357,888 (1 per 485 persons); hospital beds (2005) 443,210 (1 per 416 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 25.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,244 (vegetable products 79%, animal products 21%); 171% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 287,159 (army 65.8%, navy 11.4%, air force 22.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$68.
Did you know
The city of Rio de Janeiro lies on a strip of Brazil’s Atlantic coast, close to the Tropic of Capricorn, where the shoreline is oriented east-west, the city facing south. It was founded on an inlet of this stretch of the coast, Guanabara Bay, at the entrance to which is the landmark peak called Sugar Loaf.
Background
Little is known about Brazil’s early indigenous inhabitants. Though the area was theoretically allotted to Portugal by the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, it was not formally claimed by discovery until Pedro Alvares Cabral accidentally touched land in 1500. It was first settled by the Portuguese in the early 1530s on the southeastern coast and at Sao Vicente (near modern Sao Paulo); the French and Dutch created small settlements over the next century. A viceroyalty was established in 1640, and Rio de Janeiro became the capital in 1763. In 1808 Brazil became the refuge and seat of the government of John VI of Portugal when Napoleon invaded Portugal; ultimately the Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil, and the Algarves was proclaimed, and John ruled from Brazil in 1815-21. On John’s return to Portugal, his son Pedro I proclaimed Brazilian independence. In 1889 his successor, Pedro II, was deposed, and a constitution mandating a federal republic was adopted. The 20th century saw increased immigration and growth in manufacturing along with frequent military coups and suspensions of civil liberties. Construction of a new capital at Brasilia, intended to spur development of the country’s interior, worsened the inflation rate. After 1979 the military government began a gradual return to democratic practices, and in 1989 the first popular presidential election in 29 years was held.
Recent Developments
Brazil confirmed its spot among world energy giants in recent years. In 2007 the country was completely self-sufficient with respect to energy, largely because of its development and use of sugarcane biofuel, which that year passed hydroelectricity as the country’s second largest energy source (after petroleum). A number of stunning discoveries had international impacts as well. In November 2007 Brazil announced an offshore oil field, named Tupi, that could potentially almost double the country’s petroleum reserves. This was followed in January 2008 by the discovery of an offshore natural-gas field, nicknamed Jupiter, that was estimated to be as large as Tupi. Finally, in April the government announced the discovery of an offshore oil field that, if confirmed in volume, would amount to the world’s third largest known oil reserve. While these discoveries would take years to confirm and exploit, their announcements nonetheless moved Brazil into the spotlight as a potential world supplier of oil and natural gas. The economy showed signs of strengthening. GDP growth in 2007 was 9.7%, and urban unemployment had fallen to 8.6% in March 2008.
Brunei
Official name: Negara Brunei Darussalam (State of Brunei, Abode of Peace). Form of government: monarchy (sultanate) with one advisory body (Legislative Council [29]). Head of state and government: Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu’izzadin Waddaulah (from 1967). Capital: Bandar Seri Begawan. Official language: Malay. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Brunei dollar (B$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = B$1.36.
Demography
Area: 2,226 sq mi, 5,765 sq km. Population (2007): 393,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 176.5, persons per sq km 68.2. Urban (2005): urban 73.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 52.77%; female 47.23%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 29.5%; 15-29, 28.4%; 30-44, 24.1%; 45-59, 13.2%; 60-74, 4.0%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2003): Malay 66.6%; Chinese 10.9%; other indigenous 3.6%; other 18.9%. Religious affiliation (2004): Muslim 67%; Buddhist 13%; Christian 10%; traditional beliefs/other 10%. Major cities (2004): Bandar Seri Begawan (urban agglomeration) 81,500; Kuala Belait 28,400; Seria 23,500. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering the South China Sea and Malaysia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 19.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.10. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 74.6 years; female 77.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:B$8,441,000,000 (tax revenue 62.2%, of which taxes on petroleum and natural gas companies 59.1%; nontax revenue 37.8%, of which dividends paid by petroleum companies 22.9%, petroleum and natural gas royalties 10.0%). Expenditures: B$5,086,000,000 (current expenditure 80.1%; capital expenditure 19.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): vegetables 10,500; fruits 5,565, of which pineapples 990, bananas 680; cassava 1,800; livestock (number of live animals) 5,000 buffalo, 13,000,000 chickens; roundwood 228,637 cu m, of which fuelwood 5%; fisheries production (2004) 3,136 (from aquaculture 23%). Mining and quarrying: petroleum, natural gas, sand and gravel for construction. Manufacturing (value added in B$’000,000; 2005): liquefied natural gas 1,672; textiles and apparel 197; other manufactures 83. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 2,913,000,000 ([2004] 2,726,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 68,300,000 ([2004] 650,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,189,000 (1,187,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 12,200,000,000 ([2004] 1,457,000,000). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$11,481,000,000 (US$30,058 per capita). Population economically active (2001): total 157,594 (foreign workers accounted for 70% of the 160,500 economically active in 2004); activity rate of total population 45.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 65.9%; female 41.2%; unemployed [2005] 4.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): none. Households. Average household size (2002) 5.6; expenditure (2002): food and nonalcoholic beverages 28.8%, transportation 22.5%, housing and energy 8.8%, household furnishings 8.6%, recreation and entertainment 8.1%, clothing and footwear 5.6%, communications 5.5%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.5%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 1.1%; overall forest area (2005) 52.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 37; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,085. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): remittances (2003) 139.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$1,491,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 32.1%; basic manufactures 24.6%; food and live animals 17.4%; chemicals and chemical products 9.3%). Major import sources: Malaysia 24.4%; Singapore 18.7%; US 9.7%; Japan 9.1%; China 6.3%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$6,249,000,000 (crude petroleum 62.8%; liquefied natural gas 31.3%; machinery and transport equipment 2.0%). Major export destinations: Japan 36.7%; Indonesia 18.6%; South Korea 12.6%; Australia 9.6%; US 7.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004; privately owned only): length 19 km. Roads (2004): total length 3,560 km (paved 78%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 212,000; trucks and buses (2002) 20,000. Airtransport (2005; Royal Brunei Airlines only): passenger-km 3,767,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 134,127,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 35,000 (95); televisions (2001): 215,000 (648); telephone landlines (2006): 80,000 (210); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 254,000 (665); personal computers (2004): 31,000 (87); total Internet users (2006): 166,000 (434); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 11,000 (28).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1991). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 17.5%; primary education 43.3%; secondary 26.3%; postsecondary and higher 12.9%. Literacy (2002): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 93.9%; males literate 96.3%; females literate 91.4%. Health (2004): physicians 463 (1 per 773 persons); hospital beds 943 (1 per 379 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 8.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,610 (vegetable products 77%, animal products 23%); 137% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 7,000 (army 70.0%, navy 14.3%, air force 15.7%); British troops (a Gurkha batallion) 1,120; Singaporean troops 500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.9%; per capita expenditure US$684.
Background
Brunei traded with China in the 6th century AD. Through allegiance to the Javanese Majapahit kingdom (13th-15th century), it came under Hindu influence. In the early 15th century, with the decline of the Majapahit kingdom, many people converted to Islam, and Brunei became an independentsultanate. When Ferdinand Magellan’s ships visited in 1521, the sultan of Brunei controlled almost all of Borneo and its neighboring islands. Beginning in the late 16th century, Brunei lost power because of the Portuguese, Dutch, and, later, British activities in the region. By the 19th century, the sultanate of Brunei included Sarawak (present-day Brunei) and part of North Borneo (now part of Sabah). In 1841 a revolt took place against the sultan, and a British soldier, James Brooke, helped put it down; he was later proclaimed governor. In 1847 the sultanate entered into a treaty with Great Britain and by 1906 had yielded all administration to a British resident. Brunei rejected membership in the Federation of Malaysia in 1963, negotiated a new treaty with Britain in 1979, and achieved independence in 1984, with membership in the Commonwealth.
Recent Developments
Brunei made efforts in 2007 to diversify the economy. The government launched a landmark project to build the country’s first petrochemical production plant, a US$400 million methanol plant that was being constructed in a joint venture with Japan’s Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co. and Itochu Corp. Brunei and Malaysia reached a tentative agreement in resolving maritime border issues during the Augustvisit to Bandar Seri Begawan of Malaysian Prime Minister Abdullah Ahmad Badawi, who met with Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu’zzaddin Waddaulah. The new parliament building in the capital neared completion.
Bulgaria
Official name: Republika Bulgariya (Republic of Bulgaria). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [240]). Chief of state: President Georgi Purvanov (from 2002). Head of government: Prime Minister Sergey Stanishev (from 2005). Capital: Sofia. Official language: Bulgarian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 lev (Lw; plural leva) = 100 stotinki; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 1.24 leva.
Demography
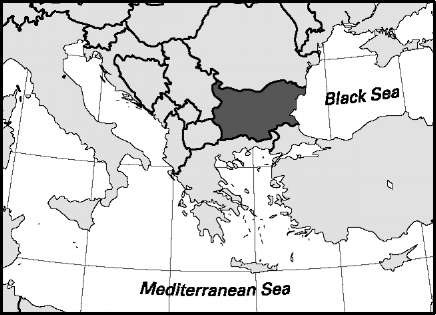
Area: 42,858.1 sq mi, 111,002 sq km. Population (2007): 7,645,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 178.4, persons per sq km 68.9. Urban (2005): 70.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.55%; female 51.45%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 13.8%; 15-29, 21.2%; 30-44, 20.9%; 45-59, 21.3%; 60-74, 15.9%; 75-84, 6.0%; 85 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2001): Bulgarian 83.9%; Turkish 9.4%; Rom (Gypsy) 4.7%; other 2.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Bulgarian Orthodox 81%; Sunni Muslim 12%; Evangelical Protestant 2%; Catholic 1%; other 4%. Major cities (2005): Sofia 1,138,950; Plovdiv 341,464; Varna 312,026; Burgas 189,529; Ruse 158,201. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Romania, the Black Sea, Turkey, Greece, Macedonia, and Serbia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 51.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.31. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.0 years; female 76.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: 17,030,000,000 leva (tax revenue 79.7%, of which VAT 28.2%, social insurance 20.6%; nontax revenue 20.3%). Expenditures: 17,008,000,000 leva (social insurance 33.1%; economic services 14.4%; defense and security 12.2%; health 11.8%; education 10.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2007): US$7,253,300,000. Gross national income (2006): US$30,782,000,000 (US$4,002 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 3,478,000, corn (maize) 1,586,000, sunflower seeds 934,900; livestock (number of live animals) 1,692,507 sheep, 931,402 pigs, 671,579 cattle; roundwood 5,862,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 46%; fisheries production (2004) 10,739 (from aquaculture 23%). Mining and quarrying (2004): copper (metal content) 107,000; iron (metal content) 27,000; gold 2,431 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): refined petroleum products, n.a.; wearing apparel 359; food products 320; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 278. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 44,196,000,000 ([2004] 35,742,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 33,000 (4,265,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 26,452,000 (26,292,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 220,000 (38,757,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 4,669,000 (3,563,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 354,000,000 (3,301,000,000). Households (2006). Average household size (2004) 2.7; income per household 5,204 leva (US$3,167); sources of income: wages and salaries 51.8%, transfers 29.9%, self-employment 8.1%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 36.9%, housing and energy 16.0%, communications 5.8%, health 5.5%, transportation 5.0%. Population economically active (2005): total 3,314,200; activity rate of total population 49.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2003] 60.9%; female 44.4%; unemployed [January 2006] 10.7%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 30.0%, in permanent crops 1.9%, in pasture 16.2%; overall forest area (2005) 32.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,383; remittances (2006) 1,695; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,919. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,293; remittances (2006) 47.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. for commodities and trading partners): >18,375,-000,000 (crude petroleum and natural gas 17.4%; transport equipment and parts 13.8%; machinery and apparatus 12.1%; textiles 7.7%; base and other metals 6.6%). Major import sources: Russia 17.3%; Germany 12.4%; Italy 8.7%; Turkey 6.0%; Greece 4.9%. Exports (2006): €11,982,600,000 (base and fabricated metals 21.6%, of which iron and steel 7.4%; mineral fuels 15.5%, of which petroleum products 13.3%; machinery and transport equipment 14.3%; clothing and footwear 13.4%). Major export destinations: Turkey 11.4%; Italy 10.1%; Germany 9.6%; Greece 8.9%; Belgium 6.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): track length 6,238 km; passenger-km 2,404,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,212,000,000. Roads (2004): length 44,033 km (paved 99%). Vehicles (2004): cars 2,438,383; trucks and buses 353,681. Airtransport (2003): pas-senger-km 3,005,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 21,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 961,000 (124); televisions (2002): 3,620,000 (453); telephone landlines (2006): 2,399,000 (313); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 8,253,000 (1,076); personal computers (2004): 461,000 (59); total Internet users (2006): 1,870,000 (244); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 384,000 (50).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling to complete primary education 28%; secondary 50%; higher 22%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.6%; males 99.1%; females 98.2%. Health (2006): physicians 28,030 (1 per 274 persons); hospital beds 50,688 (1 per 152 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 10.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,839 (vegetable products 77%, animal products 23%); 143% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 51,000 (army 49.0%, navy 8.6%, air force 25.7%, other 16.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.4%; per capita expenditure US$74.
The historical, cultural, transport, industrial, and tourist center of Bulgaria is the town of Veliko Tarnovo, which served as the medieval capital of Bulgaria. During its heyday in the 12th-14th centuries, European royal circles glorified it as “the third Rome and the second Constantinople.”
Background
Evidence of human habitation in Bulgaria dates from prehistoric times. Thracians were its first recorded inhabitants, dating from c. 3500 bc, and their first state dates from about the 5th century BC; the area was subdued by the Romans, who divided it into the provinces of Moesia and Thrace. In the 7th century ad the Bulgars took the region to the south of the Danube. The Byzantine Empire in 681 formally recognized Bulgar control over the area between the Balkans and the Danube. In the second half of the 14th century, Bulgaria fell to the Turks and ultimately lost its independence. At the end of the Russo-Turkish War (1877-78), Bulgaria rebelled. The ensuing Treaty of San Stefano was unacceptable to the Great Powers, and the Congress of Berlin (1878) resulted. In 1908 the Bulgarian ruler, Ferdinand, declared Bulgaria’s independence. After its involvement in the Balkan Wars (1912-13), Bulgaria lost territory. It sided with the Central Powers in World War I and with Germany in World War II. A communist coalition seized power in 1944, and in 1946 a people’s republic was declared. Like other eastern European countries in the late 1980s, Bulgaria experienced political unrest; its communist leader resigned in 1989. A new constitution proclaiming a republic was implemented in 1991. The rest of the decade brought economic turmoil.
Recent Developments
Bulgaria joined the the European Union in January 2007. Foreign investment poured into the country, and though the rate of unemployment plummeted from 9.1% in 2006 to 6.9% in 2007, Bulgarian wages stayed low, while prices continued to increase rapidly. Major contributors to the rises were the 7.8% increase in energy prices and an average 3.9% price hike in food items; the latter rise was worsened by prolonged drought and a negative outlook for the fall harvest. Real-estate prices saw rapid growth of 15.0% for the first six months of the year. Overall price pressure prompted educators to stage protest strikes in their quest for higher salaries, and the government agreed to partially satisfy their demands.
Burkina Faso
Official name: Burkina Faso. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [111]). Chief of state: President Blaise Com-paore (from 1987). Head of government: Prime Minis-terTertius Zongo (from 2007). Capital: Ouagadougou. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged since 1 Jan 2002 to the euro [€] at €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
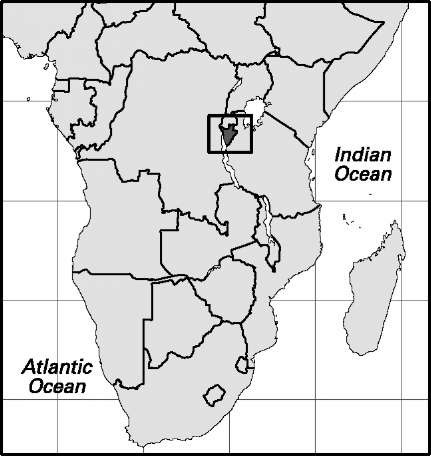
Area: 103,456 sq mi, 267,950 sq km. Population (2007): 14,326,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 138.5, persons per sq km 53.5. Urban (2005): 18.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.78%; female 50.22%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 46.7%; 15-29, 28.0%; 30-44,14.8%; 45-59, 6.5%; 60-74, 3.3%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (1995): Mossi 47.9%; Fulani 10.3%; Lobi 6.9%; Bobo 6.9%; Mande 6.7%; Senufo 5.3%; Grosi 5.0%; Gurma 4.8%; Tuareg 3.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 48%; traditional beliefs 32%; Roman Catholic 12%; Protestant/independent Christian 8%. Major cities (2005): Ouagadougou 1,488,176; Bobo-Dioulasso 452,349; Koudougou 142,360; Tenkodogo 130,084; Solenzo 123,488. Location: western Africa, bordering Mali, Niger, Benin, Togo, Ghana, and Cote d’Ivoire.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 45.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 30.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.47. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 47.3 years; female 50.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:CFAF 793,000,000,000 (tax revenue 52.3%, of which taxes on goods and services 29.3%; loans 23.2%; grants 18.5%; nontax revenue 3.6%; other 2.4%). Expenditures: CFAF 892,100,000,000 (current expenditure 50.1%; development expenditure 49.9%). Public debt (external; 2005): US$1,920,000,000. Households. Average household size (2003) 6.3; expenditure (2003): food, beverages, and tobacco 48.8%, housing and energy 17.8%, transportation 7.0%, clothing 6.8%, health 4.4%, recreation and culture 4.1%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sorghum 1,552,911, millet 1,196,253, corn (maize) 799,052; livestock (number of live animals) 10,708,992 goats, 8,010,158 cattle, 7,009,407 sheep; roundwood 13,067,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 91%; fisheries production (2004) 9,005. Mining and quarrying (2005): gold 1,397 kg. Manufacturing (value added in CFAF ’000,000; 1999): food products, beverages, and tobacco 126,125; textiles 46,217; chemicals and chemical products 9,335. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 516,000,000 ([2004] 400,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (352,000). Population economically active (1996): total 5,075,615; activity rate 49.2% (participation rates: over age 10, 70.0%; female 48.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$6,226,000,000 (US$434 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 17.7%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 21.9%; overall forest area (2005) 29.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 19; remittances (2005) 50; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 17; official development assistance (2005) 660. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2001) 22; remittances (2005) 44.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 619,000,000,000 (mineral fuels 24.6%; machinery and apparatus 14.3%; chemicals and chemical products 14.1%; transport equipment 9.1%). Major import sources: France 18.7%; Cote d’Ivoire 18.0%; Togo 11.4%; Benin 6.8%; Ghana 5.9%. Exports (2005): CFAF 175,000,000,000 (raw cotton 74.5%; sesame 2.9%; cigarettes 2.1%; sugar 1.5%). Major export destinations: Togo 41.1%; Ghana 16.7%; Cote d’Ivoire 10.5%; France 9.8%; Switzerland 9.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2004) 622 km; passenger-km (2003) 9,980,000; metric ton-km cargo (2005) 674,900,000. Roads (2006): total length 15,272 km (paved 17%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 84,161; trucks and buses 38,261. Air transport (2005; combined data for Ouagadougou and Bobo-Dioulasso airports only): passenger arrivals 134,247, passenger departures 137,373; cargo unloaded 2,837 metric tons, cargo loaded 1,347 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 12,000 (0.9); televisions (2004): 156,000 (12); telephone landlines (2006): 95,000 (7); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,017,000 (75); personal computers (2005): 31,000 (2.4); total Internet users (2006): 80,000 (5.9); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,700 (0.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 85.4%; incomplete to complete primary education 7.9%; incomplete to complete secondary 5.5%; higher 1.2%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 26.6%; males literate 36.8%; females literate 16.6%. Health: physicians (2004) 369 (1 per 35,439 persons); hospital beds (2001) 15,801 (1 per 735 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 91.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,593 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 144% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 10,800 (army 98.1%, air force 1.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.3%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Background
Probably in the 14th century, the Mossi and Gurma peoples established themselves in eastern and central areas of what is now Burkina Faso. The Mossi kingdoms of Yatenga and Ouagadougou existed into the early 20th century. A French protectorate was established over the region (1895-97), and its southern boundary was demarcated through an Anglo-French agreement. It was part of the Upper Senegal-Niger colony and then became a separate colony in 1919. Named Upper Volta, it was constituted an overseas territory within the French Union in 1947, became an autonomous republic within the French Community in 1958, and achieved total independence in 1960. Since then, the country has been ruled primarily by the military and has experienced several coups; following one in 1983, the country received its present name. A new constitution, adopted in 1991, restored multiparty rule.
Recent Developments
Burkina Faso Pres. Blaise Compaore expanded his role in international affairs with his election in 2007 as head of both the Economic Community of West African States and the West African Economic and Monetary Union. Results of the December 2006 census published in April showed a total population of 13,730,258, an increase of almost 3.5 million people in 10 years. Despite years of internationally funded aid programs, Burkina Faso remained among the poorest countries in the world, with nearly half the population living on less than US$1 daily. A deadly meningitis epidemic, low cotton prices, and severe summer flooding added to Burkina Faso’s economic woes.
Burundi
Official name: Republika y’u Burundi (Rundi); Republique du Burundi (French) (Republic of Burundi). Form of government: republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [49]; National Assembly [100]). Head of state and government: President Pierre Nkurunziza (from 2005), assisted by Vice President Yves Savin-guvu (from 2007). Capital: Bujumbura. Official languages: Rundi; French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Burundi franc (FBu) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = FBu 1,194.46.
Demography
Area: 10,740 sq mi, 27,816 sq km. Population (2007): 8,391,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 837.4, persons per sq km 323.4. Urban (2005): 10.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.82%; female 51.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 45.1%; 15-29, 29.0%; 30-44, 13.7%; 45-59, 8.2%; 60-74, 3.2%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Hutu 80.9%; Tutsi 15.6%; Lingala 1.6%; Twa Pygmy 1.0%; other 0.9%. Religious affiliation (2004): Christian 67%, of which Roman Catholic 62%, Protestant 5%; traditional beliefs 23%; Muslim 10%. Major cities (2004): Bujumbura 340,300; Gitega 46,900; Muyinga 45,300; Ngozi 40,200; Ruyigi 36,800. Location: central Africa, bordering Rwanda, Tanzania, Lake Tanganyika, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 45.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 16.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per I,000 population (2005): 29.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 6.80. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 47.0 years; female 49.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: FBu 220,170,000,000 (tax revenue 71.3%, of which sales tax 37.8%, taxes on international trade 11.7%, corporate income tax II.1%, personal income tax 8.7%; grants 18.8%; nontax revenue 6.9%; other 3.0%). Expenditures: FBu 319,061,000,000 (current expenditure 70.1%, of which debt service 6.4%; capital expenditure 27.9%; other 2.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; September 2006): US$1,227,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): bananas 1,600,000, sweet potatoes 835,000, cassava 710,000; livestock (number of live animals) 750,000 goats, 396,000 cattle, 243,000 sheep; roundwood 13,067,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production (2004) 13,631 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): columbite-tantalite ore 42,592 kg; gold 3,905 kg. Manufacturing (2005): beer 1,012,500 hectolitres; carbonated beverages 143,600 hectolitres; cottonseed oil 135,900 litres. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 99,200,000 (119,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (70,000); peat (metric tons; 2005) 4,700 ([2000] 12,000). Households (2004). Average household size 5.6; average annual income per household FBu 168,000 (US $153); sources of income: agriculture/livestock 91%, other 9%; expenditure: food 46%, debt service 14%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco 8%, transportation 6%, health 5%, clothing 4%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1.5; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) negligible; official development assistance (2005) 365. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 60; remittances (2005) 1.0. Gross national income (2006): US$903,000,000 (US$110 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 3,464,000; activity rate of total population 49.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 92.2%; female 52.1%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 38.6%, in permanent crops 14.2%, in pasture 38.6%; overall forest area (2005) 5.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): FBu 442,500,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 21.3%; transportation equipment 15.7%; mineral fuels 13.4%; fabricated metals 7.2%; pharmaceuticals 6.6%). Major import sources: Saudi Arabia 12.6%; Belgium/Luxembourg 11.7%; Kenya 8.2%; Japan 7.8%; Russia 4.7%. Exports (2006): FBu 60,400,000,000 (coffee 67.7%; tea 17.0%; hides and skins 2.6%; cotton fabric 1.9%). Major export destinations.Switzerland 34.4%; UK 12.3%; Pakistan 7.8%; Rwanda 5.1%; other EU 24.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 12,322 km (paved 7%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 19,800; trucks and buses 14,400. Air transport (2005; figures for Bujumbura airport only): passenger arrivals 73,072, passenger departures 63,908; cargo unloaded 3,093 metric tons, cargo loaded 188 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,500 (0.3); televisions (2004): 280,000 (37); telephone landlines (2005): 31,000 (4.1); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 153,000 (20); personal computers (2004): 34,000 (4.8); total Internet users (2006): 60,000 (7.7).
Education and health
Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 51.6%; males literate 58.5%; females literate 45.2%. Health (2004): physicians 200 (1 per 37,581 persons); hospital beds (1999) 3,380 (1 per 1,657 persons); infant mortality rate per I,000 live births (2005) 64.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,693 (vegetable products 98%, animal products 2%); 94% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 50,500 (army 89.1%, gendarmerie 10.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 6.2%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Background
Original settlement by the Twa people was followed by Hutu settlement, which occurred gradually and was completed by the 11th century. The Tutsi arrived 300-400 years later; though a minority, they established the kingdom of Burundi in the 16th century. In the 19th century the area came within the German sphere of influence, but the Tutsi remained in power. Following World War I the Belgians took control of the area, which became a UN trusteeship afterWorld War II. Colonial-period conditions had intensified Hutu-Tutsi ethnic animosities, and as independence neared, hostilities flared. Independence was granted in 1962 in the form of a kingdom ruled by the Tutsi. In 1965 the Hutu rebelled but were brutally repressed. The rest of the 20th century saw violent clashes between the two groups, leading to charges of genocide in the 1990s. The very unstable government that existed in these surroundings was overthrown by the military in 1996.
Recent Developments
Progress toward reconciliation made in 2006 between the government of Burundi and the last remaining rebel group was reversed in 2007. The original ceasefire deal, signed by Pres. Pierre Nkurunziza and the National Liberation Forces (FNL) leader Agathon Rwasa, was never implemented owing to unresolved issues, namely the release of FNL prisoners. Violence in Bujumbura increased significantly during the summer of 2007, and in September the FNL turned down calls by the UN for a return to the negotiating table.
Cambodia
Official name: Preah Reach Ana Pak Kampuchea (Kingdom of Cambodia). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [61]; National Assembly [123]). Chief of state: King Norodom Sihamoni (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Hun Sen (from 1998). Capital: Phnom Penh. Official language: Khmer. Official religion: Buddhism. Monetary unit: 1 riel = 100 sen; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 4,106.00 riels.
Demography
Area: 69,898 sq mi, 181,035 sq km. Population (2007): 13,893,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 202.1, persons per sq km 78.0. Urban (2004): 15.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.75%; female 51.25%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 36.6%; 15-29, 30.5%; 30-44, 18.4%; 45-59, 9.4%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Khmer 85.2%; Chinese 6.4%; Vietnamese 3.0%; Cham 2.5%; Lao 0.6%; other 2.3%. Religious affiliation (2000): Buddhist 84.7%; Chinese folk religionist 4.7%; traditional beliefs 4.3%; Muslim 2.3%; Christian 1.1%; other 2.9%. Major urban areas (1998): Phnom Penh (2005) 1,364,000; Battambang 124,290; Sisophon 85,382; Siemreap 83,715; Sihanoukville 66,723. Location: southeastern Asia, bordering Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and the Gulf of Thailand.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 26.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.37. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 57.4 years; female 61.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: 3,280,300,000,000 riels (tax revenue 58.3%; nontax revenue 17.2%; grants 20.0%; other 4.5%). Expenditures: 3,294,700,000,000 riels (current expenditure 59.7%; development expenditure 40.3%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 5,986,000, cassava 535,600, corn (maize) 247,800; livestock (number of live animals) 3,100,000 cattle, 2,500,000 pigs, 650,000 buffalo, 120,000 crocodiles; roundwood 9,334,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 99%; fisheries production (2004) 326,652 (from aquaculture 6%); aquatic plants production 16,840 (from aquaculture 100%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gold, n.a.; gemstones, n.a.; crude stones 600,000. Manufacturing (value added in ’000,000,000 riels; 2002): wearing apparel 1,808; food products 392; base and fabricated metals 120. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 130,000,000 (130,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) negligible (174,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.1; average annual extrapolated monetary and nonmonetary income (1993-94): 2,031,000 riels (US$787); sources of income (1993-94): monetary 67.4%, of which nonagricultural (mostly self-employment) 36.8%, agricultural 18.1%, wages and salaries 9.1%; nonmonetary 32.6%, of which agricultural 11.4%; household expenditure (2002): food, beverages, and tobacco 62.6%, housing and energy 19.7%, health 6.0%, transportation and communications 3.4%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 840; remittances (2005) 200; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 178; official development assistance (2005) 538. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 97; remittances (2005) 144. Gross national income (2006): US$6,177,000,000 (US$435 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,155,000,000. Population economically active (2004): total 7,557,600; activity rate of total population 55% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 82.6%; female 49.4%; unemployed [2001] 1.8%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 21.0%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 8.5%; overall forest area (2005) 59.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$4,254,000,000 (retained imports 97.3%; imports for reexport 2.7%). Major import sources (2004): Thailand 23.9%; Hong Kong 15.0%; China 13.5%; Singapore 11.5%; Vietnam 7.6%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$2,910,000,000 (domestic exports 95.3%, of which garments 77.7%, rice 6.1%, rubber 4.1%, fish 2.6%, sawn timber and logs 0.5%; reexports 4.7%). Major export destinations (2004): US 56.2%; Germany 11.5%; UK 7.0%; Canada 4.3%; Vietnam 3.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length 602 km; pas-senger-km (2000) 45,000,000; metric ton-km (1999) 76,171,000. Roads (2004): total length 38,257 km (paved 6%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 235,298; trucks and buses 35,448. Air transport (2005-06): passenger-km 198,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,214,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 36,000 (2.7); televisions (2003): 103,000 (8); telephone landlines (2006): 33,000 (2.3); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,140,000 (79); personal computers (2004): 38,000 (2.6); total Internet users (2005): 44,000 (3.1); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 1,000 (0.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of literate population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 4.6%; incomplete primary education 54.0%; complete primary 23.7%; incomplete secondary 11.3%; secondary/vocational 5.3%; higher 1.1%. Literacy (2004): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 74.4%; males literate 82.1%; females literate 67.4%. Health: physicians (2004) 2,122 (1 per 6,169 persons); hospital beds (2002) 9,800 (1 per 1,405 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 68.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,370 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 134% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 124,300 (army 60.3%, navy 2.3%, air force 1.2%, provincial forces 36.2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$8.
The Kizuna bridge became the first bridge ever to span the Mekong River when it opened to the public on 4 Dec 2001. The Mekong flows through Cambodia for about 500 km (300 mi) and is considered the country’s most important river.
Background
In the early Christian era, what is now Cambodia was under Hindu and, to a lesser extent, Buddhist influence. The Khmer state gradually spread in the early 7th century and reached its height under Jayavarman II and his successors in the 9th-12th centuries, when it ruled the Mekong Valley and the tributary Shan states and built Angkor. Widespread adoption of Buddhism occurred in the 13th century, resulting in a script change from Sanskrit to Pali. From the 13th century Cambodia was attacked by Annam and Siamese city-states and was alternately a province of one or the other. The area became a French protectorate in 1863. It was occupied by the Japanese in World War II and became independent in 1954. Cambodia’s borders were the scene of fighting in the Vietnam War from 1961, and in 1970 its northeastern and eastern areas were occupied by the North Vietnamese and penetrated by US and South Vietnamese forces. An indiscriminate US bombing campaign alienated much of the population, enabling the communist Khmer Rouge under Pol Pot to seize power in 1975. Their regime of terror resulted in the deaths of at least one million Cambodians. Vietnam invaded in 1979 and drove the Khmer Rouge into the western hinterlands, but it was unable to effect reconstruction of the country, and Cambodian infighting continued. A peace accord was reached by most Cambodian factions under UN auspices in 1991, and elections were held in 1993. In 2004 King Norodom Sihanouk abdicated, and his son Sihamoni was named his successor.
Recent Developments
In Cambodia in 2007 the Khmer Rouge Tribunal continued to move forward in a slow, almost tortuous process. In July prosecutors recommended that five senior Khmer Rouge leaders be tried for genocide and crimes against humanity committed during the Pol Pot regime (1975-79). Although only two were officially charged, the Cambodian press speculated that others named internally might include Khieu Samphan, head of state during the regime. New reports predicted that Cambodian offshore oil fields might yield more than initially expected. A September IMF study indicated that Cambodia could begin generating approximately US$174 million in oil income by 2011, with production peaking at US$1.7 billion in 2021-significant revenue in relation to the Cambodian economy. The country was expanding its navy to protect the offshore sites.
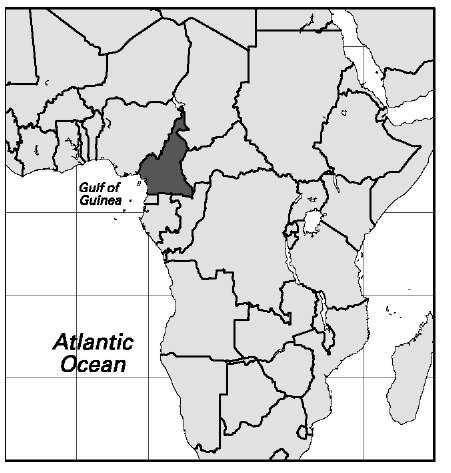
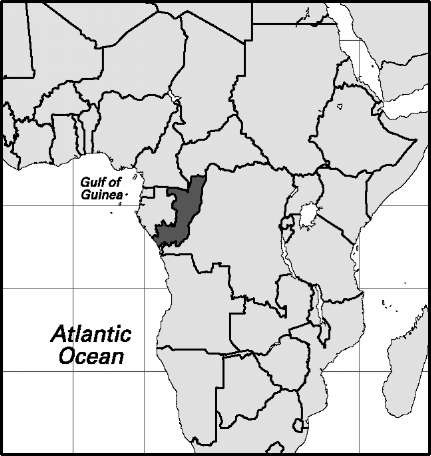
Cameroon
Official name: Republique du Cameroun (French); Republic of Cameroon (English). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [180]). Chief of state: President Paul Biya (from 1982). Head of government: Prime Minister Ephraim Inoni (from 2004). Capital: Yaounde. Official languages: French; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 183,569 sq mi, 475,442 sq km. Population (2007): 18,060,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 100.4, persons per sq km 38.8. Urban (2004): 53.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.15%; female 49.85%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 41.5%; 15-29, 29.0%; 30-44, 15.7%; 45-59, 8.8%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75-84, 0.8%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (1983): Fang 19.6%; Bamileke and Bamum 18.5%; Duala, Luanda, and Basa 14.7%; Fulani 9.6%; Tikar 7.4%; Mandara 5.7%; Maka 4.9%; Chamba 2.4%; Mbum 1.3%; Hausa 1.2%; French 0.2%; other 14.5%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 27.4%; traditional beliefs 22.2%; Protestant 20.2%; Sunni Muslim 20.0%; nonreligious/other 10.2%. Major urban areas (2004): Douala 1,532,800; Yaounde 1,434,700; Garoua 409,000; Kousseri 332,900; Bamenda 298,500. Location: western Africa, bordering Chad, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, the Bight of Biafra, and Nigeria.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 35.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 22.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.58. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 51.7 years; female 53.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 1,590,000,000,000 (non-oil revenue 69.4%, of which VAT 22.0%, direct taxes 16.5%, customs duties 11.9%, nontax revenue 7.9%; oil revenue 27.6%; grants 3.0%). Expenditures: CFAF 1,278,000,000,000 (current expenditure 82.6%, of which interest on public debt 10.1%; capital expenditure 16.1%; other 1.3%). Gross national income (2006): US$17,707,000,000 (US$974 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.8; expenditure (1993): food 49.1%, housing 18.0%, transportation and communications 13.0%, health 8.6%, clothing 7.6%, recreation 2.4%. Population economically active (2003): total 6,093,000; activity rate of total population 38.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 68.4%; female 39.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,521,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 2,139,000, sugarcane 1,450,000, plantains 1,356,000; livestock (number of live animals) 6,000,000 cattle, 4,400,000 goats, 3,800,000 sheep; roundwood 11,285,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 84%; fisheries production (2004) 108,330. Mining and quarrying (2005): pozzolana 600,000; limestone 130,000; gold 1,500 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): food products 97; refined petroleum 88; beverages 78. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 4,004,000,000 (3,264,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 21,900,000 ([2004] 14,043,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,752,000 (917,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.8%, in permanent crops 2.6%, in pasture 4.3%; overall forest area (2005) 45.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 36; remittances (2005) 31; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 4.0; official development assistance (2005) 358 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2003) 212; remittances (2005) 63; FDI (2001-03 avg.) 24.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 1,524,200,000,000 (crude petroleum 27.8%; machinery and apparatus 11.6%; chemicals and chemical products 11.1%; cereals 7.4%; motor vehicles 6.1%). Major import sources: Nigeria 21.0%; France 17.7%; China 5.0%; US 4.6%; Japan 3.9%. Exports (2005): CFAF 1,476,000,000,000 (crude petroleum 44.8%; fuels and lubricants 12.2%; sawn wood 12.0%; cocoa beans 7.5%; aluminum 4.7%; raw cotton 4.7%; bananas 2.4%; coffee 2.3%). Major export destinations: Spain 19.7%; France 12.7%; Italy 11.7%; The Netherlands 7.6%; US 6.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 1,016 km; passenger-km 323,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,119,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 50,000 km (paved 10%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 175,981; trucks and buses 59,399. Air transport (2001): passenger-km 796,567,000; metric ton-km cargo 23,255,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 59,000 (3.5); televisions (2004): 720,000 (43); telephone landlines (2005): 100,000 (6.1); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 2,252,000(133); personal computers (2005): 200,000 (12); total Internet users (2006): 370,000 (22).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004): Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 32.9%; primary education 35.3%; secondary 26.2%; higher 4.2%; other/unknown 1.4%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 74.6%; males literate 81.5%; females literate 67.9%. Health (2004): physicians 2,966 (1 per 5,609 persons); hospital beds 38,067 (1 per 437 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 67.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,634 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 142% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 14,100 (army 88.7%, navy 9.2%, air force 2.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.3%; per capita expenditure US$13.
Background
The Cameroon area had long been inhabited before European colonization. Bantu speakers from equatorial Africa settled in the south, followed by Muslim Fulani from the Niger River basin, who settled in the north. Portuguese explorers visited in the late 15th century and established a foothold, but they lost control to the Dutch in the 17th century. In 1884 the Germans took control and extended their protectorate over Cameroon. In World War I joint French-British action forced the Germans to retreat, and after the war the region was divided into French and British administrative zones. After World War II the two areas became UN trusteeships. In 1960 the French trust territory became an independent republic. In 1961 the southern part of the British trustterritory voted for union with the new republic of Cameroon, and the northern partvoted for union with Nigeria. In recent decades economic problems have produced unrest in the country.
Recent Developments
Teachers complained in 2007 that Franglais (a mixture of English, French, and the creole language) was having a profound effect on how students spoke and wrote French and English, Cameroon’s two official languages. In January, Chinese Pres. Hu Jintao paid a state visit to Yaounde. Presidents Hu and Paul Biya signed a series of cooperative agreements and concessionary loans, including an interest-free US$3.86 million loan for projects to be determined at a future date by the Cameroonian government.
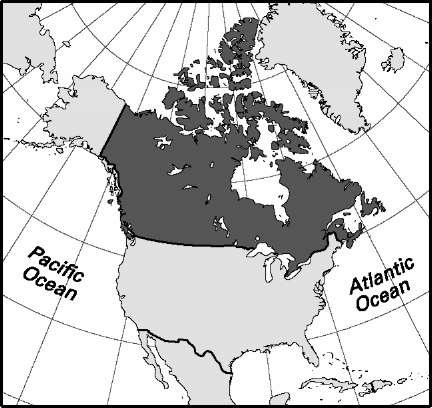
Canada
Official name: Canada. Form of government: federal multiparty parliamentary state with two legislative houses (Senate [105]; House of Commons [308]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Michaelle Jean (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Stephen Harper (from 2006). Capital: Ottawa. Official languages: English; French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Canadian dollar (Can$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Can$1.02.
Demography
Area: 3,855,103 sq mi, 9,984,670 sq km. Population (2007): 32,945,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 9.4, persons per sq km 3.6. Urban (2003): 80.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.52%; female 50.48%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 17.3%; 15-29, 20.4%; 30-44, 22.3%; 45-59, 21.9%; 60-74, 11.8%; 75-84, 4.7%; 85 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic origin (2000): Anglo-Canadian 45.5%; French-Canadian 23.5%; Chinese 3.4%; British expatriates 3.3%; Indo-Pakistani 2.6%, of which Punjabi 2.3%; German 2.4%; Italian 2.2%; US white 1.8%; Metis (part Indian) 1.8%; Indian 1.5%, of which de-tribalized 0.5%; Jewish 1.4%; Arab 1.3%; Ukrainian 1.2%; Eskimo (Inuit) 0.1%; other 8.0%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 77.1%, of which Roman Catholic 43.2%, Protestant 28.3%, unspecified Christian 2.6%, Orthodox 1.7%, other Christian 1.3%; Muslim 2.0%; Jewish 1.1%; Hindu 1.0%; Buddhist 1.0%; Sikh 0.9%; nonreligious 16.5%; other 0.4%. Major metropolitan areas (2006): Toronto 5,113,149; Montreal 3,635,571; Vancouver 2,116,581; Ottawa-Hull 1,130,761; Calgary 1,079,310; Edmonton 1,034,945; Quebec 715,515; Winnipeg 694,668; Hamilton 692,911; London 457,720. Location: northern North America, bordering the Arctic Ocean, the North Atlantic Ocean, the US, and the North Pacific Ocean. Place of birth (2001): 81.6% native-born; 18.4% foreign-born, of which in the UK 2.0%, elsewhere in Europe 5.7%, Asia 5.8%, US 0.8%, other 4.1%. Mobility (2001). Population living in the same residence as in 1996: 58.1%; different residence, same municipality 22.4%; same province, different municipality 3.3%; different province 12.7%; different country 3.5%. Households. Total number of households (2004) 11,952,550. Average household size (2004) 2.7; 1 person (1997) 25.2%, 2 persons 33.0%, 3 persons 16.7%, 4 persons 16.3%, 5 or more persons 8.8%. Family households (2001): 8,371,020 (72.4%), nonfamily 3,191,955 (27.6%, of which 1 person 75.6%). Immigration (2004): permanent immigrants admitted 235,824; from Asia 48.6%, of which China 15.4%, India 10.8%, Philippines 5.6%; Europe 17.8%, of which UK 2.6%, France 2.1%; US 3.2%; refugee arrivals 26,526; overall refugee population (2004) 141,398.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005-06): 10.6 (world avg. 20.3); (1997) within marriage 72.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005-06): 7.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005-06): 3.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.61. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 76.9 years; female 83.7 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: incomplete primary and complete primary education 8.8%; incomplete secondary 15.7%; complete secondary 19.3%; some university/highervocational 39.0%; bachelor’s degree or higher 17.2%. Quality of working life. Average workweek (2005): 35.2 hours. Annual rate per 100,000 workers for (2005): injury, accident, or industrial illness 2,090; death 6.8. Average days lost to labor stoppages per 1,000 employee-workdays (2001): 0.7. Average commuting distance (2001): 7.2 km; mode of transportation: automobile 80.7%, public transportation 10.5%, walking 6.6%, other 2.2%. Labor force covered by a pension plan (2001): 33.6%. Access to services. Proportion of households having access to: electricity (2002) 100%; public water supply (1996) 99.8%; public sewage collection (1996) 99.3%. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last national election (January2006): 64.9%. Population over 18 years of age participating in voluntary work (2000): 26.7%. Union membership as percentage of civilian labor force (2003) 25.0%. Attendance at religious services on a weekly basis (2006): 17%. Social deviance (2004). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: violent crime 946.1, of which assault 731.8, sexual assault 73.7, homicide 2.0; property crime 3,990.9, of which auto theft 530.7, breaking and entering 859.9. Material well-being (2003). Households possessing: automobile 62.4%; telephone 96.3%; cellular phone 53.9%; color television 99.0%; central air conditioner 39.3%; cable television 65.1%; home computers 66.8%; Internet access 56.9%.
National economy
Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$1,249,635,000,000 (US$38,360 per capita). Budget (2005-06). Revenue:Can$229,660,-000,000 (income tax 62.9%; sales tax 15.4%; contributions to social security 9.6%; other 12.1%). Expenditures: Can$216,156,000,000 (social services and welfare 37.1%; defense and social protection 11.2%; health 10.0%; public debt interest 9.9%; resource conservation and industrial development 3.8%; education 2.3%). Public debt (January 2007): US$582,601,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 26,775,000, barley 12,481,200, rapeseed 9,660,200, corn (maize) 9,460,800, potatoes 4,386,500, oats 3,432,300, soybeans 3,161,300, dry peas 3,099,800, lentils 1,277,900, linseed 1,082,000, tomatoes 839,250, apples 394,100, canary seed 227,200, mustard seed 201,400, cranberries and blueberries 139,099, mushrooms 80,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2006) 14,329,000 pigs, 14,315,000 cattle, 590,500 sheep; roundwood 199,345,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 1%; fisheries production 1,255,821 (from aqua-culture 12%). Mining and quarrying (value of production in Can$’000,000; 2005): nickel 3,302 (world rank: 3); potash 2,839 (world rank: 1); copper 2,455 (world rank: 8); gold 2,041 (world rank: 8); diamonds (gemstones) 1,684 (world rank: 4); iron ore 1,496 (world rank: 9); sand and gravel 1,165; stone 1,133; zinc 998 (world rank: 4); salt 420 (world rank: 5); silver 299 (world rank: 6); lime 262; gypsum 100 (world rank: 3); cobalt 91 (world rank: 4). Manufacturing (value added in Can$’000,000,000 of 1997; 2005): transportation equipment 28.1; food 17.6; chemicals 17.2; fabricated metal products 14.2; wood industries 13.7; machinery 12.5; primary metals 12.3; paper products 11.4; rubber and plastic products 10.3; computers and electronic products 10.3. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 567,600,000,000 (556,600,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 29,261,000 (18,057,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 36,700,000 (40,804,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 1,146,000,000 (840,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 117,367,000 (107,573,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 180,000,000,000 (93,300,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 17,825,800; activity rate of total population 55.6% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 67.5%; female 46.7%; unemployed [February 2007] 6.1%). Households. Average household size (2004) 2.7; average annual income per family (2003) Can$72,700 (US$51,888); sources of income (2001): wages, salaries, and self-employment 71.8%, transfer payments 14.0%, other 14.2%; expenditure (2004): housing 26.9%, transportation 19.0%, food 15.2%, recreation 9.3%, household operations 6.4%, clothing 5.5%, household furnishings 4.1%, health 3.7%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco 3.3%, education 2.4%, other 4.2%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.0%, in permanent crops 0.7%, in pasture 1.7%; overall forest area (2005) 33.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 13,584; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 18,558. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 18,341; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 32,331.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): Can$404,535,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 24.7%; transport equipment 23.4%, of which road vehicles and parts 19.7%; chemicals and chemical products 7.3%; base metals 6.9%; food products 5.8%; crude petroleum 5.6%). Major import sources (2006): US 65.5%; Japan 2.9%; UK 2.4%; other EU 8.0%. Exports (2006): Can$458,166,-900,000 (transport equipment 22.7%, of which road vehicles and parts 18.1%; machinery and apparatus 16.4%; base metals and alloys 9.9%; crude petroleum 8.4%; food products 6.9%; chemicals and chemical products 6.8%; natural gas 6.0%; wood and wood pulp 4.9%; paper and paperboard 2.4%). Major export destinations (2006): US 78.9%; UK 2.6%; Japan 2.3%; other EU 4.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 72,168 km; pas-senger-km 1,472,781,000; metric ton-km cargo 352,133,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 1,408,900 km (paved 35%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 18,123,885; trucks and buses 785,649. Airtransport (2003): passenger-km 90,136,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,880,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 5,350,000 (167); televisions (2003): 22,384,000 (707); telephone land-lines (2005): 20,780,000 (501); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 17,017,000 (525); personal computers (2004): 22,390,000 (701); total Internet users (2005): 20,000,000 (620); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 7,676,000 (236).
Education and health
Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2004) 67,087 (1 per 476 persons); hospital beds (2002-03) 115,120 (1 per 274 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 4.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,486 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 62,100 (army 53.2%, navy 19.3%, air force 27.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$403.
Background
Originally inhabited by American Indians and Inuit, Canada was visited c. AD 1000 by Scandinavian explorers, whose discovery is confirmed by archaeological evidence from Newfoundland. Fishing expeditions off Newfoundland by the English, French, Spanish, and Portuguese began as early as 1500. The French claim to Canada was made in 1534 when Jacques Cartier entered the Gulf of St. Lawrence. A small settlement was made in Nova Scotia (Acadia) in 1605, and in 1608 Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec. Fur trading was the impetus behind the early colonizing efforts. In response to French activity, the English in 1670 formed the Hudson’s Bay Company.
The British-French rivalry for the interior of upper North America lasted almost a century. The first French loss occurred in 1713 at the conclusion of Queen Anne’s War (War of the Spanish Succession) when Nova Scotia and Newfoundland were ceded to the British. The Seven Years’ War (French and Indian War) resulted in France’s expulsion from continental North America in 1763. After the US War of Independence, the population was augmented by Loyalists fleeing the US, and the increasing number arriving in Quebec led the British to divide the colony into Upper and Lower Canada in 1791. The British reunited the two provinces in 1841. Canadian expansionism resulted in the confederation movement of the mid-19th century, and in 1867 the Dominion of Canada, comprising Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec, and Ontario, came into existence. After confederation, Canada entered a period of westward expansion.
The prosperity that accompanied Canada into the 20th century was marred by continuing conflict between the English and French communities. Through the Statute of Westminster (1931), Canada was recognized as an equal of Great Britain. With the Constitution Act of 1982, the British gave Canada total control over its constitution and severed the remaining legal connections between the two countries. French Canadian unrest continued to be a major concern, with a movement growing for Quebec separatism in the late 20th century. Referendums for more political autonomy for Quebec were rejected in 1992 and 1995, but the issue remained unresolved. In 1999 Canada formed the new territory of Nunavut, and in December 2001 Newfoundland was renamed Newfoundland and Labrador.
Recent Developments
Canadian Defense Minister Gordon O’Connor found himself embroiled in a scandal in April 2007 when the media reported claims of torture from prisoners who were detained by Canadian troops and were being held by Afghan security forces. O’Connor had stated in the House of Commons in May 2006 that the International Committee of the Red Cross had signed an agreement with Canada to examine prison conditions and to report any inhumane or illegal treatment. In March 2007, however, the Red Cross disputed that such a deal had ever existed. O’Connor apologized for misleading Parliament and announced that a new deal with the Afghan government had been signed, but in August he was demoted to minister of national revenue in a cabinet shuffle. In the speech from the throne to open Parliament, Prime Minister Stephen Harper announced plans for new legislation to toughen crime statutes and to enhance initiatives to assert the country’s claims to Arctic sovereignty. The speech also indicated that Canada would not meet its Kyoto Protocol carbon-emissions-reduction targets. Canada demanded in early 2008 that its NATO allies provide more helicopters and unmanned drones and 1,000extra troops in Afghanistan, warningthatfailure to do so would lead to the withdrawal of Canadian troops after the scheduled end of their deployment in February 2009. After these demands were met at the NATO summit in Bucharest, Romania, in April 2008, Canada announced thatitwasextendingthe mandate for its force in Afghanistan, numbering about 2,500 troops, through 2011. Quebec garnered many national headlines in 2007. In September a special commission investigating the issue of tolerance for multi-culturalism and “reasonable accommodation” for minority groups in the province began to hold hearings. The commission, called by Premier Jean Charest, was the result of several widely reported incidents in which Quebecers revealed deep concerns aboutsome religious and ethnic minorities. Early in the year the small rural town of Herouxville adopted a code of “norms” for prospective immigrants. Although the town had only a single immigrant family among its 1,338 residents, concerns about new cultural groups in larger centers prompted a code that prohibited stoning or burning women with acid, wearing face-covering garments, or carrying ceremonial weapons (such as the Sikh kirpan). The overall economy performed exceptionally well in 2007. The Canadian dollar, which had soared in value since 2002, in September closed above the US dollar for the first time since November 1976. In October the country’s unemployment rate reached its lowest level since November 1974, falling to 5.8% (though by April 2008 it had risen to 6.1%). Sovereignty over the Arctic was a growing international issue in 2007 as global warming reduced the ice pack and opened the possibility of future access to Arctic natural resources and shipping routes. The government in July announced plans to build up to eight new ships to patrol the Northwest Passage and other Arctic waterways. In August, barely a week after Russian scientists planted a flag on the seabed under the North Pole, Prime Minister Harper spoke at the end of a three-day trip to the Canadian Arctic. He reiterated Canadian sovereignty over the region and announced the construction in Nunavut of new facilities on Resolute Bay and of a port at Nanisivikto bolster Canada’s jurisdiction over its northern coast.
Cape Verde
Official name: Republica de Cabo Verde (Republic of Cape Verde). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [72]). Chief of state: President Pedro Pires (from 2001). Head of government: Prime Minister Jose Maria Neves (from 2001). Capital: Praia. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 escudo (C.V.Esc.) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = C.V.Esc. 69.90 (pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = C.V.Esc. 110.27).
Demography
Area: 1,557 sq mi, 4,033 sq km. Population (2007): 496,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 318.6, persons per sq km 123.0. Urban (2003): 55.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.47%; female 51.53%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 39.4%; 15-29, 31.0%; 30-44, 16.6%; 45-59, 7.5%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75-84,1.2%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Cape Verdean mestigo (black-white admixture) 69.6%; Fulani 12.2%; Balanta 10.0%; Mandyako 4.6%; Portuguese white 2.0%; other 1.6%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 95.1%, of which Roman Catholic 88.1%, Protestant 3.3%, independent Christian 2.7%; Muslim 2.8%; other 2.1%. Major cities (2005): Praia 111,500; Mindelo 70,000; Santa Maria (2000) 13,220; Assomada 11,900; Pedra Badejo 10,700. Location: off the coast of western Africa; consists of 10 islands in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 24.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.90. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 68.3 years; female 76.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: C.V.Esc. 34,603,000,000 (tax revenue 68.1%, of which consumption taxes 28.6%, taxes on income and profits 22.0%; grants 20.2%; nontax revenue 11.0%; net lending 0.7%). Expenditures: C.V.Esc. 36,309,000,000 (current expenditure 59.7%; capital expenditure 34.8%; other 5.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$545,800,000. Gross national income (2006): US$1,089,000,000 (US$2,099 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 14,000, fruits 9,000, pulses 7,000; livestock (number of live animals) 205,000 pigs, 112,500 goats; roundwood 1,542 cu m, of which fuelwood 100%; fisheries production (2004) 8,446. Mining and quarrying (2005): salt 1,600. Manufacturing (1999): flour 15,901; soap 1,371; frozen fish (2002) 900. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004)220,000,000 (220,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (89,000). Population economically active (2003): total 157,000; activity rate of total population 32.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64 58%; female 34%; unemployed [2006] 21.1%). Households. Average household size (2006) 4.9; expenditure (1997): food 38.7%, transportation 13.6%, alcoholic beverages 10.1%, housing 7.7%, household furnishings 6.0%, energy 5.0%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 11.4%, in permanent crops 0.7%, in pasture 6.2%; overall forest area (2005) 20.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 122; remittances (2006) 123; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 15; official development assistance (2005) 161. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 67; remittances (2004) 1.0.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): C.V.Esc. 47,578,000,000 (food and agricultural products 27.2%; machinery and apparatus 10.7%; mineral fuels 8.6%; transport equipment 5.4%; iron and steel 5.2%; cement 4.5%). Major import sources:Portugal 30.9%; The Netherlands and Belgium 13.3%; US 12.8%; Spain 7.6%; Brazil 5.4%. Exports (2006): C.V.Esc. 7,286,000,000 (reexports [significantly, resold fuel (bunkering) to passing ships and aircraft] 75.9%; domestic exports 18.2%, of which fresh fish 10.5%, clothing 6.7%, footwear 3.3%). Major export destinations (domestic exports only): Portugal 49.8%; Spain 27.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2001): total length 1,400 km (paved [2000] 69%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 23,811; trucks and buses 5,032. Air transport (2002): passenger-km 279,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 5,000 (11); televisions (2003): 48,000 (105); telephone landlines (2006): 72,000 (138); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 109,000 (210); personal computers (2004): 48,000 (102); total Internet users (2005): 25,000 (53); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,800 (3.7).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1990). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 47.9%; primary 40.9%; incomplete secondary 3.9%; complete secondary 1.4%; higher 1.5%; unknown 4.4%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 78.9%; males literate 86.5%; females literate 71.9%. Health (2005): physicians 241 (1 per 1,976 persons); hospital beds 950 (1 per 501 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 30.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,875 (vegetable products 84%, animal products 16%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,200 (army 83.3%, air force 8.3%, coast guard 8.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$15.
Background
When visited by the Portuguese in 1456-60, the islands were uninhabited. In 1460 Diogo Gomes sighted and named Maio and Sao Tiago, and in 1462 the first settlers landed on Sao Tiago, founding the city of Ribeira Grande. The city’s importance grew with the development of the slave trade, but its wealth attracted pirates so often that it was abandoned after 1712. The prosperity of the Portuguese-controlled islands vanished with the decline of the slave trade in the 19th century but later improved because of their position on the great trade routes between Europe, South America, and southern Africa. In 1951 the colony became an overseas province of Portugal. Many islanders preferred outright independence, and it was finally granted in 1975. At one time associated politically with Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde split from it in 1981.
Recent Developments
Cape Verde enjoyed political stability and a tourism boom in 2007. New direct flights brought Europeans from Portugal and Britain, and new international airports were being built on two of the islands. Few of the more than 500,000 Cape Verdeans living abroad (half of them in the US) returned, however, and they continued to outnumber those living on the islands. The large sums in remittances sent home, along with donor money from the European Development Fund, Japan, and others, continued to keep Cape Verde afloat.
Central African Republic
Official name: Republique Centrafricaine (Central African Republic). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [105]). Chief ofstate: President Frangois Bozize (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Faustin Archange Touadera (from 2008). Capital: Bangui. Official languages: French; Sango. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged to the euro [>] at the rate of >1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 240,324 sq mi, 622,436 sq km. Population (2007): 4,343,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 18.1, persons per sq km 7.0. Urban (2005): 38.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.72%; female 51.28%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 42.7%; 15-29, 28.1%; 30-44, 14.7%; 45-59, 8.8%; 60-74, 4.6%; 75-84, 1.0%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnolinguistic composition (2004): Gbaya (Baya) 33%; Banda 27%; Mandjia 13%; Sara 10%; Mbum 7%; Ngbaka 4%; other 6%. Religious affiliation (2005): independent Christian 20.2%; Roman Catholic 19.8%; traditional beliefs 19.5%; Protestant 16.4%; Sunni Muslim 14.5%; nonreligious/other 9.6%. Major cities (2003): Bangui 622,771; Bimbo 124,176; Berberati 76,918; Carnot 45,421; Bambari 41,356. Location: central Africa, bordering Chad, The Sudan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Cameroon.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 33.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 18.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.41. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 43.5 years; female 43.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 88,000,000,000 (taxes 57.5%, of which indirect domestic taxes 30.0%, direct taxes on income and profits 16.7%, taxes on international trade 10.8%; grants 33.5%; nontax revenue 9.0%). Expenditures: CFAF 120,400,000,000 (current expenditure 62.6%; development expenditure 31.9%; interest payments 5.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$871,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 563,000, yams 350,000, peanuts (groundnuts) 140,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,423,000 cattle, 3,087,000 goats, 805,000 pigs; roundwood 2,832,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 71%; fisheries production (2004) 15,000. Mining and quarrying (2005): diamonds 380,000 carats (official figure; a roughly equal amount was smuggled out of the country in 2004). Manufacturing (2002): refined sugar 10,570; palm oil 2,743; soap 1,625. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 110,000,000 (110,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (82,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.3; average annual income per household (1988) CFAF 91,985 (US$435); expenditure (1991): food 70.5%, clothing 8.5%, energy 7.3%. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$1,416,000,000 (US$332 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 1,786,000; activity rate of total population 45.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 80.4%; female 46.2%; unemployed [Bangui only; 2001] 23%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1.0; official development assistance (2005) 95. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 32. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3.1%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 5.0%; overall forest area (2005) 36.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 90,300,000,000 (petroleum products 19.6%; unspecified 80.4%). Major import sources:France 17%; The Netherlands 10%; Cameroon 10%; US 7%. Exports (2005): CFAF 67,400,000,000 (diamonds 48.7%; wood and wood products 38.3%; cotton 1.6%; coffee 1.3%). Major export destinations: Belgium 35%; France 10%; Spain 9%; Italy 8%; China 7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2005): total length (national roads only; much of the 15,600-km local road network is unusable) 10,000 km (paved 7%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 5,300; trucks and buses 6,300. Air transport (2003): passenger arrivals (departures) (Bangui airport only) 19,250 (19,107); metric ton-km cargo 7,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 4,000 (1); televisions (2004): 24,000 (6.1); telephone landlines (2005): 10,000 (2.5); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 100,000 (25); personal computers (2005): 12,000 (3); total Internet users (2006): 13,000 (3.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1994-95). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 55.1%; at least some primary education 30.5%; at least some secondary education 14.4%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 42.7%; males literate 53.8%; females literate 32.0%. Health: physicians (2004) 331 (1 per 11,867 persons); hospital beds (2001) 4,365 (1 per 879 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 85.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,104 (vegetable products 86%, animal products 14%); 117% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,550 (army 54.9%; air force 5.9%; paramilitary [gendarmerie] 39.2%); French troops (2006) 200. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Background
For several centuries before the arrival of Europeans, the territory was subjected to slave traders. The French explored and claimed central Africa and in 1889 established a post at Bangui. In 1898 they partitioned the colony among commercial concessionaires. United with Chad in 1906 to form the French colony of Ubangi-Shari, it later became part of French Equatorial Africa. It was separated from Chad in 1920 and became an overseas territory in 1946. Named an autonomous republic within the French Community in 1958, the country achieved independence in 1960. In 1966 the military overthrew a civilian government and installed Jean-Bedel Bokassa, who in 1976 declared himself Emperor Bokassa I and renamed the country the Central African Empire. He was overthrown in 1979, but the military again seized power in the 1980s. Elections in 1993 led to the installation of a civilian government.
Recent Developments
The crisis in the northern Central African Republic (CAR) worsened during 2007, with tens of thousands of civilians forced to flee as fighting between dissident groups and the army intensified. Relief agencies estimated that at least one million people were in need of basic provisions. An agreement signed between the governments of Chad and the CAR to allow their military forces to cross each other’s border to pursue rebels wreaked further misery upon civilians caught in the cross fire. Two volunteer health workers were abducted in May by rebels, and Doctors Without Borders reported the fatal shooting in June of one of its workers. The following day all aid agencies in the north of the country suspended operations.
Chad
Official name: Jumhuriyah Tshad (Arabic); Republique du Tchad (French) (Republic of Chad). Form of government: unitary republic with one legislative body (National Assembly [155]). Chief of state: President Idriss Deby (from 1990). Head of government: Prime Minister Delwa Kassire Koumakoye (from 2007). Capital: N’Djamena. Official languages: Arabic; French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 495,755 sq mi, 1,284,000 sq km. Population (2007): 10,239,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 20.7, persons per sq km 8.0. Urban (2005): 25.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.82%; female 51.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 48.0%; 15-29, 26.7%; 30-44, 13.7%; 45-59, 7.3%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnolinguistic composition (1993): Sara 27.7%; Sudanic Arab 12.3%; Mayo-Kebbi peoples 11.5%; Kanem-Bornu peoples 9.0%; Ouaddai peoples 8.7%; Hadjeray (Had-jarai) 6.7%; Tangale (Tandjile) peoples 6.5%; Gorane peoples 6.3%; Fitri-Batha peoples 4.7%; Fulani (Peul) 2.4%; other 4.2%. Religious affiliation (2005): Sunni Muslim 57.0%; animist 18.8%; Protestant 10.5%; other (significantly Roman Catholic and nonreligious) 13.7%. Major cities (2000): N’Djamena (urban agglomeration; 2005) 888,000; Moundou 108,728; Sarh 95,050; Abeche 63,165; Kelo 36,643. Location: central Africa, bordered by Libya, The Sudan, the Central African Republic, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Niger.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 46.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 16.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 29.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 6.32. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 45.6 years; female 48.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 311,100,000,000 (tax revenue 45.9%; petroleum revenue 43.7%; nontax revenue 10.4%). Expenditures: CFAF 482,000,000,000 (capital expenditure 61.9%; current expenditure 38.1%, of which wages and salaries 13.9%, materials and supply 7.8%, transfer payments 7.1%, defense 6.3%, debt service 2.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,537,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sorghum 582,600, millet 578,300, peanuts (groundnuts) 450,000, gum arabic (2006) 20,000; livestock (number of live animals) 6,540,000cattle, 5,843,000goats, 740,000 camels; roundwood 7,249,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 90%; fisheries production (2004) 70,000. Mining and quarrying (2005): natron 12,000; salt 10,000; gold 150 kg. Manufacturing (2004-05): cotton fiber 88,158; refined sugar 51,823; woven cotton fabrics (2000) 1,000,000 meters. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 99,000,000 (99,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 62,000,000 (n.a.); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 59,000 (41,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.0; average annual income per household (1993) CFAF 96,806 (US$458); sources of income (1995-96; urban): informal-sector employment and entrepreneurship 36.7%, transfers 24.8%, wages 23.6%, ownership of real estate 8.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 656; official development assistance (2005) 380. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2002) 80. Population economically active (2003): total 3,385,000; activity rate of total population 37.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.2%; female 47.3%). Gross national product (2006): US$3,509,000,000 (US$335 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.9%, in permanent crops 0.02%, in pasture 35.7%; overall forest area (2005) 9.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 323,500,000,000 (nonpetro-leum private sector 42.7%; public sector 19.3%; petroleum sector 15.6%). Major import sources: France 21%; Cameroon 15%; US 12%; Belgium 7%; Portugal 5%. Exports (2004): CFAF 1,152,300,000,000 (crude petroleum 84.5%; live cattle 10.4%; cotton 3.3%). Major export destinations: US 78%; China 10%; Taiwan 4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2002): total length 33,400 km (paved 1%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 8,900; trucks and buses 12,400. Air transport: passenger-km (2001) 130,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 7,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 55,000 (5.9); telephone landlines (2006): 13,000 (1.3); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 466,000 (47); personal computers (2004): 15,000 (1.6); total Internet users (2006): 60,000 (6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 74.5%; primary education 17.4%; secondary education 6.8%; higher education 1.3%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 47.5%; males 56.0%; females 39.3%. Health: physicians (2004) 345 (1 per 27,180 persons); hospital beds (1998) 4,105 (1 per 1,908 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 93.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,190 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 120% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 25,350 (army 78.9%; air force 1.4%; other 19.7%); French peacekeeping troops (November 2006) 1,550. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$6.
Mount Koussi, the highest summit in the Sahara (11,204 feet [3,415 metres]), is situated 109 miles (176 km) north-northwest of Faya in the Tibesti massif of northwestern Chad. It is an extinct volcano with a crater approximately 12 miles (19 km) wide and 4,000 feet (1,200 metres) deep.
Background
About AD 800 the kingdom of Kanem was founded in north-central Africa, and by the early 1200s its borders had expanded to form a new kingdom, Kanem-Bornu, in the northern regions of the area. Its power peaked in the 16th century with its command of the southern terminus of the trans-Sahara trade route to Tripoli. Around this time the rival kingdoms of Baguirmi and Wadai evolved in the south. In the years 1883-93 all three kingdoms fell to the Sudanese adventurer Rabih al-Zubayr, who was in turn pushed out by the French in 1900. Extending their power, the French in 1910 made Chad a part of French Equatorial Africa. Chad became a separate colony in 1920 and was made an overseas territory in 1946. The country achieved independence in 1960. This was followed by decades of civil war and frequent intervention by France and Libya.
Recent Developments
Chad continued to be affected in 2007 by both the conflict across its border in the Darfur region of The Sudan and the ongoing low-intensity warfare between various rebel factions and the government of Pres. Idriss Deby. At the beginning of 2008 there were an estimated 233,000 Sudanese refugees from Darfur in camps in eastern Chad, and more than 100,000 Chadians in the east had been forced from their homes. As raids by mounted armed men from Darfur continued, UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon and the French government called for a UN-European Union peacekeeping force to be established in eastern Chad to protect the camps. This force, initially of 1,800 soldiers, was deployed in March 2008. In its 2007 report, Transparency International once again found Chad to be one of the most corrupt countries in the world.
Chile
Official name: Republica de Chile (Republic of Chile). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [38]; Chamber of Deputies [120]). Head of state and government: President Michelle Bachelet (from 2006). Capital: Santiago (legislative bodies meet in Valparaiso). Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 peso (Ch$) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Ch$528.00.
Demography
Area: 291,930 sq mi, 756,096 sq km. Population (2007): 16,598,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 56.9, persons per sq km 22.0. Urban (2003): 87.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.47%; female 50.53%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 24.9%; 15-29, 24.3%; 30-44, 23.0%; 45-59, 16.2%; 60-74, 8.3%; 75-84, 2.5%; 85 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2002): mestizo 72%; white 22%; Amerindian 5%, of which Araucanian (Ma-puche) 4%; other 1%. Religious affiliation (2002): Roman Catholic 70.0%; Protestant/independent Christian 15.1%; other Christian 2.0%; atheist/nonre-ligious 8.3%. Major urban agglomerations (2002): Santiago 5,428,590; Valparaiso/Vina del Mar 803,683; Concepcion 666,381; La Serena/Co-quimbo 296,253; Antofagasta 285,255. Location: southern South America, bordering Peru, Bolivia, Argentina, the South Atlantic Ocean, and the South Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.00. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 73.5 years; female 80.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:Ch$15,680,877,000,000 (tax revenue 71.3%; copper revenue 15.6%; other 13.1%). Expenditures: Ch$10,582,361,000,000 (subsidies and grants 31.0%; pension payments 28.7%; wages and salaries 23.8%; goods and services 11.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$9,096,000,000. Population economically active (2005): total 6,345,400; activity rate of total population 39.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 59.3%; female 35.6%; unemployed [2006] 7.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugar beets 2,800,000, grapes 2,250,000, wheat 1,852,000; livestock (number of live animals) 4,200,000 cattle, 3,450,000 pigs, 3,400,000 sheep; roundwood 46,051,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 29%; fisheries production 5,028,539 (from aquaculture 14%); aquatic plants production 425,343 (from aquacul-ture 4%). Mining (2004): copper (metal content; 2005) 5,320,500; iron ore (metal content) 4,477,000; lithium carbonate 41,667. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): food products 2,041; nonferrous base metals 1,877; beverages 962; refined petroleum 845. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 51,575,000,000 ([2004] 49,100,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 188,000 (4,435,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 1,210,000 ([2005] 86,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 10,118,000 (10,641,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 1,967,000,000 (8,436,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.6%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 17.3%; overall forest area (2005) 21.5%. Gross national income (2006): US$126,436,000,000 (US$7,679 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.4; average annual income per household (2001) Ch$6,804,000 (US$9,530); sources of income (2001): wages and salaries 39.5%, transfer payments 19.7%, rent on property 14.5%, self-employment 9.8%, other 16.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,256; remittances (2006) 3; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 4,979. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,057; remittances (2006) 6; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1,446.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$32,021,-400,000 (capital goods 22.3%; consumer goods 14.7%; crude petroleum 11.8%; free zone imports 5.1%). Major import sources (2004): Argentina 18.5%; US 15.1%; Brazil 12.4%; China 8.3%. Exports (2005): US$39,881,400,000 (copper 45.9%; foodstuffs 12.0%, of which salmon and trout 4.2%; fruits 5.3%; wood and wooden furniture 4.5%; paper and paper products 4.2%). Major export destinations (2004): US 14.8%; Japan 12.0%; China 10.4%; South Korea 5.8%; The Netherlands 5.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length 8,707 km; passenger-km (2004) 830,259,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,899,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 80,505 km (paved 22%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 1,406,796; trucks and buses 681,974. Air transport (2005; LAN Chile Group, Aerolineas Del Sur, Aerovfas DAP, and Sky Service only): passenger-km 18,977,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,757,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 816,000 (52); televisions (2004): 4,305,000 (268); telephone landlines (2006): 3,326,000 (202); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 12,451,000 (756); personal computers (2005): 2,800,000 (172); total Internet users (2006): 4,156,000 (252); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 978,000 (60).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/other 5.4%; incomplete primary education 24.6%; complete primary 8.7%; secondary 43.9%; higher technical 4.9%; university 12.5%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 95.7%; males literate 95.8%; females literate 95.6%. Health: physicians (2004) 20,726 (1 per 778 persons); hospital beds (2003) 39,782 (1 per 401 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 8.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,079 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%); 160% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 78,098 (army 61.1%, navy 24.8%, air force 14.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.8%; per capita expenditure US$270.
Background
Originally inhabited by native peoples, including the Mapuche, the Chilean coast was invaded by the Spanish in 1536. A settlement begun at Santiago in 1541 was governed under the Viceroyalty of Peru but became a separate captaincy general in 1778. It revolted against Spanish rule in 1810; its independence was finally assured by the victory of Jose de San Martfn in 1818, and the area was then governed by Bernardo O’Higgins to 1823. In the War of the Pacific against Peru and Bolivia, it won the rich nitrate fields on the coast of Bolivia, effectively forcing that country into a landlocked position. Chile remained neutral in World War I and in World War II but severed diplomatic ties with the Axis in 1943. In 1970 Salvador Allende was elected president, becoming the first avowed Marxist to be elected chief of state in Latin America. Following economic upheaval, he was ousted in 1973 in a coup led by Gen. Augusto Pinochet, whose military junta for many years harshly suppressed all internal opposition. A national referendum in 1988 rejected Pinochet, and elections held in 1989 returned the country to civilian rule.
Recent Developments
A series of problems eroded Chilean Pres. Michelle Bachelet’s popularity in 2007. Among these was the disastrous implementation of Transantiago, a plan to reorganize and better integrate Santiago’s bus and subway system, and a large number of student disturbances and labor mobilizations. There was also some positive news, however. In the realm of human rights, arrests and trials continued of those who had committed offenses during the military dictatorship. A key Bachelet promise to help women was realized with the establishment of more preschools and women’s domestic-violence shelters. The economic picture continued to be strong. The price of copper, Chile’s largest single export, reached its highest level in more than 40 years, and there were both a large budget surplus and a positive trade balance. Economic growth, though slower than in the preceding year, ran at close to 5%. The Bachelet government approved the development of alternative energy, including nuclear power and additional dams for hydroelectric generation, both of which were opposed by environmentalists.
China
Official name: Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo (People’s Republic of China). Form of government: single-party people’s republic with one legislative house (National People’s Congress [2,980]). Chief of state: President Hu Jintao (from 2003). Head of government: Premier Wen Jiabao (from 2003). Capital: Beijing (Peking). Official language: Mandarin Chinese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Renminbi (yuan) (Y) = 10 jiao = 100 fen; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Y 6.86.
Demography
Area: 3,696,100 sq mi, 9,572,900 sq km. Population (2007): 1,317,925,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 356.6, persons per sq km 137.7. Urban (2006): 43.9%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.52%; female 48.48%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 19.3%; 15-29, 22.1%; 30-44, 27.2%; 45-59, 19.0%; 60-74, 9.6%; 75-84, 2.4%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): Han (Chinese) 91.53%; Chuang 1.30%; Manchu 0.86%; Hui 0.79%; Miao 0.72%; Uighur 0.68%; Tuchia 0.65%; Yi 0.62%; Mongolian 0.47%; Tibetan 0.44%; Puyi 0.24%; Tung 0.24%; Yao 0.21%; Korean 0.15%; Pai 0.15%; Hani 0.12%; Kazakh 0.10%; Li 0.10%; Tai 0.09%; other 0.54%. Religious affiliation (2005): nonreligious 39.2%; Chinese folk-religionist 28.7%; Christian 10.0%, of which unregistered Protestant 7.7%, registered Protestant 1.2%, unregistered Roman Catholic 0.5%, registered Roman Catholic 0.4%; Buddhist 8.4%; atheist 7.8%; traditional beliefs 4.4%; Muslim 1.5%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Shanghai 14,503,000; Beijing 10,717,000; Guangzhou 8,425,000; Shenzhen 7,233,000; Wuhan 7,093,000; Tianjin 7,040,000; Chongqing 6,363,000; Shenyang 4,720,000; Dongguan 4,320,000; Chengdu 4,065,000; Xi’an 3,926,000; Harbin 3,695,000; Nanjing 3,621,000; Guiyang 3,447,000; Dalian 3,073,000; Changchun 3,046,000; Zibo 2,982,000; Kunming 2,837,000; Hangzhou 2,831,000; Qingdao 2,817,000; Taiyuan 2,794,000; Jinan 2,743,000; Zhengzhou 2,590,000; Fuzhou 2,453,000; Changsha 2,451,000; Lanzhou 2,411,000. Location: eastern Asia, bordering Mongolia, Russia, North Korea, the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, the South China Sea, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), India, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan. Households. Average household size (2004) 3.6, of which urban households 3.0, rural households 4.1; 1 person 7.8%, 2 persons 19.6%, 3 persons 31.4%, 4 persons 21.8%, 5 persons 12.4%, 6 or more persons 7.0%; non-family households 0.8%. Mobility (2004). Population residing in registered enumeration area 91.3%; population not residing in registered enumeration area for more than 6 months 7.4%; remainder 1.3%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.72. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 70.9 years; female 74.3 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no schooling and incomplete primary 15.6%; completed primary 35.7%; some secondary 34.0%; complete secondary 11.1%; some postsecondary through advanced degree 3.6%. Quality of working life. Average workweek (1998) 40 hours. Annual rate per 100,000 workers of death in mining, industrial, or commercial enterprises (2006) 3.33. Death toll from work accidents (2006) 112,822. Access to services. Percentage of population having access to electricity (2003) 97.7%. Percentage of total (urban, rural) population with safe public water supply (2002) 83.6% (94.0%, 73.0%). Sewage system (1999): total (urban, rural) households with flush apparatus 20.7% (50.0%, 4.3%), with pit latrines 69.3% (33.6%, 86.7%), with no latrine 5.3% (7.8%, 4.1%). Social participation. Trade union membership in total labor force (2004) 18%. Social deviance. Annual reported arrest rate per 100,000 population (2004) for: thievery 197; robbery 23. Material well-being. Urban households possessing (number per household; 2004): bicycles 1.4; color televisions 1.3; washing machines 1.0; refrigerators 0.9; air conditioners 0.7; cameras 0.5. Rural families possessing (number per household; 2004): bicycles 1.2; color televisions 0.8; washing machines 0.4; refrigerators 0.2; air conditioners 0.05; cameras 0.04.
National economy
Gross national income (2006): US$2,641,846,-000,000 (US$2,035 per capita). Budget (2004). Revenues 2,639,647,000,000 (tax revenue 91.5%, of which VAT 34.2%, corporate income taxes 15.0%, business tax 13.6%, consumption tax 5.7%; nontax revenue 8.5%). Expenditures: Y 2,848,689,000,000 (economic development 27.8%, of which agriculture 8.3%; social, cultural, and educational development 26.3%; administration 19.4%; defense 7.7%; other 18.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$82,853,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): grains-rice 184,254,000, corn (maize) 131,145,000, wheat 96,160,250, barley 3,200,000; oilseeds-soybeans 16,900,300, peanuts (groundnuts) 14,638,500, rapeseed 11,300,010, sunflower seeds 1,850,000; fruits and nuts-watermelons 69,315,000, apples 25,006,500, citrus 16,019,500, cantaloupes 15,138,000, pears 11,625,000, bananas 6,390,000; other-sweet potatoes 107,676,100, sugarcane 92,130,000, potatoes 73,776,500, cabbage 34,101,000, tomatoes 31,644,040, cucumbers 26,559,600, onions 19,047,000, eggplants 17,030,300, seed cotton 16,305,000, chilies and peppers 12,531,000, garlic 11,093,500, asparagus 5,906,000, spinach 4,494,000, tobacco leaves 2,505,500, tea 900,500, silkworm cocoons (2003) 667,000; livestock (number of live animals) 488,809,978 pigs, 195,758,954 goats, 170,882,215 sheep, 115,229,500 cattle, 22,745,250 water buffalo, 4,360,243,000 chickens, 725,018,000 ducks; roundwood 286,103,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 67%; fisheries production 49,467,309 (from aquaculture 66%); aquatic plants production 11,103,395 (from aquaculture 97%). Mining and quarrying (2005): metal content of mine output-iron ore 138,000,000 (world rank: 3), zinc 2,450,000 (world rank: 1), manganese 1,100,000 (world rank: 5), lead 1,000,000 (world rank: 1), copper 740,000 (world rank: 7), antimony 120,000 (world rank: 1), tin 110,000 (world rank: 1), tungsten 61,000 (world rank: 1), silver 2,500 (world rank: 3), gold 225 (world rank: 2); metal ores-bauxite 18,000,000 (world rank: 3), vanadium 17,000 (world rank: 1); nonmetals-salt 44,547,000 (world rank: 2), phosphate rock 9,130,000 (world rank: 2), magne-site 4,700,000 (world rank: 1), barite 4,200,000 (world rank: 1), talc 3,000,000 (world rank: 1), fluorspar 2,700,000 (world rank: 1), asbestos 520,000 (world rank: 2), strontium 140,000 (world rank: 2). Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): electrical machinery 66,521; industrial chemicals, paints, and soaps 45,727; transport equipment 35,000; iron and steel 34,119; nonelectrical machinery 31,395; food products 25,776; textiles 23,036; tobacco products 19,010; cement, bricks, and tiles 16,334; refined petroleum 15,554; fabricated metal products 11,731; wearing apparel 11,073; nonferrous base metals 10,899. Distribution of industrial production (percentage of total value added by sector; 2004): directly state-owned and state-controlled enterprises 42.4%; private enterprises 15.1%; collectives 5.3%; remainder 37.2%. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 2,834,400,000,000 ([2004] 2,178,000,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2006) 2,380,000,000 (2,370,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 1,347,000,000 (2,346,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 212,352,000 (244,178,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 58,550,000,000 (55,600,000,000). Population economically active (2003): total 766,430,000; activity rate of total population 59.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 82.4%; female 44.6%; registered unemployed in urban areas [2005] 4.2%). Households. Average annual per capita disposable income of household (2006): rural households Y 3,587 (US$450), urban households Y 11,579 (US$1,452). Sources of income (2004): rural households-income from household businesses 59.5%, wages 34.0%, transfers and property 6.5%; urban households-wages 70.6%, transfers 22.9%, business income 4.9%, property 1.6%. Expenditure: rural (urban) households-food 47.2% (37.8%), housing and energy 14.8% (10.2%), education and recreation 11.3% (14.4%), transportation and communications 8.8% (11.7%), clothing 5.5% (9.6%), medicine and medical service 6.0% (7.4%), household furnishings 4.1% (5.7%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 33,950; remittances (2005) 22,492; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 57,232; official development assistance (2005) 1,962 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 21,800; remittances (2005) 2,602; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 4,472. Land use as % of total land area (2004): in temporary crops or permanent crops 13.5%, in pasture 41.5%; overall forest area (2005) 21.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$561,229,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 41.7%; mineral fuels 8.6%; professional and scientific equipment 7.4%; plastics and related products 5.0%; organic chemicals 4.2%; iron and steel 4.2%). Major import sources:Japan 16.8%; Taiwan 11.5%; South Korea 11.1%; US 8.0%; Germany 5.4%; Malaysia 3.2%; Singapore 2.5%; Russia 2.2%; Hong Kong 2.1%; Australia 2.1%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$593,326,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 41.8%; wearing apparel and accessories 11.3%; iron and steel [including finished products] 4.2%; chemicals and chemical products 4.1%; transport equipment 3.5%). Major export destinations: US 21.1%; Hong Kong 17.0%; Japan 12.4%; South Korea 4.7%; Germany 4.0%; The Netherlands 3.1%; UK 2.5%; Taiwan 2.3%; Singapore 2.1%; France 1.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length (2004) 74,400 km; passenger-km 662,200,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,195,400,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 1,870,661 km (paved 81%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 17,359,100; trucks 8,930,000. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 236,990,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,430,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 96,600,000 (74); televisions (2003): 493,902,000 (381); telephone landlines (2007): 367,810,000 (279); cellular telephone subscribers (2007): 461,080,000 (350); personal computers (2004): 52,990,000 (40); total Internet users (2006): 137,000 (104); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 50,916,000(39).
Education and health
Literacy (2000): total population ages 15 and over literate 90.9%; males literate 95.1%; females literate 86.5%. Health (2006): physicians 1,970,000 (1 per 668 persons); hospital beds 3,216,000 (1 per 409 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 24.4. Food (2003): daily per capita caloric intake 2,740 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 142% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 2,255,000 (army 71.0%, navy 11.3%, air force 17.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.0%; per capita expenditure US$34.
Background
The discovery of Peking man (Homo erectus) in 1927 dated the advent of early humans in what is now China to the Middle Pleistocene, about 900,000 to 130,000 years ago. Chinese civilization probably spread from the Huang He (Yellow River) valley, where it existed c. 3000 bc. The first dynasty for which there is definite historical material is the Shang (c. 16th century bc), which had a writing system and a calendar. The Zhou, a subject state of the Shang, overthrew its Shang rulers in the 11th century BC and ruled until the 3rd century BC. Taoism and Confucianism were founded in this era.
A time of conflict, called the Warring States period, lasted from the 5th century bc until 221 bc, when the Qin (Ch’in) dynasty (from whose name China is derived) was established after its rulers had conquered rival states and created a unified empire. The Han dynasty was established in 206 bc and ruled until ad 220. A time of turbulence followed, and Chinese reunification was not achieved until the Sui dynasty was established in 581.
After the founding of the Song dynasty in 960, the capital was moved to the south because of northern invasions. In 1279 this dynasty was overthrown and Mongol (Yuan) domination began. During this time Marco Polo visited Kublai Khan. The Ming dynasty followed the period of Mongol rule and lasted from 1368 to 1644, cultivating antiforeign feelings to the point that China closed itself off from the rest of the world.
Peoples from Manchuria overran China in 1644 and established the Qing (Manchu) dynasty. Ever-increasing incursions by Western and Japanese interests led in the 19th century to the Opium Wars, the Taiping Rebellion, and the Sino-Japanese War, all of which weakened the Manchus.
The dynasty fell in 1911, and a republic was proclaimed in 1912 by Sun Yat-sen. The power struggles of warlords weakened the republic. Under Sun’s successor, Chiang Kai-shek, some national unification was achieved in the 1920s, but Chiang soon broke with the Communists, who then formed their own armies. Japan invaded northern China in 1937; its occupation lasted until 1945. The Communists gained support after the Long March (1934-35), in which Mao Zedong emerged as their leader.
Upon Japan’s surrender at the end of World War II, a fierce civil war began; in 1949 the Nationalists fled to Taiwan and the Communists proclaimed the People’s Republic of China. The Communists undertook extensive reforms, but pragmatic policies alternated with periods of revolutionary upheaval, most notably in the Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution. The chaos of the latter led, after Mao’s death in 1976, to a turn to moderation under Deng Xiaoping, who undertook economic reforms and renewed China’s ties to the West. The government established diplomatic ties with the US in 1979. It suppressed the Tiananmen Square student demonstration in 1989. The economy has been in transition since the late 1970s, moving from central planning and state-run industries to a mixture ofstate-owned and private enterprises in manufacturing and services. The death of Deng in 1997 marked the end of a political era, but power passed peacefully to Jiang Zemin. In 1997 Hong Kong reverted to Chinese rule, as did Macao in 1999.
Recent Developments
China’s economy continued its recent meteoric rise. GDP grew by almost 12% and the trade surplus approached US$260 billion in 2007; foreign-exchange reserves were up a spectacular US$153.9 billion in the first quarter of 2008 from year’s end 2007; and the Chinese renminbi continued to appreciate against the US dollar at an annual rate of about 5%. Massive trade surpluses boosted the country’s currency reserves to a record US$1.33 trillion in September 2007.
Chinese exporters struggled to redeem their image after a succession of product recalls of tainted goods. Early in 2007 toy manufacturer Mattel recalled nearly 20 million Chinese-made products, most of which contained lead-tainted paint. In July the former head of China’s State Food and Drug Administration was executed for having taken bribes from pharmaceutical companies and having approved fake drugs.
The environmental consequences of China’s economic boom came under increased government scrutiny. Reports emerged showing that just 1% of China’s approximately 560 million urban residents were breathing air considered safe by the EU, and some 500 million people lacked access to clean drinking water. Meanwhile, it was reported in 2008 that China had become the global leader in greenhouse-gas emissions in 2006.
There were signs in 2007 that China was moderating its foreign policy—possibly ahead of the Beijing Olympic Games in 2008. China opposed international sanctions against the Sudanese government but supported the deployment of peacekeepers to The Sudan and helped persuade the government to accept them. (China imported 7% of its oil from The Sudan, and in a sign of close relations Pres. Hu Jintao visited the country in February 2007.) Relations with the US got off to a rocky start after China shot down a weather satellite during an unannounced test, demonstrating the country’s military-space capabilities. Continuing trade tensions led US lawmakers to introduce legislation intended to force China to revalue its currency.
In May 2008 a 7.9-magnitude earthquake struck in China’s Sichuan province. More than 6,900 schools were destroyed, and engineers feared that serious damage had been inflicted on hundreds of dams in the area. As many as 5,000,000 people were made homeless, and more than 68,000 people perished.
Colombia
Official name: Republica de Colombia (Republic of Colombia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [102]; House of Representatives [166]). Head of state and government: President Alvaro Uribe Velez (from 2002). Capital: Bogota. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 peso (Col$) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Col$1,905.60.
Demography
Area: 440,762 sq mi, 1,141,568 sq km. Population (2007): 42,870,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 97.2, persons per sq km 37.5. Urban (2005): 72.7%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.25%; female 50.75%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 30.3%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44, 21.6%; 45-59, 13.4%; 60-74, 5.6%; 75-84, 1.6%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 47.3%; mulatto 23.0%; white 20.0%; black 6.0%; black-Amerindian 1.0%; Amerindian/other 2.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 92.5%; Protestant 2.8%; independent Christian 2.4%; Mormon 0.3%; Muslim 0.2%; other 1.8%. Major cities (2005): Bogota 6,763,325; Medellin 2,187,356; Cali 2,039,626; Barranquilla 1,109,067; Cartagena 845,801. Location: northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, Venezuela, Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, the Pacific Ocean, and Panama.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.54. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 68.2 years; female 76.0 years.
National economy
53.1%; debt service 19.0%; other 27.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$22,491,-000,000. Population economically active (2005): total 20,575,200; activity rate 46.1% (participation rates: ages 12-55, 65.7%; female 42.1%; unemployed 11.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 39,850,000, plantains 3,457,000, rice 2,502,000 (also major producer of cut flowers; export value [2006] US$1,000,000,000); livestock (number of live animals) 25,699,000 cattle, 3,332,993 sheep, 2,553,621 horses; roundwood 9,658,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 83%; fisheries production 181,074 (from aquaculture 33%). Mining and quarrying (2004): nickel (metal content) 75,032; gold 37,739 kg; emeralds 9,825,000 carats. Manufacturing (value added in Col$’000,000,000; 2003): processed food 6,471; chemicals 5,737; petroleum products 3,712. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 50,291,000,000 (48,657,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 53,700,000 (3,144,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 189,200,000 (112,400,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 14,106,000 (9,164,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 6,354,000,000 (6,219,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.0%, in permanent crops 1.3%, in pasture 34.5%; overall forest area (2005) 58.5%. Gross national income (2006): US$125,898,000,000 (US$2,763 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.8; sources of income (2002): wages 42.6%, self-employment 38.9%; expenditure (1992): food 34.2%, transportation 18.5%, housing 7.8%, health care 6.4%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,218; remittances (2006) 4,200; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 3,946; official development assistance (2005) 838 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,127; remittances (2006) 66; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1,315.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$26,162,-000,000 (chemicals and chemical products 20.2%; transportation equipment 15.3%; nonelectrical machinery 11.2%; telecommunications equipment 8.6%). Major import sources: US 26.5%; Mexico 8.8%; China 8.5%; Brazil 7.2%; Venezuela 5.7%. Exports (2006): US$24,391,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 26.0%; coal 11.9%; chemicals and chemical products 7.4%; base metals 6.6%; food, beverages, and tobacco 6.5%; coffee 6.0%; textiles and clothing 5.4%). Major export destinations: US 39.6%; EU 13.7%; Venezuela 11.1%; Ecuador 5.1%; Peru 2.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2004) 3,304 km; metric ton-km cargo (1999) 473,000,000. Roads (2000): total length 112,998 km (paved 23%). Vehicles (1999): cars 1,803,201; trucks 319,294. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 7,764,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 252,852,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 1,294,000 (30); televisions (2004): 11,358,000 (268); telephone landlines (2006): 7,865,000 (170); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 29,763,000 (643); personal computers (2005): 1,892,000 (44); total Internet users (2006): 6,705,000 (145); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 628,000 (14).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no schooling/unknown 10.2%; primary education 40.1%; secondary 34.2%; higher 15.5%. Literacy (2003): population ages 15 and over literate 92.5%; males literate 92.4%; females literate 92.6%. Health (2004): physicians 59,235 (1 per 714 persons); hospital beds 50,773 (1 per 833 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 20.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,744 (vegetable products 83%, animal products 17%); 150% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 207,000 (army 86.0%, navy 10.6%, air force 3.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.7%; per capita expenditure US$106.
Background
The Spanish arrived in what is now Colombia c. 1500 and by 1538 had defeated the area’s Chibchan-speaking Indians and made the area subject to the Viceroyalty of Peru. After 1740 authority was transferred to the newly created Viceroyalty of New Granada. Parts of Colombia threw off Spanish jurisdiction in 1810, and full independence came after Spain’s defeat by Simon Bolivar in 1819. Civil war in 1840 checked development. Conflict between the Liberal and Conservative parties led to the War of a Thousand Days (1899-1903). Years of relative peace followed, but hostility erupted again in 1948; the two parties agreed in 1958 to a scheme for alternating governments. A new constitution was adopted in 1991, but democratic power remained threatened by civil unrest. Many leftist rebels and right-wing paramilitary groups funded their activities through kidnappings and narcotics trafficking.
Recent Developments
Problems continued in Colombia stemming from the presence of right-wing paramilitaries—the United Self-Defense Forces of Colombia—and those on the left— the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) and the National Liberation Army. FARC continued to demand a demilitarized zone before it would begin to discuss a prisoner exchange, and the government continued to refuse to cede territory to the group. The 11 provincial legislators held by FARC since 2002 were killed when the guerrillas came under attack from what the FARC said was an “unidentified group.” Colombian troops raided a FARC base in Ecuador and killed the group’s second in command, Raul Reyes, in March 2008. Ecuador and Venezuela both massed troops on their borders with Colombia.
Comoros
Official name: Udzima wa Komori (Comorian); L’U-nion des Comores (French) (Union of the Comoros). Form of government: federal republic with one legislative house (Federal Assembly [33]). Head of state and government: President Ahmed Abdallah Mo-hamed Sambi (from 2006). Capital: Moroni. Official languages: Comorian (Shikomor); Arabic; French. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Comorian franc (CF; pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = CF 491.97) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CF 312.27.
Demography
Area: 719 sq mi, 1,862 sq km. Population (2007): 629,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 874.8, persons per sq km 337.8. Urban (2003): 35.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.61%; female 50.39%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 42.7%; 15-29, 26.6%; 30-44, 17.8%; 45-59, 8.2%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2000): Co-morian (a mixture of Bantu, Arab, Malay, and Malagasy peoples) 97.1%; Makua 1.6%; French 0.4%; Arab 0.1%; other 0.8%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 98.4%; other 1.6%. Major cities (2002): Moroni (urban agglomeration [2003]) 53,000; Mutsamudu 21,558; Domoni 13,254; Fom-boni 13,053; Tsembehou 10,552. Location: western Indian Ocean, lying between Madagascar and Mozambique.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 36.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 28.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.03. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 60.0 years; female 64.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: CF 30,509,000,000 (tax revenue 58.3%, of which taxes on international trade 31.0%, income and profit taxes 20.3%; grants 21.4%; nontax revenue 20.3%). Expenditures: CF 30,425,000,000 (current expenditures 77.3%, of which education 25.1%, health 15.6%, interest on debt 3.9%; development expenditures 22.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$301,-000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): coconuts 77,000, bananas 65,000, cassava 58,000; livestock (number of live animals) 115,000 goats, 45,000 cattle, 21,000 sheep; roundwood 8,650; fisheries production 15,070. Mining and quarrying: sand, gravel, and crushed stone from coral miningfor local construction. Manufacturing: products of small-scale industries include processed vanilla and ylang-ylang, cement, handicrafts, soaps, soft drinks, woodwork, and clothing. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 36,000,000 (35,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (29,000). Population economically active (2000): total 287,000; activity rate of total population 41.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 73.2%; female 40.4%; unemployed [2005] 13.3%). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.8; average annual income per household (2004) CF 699,000 (US$1,764); sources of income (2004): wages/self-employment 36.9%, value of self-produced food 27.7%, value of principal dwelling 23.9%; expenditure (1999): food, beverages, and tobacco products 68.0%, housing and energy 15.5%, clothingand footwear 4.7%, education 4.2%. Gross national income (2006): US$397,000,000 (US$485 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14; remittances (2005) 12; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1.0; official development assistance (2005) 25. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 3.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 36%, in permanent crops 23%, in pasture 7%; overall forest area (2005)2.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): CF 33,917,000,000 (food products 30.3%, of which rice 14.3%, meat 8.9%; petroleum products 20.9%; vehicles 11.5%; cement 5.1%). Major import sources: France 23%; South Africa 11%; United Arab Emirates 7%; Kenya 7%; Mauritius 6%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): CF 5,777,000,000 (cloves 49.9%; vanilla 30.8%; ylang-ylang 14.7%). Major export destinations: US 42%; France 18%; Singapore 16%; Turkey 5%; Germany 4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 793 km (paved 70%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 9,100; trucks and buses 4,950. Air transport (2001): passengers arriving/departing Moroni 108,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2002): 13,000 (23); telephone landlines (2005): 17,000 (28); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 16,000 (26); personal computers (2004): 5,000 (6.3); total Internet users (2006): 21,000 (26).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1996). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 72.7%; primary education 11.0%; secondary 15.1%; unknown 1.2%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 56.8%; males literate 63.9%; females literate 49.7%. Health (2004): physicians 48 (1 per 12,417 persons); hospital beds (1995) 1,450 (1 per 342 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 72.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,766 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 97% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): the Comoros small standing army is not necessarily accepted by each of the islands; each island also has its own armed security. France provides training for military personnel. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.5%; per capita expenditure US$21.
Background
The Comoros islands were known to European navigators from the 16th century. In 1843 France officially took possession of Mayotte and in 1886 placed the other three islands under protection. Subordinated to Madagascar in 1912, the Comoros became an overseas territory of France in 1947. In 1961 they were granted autonomy. In 1974 majorities on three of the islands voted for independence, which was granted in 1975. The following decade saw several coup attempts, which culminated in the assassination of the president in 1989. French intervention permitted multiparty elections in 1990, but the country remained in a state of chronic instability. Anjouan and Moheli seceded from the Comoros federation in 1997. The army took control of the government in 1999. A referendum at the end of 2001 renamed the country the Union of the Comoros and granted the three main islands partially autonomous status.
Recent Developments
Comoros endured serious political crisis in 2007. Although the three autonomous islands each chose local presidents every five years, Anjouan Pres. Col. Mohamed Bacar, elected to the office in 2002 after having seized power a year earlier in a coup, defied federal orders to step down in 2007. The government postponed the Anjouan elections, but Bacar claimed victory in elections that he staged. Comoran troops, backed by African Union forces, invaded Anjouan in March 2008, and Bacar was captured and transported to Reunion to face charges.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Official name: Republique Democratique du Congo (Democratic Republic of the Congo). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [108]; National Assembly [500]). Chief of state: President Joseph Kabila (from 2001). Head of government: Prime Minister Antoine Gizenga (from 2006). Capital: Kinshasa. Official languages: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: Congo franc (FC); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = FC 552.00.
Demography
Area: 905,355 sq mi, 2,344,858 sq km. Population (2007): 62,636,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 69.2, persons per sq km 26.7. Urban (2005): 32.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.48%; female 50.52%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 47.2%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44,14.2%; 45-59, 7.4%; 60-74, 3.4%; 75-84, 0.6%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (1983): Luba 18.0%; Kongo 16.1%; Mongo 13.5%; Rwanda 10.3%; Azande 6.1%; Bangi and Ngale 5.8%; Rundi 3.8%; Teke 2.7%; Boa 2.3%; Chokwe 1.8%; Lugbara 1.6%; Banda 1.4%; other 16.6%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 50%; Protestant 20%; Kimbanguist (indigenous Christian) 10%; Muslim 10%; traditional beliefs and syncretic sects 10%. Major urban areas (2004): Kinshasa 7,273,947; Lubumbashi 1,283,380; Mbuji-Mayi 1,213,726; Kananga 720,362; Kisangani 682,599. Location: central Africa, bordering the Central African Republic, The Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the South Atlantic Ocean, and the Republic of the Congo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 49.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 30.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 6.70. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 44.3 years; female 47.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: FC 564,900,000,000 (grants 31.1%; customs and excise taxes 25.7%; direct and indirect taxes 19.7%; petroleum royalties and taxes 17.4%). Expenditures: FC 655,500,000,000 (currentexpenditure 65.3%, of which intereston external debt 14.8%; capital expenditure 17.4%; expenditure on demobilization and reintegration 14.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$10,822,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2005): cassava 14,975,000, sugarcane 1,800,000, plantains 1,193,000; livestock (number of live animals) 4,022,000 goats, 959,000 pigs, game meat 88,735 metric tons; roundwood (2005) 74,719,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 95%; fisheries production 222,965 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2005): copper (metal content) 92,000; cobalt (metal content) 22,000; silver 53,553 kg. Manufacturing (2004): cement 402,500; flour 199,000; steel 130,000. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 6,852,000,000 (5,402,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 108,000 (153,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 10,000,000 (negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (376,000). Households. Expenditure (1995): food 61.4%, housing and energy 13.9%, clothing and footwear 4.8%, other 19.9%. Gross national income (2006): US$7,784,000,000 (US$128 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 21,718,000; activity rate 40.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 77.1%; female 41.1%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 343; official development assistance (2005) 1,828. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1997) 7.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporarycrops 3.0%, in permanent crops 0.5%, in pasture 6.6%; overall forest area (2005) 58.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$2,465,000,000 (aid-related imports 22.9%; other imports 77.1%). Major import sources (2004): South Africa 18.5%; Belgium 15.6%; France 10.9%; US 6.2%; Germany 5.9%. Exports (2005): US$2,042,000,000 (diamonds 48.4%; crude petroleum 20.0%; cobalt [2004] 15.0%; copper [2004] 3.3%). Major export destinations: Belgium 42.5%; Finland 17.8%; Zimbabwe 12.2%; US 9.2%; China 6.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length (2004) 5,138 km; passenger-km 152,930,000; metric ton-km cargo 506,010,000. Roads (2004): total length 153,497 km (paved 2%). Vehicles (1999): passenger cars 172,600; trucks and buses 34,600. Air transport (1999): pas-senger-km 263,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 39,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 146,000 (2.7); telephone landlines (2006): 9,700 (0.2); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,416,000 (74); total Internet users (2006): 180,000 (3); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,500 (0.03).
Education and health
Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 65.5%; males literate 76.2%; females literate 55.1%. Health: physicians (2004) 5,827 (1 per 9,585 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 116.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,398 (vegetable products 97%, animal products 3%); 76% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 64,800 (army 92.6%, air force 4.6%, navy 2.8%); UN peacekeepers (June 2007): 16,600 troops; 1,000 police. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.4%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Congo was known as Zaire, an attempt by then-ruler Mobutu Sese Seko to return to the source of the nation’s identity and authenticity. After Mobutu’s overthrow in 1997, however, the name of the country before 1971, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, was restored.
Background
Prior to European colonization, several native kingdoms had emerged in the Congo region, including the 16th-century Luba kingdom and the Kuba federation, which reached its peak in the 18th century. European development began late in the 19th century when King Leopold II of Belgium financed Henry Morton Stanley’s exploration of the Congo River. The 1884-85 Berlin West Africa Conference recognized the Congo Free State with Leopold as its sovereign. The growing demand for rubber helped finance the exploitation of the Congo, but abuses against native peoples outraged Western nations and forced Leopold to grant the Free State a colonial charter as the Belgian Congo (1908). Independence was granted in 1960, and the country’s name was changed to Zaire in 1971. The post-independence period was marked by unrest, culminating in a military coup that brought Gen. Mobutu Sese Seko to power in 1965. Mismanagement, corruption, and increasing violence devastated the infrastructure and economy. Mobutu was deposed in 1997 by Laurent Kabila, who restored the country’s name to Democratic Republic of the Congo. Regional instability and desire for Congo’s mineral wealth led to military involvement by numerous African countries. Kabila was assassinated in 2001 and succeeded by his son Joseph.
Recent Developments
Fighting broke out in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) in March 2007 between supporters of the the victorious Pres. Joseph Kabila and his opponent in the 2006 presidential election, Jean-Pierre Bemba. After several hundred people were killed, the violence was broughttoanend by the intervention ofthe peacekeeping UN Organization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the EU. Troubles in North Kivu province on the eastern frontier proved less easy to settle. Although government troops inflicted heavy casualties there on Rwandan rebel militia fighters, the rebels continued to harass the civilian population and forced some 650,000 people to flee their homes. Relations with Uganda were also strained. Uganda threatened in March to send troops to the DRC to deal with rebels, who, Kampala claimed, were threatening the southwestern border from the Ituri district, and expanded the threats in August, accusing the Congolese authorities of encroaching upon Uganda’s exploration for oil near Lake Albert.
Republic of the Congo
Official name: Republique du Congo (Republic of the Congo). Form of government: republic with two legislative houses (Senate [66]; National Assembly [137]). Chief of state: President Denis Sassou-Nguesso (from 1997). Head of government: Prime Minister Isidore Mvouba (from 2005). Capital: Brazzaville. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 132,047 sq mi, 342,000 sq km. Population (2007): 3,768,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 28.5, persons per sq km 11.0. Urban (2005): 53.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.68%; female 50.32%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 46.4%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44, 14.9%; 45-59, 7.3%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2000): Kongo 21.2%; Yombe 11.5%; Teke 10.7%; Kougni 8.0%; Mboshi 5.4%; Ngala 4.2%; Sundi 4.0%; other 35.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 49%; independent Christian 13%; Protestant 11%; Muslim 2%; other (mostly traditional beliefs and nonreligious) 25%. Major cities (2005): Brazzaville 1,174,005; Pointe-Noire 663,359; Dolisie 106,262; Nkayi 56,686; Ouesso 24,322. Location: west-central Africa, bordering Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the South Atlantic Ocean, and Gabon.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 42.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 29.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.07. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 51.7 years; female 54.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 1,300,100,000,000 (petroleum revenue 80.6%; nonpetroleum receipts 16.9%; grants 2.5%). Expenditures:CFAF 736,400,000,000 (current expenditure 77.0%, of which interest 20.4%, wages and salaries 17.7%; capital expenditure 23.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,161,000,000. Households. Average household size (2000) 5.9. Gross national income (2006): US$5,787,000,000 (US$1,569 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 900,000, sugarcane 460,000, oil palm fruit 90,000; livestock (number of live animals) 295,000 goats, 115,000 cattle, 99,000 sheep; roundwood 2,265,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 60%; fisheries production 58,448. Mining and quarrying (2005): gold 20 kg; diamonds 50,000 carats. Manufacturing (2000): residual fuel oil 206,000; refined sugar (2001) 71,814; distillate fuel oils 62,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 399,000,000 (802,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 82,900,000 ([2004] 5,944,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 535,000 (288,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 124,700,000 (124,700,000). Population economically active (2000): total 1,232,000; activity rate of total population 35.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 60.3%; female [1997] 43.4%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 34; remittances (2004) 1; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 321; official development assistance (2005) 1,557 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 103; remittances (2003) 24. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.4%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 29.3%; overall forestarea (2005) 65.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 746,400,000,000 (nonpetro-leum sector 85.9%; petroleum sector 14.1%). Major import sources (2002): France 26%; US 11%; Italy 8%; Lebanon 6%; The Netherlands 5%. Exports (2005): CFAF 2,484,300,000,000 (crude petroleum 92.5%; wood and wood products 4.6%; refined petroleum 1.2%). Major export destinations (2002): Taiwan 27%; North Korea 11%; US 10%;South Korea 7%; France 7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (1998): length 894 km; passen-ger-km 242,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 135,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 17,289 km (paved 5%). Vehicles (1997): passenger cars 37,240; trucks and buses 15,500. Air transport (2002): pas-senger-km 27,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2002): 40,000 (12); telephone landlines (2005): 16,000 (4); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 490,000 (136); personal computers (2005): 19,000 (4.8); total Internet users (2006): 70,000 (17).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1984). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 58.7%; primary education 21.4%; secondary education 16.9%; postsecondary 3.0%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 85.8%; males literate 91.2%; females literate 80.8%. Health: physicians (2000) 540 (1 per 5,745 persons); hospital beds (2001) 5,195 (1 per 623 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 85.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,026 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 111% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 10,000 (army 80.0%, navy 8.0%, air force 12.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$22.
Background
In precolonial days the Congo area was home to several thriving kingdoms, including the Kongo, which had its beginnings in the 1st millennium ad. The slave trade began in the 15th century with the arrival ofthe Portuguese; it supported the local kingdoms and dominated the area until its suppression in the 19th century. The French arrived in the mid-19th century and established treaties with two of the kingdoms, placing them under French protection prior to their becoming part of the colony of French Congo. In 1910 the French possessions were renamed French Equatorial Africa, and Congo became known as Middle (Moyen) Congo. In 1946 Middle Congo became a French overseas territory and in 1958 voted to become an autonomous republic within the French Community. Full independence came two years later. The area has suffered from political instability since independence. Congo’s first president was ousted in 1963. A Marxist party, the Congolese Labor Party, gained strength, and in 1968 another coup, led by Maj. Marien Ngouabi, created the People’s Republic of the Congo. Ngouabi was assassinated in 1977. A series of military rulers followed, at first militantly socialist but later oriented toward social democracy. Fighting between local militias that began in 1997 badly disrupted the economy.
Recent Developments
Congolese health authorities blamed poor hygiene for the severe cholera outbreak (about 6,500 cases were reported) in Pointe-Noire in January 2007; at least 62 people died. In July the Ministry of Health announced that 400,000 children under the age of five had been vaccinated against polio, despite a continuing shortage of trained medical staff. Sponsored by the government and UNICEF, a special train left Pointe-Noire in August, carrying 300,000 insecticide-treated anti-malaria mosquito nets for delivery to remote medical clinics along the southwestern coast.
Costa Rica
Official name: Republica de Costa Rica (Republic of Costa Rica). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Legislative Assembly [57]). Head of state and government: President Oscar Arias Sanchez (from 2006). Capital: San Jose. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 Costa Rican colon (0) = 100 centimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 0519.64.
Demography
Area: 19,730 sq mi, 51,100 sq km. Population (2007): 4,445,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 225.3, persons per sq km 87.0. Urban (2003): 60.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.76%; female 49.24%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 28.4%; 15-29, 28.1%; 30-44, 21.5%; 45-59, 13.7%; 60-74, 5.9%; 75-84, 1.8%; 85 and over, 0.6%. Ethnic composition (2000): white 77.0%; mestizo 17.0%; black/mulatto 3.0%; East Asian (mostly Chinese) 2.0%; Amerindian 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic (practicing) 47%; Roman Catholic (nonpracticing) 25%; Evangelical Protestant 13%; nonreligious 10%; other 5%. Major cities (district population; 2006): San Jose (urban agglomeration; 2003) 1,085,000; Limon 68,215; Alajuela 49,376; San Isidro de El General 46,490; San Francisco 45,972. Location: Central America, bordering Nicaragua, the Caribbean Sea, Panama, and the North Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 38.4%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.97. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 77.0 years; female 81.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:01,860,988,000,000 (taxes on goods and services 38.5%; social security contributions 27.2%; income tax 14.4%; importduties 5.0%; grants 3.7%). Expenditures: 01,951,392,-000,000(currentexpenditures92.9%,ofwhichwages 37.7%, transfers 25.8%, interest on debt 17.2%; development expenditures 7.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; February 2006): US$3,893,400,000. Gross national income (2006): US$21,367,000,000 (US$4,857 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 3,615,582, bananas 2,220,000, pineapples 1,605,237; livestock (number of live animals) 1,000,000 cattle, 550,000 pigs, 19,500,000 chickens; roundwood 4,636,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 74%; fisheries production 46,378 (from aquaculture 52%). Mining and quarrying (2004): limestone 920,000; gold 500 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): food products 734; beverages 188; paints, soaps, and pharmaceuticals 169. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 8,210,000,000 (7,972,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004)none(3,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 288,000 (1,541,000). Population economically active (2005): total 1,903,068; activity rate of total population 44.6% (participation rates: ages 12-59, 60.8%; female 36.2%; unemployed 6.6%). Households (2004-05). Average household size 3.7; average annual household income 04,225,680 (US$9,214); sources of income: wages and salaries 67.9%, rent 11.0%, transfers 10.9%, self-employment 8.1%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 21.9%, housing and energy 19.3%, transportation 14.8%, recreation and culture 7.9%, wearing apparel 6.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,666; remittances (2006) 520; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 593. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 470; remittances (2006) 246. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.4%, in permanent crops 5.9%, in pasture 45.8%; overall forestarea (2005) 46.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$9,640,100,000 (machinery and apparatus 34.2%; chemicals and chemical products 11.0%; mineral fuels 10.5%; plastics 7.0%; fabricated metal products 6.8%). Major import sources:US 40.1%; Japan 5.8%; Mexico 5.0%; Venezuela 4.9%; Ireland 4.5%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$7,150,690,000 (machinery and apparatus 29.8%; food products 24.8%, of which bananas 6.8%, pineapples 4.6%, coffee 3.7%; professional and scientific equipment 8.1%; textiles 7.5%; chemicals and chemical products 6.0%). Major export destinations: US 40.2%; Hong Kong 6.8%; The Netherlands 6.3%; Guatemala 4.0%; Nicaragua 3.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): 278 km. Roads (2004): total length 35,330 km (paved 24%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 620,992; trucks and buses 220,456. Airtransport(2005; Lacsa [Costa Rican Airlines] only): passenger-km 2,284,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 10,351,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 477,000 (115); televisions (2004): 1,068,000 (257); telephone landlines (2006): 1,351,000 (307); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,444,000 (328); personal computers (2005): 1,000,000 (233); total Internet users (2006): 1,214,000 (276); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 59,000 (14).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 5 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 12.8%; incomplete primary education 23.3%; complete primary 24.5%; incomplete secondary 18.2%; complete secondary 8.5%; higher 12.7%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 96.0%; males literate 95.9%; females literate 96.1%. Health (2004): physicians 6,600 (1 per 644 persons); hospital beds (2003) 5,908 (1 per 714 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 9.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,618 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 136% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Paramilitary expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.4%; per capita expenditure US$24. The army was officially abolished in 1948. Paramilitary (police) forces had 8,400 members in 2006.
Background
Christopher Columbus landed in Costa Rica in 1502 in an area inhabited by a number of small, independent Indian tribes. These peoples were not easily dominated, and it took almost 60 years for the Spanish to establish a permanent settlement. Ignored by the Spanish crown because of its lack of mineral wealth, the colony grewslowly. Coffee exports and the construction of a rail line improved its economy in the 19th century. It joined the short-lived Mexican Empire in 1821, was a member of the United Provinces of Central America, 1823-38, and adopted a constitution in 1871. In 1890 Costa Ricans held what is considered to be the first free and honest election in Central America, beginning a tradition of democracy for which Costa Rica is renowned. In 1987 then president Oscar Arias Sanchez was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. During the 1990s Costa Rica struggled with its economic policies. It suffered severe damage from a hurricane in 1996.
Recent Developments
In Costa Rica’s first-ever national referendum, held on 7 October 2007, citizens voted in favor of the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) with the United States. Pres. Oscar Arias Sanchez, who spent much of his term trying to secure passage ofthe agreement, said that the treaty would bring long-term economic growth. In June Costa Rica established diplomatic relations with China in an effort to promote trade and economic cooperation, meanwhile breaking off 60 years of formal ties with Taiwan. Economic growth remained strong, hovering near 7%. In October, Costa Rica was elected to serve as a member of the UN Security Council in 2008-09.
Cote d’Ivoire
Official name: Republique de Cote d’Ivoire (Republic of Cote d’Ivoire). Form of government: transitional regime with one legislative house (National Assembly [223]). Chief of state and government: President Laurent Gbagbo (from 2000), assisted by Prime Minister Guillaume Soro (from 2007). Capital: Abidjan. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged to the euro [€] at the rate of €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 123,863 sq mi, 320,803 sq km. Population (2007): 19,262,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 155.5, persons per sq km 60.0. Urban (2005): 45.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.82%; female 49.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 41.7%; 15-29, 29.4%; 30-44, 14.7%; 45-59, 9.1%; 60-74, 4.3%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnolinguistic composition (1998): Akan 42.1%; Mande 26.5%; other 31.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): traditional beliefs 37%; Christian 32%, of which Roman Catholic 17%, Protestant 8%, independent Christian 7%; Muslim 28%; other 3%. Major cities (2005): Abidjan (agglomeration) 3,576,000; Bouake 573,700; Daloa 215,100; Yamoussoukro (2003) 185,600; Korhogo (2003) 115,000. Location: western Africa, bordering Mali, Burkina Faso, Ghana, the Atlantic Ocean, Liberia, and Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 36.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 16.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.76. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 46.7 years; female 48.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 1,566,000,000,000 (tax revenue 79.9%; nontax revenue 14.1%; grants 6.0%). Expenditures:CFAF 1,536,600,000,000 (current expenditure 78.4%; interest on public debt 11.5%; remainder 10.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$9,007,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): yams 3,000,000, oil palm fruit 1,882,000, cassava 1,500,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,523,000 sheep, 1,500,000 cattle; roundwood 10,047,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 87%; fisheries production 55,866 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gold 1,638 kg; diamonds 300,000 carats (A UN embargo on rough diamond exports was rescinded in November 2007). Manufacturing (value added in CFAF ’000,000,000; 1997): food 156.6, of which cocoa and chocolate 72.4, vegetable oils 62.7; chemicals 60.2. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 5,370,000,000 (2,973,800,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 9,485,000 (26,400,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 3,248,000 (906,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 2,200,000,000 ([2004] 1,000,000,000). Population economically active (2003): total 6,544,000; activity rate of total population 37.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 65.5%; female 28.9%). Households. Average household size (2004) 8.0; expenditure (1996): food 32.2%, housing and energy 13.9%, hotels and restaurants 12.3%, transportation 9.6%, clothing 7.4%, household equipment 5.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2003) 50; remittances (2005) 160; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 225; official development assistance (2005) 236 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2001) 192; remittances (2005) 592. Gross national income (2006): US$17,052,000,000 (US$902 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.4%, in permanent crops 11.3%, in pasture 40.9%; overall forest area (2005) 32.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 2,687,000,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 40.1%; crude and refined petroleum 32.3%; food products 17.0%). Major import sources (2004): France 24.3%; Nigeria 19.2%; UK 4.0%; China 4.0%; Italy 3.8%. Exports (2005): CFAF 3,950,000,000,000 (cocoa beans and products 27.5%; crude petroleum and petroleum products 26.9%; wood and wood products 3.8%; coffee 2.1%). Major export destinations (2004): US 11.6%; The Netherlands 10.3%; France 9.5%; Italy 5.5%; Belgium 4.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (1999): route length (2004) 660 km; passenger-km 93,100,000; metric ton-km cargo 537,600,000. Roads (2004): total length 80,000 km (paved 8%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 113,900; trucks and buses 54,900. Air transport (2002; Abidjan airport only): passenger arrivals and departures 821,400; cargo unloaded and loaded 16,699 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 83,000 (4.7); televisions (2004): 880,000 (52); telephone landlines (2006): 261,000 (14); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,065,000 (220); personal computers (2004): 262,000 (16); total Internet users (2006): 300,000 (16); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 1,200 (0.07).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1998-99). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 63.0%; primary education 19.4%; secondary 14.3%; higher 3.3%. Literacy (2003): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 50.9%; males literate 57.9%; females literate 43.6%. Health: physicians (2004) 2,081 (1 per 8,143 persons); hospital beds (2001) 5,981 (1 per 2,660 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 119.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,268 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 123% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 17,050 (army 38.1%, navy 5.3%, air force 4.1%, presidential guard 7.9%, gendarmerie 44.6%); Peacekeeping troops (June 2007): UN 7,900, French 3,500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$11.
Background
Europeans came to the area to trade in ivory and slaves beginning in the 15th century, and local kingdoms gave way to French influence in the 19th century. The French colony of Cote d’Ivoire was founded in 1893, and full occupation took place during 1908-18. In 1946 it became a territory in the French Union. Cote d’Ivoire achieved independence in 1960, when Felix Houphouet-Boigny was elected president. The country’s first multiparty presidential elections were held in 1990. In 2002 the country began to fracture politically into north and south, and civil war ensued.
Recent Developments
Promising steps were taken in 2007 toward unifying Cote d’Ivoire, which had been divided by nearly five years of civil war. On 4 March at a meeting in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, Ivoirian Pres. Laurent Gbagbo and New Forces leader Guillaume Soro signed a peace agreement calling for a new transitional government. Weeks later the president also created a new military command to be composed equally of government and rebel soldiers, with the objective to disarm all militias. Soro took office as prime minister in April. A general amnesty was declared in April for all crimes committed during the civil war. The government announced plans to issue new identity papers for millions of undocumented Ivoirians.
Croatia
Official name: Republika Hrvatska (Republic of Croatia). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (House of Representatives [153]). Head of state: President Stipe Mesic (from 2000). Head of government: Prime Minister Ivo Sanader (from 2003). Capital: Zagreb. Official language: Croatian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 kuna (kn; plural kune) = 100 lipa; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = kn 4.58.
Demography
Area: 21,851 sq mi, 56,594 sq km. Population (2007): 4,440,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 203.2, persons per sq km 78.5. Urban (2005): 56.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.17%; female 51.83%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 16.1%; 15-29, 20.2%; 30-44, 20.9%; 45-59, 20.7%; 60-74, 15.9%; 75-84, 5.3%; 85 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2001): Croat 89.6%; Serb 4.5%; Bosniac 0.5%; Italian 0.4%; Hungarian 0.4%; other 4.6%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 92.6%, of which Roman Catholic 87.8%, Eastern Orthodox 4.4%; Muslim 1.3%; nonreligious/athe-ist 5.2%; other 0.9%. Major cities (2001): Zagreb 691,724; Split 175,140; Rijeka 143,800; Osijek 90,411; Zadar 69,556. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Slovenia, Hungary, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the Adriatic Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.5 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 89.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -2.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.42. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.8 years; female 78.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: kn 95,236,000,000 (tax revenue 61.4%, of which VAT 36.7%, excise taxes 12.1%; social security contributions 35.6%; nontax revenue 2.8%; grants 0.2%). Expenditures: kn 95,948,000,000 (social security and welfare 43.5%; compensation of employees 25.3%; interest payments 4.9%). Population economically active (2005): total 1,802,000; activity rate 40.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 58.3%; female 45.5%; unemployed [July 2005-June 2006] 12.7%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): corn (maize) 2,100,000, sugar beets 1,000,000, wheat 850,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,205,000 pigs, 796,000 sheep, 471,000 cattle; roundwood 4,018,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 23%; fisheries production 48,465 (from aqua-culture 28%). Mining and quarrying (2004): ceramic clay 637,000; ornamental stone 1,000,000 sq m. Manufacturing (value added in kn ’000,000; 2004): food products and beverages 7,112; refined petroleum 4,005; chemicals and chemical products 2,774. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 12,722,000,000 ([2004] 14,163,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) negligible (1,106,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 7,740,000 ([2004] 37,200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 4,824,000 (4,218,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 2,198,000,000 (2,934,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$40,251,000,000 (US$8,835 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; December 2006): US$8,350,000,000. Households (2005). Average household size (2001) 3.0; average annual income per household kn 69,180 (US$11,629); sources: wages 51.0%, pensions 17.9%, self-employment 16.5%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 33.2%, housing and energy 13.6%, transportation 10.9%, clothing and footwear 7.7%, recreation and culture 6.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,460; remittances (2006) 1,234; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 1,528. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 751; remittances (2006) 274; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 267. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 26.1%, in permanent crops 2.2%, in pasture 27.8%; overall forest area (2005) 38.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$16,589,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 21.4%; chemicals and chemical products 11.2%; road vehicles 10.0%; crude and refined petroleum 8.9%; food and live animals 7.2%). Major import sources: Italy 17.0%; Germany 15.5%; Russia 7.3%; Slovenia 7.1%; Austria 6.8%. Exports (2002): US$4,899,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 17.0%; ships and tankers 13.5%; clothing 7.9%; petroleum products 7.9%; food products 6.3%; pharmaceuticals 3.1%). Major export destinations: Italy 22.9%; Bosnia and Herzegovina 14.4%; Germany 11.2%; Austria 9.4%; Slovenia 7.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length (2004) 2,726 km; passenger-km 1,339,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,183,000,000. Roads:total length (2004) 28,472 km (paved [2003] 85%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 1,435,781; trucks and buses 174,612. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 1,857,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 382,000 (85); televisions (2003): 1,401,000 (315); telephone landlines (2006): 1,832,000 (402); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 3,650,000 (821); personal computers (2004): 842,000 (191); total Internet users (2006): 1,576,000 (346); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 252,000 (57).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no schooling/unknown 3.5%; incomplete primary education 15.8%; primary 21.7%; secondary 47.1%; postsecondary and higher 11.9%. Literacy (2003): population ages 15 and over literate 98.5%; males literate 99.4%; females literate 97.8%. Health (2005): physicians 8,216 (1 per 541 persons); hospital beds 24,000 (1 per 185 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 5.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,811 (vegetable products 78%, animal products 22%); 140% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 20,800 (army 67.5%, navy 12.0%, air force and air defense 11.1%, headquarters staff 9.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$138.
Background
The Croats, a southern Slavic people, arrived in the area in the 7th century ad and in the 8th century came under Charlemagne’s rule. They converted to Christianity soon afterward and formed a kingdom in the 10th century. Most of Croatia was taken by the Turks in 1526; the rest voted to accept Austrian rule. In 1867 it became part of Austria-Hungary, with Dalma-tia and Istria ruled by Vienna and Croatia-Slavonia a Hungarian crown land. In 1918, after the defeat of Austria-Hungary in World War I, it joined other south Slavic territories to form the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, renamed Yugoslavia in 1929. During World War II an independent state of Croatia was established by Germany and Italy, embracing Croatia-Slavonia, part of Dalmatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina; after the war Croatia was rejoined to Yugoslavia as a people’s republic. It declared its independence in 1991, sparking insurrections by Croatian Serbs, who carved out autonomous regions with Serbian-led Yugoslav army help; Croatia had taken back most of these regions by 1995. With some stability returning, Croatia’s economy began to revive in the late 1990s.
Recent Developments
Croatia continued in 2007 to redress problems stemming from its war of national liberation during the 1990s, bringing to trial several suspected war criminals. In June retired generals Mirko Norac and Rahim Ademi were charged with the unlawful killing in 1993 of at least 29 Serbian civilians. In October, Branimir Glavas faced trial for having tortured and murdered Serb civilians in 1991 as war commander in the besieged city of Osijek. Croatian GDP growth for 2007 was an estimated 9.8%; inflation held steady at 2.9%; unemployment dropped to 9.5%; and the budget deficit was trimmed to 3.0% of GDP. Tourism, meanwhile, grew an estimated 8.0% year-on-year and generated more than US$10.5 billion in revenue, a record. In April 2008 Croatia was invited to begin negotiations for eventual membership in NATO.