The information about the countries of the world that follows has been assembled and analyzed by Encyclopedia Britannica editors from hundreds of private, national, and international sources. Included are all the sovereign states of the world as well as the major dependent, or nonsovereign, areas. The historical background sketches have been adapted, augmented, and updated from Britannica Concise Encyclopedia and the statistical sections from Britannica World Data, which is published annually in conjunction with Britannica Book of the Year. The section called Recent Developments also has been adapted from material appearing in recent issues of the yearbook, as well as from other sources inside and outside Britannica. The locator maps have been prepared by Bri-tannica’s Cartography Department. Several countries, including those with the largest economies, are given expanded coverage in this section.
All information is the latest available to Britannica. It must be understood that in many cases it takes several years for the various countries or agencies to gather and process statistics—the most current data available will normally be dated several years earlier.
A few definitions of terms used in the articles may be useful. Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of goods and services produced in a country during a given accounting period, usually a year. Unless otherwise noted, the value is given in current prices of the year indicated. Gross national income (GNI) is essentially GDP plus income from foreign transactions minus payments made outside the country. Imports are material goods legally entering a country (or customs area) and subject to customs regulations and exclude financial movements. The value of goods imported is given free on board (f.o.b.) unless otherwise specified; the value of goods exported and imported f.o.b. is calculated from the cost of production and excludes the cost of transport. The principal alternate basis for valuation of goods in international trade is that of cost, insurance, and freight (c.i.f.); its use is restricted to imports, as it comprises the principal charges needed to bringthe goods to the customs house in the country of destination. Exports are material goods legally leaving a country and subject to customs regulations. Valuation of goods exported is also f.o.b. unless otherwise specified. The fAo recommended minimum daily per capita caloric intake varies by region and is calculated from age and sex distributions, average body weights, and environmental temperatures.
The symbol $ is always given with its country identifier (“US,” “A,” etc.) to avoid confusion. “CfA franc” stands for Communaute Financiere Africaine franc. A few helpful conversions for the statistical section are given at the foot of the left-hand pages.
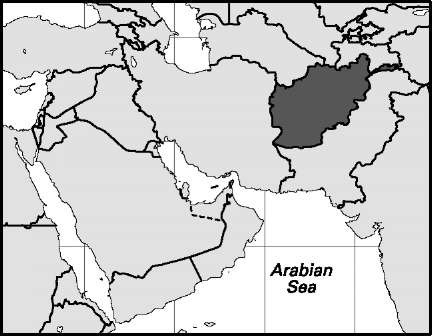
Afghanistan
Official name: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Afghanestan [Dari (Persian)] Da Afghanestan Eslami Jamhuriyat [Pashto]). Form of government: Islamic republic with two legislative bodies (House of Elders [102]; House of the People [249]). Chief of state and head of government: President Hamid Karzai (from 2002). Capital: Kabul. Official languages: Dari (Persian); Pashto; six additional local languages have official status per the 2004 constitution. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 (new) afghani (Af) = 100 puls (puli); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Af 49.98.
Demography
Area: 249,347 sq mi, 645,807 sq km. Population (2007): 27,145,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 108.9, persons per sq km 42.0. Urban (2006): 21.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.14%; female 48.86%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 44.6%; 15-29, 26.7%; 30-44, 16.0%; 45-59, 8.6%; 60-74, 3.5%; 75 and over 0.6%. Ethnolinguistic composition (2004): Pashtun 42%; Tajik 27%; Haz-ara 9%; Uzbek 9%; Chahar Aimak 4%; Turkmen 3%; other 6%. Religious affiliation (2004): Sunni Muslim 82%; Shi’i Muslim 17%; other 1%. Major cities (2006): Kabul 2,536,300; Herat 349,000; Kandahar (Qandahar) 324,800; Mazar-e Sharif 300,600; Jalalabad 168,600. Location: southern Asia, bordering Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, China, Pakistan, Iran, and Turkmenistan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 46.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.69. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 43.2 years; female 43.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:Af 67,531,000,000 (grants for development revenue 51.3%; grants for current revenue 24.8%; domestic revenue 23.9%, of which taxes 18.2%). Expenditures: Af 91,417,000,000 (development expenditure 64.0%; current expenditure 36.0%). Gross national income (2006): US$8,309,000,000 (US$319 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$8,000,-000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 4,265,000, rice 470,000, grapes 350,000, opium poppy 4,100 (represents 87% of world production); livestock (number of live animals) 8,800,000 sheep, 7,300,000 goats, 180,000 camels; roundwood 3,226,629 cu m, of which fuelwood 45%; fisheries production (2004) 1,000. Mining and quarrying (2004): salt 38,000; gemstones (particularly lapis lazuli) n.a. Manufacturing (value added in Af ’000,000; 2005-06): food 48,575; chemicals 1,206; cement, bricks, and ceramics 809. Energy production (consumption). electricity (kW-hr; 2004-05) 783,000,000 (623,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 34,000 (34,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (183,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 3,050,000 (3,050,000). Households (2003). Average household size 8.0; sources of income: wages and salaries 49%, self-employment 47%; expenditure (2004): food 60.6%, housing and energy 16.5%, clothing 9.1%. Population economically active (1994): total 5,557,000; activity rate of total population 29.4% (participation rates: female 9.0%; unemployed [2005] 8.5%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.1%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 46.0%; overall forest area (2005) 1.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 1.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 20; official development assistance (2005) 2,775. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1997) 1.0.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; c.i.f.): US$2,471,000,000 (machinery and equipment 12.2%; base and fabricated metals 10.6%; fabrics, clothing, and footwear 10.3%; mineral fuels 10.0%; flour 5.1%). Major import sources. Japan 16.8%; Pakistan 15.9%; China 12.8%; Russia 9.2%; Uzbekistan 8.3%. Exports (2005-06; f.o.b.): US$384,000,000 (carpets and handicrafts 39.6%; dried fruits 33.4%; skins 8.4%; fresh fruits 8.4%). Major export destinations. Pakistan 77.6%; India 6.0%; Russia 3.4%; UAE 2.9%; Germany 1.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): none. Roads (2005): total length 34,782 km (paved 7%). Vehicles (2004-05): passenger cars 197,449; trucks and buses 123,964. Airtransport (2004-05): passenger-km 681,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 20,624,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 312,000 (14); telephone landlines (2005): 100,000 (4); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 1,200,000 (48); total Internet users (2005): 30,000 (1.3); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 220 (0.01).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): total population age 15 and over literate 28.1%; males 43.1%; females 12.6%. Health: physicians (2005) 4,747 (1 per 5,000 persons); hospital beds (2004; public hospitals only) 9,667 (1 per 2,381 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 160.2.
Military
Forces 35,000 (including 12,000 US troops); other US 14,000. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 9.9%; per capita expenditure US$31.
The Karakoram Range is a great mountain system extending some 300 miles (500 km) from the easternmost extension of Afghanistan in a southeasterly direction along the watershed between Central and
South Asia. Found there are the greatest concentration of high mountains in the world and the longest glaciers outside the high latitudes.
Background
The area was part of the Persian empire in the 6th century bc and was conquered by Alexander the Great in the 4th century bc. Hindu influence entered with the Hephthalites and Sasanians; Islam became entrenched during the rule of the Saf-farids, c. AD 870. Afghanistan was divided between the Mughal empire of India and the Safavid empire of Persia until the 18th century, when other Persians under Nadir Shah took control. Great Britain and Russia fought several wars in the area in the 19th century. From the 1930s Afghanistan had a stable monarchy; it was overthrown in the 1970s. The rebels’ intention was to institute Marxist reforms, but the reforms sparked rebellion, and troops from the USSR invaded to establish order. Afghan guerrillas prevailed, and the Soviet Union withdrew in 1988-89. In 1992 rebel factions overthrew the government and established an Islamic republic, but fighting among factions continued. In 1996 the government was taken over by the Taliban faction. A US-led coalition invaded Afghanistan and overthrew the Taliban government in late 2001.
Recent Developments
With only a small national army of its own in 2007, Afghanistan, supported by almost 50,000 NATO and US soldiers, faced a Taliban resistance that had refocused its tactics. There was an upsurge in suicide bombing, kidnapping, and other tactics similar to those used by insurgents in Iraq. As well, though Taliban leaders had disapproved of and greatly reduced opium cultivation while in power, in 2007 poppy growing provided significant monetary support for their cause and contributed almost one-third of Afghanistan’s overall GDP; it was estimated that as much as 93% of the world’s opium came from Afghanistan. Afghanistan’s relations with the US, though extremely close, were complicated when it came to Pakistan and Iran. Pres. Hamid Karzai blamed Pakistan for not doing enough to cut off aid and shelter to the Taliban in Pakistan, and he saw the US as reluctant to push Pakistan on this point. US officials, for their part, repeatedly blamed Iran for supplying weapons to the Taliban, but several times during the year Karzai spoke of his country’s close relations with Iran.
Albania
Official name: Republika e Shqiperise (Republic of Albania). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Assembly [140]). Chief of state: President Bamir Topi (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Sali Berisha (from 2005). Capital: Tirana (Tirane). Official language: Albanian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 lek = 100 qindars; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 77.27 leks.
Demography
Area: 11,082 sq mi, 28,703 sq km. Population (2007): 3,176,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 286.6, persons per sq km 110.7. Urban (2005): 44.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.82%; female 50.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 26.9%; 15-29, 25.3%; 30-44, 19.8%; 45-59, 16.0%; 60-74, 9.3%; 75-84, 2.4%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Albanian 91.7%; Vlach (Aromanian) 3.6%; Greek 2.3%; other 2.4%. Traditional religious groups (2005): Muslim 68%, of which Sunni 51%, Bektashi 17%; Orthodox 22%; Roman Catholic 10%. Major cities (2001): Tirana (Tirane) 343,078; Durres 99,546; Elbasan 87,797; Shkoder 82,455; Vlore 77,691. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Montenegro, Kosovo, Macedonia, Greece, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2004): 13.8 (world avg. 21.1). Death rate per 1,000 population (2004): 5.7 (world avg. 8.8). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.03. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 74.8 years; female 80.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:199,600,000,000 leks (tax revenue 91.3%, of which turnover tax/VAT 31.7%, social security contributions 18.4%, customs duties and excise taxes 17.0%, taxes on income and profits 11.8%; other revenue 8.7%). Expenditures: 245,100,000,000 leks (current expenditure 79.4%, of which social security and welfare 22.5%, wages and salaries 22.5%, debt service 12.2%; development expenditure 20.6%). Gross national income (2006): US$9,542,000,000 (US$3,008 per capita).
Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US $1,375,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): alfalfa for forage and silage 1,800,000, wheat 260,000, corn (maize) 219,900; livestock (number of live animals) 1,760,000 sheep, 941,000 goats, 655,000 cattle; roundwood 296,200 cu m, of which fuelwood 75%; fisheries production (2004) 5,132 (from aqua-culture 31%). Mining and quarrying (2004): chromium ore 148,392. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): base metals 31; textiles 29; leather (all forms) 29. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 5,559,000,000 (5,762,000,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 109,000 (118,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 2,769,000 (2,769,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 270,000 (1,183,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 16,299,000 (16,299,000). Population economically active (2005): total 1,085,000; activity rate of total population 34.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 57.8%; female 39.6%; unemployed [October 2005-September 2006] 14.0%). Households (2002). Average household size 4.3; average annual income per household: 401,928 leks (US$2,868); sources of income (2000; urban areas only): wages and salaries/self-employment 64.2%, transfers/pensions 14.8%, other 21.0%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 68.2%, energy 9.2%, transportation and communications 6.6%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 854; remittances (2006) 1,359; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 222; official development assistance (2005) 301 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 786; remittances (2006) 27. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 21.1%, in permanent crops 4.4%, in pasture 15.4%; overall forest area (2005) 29.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): 299,134,000,000 leks (nonelectrical and electrical machinery 20.2%; food, beverages, and tobacco 17.9%; construction materials and base and fabricated metals 16.0%; mineral products 13.9%; textiles and footwear 11.7%). Major import sources:Italy 28.1%; Greece 15.7%; Turkey 7.6%; China 6.0%; Germany 5.7%. Exports (2006): 77,633,000,000 leks (textiles and footwear 54.7%; construction materials and base and fabricated metals 16.8%; food, beverages, and tobacco 7.9%). Major export destinations: Italy 72.6%; Greece 9.6%; Germany 3.2%; Macedonia 1.6%; Turkey 1.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length (2005) 447 km; passenger-km 89,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 32,000,000. Roads (2002): total length 18,000 km (paved 39%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 190,004; trucks and buses 71,875. Air transport (2005; Albanian Air only): passenger-km 152,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 76,000 (25); televisions (2003): 989,000 (318); telephone landlines (2004): 275,000 (88); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 1,260,000 (403); personal computers (2002): 36,000 (12); total Internet users (2005): 188,000 (60).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Population ages 20 and over having: no formal schooling/incomplete primary education 7.8%; primary 55.6%; lower secondary 2.7%; upper secondary 17.9%; vocational 8.8%; university 7.2%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.7%; males 99.2%; females 98.3%. Health: physicians (2004) 3,699 (1 per 845 persons); hospital beds (2005) 9,284 (1 per 339 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 20.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,918 (vegetable products 70%, animal products 30%); 147% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (March 2006): 21,500 (army 74.4%, navy 9.3%, air force 16.3%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$37.
Background
The Albanians are descended from the Illyrians, an ancient Indo-European people who lived in central Europe and migrated south by the beginning of the Iron Age. Of the two major Illyrian migrating groups, the Ghegs settled in the north and the Tosks in the south, along with Greek colonizers. The area was under Roman rule by the 1st century bc; after ad 395 it was connected administratively to Constantinople. Turkish invasion began in the 14th century and continued into the 15th century; though the national hero, Skan-derbeg, was able to resist them for a time, after his death (1468) the Turks consolidated their rule. The country achieved independence in 1912 and was admitted into the League of Nations in 1920. It was briefly a republic in 1925-28, then became a monarchy under Zog I, whose initial alliance with Benito Mussolini led to Italy’s invasion of Albania in 1939. After the war a socialist government under Enver Hoxha was installed. Gradually Albania cut itself off from the nonsocialist international community and eventually from all nations, including China, its last political ally. By 1990 economic hardship had produced antigovernment demonstrations, and in 1992 a noncommunist government was elected and Albania’s international isolation ended. In 1997 it plunged into chaos, brought on by the collapse of pyramid investment schemes. In 1999 it was overwhelmed by ethnic Albanians seeking refuge from Yugoslavia.
Recent Developments
Albania was affected by two major international events in 2008. Neighboring Kosovo, which as a UN-administered province of Serbia was more than 90% ethnic Albanian, declared its independence on 17 February. At the NATO summit in April in Bucharest, Romania, Albania was invited to begin the application
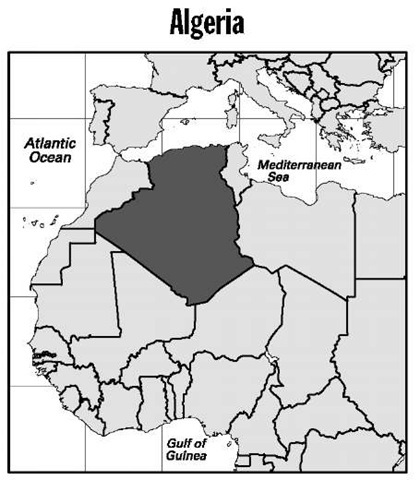
Algeria
Official name: Al-Jumhuriyah al-Jazairiyah al-Dimuqratiyah al-Sha’biyah (Arabic) (People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative bodies (Council of the Nation [144; includes 48 nonelected seats appointed by the president]; National People’s Assembly [389]). Chief of state: President Abdelaziz Boute-flika (from 1999). Head of government: Prime Minister Abdelaziz Belkhadem (from 2006). Capital: Algiers. Official languages: Arabic; Tamazight is designated as a national language. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Algerian dinar (DA) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = DA 62.72.
Demography
Area: 919,595 sq mi, 2,381,741 sq km. Population (2007): 33,858,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 36.8, persons per sq km 14.2. Urban (2005): 60.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.46%; female 49.54%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 29.7%; 15-29, 32.1%; 30-44, 21.0%; 45-59, 10.8%; 60-74,5.0%; 75-84,1.2%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Algerian Arab 59.1%; Berber 26.2%, of which Arabized Berber 3.0%; Bedouin Arab 14.5%; other 0.2%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 99.7%, of which Sunni 99.1%, Ibadiyah 0.6%; Christian 0.3%. Major cities (1998): Algiers 1,519,570; Oran 692,516; Constantine 462,187; Annaba 348,554; Batna 242,514. Location: northern Africa, borderingthe MediterraneanSea,Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara, and Morocco.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.89. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 71.7 years; female 74.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:DA 3,081,700,000,000 (hydrocarbon revenue 76.3%; nonhydrocarbon revenue 23.7%). Expenditures:DA 1,985,900,000,000 (current expenditure 65.1%; capital expenditure 34.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$15,476,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 2,415,000, potatoes 2,156,000, barley 1,033,000; livestock (number of live animals) 18,909,100 sheep, 3,590,000 goats; roundwood 7,742,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 99%; fisheries production (2004) 140,588. Mining and quarrying (2004): iron ore I,414,000; phosphate rock 784,000; zinc (metal content; 2003) 5,201. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1997): food products 463; cement, bricks, and tiles 393; iron and steel 118. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 31,250,000,000 (31,264,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004)none (615,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 471,000,000 (146,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 39,061,000 (11,209,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 81,291,000,000 (21,173,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3.2%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 13.3%; overall forestarea (2005) 1.0%. Households. Average household size (2004) 6.2; disposable income per household (2002) US$5,700;sources of income (2004): self-employment 39.9%, wages and salaries 36.9%, transfers 23.2%. Gross national income (2006): US$111,547,000,000 (US$3,345 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 10,109,600; activity rate of population 30% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [1998] 52.6%; female 16.9%; unemployed 12.3%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 184; remittances (2005) 1,950; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 955; official development assistance (2005) 511 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 370.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$17,954,000,000 (industrial equipment 37.2%; semifinished products 19.1%; food 18.9%; consumer goods 14.5%). Major import sources: France 22.6%; Italy 8.5%; Germany 6.5%; US 6.0%; China 5.0%. Exports (2004): US$32,220,000,000 (crude petroleum 39.0%; natural and manufactured gas 34.4%; condensate 15.1%; refined petroleum 9.4%). Major export destinations: US 23.6%; Italy 16.1%; France 11.4%; Spain II.2%; The Netherlands 7.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 3,973 km; (2000) passenger-km 1,142,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,029,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 108,302 km (paved 70%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 1,692,148; trucks and buses 948,553. Air transport (2005; Air Algerie only): passenger-km 3,101,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 36,177,000.
Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 873,000 (27); televisions (2003): 3,633,000 (114); telephone landlines (2005): 3,200,000 (97); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 13,661,000 (416); personal computers (2005): 1,920,000 (58); total Internet users (2005): 1,920,000 (58); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 195,000 (5.9).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1998). Percentage of economically active population age 6 and over having: no formal schooling 30.1%; primary education 29.9%; lower secondary 20.7%; upper secondary 13.4%; higher 4.3%; other 1.6%. Literacy (2005): total population age 15 and over literate 72.1%; males literate 80.6%; females literate 63.4%. Health: physicians (2003) 36,347 (1 per 877 persons); hospital beds (1999) 57,796 (1 per 520 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 29.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,510 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 188% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 137,500 (army 87.3%, navy 5.4%, air force 7.3%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.9%; per capita expenditure US$89.
Background
Phoenician traders settled the area early in the 1st millennium bc; several centuries later the Romans invaded, and by ad 40 they had control of the Mediterranean coast. The fall of Rome in the 5th century led to invasion by the Vandals and later by Byzantium. The Islamic invasion began in the 7th century; by 711 all of northern Africa was under the control of the Umayyad caliphate. Several Islamic Berber empires followed, most prominently the Almoravid (c. 1054-1130), which extended its domain to Spain, and the Almohad (c. 1130-1269). The Barbary Coast pirates, operating in the area, had menaced Mediterranean trade for centuries, and France seized this pretext to enter Algeria in 1830. By 1847 France had established control in the region, and by the late 19th century it had instituted civil rule. Popular movements resulted in the bloody Algerian War (1954-62); independence was achieved following a referendum in 1962. In the 1990s Islamic fundamentalists opposing the military brought Algeria to a state of civil war.
Recent Developments
Attacks by the Salafist Group for Preaching and Combat, which claimed to have joined al-Qaeda in September 2006, increased in 2007. In April coordinated suicide bombings, the first in Algeria in many years, wrecked the offices of the prime minister and left 33 persons dead, while a suicide bomber killed 22 persons on 6 September. Two days later a naval barracks in Dellys was attacked by a car bomb, killing 34. In December two car bombs in Algiers, one at a UN compound, killed 37 people.
American Samoa
Official name: American Samoa (English); Amerika Samoa (Samoan). Political status: unincorporated and unorganized territory of the US with two legislative houses (Senate [18]; House of Representatives [20]). Chief of state: US President George W. Bush (from 2001). Head of government: Governor Togiola Tulafono (from 2003). Capital: Fagatogo (legislative and judicial) and Utulei (executive). Official languages: English; Samoan. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar ($) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 77 sq mi, 200 sq km. Population (2007): 64,400. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 833.1, persons per sq km 321.7. Urban (2003): 54.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.42%; female 48.58%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 34.7%; 15-29, 24.9%; 30-44, 22.4%; 45-59, 13.0%; 60-74, 4.1%; 75 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): Samoan 88.2%; Tongan 2.8%; Asian 2.8%; Caucasian 1.1%; other 5.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 38%, of which Congregational 21%; Mormon 19%; Roman Catholic 15%; other (including non-religious) 28%. Major villages (2000): Tafuna 8,406; Nu’uuli 5,154; Pago Pago 4,278 (urban agglomeration [2001] 15,000); Leone 3,568; Fagatogo 2,096. Location: group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 26.3 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 65.9%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.16. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 72.5 years; female 79.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:US$188,877,568 (US government grants 44.9%; taxes 29.0%; charges for services 4.1%; other 22.0%). Expenditures: US$192,421,535 (general government 32.1%; education and culture 27.9%; health and welfare 19.3%; public safety 6.7%). Gross domestic product (2002): US$559,000,000 (US$9,040 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 4,700, taros 1,500, bananas 750; livestock (number of live animals) 10,500 pigs, 38,000 chickens; fisheries production (2004) 4,043, of which tuna, bonitos, and billfish 4,025. Manufacturing (value of exports in US$; 2003): canned tuna 467,700,000; pet food 9,800,000; other manufactures include garments, handicrafts, soap, and alcoholic beverages. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 189,000,000 (167,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2002) none (93,000). Population economically active (2000): total 17,664; activity rate of total population 30.8% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 52.0%; female 41.5%; unemployed 5.1%). Households. Average household size (2005) 5.7; income per household (2000): US$24,000; expenditure (1995): food and beverages 30.9%, housing and furnishings 25.8%, church donations 20.7%, transportation and communications 9.4%, clothing 2.9%, other 10.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (1998) 10. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1996) 2.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10%, in permanent crops 15%; overall forest area (2005) 90%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$506,200,000 (fish for cannery 43.9%; consumer goods 18.0%; other food 17.0%; mineral fuels 8.8%). Major import sources (2000): US 56.7%; Australia 14.9%; New Zealand 11.1%; Fiji 5.7%; Samoa 3.1%. Exports (2005): US$373,-800,000 (canned tuna 94.1%; pet food 5.8%; fish meal 0.1%). Major export destination (2000): US 99.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1991): total length 350 km (paved 43%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 7,349; trucks and buses 657. Air transport (2005): passenger arrivals 64,211; passenger departures 64,908; incoming cargo 920 metric tons, outgoing cargo 379 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 6,300 (195); televisions (2000): 13,000 (211); telephone landlines (2005): 11,000 (163); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 8,100 (123).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling to some secondary education 31.2%; completed secondary 42.6%; some college 19.0%; bachelor’s degree 5.0%; graduate degree 2.2%. Literacy (2000): total population ages 10 and over literate, virtually 100%. Health (2003): physicians 49 (1 per 1,253 persons); hospital beds 128 (1 per 480 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 7.0.
Military
Military defense is the responsibility of the US.
Background
The Samoan islands were probably inhabited by Polynesians 2,500 years ago. Dutch explorers first arrived in 1722. A haven for runaway sailors and escaped convicts, the islands were ruled by native chiefs until c. 1860. The US gained the right to establish a naval station at Pago Pago in 1878, and the US, Britain, and Germany administered a tripartite protectorate in 1889-99. The eastern islands were ceded to the US in 1904, and Swains Island was added in 1925. The first constitution was approved in 1960, and in 1977 the territory’s first elected governor took office.
Recent Developments
American Samoa experienced labor shortages as US nationals returned to the US for job opportunities and local reservists departed for military service in 2007. Despite its population of 59,000, the territory had to look to independent Samoa for labor for its tuna-canning plants.
Andorra
Official name: Principat d’Andorra (Principality of Andorra). Form of government: parliamentary coprinci-pality with one legislative house (General Council [28]). Chiefs of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007); Bishop of Urgell, Spain, Joan Enric Vives Sicilia (from 2003). Head of government: Chief Executive Albert Pintat Santolaria (from 2005). Capital: Andorra la Vella. Official language: Catalan. Official religion: none (Roman Catholicism enjoys special recognition in accordance with Andorran tradition). Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 179 sq mi, 464 sq km. Population (2007): 82,600. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 461.5, persons per sq km 178.0. Urban (2003): 93%. Sex distribution (2005): male 52.16%; female 47.84%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 14.8%; 15-29, 19.4%; 30-44, 29.3%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74, 10.3%; 75-84, 4.2%; 85 and over, 1.8%. Ethnic composition (by nationality; 2005): Spanish 37.4%; An-dorran 35.7%; Portuguese 13.0%; French 6.6%; British 1.3%; Moroccan 0.7%; Argentine 0.5%; other 4.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 89.1%; other Christian 4.3%; Muslim 0.6%; Hindu 0.5%; nonreligious 5.0%; other 0.5%. Major urban areas (2006): Andorra la Vella 24,211; Escaldes-En-gordany 16,391; Encamp 13,685. Location: southwestern Europe, between France and Spain.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 3.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.30. Marriage rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.9. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 80.6 years; female 86.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue. €308,500,000 (indirect taxes 70.9%; investment income 7.1%; taxes and other income 22.0%). Expenditures: €308,500,000 (current expenditures 52.6%; development expenditures 47.2%; financial operations 0.2%). Public debt (2004): US$278,000,000. Production. Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): tobacco 335 metric tons; other traditional crops include hay, potatoes, and grapes; livestock (number of live animals; 2004-05) 3,214 sheep, 1,572 cattle, 507 goats. Quarrying: small amounts of marble are quarried. Manufacturing (value of recorded exports in €’000; 2003): motor vehicles and parts 17,513; electrical machinery and apparatus 11,433; optical, photographic, and measuring apparatus 10,658. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 83,900,000 (568,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 1998) none (nearly 100,000). Households (2003). Average household size 2.8; expenditure per household €35,470 (US$40,034); expenditure: transportation 22.1%, food, beverages, and tobacco products 19.4%, housing and energy 16.1%, hotels and restaurants 7.8%, clothing and footwear 7.6%, recreation and culture 6.9%. Population economically active (2005): total 42,416; activity rate of total population 55% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2003] 75.1%; female 45.8%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$3,337,000,000 (US$44,962 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Disbursements for (US$’000,000; 2001-02): remittances 12. Land use as % of total land area (2000): in temporary and permanent crops 4%, in pasture 45%; overall forest area (2005) 36%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): €1,442,000,000 (food and beverages 16.6%; electrical machinery and apparatus 13.0%; motor vehicles 11.3%; clothing and knitwear 7.8%; perfumes, cosmetics, and soaps 7.4%; mineral fuels 4.6%). Major import sources (2005): Spain 53.2%; France 21.0%; Germany 5.6%; Japan 3.7%; Italy 3.2%. Exports (2005): €114,000,000 (food and beverages 28.7%; electrical machinery and apparatus 18.7%; motor vehicles 16.3%; optical equipment, photo equipment, and other professional goods 6.3%; perfumes, cosmetics, and soaps 3.0%). Major export destinations (2005): Spain 59.1%; France 17.0%; Germany 11.6%; UK 5.0%; Portugal 3.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): 269 km (paved 74%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 49,632; trucks and buses 4,621. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 17,000 (232); televisions (2000): 36,000 (461); telephone landlines (2005): 35,000 (459); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 65,000 (837); total Internet users (2005): 269,000 (284); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 10,300 (134).
Education and health
Literacy: resident population is virtually 100% literate. Health (2003): physicians 244 (1 per 296 persons); hospital beds 233 (1 per 310 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 4.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel: none. France and Spain are responsible for Andorra’s external security; the police force is assisted in alternate years by either French gendarmerie or Barcelona police. Andorra has no defense budget.
Background
Andorra’s independence is traditionally ascribed to Charlemagne, who recovered the region from the Muslims in 803. It was placed under the joint suzerainty of the French counts of Foix and the Spanish bishops of the See of Urgell in 1278, and it was subsequently governed jointly by the Spanish bishop of Urgell and the French head of state. This feudal system of government, the last in Europe, lasted until 1993, when a constitution was adopted that transferred most of the coprinces’ powers to the Andorran General Council, a body elected by universal suffrage. Andorra has long had a strong affinity with Catalonia; its institutions are based in Catalonian law, and it is part of the diocese of the See of Urgell (Spain). The traditional economy was based on sheep raising, but tourism has been very important since the 1950s.
Recent Developments
No snow fell in Andorra until the middle of March 2007, and the skiing season was crippled. This was a blow to the tourism industry—the country’s major source of revenue. It was feared that the number of visitors for 2007 would drop by at least 10%, but the actual number was about 2%.
Angola
Official name: Republica de Angola (Republic of Angola). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [220]). Head of state and government: President Jose Eduardo dos Santos (from 1979), assisted by Prime Minister Fernando da Piedade Dias dos Santos (from 2002). Capital: Luanda. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 kwanza (AOA) = 100 lwei; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = refloated kwanza 75.01.
Demography
Area: 481,354 sq mi, 1,246,700 sq km. Population (2007): 12,264,000. Density (2007): persons persq mi 25.5, persons per sq km 9.8. Urban (2005): 53.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.48%; female 49.52%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 43.8%; 15-29, 26.5%; 30-44,16.7%; 45-59, 8.5%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75 and over, 0.6%. Ethnic composition (2000): Ovimbundu 25.2%; Kimbundu 23.1%; Kongo 12.6%; Lwena (Luvale) 8.2%; Chokwe 5.0%; Kwanyama 4.1%; Nyaneka 3.9%; Luchazi 2.3%; Ambo (Ovambo) 2.0%; Mbwela 1.7%; Nyemba 1.7%; mixed race (Eur-african) 1.0%; white 0.9%; other 8.3%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 94.1%, of which Roman Catholic 62.1%, Protestant 15.0%; traditional beliefs 5.0%; other 0.9%. Major cities (2004): Luanda (urban agglomeration; 2005)2,766,000; Huambo 173,600; Lobito 137,400; Benguela 134,500; Namibe 132,900. Location: southern Africa, bordering the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Zambia, Namibia, and the Atlantic Ocean; the exclave of Cabinda on the Atlantic Ocean borders the Republic of the Congo and the DRC.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 45.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 25.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 19.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 6.35. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 36.5 years; female 38.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:AOA 602,187,000,000 (tax revenue 99.1%, of which taxes on petroleum 77.9%; nontax revenue 0.9%). Expenditures: AOA 591,955,000,000 (current expenditure 87.6%; development expenditure 12.4%). Households (2002). Average household size 5.0; expenditure (Luanda only): food and nonalcoholic beverages 46.1%, housing and energy 12.3%, household furnishings 6.5%, transportation 6.5%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 8,606,210, corn (maize) 720,275, sweet potatoes 659,451; livestock (number of live animals) 4,150,000 cattle, 2,050,000 goats, 780,000 pigs; roundwood 4,670,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 77%; fisheries production (2004) 240,005. Mining and quarrying (2004): diamonds 6,631,000 carats (excludes illegal production estimated to be nearly half of the legal production in 2004). Manufacturing (2003): fuel oil 639,319; cement 500,620; diesel fuel 407,542. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,339,000,000 (2,339,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 453,300,000 (21,200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,784,000 (1,836,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 730,000,000 (730,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 88; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,750; official development assistance (2005) 442. Disbursements for (US$’000,000; 2005): tourism 74; remittances 215. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$43,088,000,000 (US$2,602 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$9,428,000,000. Population economically active (1999): total 5,729,000; activity rate of total population 57.7% (participation rates: overage 10 [1991] 60.1%; female 38.4%; unemployed [2002] 70%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.6%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 43.3%; overall forest area (2005)47.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$8,353,000,000 (consumer goods 61.1%; capital goods 28.6%; intermediate goods 10.3%). Major import sources: South Korea 20.5%; Portugal 13.4%; US 12.5%; South Africa 7.4%; Brazil 7.0%. Exports (2005): US$24,109,400,000 (crude petroleum 93.7%; diamonds 4.5%; refined petroleum 1.0%). Major export destinations: US 39.8%; China 29.6%; France 7.8%; Chile 5.4%; Taiwan 4.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length of lines in operation 850 km; (2001) passenger-km 3,722,300,000. Roads (2001): total length 51,429 km (paved 10%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 117,200; trucks and buses 118,300. Air transport: passenger-km (2001; TAAG airline only) 732,968,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 64,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 51,000 (4.3); televisions (2003): 582,000 (52); telephone landlines (2005): 94,000 (7.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 1,094,000 (92); personal computers (2004): 27,000 (2.3); total Internet users (2005): 176,000 (15).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 67.4%; males literate 82.9%; females literate 54.2%. Health: physicians (2004) 1,165 (1 per 9,890 persons); hospital beds (2001) 13,810 (1 per 769 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 186.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,518 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 140% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 108,400 (army 92.3%, navy 2.2%, air force 5.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 5.7%; per capita expenditure US$140.
Background
An influx of Bantu-speaking peoples in the 1st millennium AD led to their dominance in the area by c. 1500. The most important Bantu kingdom was the Kongo; south of the Kongo was the Ndongo kingdom of the Mbundu people. Portuguese explorers arrived in 1483 and over time gradually extended their rule. Angola’s frontiers were largely determined with other European nations in the 19th century, but not without severe resistance by the indigenous peoples. Its status as a Portuguese colony was changed to that of an overseas province in 1951. Resistance to colonial rule led to the outbreak of fighting in 1961, which led ultimately to independence in 1975. Rival factions continued fighting after independence; although a peace accord was reached in 1994, forces led by Jonas M. Savimbi continued to resist government control. The killing of Savimbi in February 2002 changed the political balance and led to the signing of a cease-fire agreement in Luanda in April that effectively ended the civil war.
Recent Developments
Angola made significant advances in 2007, significantly because of its status as the second largest producer of crude oil in Africa south of the Sahara. On 1 January the country became the 12th full member of OPEC, and Angola, already China’s largest supplier of crude oil, began negotiating deals with Russia. In May the country was elected as a member of the UN Human Rights Council, and in the summer agreements on improving military relations and trade with South Africa were signed.
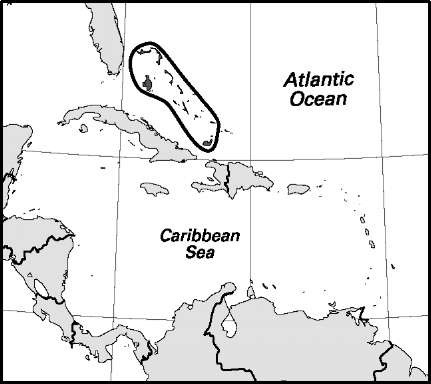
Antigua and Barbuda
Official name: Antigua and Barbuda. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [17]; House of Representatives [17]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Louise Lake-Tack (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Baldwin Spencer (from 2004). Capital: Saint John’s. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Eastern Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = EC$2.70.
Demography
Area: 171 sq mi, 442 sq km. Population (2007): 85,900. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 503.8, persons per sq km 194.5. Urban (2003): 37.7%. Sex distribution (2001): male 46.96%; female 53.04%. Age breakdown (2001): under 15, 28.3%; 15-29, 24.4%; 30-44, 25.0%; 45-59, 13.0%; 60-74, 6.2%; 75-84, 2.3%; 85 and over 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 82.4%; US white 12.0%; mulatto 3.5%; British 1.3%; other 0.8%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 74%, of which Anglican 23%, independent Christian 23%, other Protestant (including Methodist, Moravian, and Seventh-day Adventist) 28%; Rastafar-ian 2%; atheist/nonreligious 5%; other/unknown 19%. Major towns (2001): Saint John’s (2004) 23,600; All Saints 3,412; Liberta 2,239; Potters Village 2,067; Codrington 980. Location: eastern Caribbean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.9 (world avg. 20.3); (2001) within marriage 25.7%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.4 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.24. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.8 years; female 74.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: EC$1,080,000,000 (tax revenue 42.1%, of which taxes on international transactions 25.9%, income taxes 5.9%; current nontax revenue 3.6%; development revenue 1.7%; grants 52.6%). Expenditures: EC$657,500,000 (current expenditures 85.7%, of which interest payments 13.6%; development expenditures 14.3%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): tropical fruit (including papayas, guavas, soursops, and oranges) 7,900, mangoes 1,430, melons 840, “Antiguan Black” pineapples 210; livestock (number of live animals) 19,000 sheep, 14,300 cattle; fisheries production (2004) 2,527. Mining and quarrying:crushed stone for local use. Manufacturing: manufactures include cement, handicrafts, and furniture, as well as electronic components for export. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 109,000,000 (109,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (135,000). Population economically active (2001): total 39,564; activity rate of total population 51.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 77.0%; female 50.0%; unemployed 8.4%). Households (2001). Average household size 3.1; expenditure: housing 21.8%, food 21.4%, transportation and communications 15.4%, household furnishings 12.6%, clothing and footwear 11.1%.
Gross national income (2005): US$885,000,000 (US$10,920 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$519,900,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 18%, in permanent crops 5%, in pasture 9%; overall forest area (2005) 21%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 327; remittances (2005) 11; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 118. Disbursements for (US$’000,000; 2005): tourism 40.
Foreign trade
Imports (1999): US$356,000,000 (machinery and equipment 32.2%; agricultural products 24.7%; basic manufactures 15.4%; petroleum products 10.5%). Major import sources (2004): US 21.6%; Singapore 17.1%; China 9.7%; Trinidad and Tobago 6.0%; Poland 5.4%. Exports (1999): US$37,800,000 (reexports [significantly, petroleum products reexported to neighboring islands] 60.3%, domestic exports 39.7%). Major export destinations (2004): Germany 49.3%; UK 29.1%; France 3.4%; Bermuda 2.9%; US 2.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2002): total length 1,165 km (paved 33%). Vehicles: passenger cars (1998) 24,000; trucks and buses (1995) 1,342. Air transport (2001): passenger-km 304,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 200,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2001): 34,000 (449); telephone landlines (2004): 38,000 (494); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 54,000 (701); total Internet users (2005): 29,000 (373).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 0.6%; incomplete primary education 2.6%; complete primary 27.9%; secondary 43.6%; higher 25.3%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 85.8%. Health: physicians (1999) 76 (1 per 867 persons); hospital beds (1996) 255 (1 per 269 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 18.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,045 (vegetable products 67%, animal products 33%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): a 170-member defense force (army 73.5%, navy 26.5%) is part of the eastern Caribbean Regional Security System. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 0.6%; per capita expenditure US$57.
Background
Christopher Columbus visited Antigua in 1493 and named it after a church in Seville, Spain. It was colonized in 1632 by English settlers, who imported African slaves to grow tobacco and sugarcane. Barbuda was colonized by the English in 1678. In 1834 its slaves were emancipated. Antigua (with Barbuda) was part of the British colony of the Leeward Islands from 1871 until that colony was defederated in 1956. The islands achieved full independence in 1981.
Recent Developments
The World Trade Organization (WTO) ruled in favor of Antigua and Barbuda in March 2007 in its case against the US for not complying with the WTO’s 2005 ruling to cease blocking foreign Internet gambling operations from operating inside the US, and in May Antigua and Barbuda called on other WTO members to support its demand for compensation from the US. Meanwhile, Antigua and Barbuda continued to take steps to ensure that the country’s financial system was not used for money laundering.
Argentina
Official name: Republica Argentina (Argentine Republic). Form of government: federal republic with two legislative houses (Senate [72]; Chamber of Deputies [257]). Head of state and government: President Cristina Fernandez de Kirchner (from 2007), assisted by Cabinet Chief Alberto Fernandez (from 2003). Capital: Buenos Aires. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 peso (ARS) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = ARS 3.02.
Demography
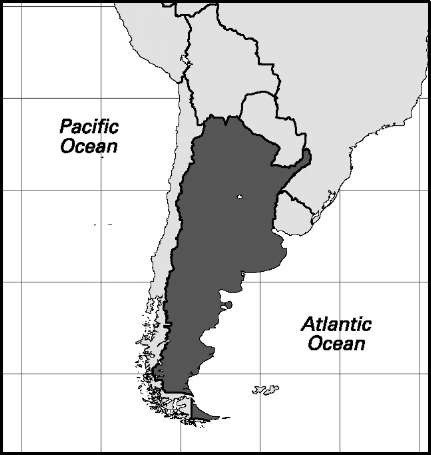
Area: 1,073,519 sq mi, 2,780,403 sq km. Population (2007): 39,531,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 36.8, persons per sq km 14.2. Urban (2003): 90.1%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.90%; female 51.10%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 26.4%; 15-29, 25.5%; 30-44, 19.1%; 45-59, 15.0%; 60-74, 9.6%; 75-84, 3.5%; 85 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): European extraction 86.4%; mestizo 6.5%; Amerindian 3.4%; Arab 3.3%; other 0.4%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 79.8%; Protestant 5.4%; Muslim 1.9%; Jewish 1.3%; other 11.6%. Major cities (2001): Buenos Aires 2,776,138 (metropolitan area 11,460,575); Cordoba 1,267,521; San Justo 1,253,921; Rosario 908,163; La Plata 563,943. Location: southern South America, bordering Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil, Uruguay, the South Atlantic Ocean, and Chile.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2004): 19.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2004): 7.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2004): 11.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.16. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 72.4 years; female 80.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: ARS 82,106,000,000 (tax revenue 77.4%; social security contributions 16.2%; nontax revenue 2.3%; other 4.1%). Expenditures: ARS 77,531,000,000 (current expenditure 88.2%, of which interest on debt 13.0%; capital expenditure 11.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$61,952,000,000. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$208,992,000,000 (US$5,340 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): alfalfa (2004) 38,783,000, soybeans 38,300,000, corn (maize) 19,500,000, sugarcane 19,300,000, wheat 16,000,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2004) 50,768,000 cattle, 12,450,000 sheep, 3,655,000 horses; roundwood 14,917,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 37%; fisheries production 933,902. Mining and quarrying(2005): copper (metal content) 187,317; silver 263,766 kg; gold 27,904 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): food products 10,152; base metals 4,031; industrial and agricultural chemicals 2,770; refined petroleum products 2,514. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 100,260,000,000 (103,729,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 51,000 (937,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 246,000,000 (161,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 25,224,000 (19,470,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 52,390,000,000 (43,459,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,753; remittances (2005) 413; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 2,981; official development assistance (2005) 115 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,817; remittances (2005) 279; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 381. Population economically active (2001): total 15,264,783; activity rate of total population 42.1% (participation rates: ages 14 and over 57.2%; female 40.9%; unemployed [October 2004-September 2005] 12.1%). Households. Average household size (2001) 3.6; average annual income per household (1996-97): ARS 12,972 (US$12,978); expenditure (1996-97): food products 26.8%, transportation and communications 15.0%, housing and energy 13.4%, health 10.2%. Land use as % of total land area (2000): in temporary crops 12.2%, in permanentcrops0.5%, in pasture 51.9%; overall for-estarea 12.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$28,689,-000,000 (electrical machinery and equipment 29.7%; transportation equipment 17.0%; chemicals 16.2%; plastic and rubber products 7.2%). Major import sources: Brazil 35.5%; US 14.1%; China 9.3%; Germany 4.5%; Mexico 2.8%. Exports (2005): US$40,106,000,000 (minerals 18.5%; vegetables 16.0%; food products 14.8%; fats and oils 8.2%; live animals 7.5%; transport equipment 7.4%; chemical products 6.1%). Major export destinations: Brazil 15.8%; US 11.4%; Chile 11.2%; China 9.1%; Spain 3.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads: route length (2003) 35,753 km; passenger-km (2004) 7,526,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 11,603,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 233,000 km (paved 31%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2000) 5,386,700; commercial vehicles and buses (1998) 1,496,567. Air transport (2003): pas-senger-km 12,485,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 113,400,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2000): 1,471,000 (40); televisions (2004): 12,500,000 (323); telephone landlines (2006): 9,460,000 (242); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 31,510,000 (805); personal computers (2005): 3,500,000 (90); total Internet users (2006): 8,184,000 (209); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,568,000 (40).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 3.7%; incomplete primary education 14.2%; complete primary 28.0%; secondary 37.1%; some higher 8.3%; complete higher 8.7%. Literacy (2001): percentage of total population ages 10 and over literate 97.4%; males literate 97.4%; females literate 97.4%. Health: physicians (2004) 122,706 (1 per 312 persons); hospital beds (2000) 150,813 (1 per 244 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 14.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,854 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%); 122% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 71,400 (army 58.0%, navy 24.5%, air force 17.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$50.
Background
Little is known of Argentina’s indigenous population before the Europeans’ arrival. The area was explored for Spain by Sebastian Cabot in 1526-30; by 1580, Asuncion, Santa Fe, and Buenos Aires had been settled. At first attached to the Viceroyalty of Peru (1620), it was later included with regions of modern Uruguay, Paraguay, and Bolivia in the Viceroyalty of the Rio de la Plata, or Buenos Aires (1776). With the establishment of the United Provinces of the Rfo de la Plata in 1816, Argentina achieved its independence from Spain, but its boundaries were not set until the early 20th century. In 1943 the government was overthrown by the military; Col. Juan Peron took control in 1946. He in turn was overthrown in 1955. He returned to power in 1973 after two decades ofturmoil.
His second wife, Isabel, became president on his death in 1974 but lost power after a military coup in 1976. The military government tried to take the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) in 1982 but was defeated by the British, with the result that the government returned to civilian rule in 1983. The government of Raul Alfonsfn worked to end the human rights abuses that characterized the former regimes. Hyperinflation led to public riots and Alfon-sfn’s electoral defeat in 1989; his Peronist successor, Carlos Menem, instituted laissez-faire economic policies. In 1999 Fernando de la Rua of the Alliance coalition was elected president, and his administration struggled with rising unemployment, foreign debt, and government corruption until the collapse of the government late in 2001.
Recent Developments
In October 2007 Cristina Fernandez de Kirchner (see Biographies) became the first woman in Argentina’s history to be directly elected president, following the decision by her husband, Nestor Kirchner, not to seek reelection. Elections to renew 130 of the 257 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 24 of the 72 seats in the Senate were held as well, and the Front for Victory and allied parties supporting the candidacy of Fernandez de Kirchner won 83 Chamber and 16 Senate seats, leading to coalition majorities in both. Fernandez de Kirchner thus was expected to have little difficulty in passing her initial legislative program. The economy experienced robust growth during the year, with GDP increasing by 8%. Optimism was tempered by an inflation rate estimated at approximately 20%.
Armenia
Official name: Hayastani Hanrapetut’yun (Republic of Armenia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (National Assembly [131]). Head of state: President Robert Kocharyan (from 1998). Head of government: Prime Minister Serzh Sarkisyan (from 2007). Capital: Yerevan. Official language: Armenian. Official religion: none, but the Armenian Apostolic Church (Armenian Orthodox Church) has special status per 1991 religious law. Monetary unit: 1 dram (AMD) = 100 lumas; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 303.00 drams.
Demography
Area: 11,484 sq mi, 29,743 sq km; in addition, about 16% of neighboring Azerbaijan (including the 1,700-sq mi [4,400-sq km] geographic region of Nagorno-Karabakh [Armenian: Artsakh]) has been occupied by Armenian forces since 1993. Population (2007): 3,002,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 261.4, persons per sq km 100.9. Urban (2006): 64.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.28%; female 51.72%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 20.9%; 15-29, 27.2%; 30-44, 19.5%; 45-59, 17.9%; 60-74, 10.2%; 75-84, 3.8%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2001): Armenian 97.9%; Kurdish 1.3%; Russian 0.5%; other 0.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Armenian Apostolic (Orthodox) 72.9%; Roman Catholic 4.0%; Sunni Muslim 2.4%; other Christian 1.3%; Yazidi 1.3%; other/nonreligious 18.1%. Major cities (2006): Yerevan 1,103,800; Gyumri 148,300; Vanadzor 105,500; Vagharshapat 56,700; Hrazdan 52,800. Location: southwestern Asia, bordering Georgia, Azerbaijan, Iran, and Turkey.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 11.7 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 88.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 8.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 3.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.33. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 70.3 years; female 76.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:AMD 374,746,900,000 (tax revenue 81.2%, of which VAT 39.2%, tax on profits 12.4%, excise tax 10.3%, income tax 7.1%; nontax revenue 18.8%). Expenditures: AMD 417,505,900,000 (defense 15.4%; education and science 14.6%; public administration 10.6%; social security 10.6%; police 8.4%; health 7.4%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$923,000,000. Households (2005). Average household size 3.8; money income per household AMD 1,720,195 (US$3,758); sources of money income: rent, self-employment, and remittances 38.9%, wages and salaries 34.5%, transfers 7.1%, other 19.5%; expenditure: food and beverages 56.6%, services 24.0%, nonfood goods 14.3%, tobacco5.1%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 17.6%, in permanent crops 2.1%, in pasture 29.6%; overall forest area (2005) 10.0%. Gross national income (2006): US$6,152,000,000 (US$2,040 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): potatoes 564,211, wheat 258,361, tomatoes 234,948; livestock (number of live animals) 573,260 cattle, 556,597 sheep, 4,590,000 chickens; roundwood 41,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 10%; fisheries production (2004) 1,031 (from aquaculture 79%). Mining and quarrying (2004): copper concentrate (metal content) 17,600; molybdenum (metal content) 3,000; gold (metal content) 2,100 kg. Manufacturing (value of production in AMD ’000,000; 2005): base and fabricated metals 259,305; food products and beverages 202,057; construction materials 23,648; 320,000 carats of cut diamonds were processed in 2004. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 5,941,000,000 ([2005] 5,503,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (300,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (1,300,000,000). Population economically active: total (2004) 1,196,500; activity rate of total population (2001) 49.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2001] 72.1%; female [2004] 48.2%; officially unemployed [2006] 7.4%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 141; remittances (2006) 1,175; foreign direct investment (2001-05) 165; official development assistance (2005) 312 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 117; remittances (2006) 148.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$1,801,735,900 (precious and semiprecious stones [mostly rough diamonds] 19.3%; food products 15.1%; mineral fuels 14.7%; machinery and apparatus 8.7%; motor vehicles 8.1%). Major import sources: Russia 13.5%; Belgium 8.0%; Germany 7.8%; Ukraine 7.0%; Turkmenistan 6.3%. Exports (2005): US$973,920,500 (base and fabricated metals 34.7%; precious and semiprecious stones [nearly all cut diamonds] 34.5%; beverages [nearly all wine and grape brandy] 8.7%; metal ores and scrap 5.3%). Major export destinations: Germany 15.6%; The Netherlands 13.7%; Belgium 12.8%; Russia 12.2%; Israel 11.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport (2005). Railroads:length 732 km; passen-ger-km 26,600,000; metric ton-km cargo 654,100,000. Roads: length 7,515 km (paved 69%). Air transport: passenger-km 959,500,000; metric ton-km cargo 10,700,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 27,000 (9); televisions (2003): 687,000 (229); telephone landlines (2005): 537,000 (180); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 320,000 (107); personal computers (2004): 200,000 (67); total Internet users (2005): 161,000 (54); broadband Internet subscribers (2004): 1,000 (0.3).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 0.7%; primary education 13.0%; completed secondary and some postsecondary 66.0%; higher 20.3%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate, virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 12,307 (1 per 242 persons); hospital beds 14,353 (1 per 208 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 12.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,379 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 120% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 48,160 (army 93.4%, air force 6.6%); Russian troops (2006) 3,500. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.7%; per capita expenditure US$46.
Background
Armenia is a successor state to a historical region in southwestern Asia. Historical Armenia’s boundaries have varied considerably, but the region extended over what is now northeastern Turkey and the Republic of Armenia. The area was later conquered by the Medes and the Macedonians and still later allied with the Roman Empire. Armenia adopted Christianity as its national religion in AD 303. It came under the rule of the Ottoman Turks in 1514. Over the next centuries, as parts were ceded to other rulers, nationalism arose among the scattered Armenians; by the late 19th century it was causing widespread disruption. Fighting between Turks and Russians escalated when part of Armenia was ceded to Russia in 1878, and it continued through World War I, leading to Armenian deaths on a genocidal scale. With the Turkish defeat, the Russian-controlled part of Armenia was set up as a Soviet republic in 1921. Armenia became a constituent republic of the USSR in 1936. With the latter’s dissolution in the late 1980s, Armenia declared its independence in 1990. It fought Azerbaijan for control over Nagorno-Karabakh until a cease-fire in 1994. About one-fifth of the population left the country beginning in 1993 because of an energy crisis. Political tension escalated, and in 1999 the prime minister and some legislators were killed in a terrorist attack on the legislature.
Recent Developments
The strong economic growth of recent years continued in Armenia as GDP increased by 13.8% in 2007. On 19 March Pres. Robert Kocharyan and Iranian Pres. Mahmoud Ahmadinejad inaugurated the first section of a pipeline that provided Armenia with Iranian natural gas. The 19 January murder in Istanbul of Armenian author Hrant Dink triggered widespread outrage in Armenia. Armenian officials nonetheless continued trying to persuade Turkey to open its border as a prelude to establishing diplomatic relations.
Aruba
Official name: Aruba. Political status: nonmetropolitan territory of The Netherlands with one legislative house (States of Aruba [21]).Chief of state: Dutch Queen Beatrix (from 1980), represented by Governor Fredis Refunjol (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Nelson O. Oduber (from 2001). Capital: Oranjestad. Official language: Dutch. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Aruban florin (Af.) = 100 cents; pegged to the US dollar at a fixed rate of Af. 1.79 = $1.
Demography
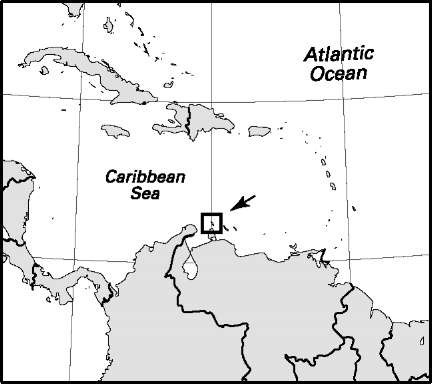
Area: 75 sq mi, 193 sq km. Population (2007): 105,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,400.0, persons per sq km 544.0. Urban (2003): 45.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 47.72%; female 52.28%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 21.2%; 15-29, 18.9%; 30-44, 26.1%; 45-59, 21.3%; 60-74, 9.6%; 75-84, 2.2%; 85 and over, 0.7%. Linguistic composition (2000): Papiamento 69.4%; Spanish 13.2%; English 8.1%; Dutch 6.1%; Portuguese 0.3%; other 2.0%; unknown 0.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 82.7%, Protestant 10.2%, other/nonreligious 7.1%. Major urban areas (2000): Oranjestad 26,355; San Nicolas 15,848. Location: southern Caribbean Sea, north of Venezuela.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 12.3 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 50.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.79. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 76.0 years; female 82.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Af. 907,300,000 (tax revenue 85.7%, of which taxes on income and profits 40.0%, sales tax 29.2%; nontax revenue 11.2%; grants 3.1%). Expenditures: Af. 1,032,200,000 (wages 29.5%; goods and services 14.8%; social securitycon-tributions 13.1%; interest 8.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing: aloes are cultivated for export; small amounts of tomatoes, beans, cucumbers, gherkins, watermelons, and lettuce are grown on hydroponic farms; divi-divi pods, sour orange fruit, sorghum, and peanuts (groundnuts) are nonhydroponic crops of limited value; fisheries production (2004) 162. Mining and quarrying: excavation of sand for local use. Manufacturing: refined petroleum, rum, cigarettes, aloe products, and soaps. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 816,000,000 (816,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 880,000 (3,335,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (247,000). Gross national income (2006): US$2,244,000,000 (US$21,625 per capita). Population economically active (2004): total 41,500; activity rate of total population 42.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2000] 70.9%; female [2000] 46.6%; unemployed [2005] 6.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$478,700,000. Households. Average household size (2000) 3.1; average annual income per household (1999) Af. 39,000 (US$21,800); expenditure (2000): housing 23.0%, transportation and communications 19.7%, food 14.7%, clothing and footwear 10.9%, household furnishings 10.0%, recreation and education 8.0%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 11%; overall forest area (2005) 2%.
Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,096; remittances (2006) 13; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 98. Disbursementsfor(US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 241; remittances (2006) 69.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): Af. 7,614,000,000 (crude petroleum 77.6%; electrical and nonelectrical machinery 4.1%; food products 2.3%). Major import sources (excluding petroleum): US 60.4%; The Netherlands 11.7%; Venezuela 2.8%; Netherlands Antilles 2.8%. Exports (2005): Af. 7,830,000,000 (refined petroleum 99.4%). Major export destinations (excluding petroleum): US 48.5%; Netherlands Antilles 21.3%; The Netherlands 15.4%; Venezuela 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1995): total length 800 km (paved 64%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 49,521; trucks and buses 1,207. Air transport (2001; Air Aruba only): passenger-km 800,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 33,900 (348); televisions (2001): 20,000 (218); telephone landlines (2002): 37,000 (397); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 98,000 (1,002); total Internet users (2002): 24,000 (257).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling or incomplete primary education 9.7%; primary education 33.9%; secondary/vocational 39.2%; advanced vocational/higher 16.2%. Literacy (2000): percentage of total population ages 13 and over literate 97.3%. Health (2005): physicians 144 (1 per 699 persons); hospital beds 310 (1 per 330 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2003-05) 6.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2005): more than 1,000 Dutch naval personnel (including 400 marines) are stationed in the Aruba/Netherlands Antilles vicinity.
Background
Aruba’s earliest inhabitants were Arawak Indians, whose cave drawings can still be seen. Though the Dutch took possession of Aruba in 1636, they did not begin to develop it aggressively until 1816. In 1986 Aruba seceded from the Federation of the Netherlands Antilles in an initial step toward independence.
Recent Developments
Aruba received high marks in September 2007 from American ratings agency Fitch, which commented favorably on the island’s market-friendly institutional environment, high per capita income, and political and social stability.
Australia
Official name: Commonwealth of Australia. Form of government: federal parliamentary state (formally a constitutional monarchy) with two legislative houses (Senate [76]; House of Representatives [150]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Michael Jeffery (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Kevin Rudd (from 2007). Capital: Canberra. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Australian dollar ($A) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = $A 1.05.
Demography
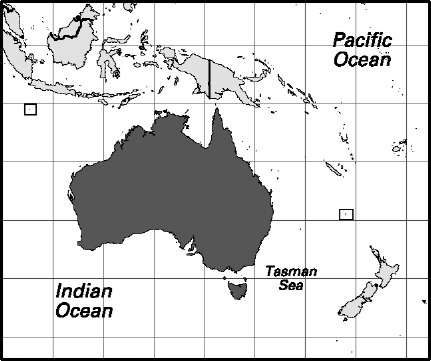
Area: 2,969,978 sq mi, 7,692,208 sq km. Population (2007): 20,857,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 7.0, persons per sq km 2.7. Urban (2005): 88.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.78%; female 50.22%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 19.8%; 15-29, 20.1%; 30-44, 21.9%; 45-59, 20.1%; 60-74, 11.7%; 75-84, 4.8%; 85 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic composition (2001): white 92%; Asian 6%; aboriginal 2%. Religious affiliation (2006): Christian 63.9%, of which Roman Catholic 25.6%, Anglican Church of Australia 18.7%, other Christian 19.6% (Uniting Church 5.7%, Presbyterian 2.9%, Orthodox 2.6%, Baptist 1.6%, Lutheran 1.3%); Buddhist 2.1%; Muslim 1.7%; Hindu 0.7%; Jewish 0.4%; no religion 18.7%; other 12.5%. Major urban centers/urban agglomerations (2001/2006): Sydney 3,502,301/ 4,293,105; Melbourne 3,160,171/3,684,461; Brisbane 1,508,161/1,820,375; Perth 1,176,542/1,507,949; Adelaide 1,002,127/138,833; Gold Coast 421,557/ (2005) 482,000; Canberra 339,727/328,441; Newcastle 279,975/512,131; Gosford (Central Coast) 255,429/n.a.; Wollongong 228,846/276,155. Place of birth (2006): 70.9% native-born; 29.1% foreign-born, of which Europe 10.5% (UK 5.2%, Italy 1.0%, Greece 0.6%, Germany 0.5%, The Netherlands 0.4%, Poland 0.3%), Asia and Middle East 7.3% (China [including Hong Kong] 1.4%, Vietnam 0.8%, India 0.7%), New Zealand 2.0%, Africa, the Americas, and other 9.3%. Location: Oceania, continent between the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean. Mobility (1999). Population ages 15 and over living in the same residence as in 1998: 84.4%; different residence between states, regions, and neighborhoods 15.6%. Households (2006). Total number of households 8,058,248. Average household size 2.6; 1 person (2003-04) 25.4%, 2 persons (2003-04) 33.9%, 3 or more persons (2003-04) 40.7%. Family households 5,665,000 (70.3%); nonfamily 2,393,000 (29.7%), of which 1-person 26.5%. Immigration (2004-05): permanent immigrants admitted 123,400, from UK 14.7%, New Zealand 14.0%, China 9.0%, India 7.6%, Sudan 4.6%, South Africa 3.7%, Philippines 3.4%, Malaysia 2.4%, Singapore 2.4%, Sri Lanka 1.9%, Vietnam 1.8%, Iraq 1.5%. Refugee arrivals 13,200. Emigration 59,200.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 67.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.81. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 78.5 years; female 83.3 years.
Social indicators
Quality of working life. Average workweek (2005) 34.7 hours. Working 50 hours a week or more (2003) 28.8%. Annual rate per 100,000 workers for: accidental injury and industrial disease (2004) 1,220; death (2004) 1.0. Proportion of employed persons insured for damages or income loss resulting from: injury 100%; permanent disability 100%; death 100%. Working days lost to industrial disputes per 1,000 employees (2006) 22. Means of transportation to work (2003): private automobile 74.5%; public transportation 12.0%; motorcycle, bicycle, and foot 5.7%. Discouraged job seekers (2006) 52,900 (0.5% of labor force). Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15-64 having: no formal schooling through incomplete secondary education 48.5%; complete secondary through postsecondary, technical, or other certificate/diploma 28.9%; bachelor’s degree 14.2%; incomplete graduate and graduate degree or diploma 5.4%; unknown 3.0%. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last national election (2007) 94%; voting is compulsory. Trade union membership in total workforce (2006) 20%. Social deviance (2005). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: murder 1.3; sexual assault (2003) 92; assault (2003) 798; auto theft 419; burglary and housebreaking (2004) 1,534; robbery 69. Incidence per 100,000 in general population of: prisoners 124; suicide 10.3. Material well-being (2005). Households possessing: automobile (1995) 85.0%; refrigerator 99.9%; washing machine 96.4%; dishwasher 41.5%.
National economy
Gross national income (2006): US$747,304,-000,000 (US$36,400 per capita). Budget (2005-06). Revenue:$A 225,513,000,000 (tax revenue 91.6%, of which individual 50.7%, corporate 21.7%, excise duties and sales tax 15.3%; nontax revenue 8.4%). Expenditures:$A 209,797,000,000 (social security and welfare 41.2%; health 17.9%; economic services 8.0%; public services 8.0%; education 7.9%; defense 7.5%; interest on public debt 2.6%; other 6.6%). Public debt (2002-03): $A 69,926,000,000. Production (gross value in $A ’000 except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2004-05): livestock (slaughtered value) 12,030,200 (cattle 7,828,800, sheep and lambs 1,949,000, poultry 1,303,700, pigs 906,000); wheat 4,316,500, wool 2,195,500, grapes 1,508,200, barley 1,233,300, sugarcane 979,500, seed cotton 945,100, apples 529,000, canola 503,000, potatoes 434,000, bananas 327,000, oranges 310,000, sorghum 270,000, oats 171,800, carrots 166,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2005) 101,125,000 sheep, 27,782,000 cattle, 2,538,000 pigs, 78,187,000 poultry; roundwood (2005) 30,529,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 10%; fisheries production (2005) 293,022 (from aquaculture 16%); aquatic plants production 14,167. Mining and quarrying (metric tons except as noted; 2005): iron ore (metal content) 280,000,000 (world rank: 3); bauxite 58,000,000 (world rank: 1); zinc (metal content) 1,400,000 (world rank: 2); ilmenite 1,140,000 (world rank: 1); copper (metal content) 930,000 (world rank: 5); lead (metal content) 760,000 (world rank: 2); nickel (metal content) 210,000 (world rank: 2); rutile 160,000 (world rank: 1); cobalt (metal content) 6,600 (world rank: 3); opal (value of production; 2003) $A 65,000,000 (world rank: 1); diamonds 22,700,000 carats (world rank by volume: 1); gold 254,000 kg (world rank: 2). Manufacturing (gross value added in $A ’000,000; 2004-05): food, beverages, and tobacco 19,076; machinery and apparatus 18,185; fabricated metal products 17,483; mineral fuels 12,817; printing and publishing 10,095; wood and paper products 6,924; cement, bricks, and ceramics 4,852; textiles and wearing apparel 2,621. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 228,918,000,000 ([2004] 230,497,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2006) 400,000,000 ([2004] 32,900,000); lignite (metric tons; 2005-06) 71,000,000 ([2004] 100,700,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 171,900,000 ([2005] 320,200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 33,302,000 (34,264,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 38,883,000,000 ([2004] 28,399,000,000). Population economically active (July 2007): total 10,952,000; activity rate of total population 52.5% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 65.0%; female [2006] 45.0%; unemployed 4.3%). Households (2003-04). Average household size (2006) 2.6; average annual disposable income per household $A 47,528 (US$33,745); sources of income: wages and salaries 57.5%, transfer payments 27.7%, self-employment 6.0%, other 8.8%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 17.1%, housing 16.1%, transportation and communications 15.6%, recreation 12.8%, household services and operation 6.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14,940; remittances (2006) 3,064; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 8,715. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11,282; remittances (2006) 2,681; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 2,536. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 6.1%, in permanent crops 0.04%, in pasture 51.0%; overall forest area (2005) 21.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; f.o.b.): $A 167,603,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 29.3%, of which telecommunications equipment 5.8%, office machines and automatic data-processing equipment 5.3%, electrical machinery 4.8%; transportation equipment 15.8%, of which motor vehicles 12.2%; crude and refined petroleum 12.7%; chemicals and related products 6.1%, of which medicines and pharmaceuticals 4.3%; textiles and wearing apparel 3.9%). Major import sources (2006-07): China 15.0%; US 13.8%; Malaysia 3.7%; Japan 9.6%; Singapore 5.6%; Germany 5.1%; UK 4.1%; Thailand 4.0%; South Korea 3.3%; New Zealand 3.1%. Exports (2005-06; f.o.b.): $A 151,792,000,000 (mineral fuels 24.9%, of which coal [all forms] 16.0%, petroleum products and natural gas 8.9%; food and beverages 12.0%, of which meat and meat preparations 4.4%, cereals and cereal preparations 3.2%; iron ore 8.2%; aluminum and aluminum ore 6.9%; gold 4.8%; machinery and apparatus 4.1%; transportation equipment 3.5%). Major export destinations (2006-07): Japan 19.4%; China 13.6%; South Korea 7.8%; US 5.8%; New Zealand 5.6%; UK 3.7%; Taiwan 3.7%; Singapore 2.7%; Indonesia 2.5%; Thailand 2.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 38,550 km; passenger-km (2004-05) 11,200,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004-05) 182,990,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 810,641 km (paved 42%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 11,189,000; trucks and buses 2,665,000. Airtransport (2006; domestic carriers only): passenger-km 88,173,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,633,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,934,000 (146); televisions (2003): 14,371,000 (722); telephone landlines (2006): 9,940,000 (483); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 19,760,000 (960); personal computers (2005): 14,007,000 (689); total Internet users (2006): 15,300,000 (743); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 3,900,000 (189).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): total population literate, virtually 100%. Health (2005-06): physicians 63,300 (1 per 322 persons); hospital beds (2005) 83,349 (1 per 244 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 5.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,101 (vegetable products 68%, animal products 32%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 51,610 (army 48.9%, navy 24.6%, air force 26.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$645.
Background
Australia has long been inhabited by Aborigines, who arrived on the continent 40,000-60,000 years ago. Estimates of the population at the time of European settlement in 1788 range from 300,000 to more than 1,000,000. Widespread European knowledge of Australia began with 17th-century explorations. The Dutch landed in 1616 and the British in 1688, but the first large-scale expedition was that of James Cook in 1770, which established Britain’s claim to Australia. The first English settlement, at Port Jackson (1788), consisted mainly of convicts and seamen; convicts were to make up a large proportion of the incoming settlers. By 1859 the colonial nuclei of all Australia’s states had been formed, but with devastating effects on the Aborigines, whose population declined sharply with the introduction of European diseases and weaponry. Britain granted its colonies limited self-government in the mid-19th century, and Australia achieved federation in 1901. Australia fought alongside the British in World War I, notably at Gallipoli, and again in World War II, preventing the occupation of Australia by the Japanese. It joined the US in the Korean and Vietnam wars. Since the 1960s the government has sought to deal more fairly with the Aborigines, and a loosening of immigration restrictions has led to a more heterogeneous population. Constitutional links allowing British interference in government were formally abolished in 1968, and Australia has assumed a leading role in Asian and Pacific affairs. During the 1990s it experienced several debates about giving up its British ties and becoming a republic.
Recent Developments
Australia’s Prime Minister John Howard was defeated in an election in November 2007, bringing an end to more than a decade of conservative government. Opposition leader Kevin Rudd of the Australian Labor Party won handily, and Howard lost not only the premiership but also his own seat in Parliament. Rudd announced major changes to Australian domestic and international policies. Immediately after taking his oath as prime minister, he fulfilled one of his campaign promises by ratifying the Kyoto Protocol, which Howard had vehemently opposed. Rudd also began the promised withdrawal of Australian combat troops from Iraq in June 2008. His new cabinet featured seven women, including Deputy Prime Minister Julia Gillard. Public opinion during the year was deeply affected by the plight of Aboriginal children in remote communities, and many people demanded that the government take measures to end domestic violence and sexual assaults. In August laws were passed allowing federal intervention in Aboriginal communities, and the government promised to spend more than $A 587 million (about US$470 million) in a wide-ranging reform program that involved banning alcohol and pornography and acquiring control of townships through five-year leases. The Australian economy remained strong. Strong company tax receipts and less expenditure on welfare provided a surplus of $A 17.3 billion (about US$14 billion) in 2007. GDP growth that year was 3.9%, and by midyear 2008 unemployment had fallen to 4.1%. The Howard government announced in 2007 that it intended to sell uranium to India for peaceful purposes. Howard also decided to canvass possible sales of uranium to Russia and signed a deal with Russian Pres. Vladimir Putin when Putin visited Australia during the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) meeting in September. The APEC summit, which was held in Sydney, was the largest gathering of international world leaders ever hosted by Australia. During the summit threats of demonstrations against US Pres. George W. Bush overshadowed more pressing concerns of global warming and climate change.
Austria
Official name: Republik Osterreich (Republic of Austria). Form of government: federal state with two legislative houses (Federal Council [64]; National Council [183]). Chief of state: President Heinz Fischer (from 2004). Head of government: Chancellor Alfred Gusenbauer (from 2007). Capital: Vienna. Official language: German. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 32,383 sq mi, 83,871 sq km. Population (2007): 8,319,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 256.9, persons per sq km 99.2. Urban (2003): 65.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.61%; female 51.39%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 16.0%; 15-29, 18.5%; 30-44, 24.1%; 45-59, 19.4%; 60-74, 14.3%; 75-84, 6.1%; 85 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic composition (2000): Austrian 86.5%; German Swiss 4.0%; German 3.5%; Bosniac 0.9%; Turkish 0.9%; Polish 0.5%; other 3.7%. Religious affiliation (2001): Christian 81.5%, of which Roman Catholic 73.7%, Protestant (mostly Lutheran) 4.7%, Orthodox 2.2%; Muslim 4.2%; nonreligious 12.0%; other 0.3%; unknown 2.0%. Major cities (2006): Vienna 1,651,437; Graz 244,604; Linz 188,362; Salzburg 148,473; Innsbruck 116,851. Location: central Europe, bordering the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and Germany.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.5 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 63.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 0.4 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.41. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 76.7 years; female 82.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €59,237,000,000 (tax revenue 97.3%, of which turnover tax 32.0%, individual income taxes 29.2%, corporate income tax 7.3%, other taxes 28.8%; nontax revenue 2.7%). Expenditures: €62,667,000,000 (social security, health, and welfare 34.4%; education 14.3%; interest 13.3%; transportation 9.6%; public safety 3.8%; defense 2.8%). Public debt (December 2006): US$194,118,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugar beets 3,084,000, corn (maize) 1,725,000, wheat 1,453,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,125,400 pigs, 2,051,000 cattle; roundwood (2004) 16,483,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 21%; fisheries production (2004) 2,667 (from aquacul-ture 85%). Mining and quarrying (2005): iron ore (metal content) 655,000; manganese (metal content) 16,000. Manufacturing (value added in €’000,000; 2004): nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 5,034; electrical machinery and electronics 4,060; fabricated metals 3,979. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 64,125,000,000 (67,207,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (4,252,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 235,000 (1,228,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 6,200,000 ([2004] 59,800,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 7,200,000 (12,029,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 2,142,000,000 (9,792,000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 4,032,200; activity rate of total population 49.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 72.4%; female 45.4%; unemployed 7.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$318,478,000,000 (US$38,244 per capita). Households. Average household size (2005) 2.3; average annual disposable income per household (2003) €28,709 (US$32,403); sources of income (1995): wages and salaries 54.8%, transfer payments 25.9%; expenditure (2004-05): housing and energy 22.3%, transportation 16.1%, recreation and culture 12.6%, food 11.7%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 16.8%, in permanent crops 0.9%, in pasture 23.3%; overall forest area (2005) 46.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 15,589; remittances (2006) 2,941; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 5,205. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 10,994; remittances (2006) 2,543; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 6,552.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): €96,499,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 36.8%, of which nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 11.5%, road vehicles 11.5%; mineral fuels 12.2%; chemicals and related products 10.9%; food products 5.2%). Major import sources: Germany 42.2%; Italy 6.6%; France 4.0%; Switzerland 3.3%; Czech Republic 3.3%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): €94,705,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 41.6%, of which nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 17.2%, road vehicles 11.8%, electrical machinery and apparatus 7.3%; chemicals and chemical products 9.8%; iron and steel 5.7%). Major export destinations: Germany 31.8%; Italy 8.6%; US 5.6%; Switzerland 4.5%; France 4.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004; federal railways only): route length 5,629 km; passenger-km (2003) 8,248,700,000; metric ton-km cargo 17,931,100,000. Roads (2003): total length 133,718 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 4,109,129; trucks and buses 342,384. Air transport (2005; Austrian Airlines Group only): pas-senger-km 22,894,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 561,882,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,570,000 (3159); televisions (2002): 2,570,000 (315); telephone landlines (2006): 3,564,000 (434); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 9,255,000 (1,128); personal computers (2005): 4,000,000 (489); total Internet users (2006): 4,200,000 (512); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,428,000 (172).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling through lower-secondary education 22%; upper secondary/higher vocational 63%; university 14%. Literacy: virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2006) 39,750 (1 per 208 persons); hospital beds (2005) 65,053 (1 per 133 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 4.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 4,023 (vegetable products 71%; animal products 29%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 39,900 (army 83.2%; air force 16.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.9%; per capita expenditure US$329.
Background
Settlement in Austria goes back some 3,000 years, when Illyrians were probably the main inhabitants. The Celts invaded c. 400 bc and established Noricum. The Romans arrived after 200 bc and established the provinces of Raetia, Noricum, and Pan-nonia; prosperity followed and the population became Romanized. With the fall of Rome in the 5th century AD, many tribes invaded, including the Slavs; they were eventually subdued by Charlemagne, and the area became ethnically Germanic. The distinct political entity that would become Austria emerged in 976 with Leopold I of Babenberg as margrave. In 1278 Rudolf I of the Holy Roman Empire (formerly Rudolf IV of Habsburg) conquered the area; Habsburg rule lasted until 1918. While in power the Habsburgs created a kingdom centered on Austria, Bohemia, and Hungary. The Napoleonic Wars brought about the creation of the Austrian Empire (1804) and the end of the Holy Roman Empire (1806). Countvon Metternich tried to assure Austrian supremacy among Germanic states, but war with Prussia led Austria to divide the empire into the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary. Nationalist sentiment plagued the kingdom, and the assassination of Francis Ferdinand by a Serbian nationalist in 1914 triggered World War I, which destroyed the Austrian empire. In the postwar carving up of Austria-Hungary, Austria became an independent republic. It was annexed by Nazi Germany in 1938 and joined the Axis powers in World War II. The republic was restored in 1955 after 10 years of Allied occupation. Austria became a member of the European Union in 1995.
Recent Developments
Despite political tensions in Austria in 2007, the governing coalition reached agreement on a number of important reforms, including the introduction of a national minimum monthly wage, increased investment in education and transport infrastructure, and the partial opening of the labor market to workers from the 10 EU member states that joined the EU in 2004. The economy grew at its fastest rate in eight years in 2007, driven by strong demand for Austrian exports (particularly from Germany) and robust business investment in the booming manufacturing and construction sectors. Household spending was relatively subdued. The country was rocked by scandal in April 2008 when it was discovered that a man had imprisoned his daughter for 24 years and fathered seven children by her.
Azerbaijan
Official name: Azerbaycan Respublikasi (Republic of Azerbaijan). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (National Assembly [124]). Head of state and government: President Ilham Aliyev (from 2003), assisted by Prime Minister Artur Rasizade (from 2003). Capital: Baku. Official language: Azerbaijani. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: The (new) manat was introduced on 1 Jan 2006, at a rate of 4,500 (old) manats (AZM) to 1 (new) manat (AZN). 1 new manat (AZN) = 100 gopik; valuation (1 Jul 2008) free rate, US$1 = AZN 0.81.
Demography
Area: 33,400 sq mi, 86,600 sq km. Population (2007): 8,120,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 242.9, persons per sq km 93.8. Urban (2006): 51.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.16%; female 50.84%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 26.3%; 15-29, 27.9%; 30-44, 22.7%; 45-59, 14.1%; 60-74, 6.7%; 75-84, 1.9%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (1999): Azerbaijani 90.6%; Lezgian (Dagestani) 2.2%; Russian 1.8%; Armenian 1.5%; other 3.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 87.0%, of which Shi’i 52.8%, Sunni 34.2%; non-religious/other 13.0%. Major cities (2006): Baku 1,132,800 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,856,000); Ganca 305,600; Sumqayit (Sumgait) 266,600; Min-gacevir (Mingechaur) 95,300. Location: eastern Transcaucasia, bordering Russia, the Caspian Sea, Iran, Turkey, Armenia, and Georgia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 81.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.33. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.6 years; female 75.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: AZN 2,055,200,000 (tax revenue 86.0%, of which VAT 29.2%, taxes on profits 17.3%, personal income tax 15.5%, taxes on international trade 10.0%; nontax revenue 14.0%). Expendi-tures:AZN 2,140,700,000 (national economy 21.6%; education 18.1%; social security/welfare 14.8%; defense/police 10.0%; health 5.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 1,527,000, vegetables 1,491,000, potatoes 1,083,100; livestock (number of live animals) 6,887,000 sheep, 2,007,000 cattle; round-wood 13,500 cu m, of which fuelwood 47%; fisheries production (2004) 9,296. Mining and quarrying (2004): limestone 800,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2005): food, beverages, and tobacco products 301; petroleum products 251; base metals, fabricated metals, and machinery 126. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 22,600,000,000 ([2004] 20,600,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 164,000,000 (55,200,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 5,875,000 (3,583,000); natural gas(cum; 2005)5,676,000,000 (9,449,000,000). Households (2003). Average household size 4.4; annual income per household AZM 2,254,450 (US$459); sources of income: wages and salaries 30.5%, self-employment 22.8%, agriculture 15.5%; expenditure: food 54.7%, household furnishings 7.1%, clothing 6.8%. Population economically active (2005): total 3,906,500; activity rate of total population 46.3% (participation rates: ages 15-61 [male], 15-56 [female] 71.8%; female 47.7%; officially unemployed 1.4%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$18,676,000,000 (US$2,222 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,344,000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 78; remittances (2006)813; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,028; official development assistance (2005) 396 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 164; remittances (2006) 301; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 739. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 22.2%, in permanent crops 2.7%, in pasture 32.5%; overall for-estarea (2005)11.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$4,211,000,000 (machinery and equipment 33.3%; mineral fuels 15.2%; base and fabricated metals 11.6%; food and agricultural products 10.6%). Major import sources: Russia 17.0%; UK 9.1%; Singapore 9.1%; Turkey 7.4%; Germany 6.1%. Exports (2005): US$4,347,000,000 (mineral fuels [mostly crude petroleum] 76.8%, of which diesel fuel 17.1%; transport equipment 6.3%; vegetables 4.5%; aluminum oxide 2.3%). Major export destinations: Italy 30.3%; France 9.4%; Russia 6.6%; Turkmenistan 6.3%; Turkey 6.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 2,122 km; pas-senger-km 881,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,524,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 59,141 km (paved 49%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 479,447; trucks and buses 117,587. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 1,587,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 313,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2001): 132,000 (16); televisions (2003): 2,750,000 (334); telephone landlines (2006): 1,189,000 (140); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 3,323,000 (392); personal computers (2005): 195,000 (23); total Internet users (2006): 829,000 (98); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,200 (0.3).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: primary education 4.1%; some secondary 9.3%; secondary 50.1%; vocational 4.2%; some higher 0.9%; higher 13.3%. Literacy (1999): 98.8%. Health (2006): physicians 30,300 (1 per 265 persons); hospital beds 68,800 (1 per 117 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 9.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,744 (vegetable products 85%, animal products 15%); 141% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 66,740 (army 85.2%, navy 3.0%, air force 11.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.5%; per capita expenditure US$37.
Background
Azerbaijan adjoins the Iranian region of the same name, and the origin of their respective inhabitants is the same. By the 9th century ad the area had come under Turkish influence, and in ensuing centuries it was fought over by Arabs, Mongols, Turks, and Iranians. Russia acquired the territory of what is now independent Azerbaijan in the early 19th century. After the Russian Revolution of 1917, Azerbaijan declared its independence; it was subdued by the Red Army in 1920 and became a Soviet Socialist Republic. It declared independence from the collapsingSovietUnion in 1991. Azerbaijan has two geographic peculiarities.
The exclave Nakhichevan is separated from the rest of Azerbaijan by Armenian territory. Nagorno-Karabakh, which lies within Azerbaijan and is administered by it, has a Christian Armenian majority. Azerbaijan and Armenia went to war over both territories in the 1990s, causing great economic disruption. Though a ceasefire was declared in 1994, the political situation remained unresolved.
Recent Developments
Economic growth continued in Azerbaijan in 2007, with an estimated 35% increase in GDP. Annual inflation reached 20%, however, and the consortium developing the huge Shah Deniz natural-gas field in the Caspian Sea warned of possible delays. In August a high-rise building under construction in Baku collapsed, killing 19 persons. During the recent building boom, many contractors had failed to secure official permits, and safety measures were being skirted. President Aliyev met in June in St. Petersburg with Armenian Pres. Robert Kocharyan to continue talks on how to resolve the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, though no marked progress was made.
The Bahamas
Official name: The Commonwealth of The Bahamas. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [16]; House of Assembly [41]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Arthur Dion Hanna (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Hubert Ingraham (from 2007). Capital: Nassau. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Bahamian dollar (B$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = B$1.00.
Demography
Area: 5,382 sq mi, 13,939 sq km. Population (2007): 331,000. Density (2006): persons per sq mi 85.1, persons per sq km 32.9. Urban (2003): 89.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.90%; female 51.10%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 27.6%; 15-29, 26.0%; 30-44, 22.2%; 45-59, 14.9%; 60-74, 7.1%; 75 and over, 2.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): local black 67.5%; mulatto 14.2%; British 12.0%; Haitian black 3.0%; US white 2.4%; other 0.9%. Religious affiliation (2000): Baptist 35.4%; Anglican 15.1%; Roman Catholic 13.5%; other Protestant/independent Christian 32.3%; other/nonreligious 3.7%. Major cities (2002): Nassau 179,300; Freeport 42,600; West End 7,800; Cooper’s Town 5,700; Marsh Harbour 3,600. Location: chain of islands in the Caribbean Sea, southeast of Florida.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.6 (world avg. 20.3); (2000) within marriage 43.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.18. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 62.2 years; female 69.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue:B$1,039,376,000 (tax revenue 89.0%, of which import taxes 39.7%, stamp taxes from imports 10.8%, departure taxes 6.7%, business and professional licenses 5.8%; nontax revenue 11.0%). Expenditures:B$1,143,469,000 (education 18.7%; health 16.9%; public order 12.3%; interest on public debt 10.3%; tourism 6.0%; defense 3.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$334,600,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 55,500, citrus fruits 21,700; livestock (number of live animals) 3,000,000 chickens; roundwood 17,000 cu m; fisheries production (2004) 11,357 (mainly lobsters, crayfish, and conch). Mining and quarrying (2004): salt 1,269,209; aragonite 19,918. Manufacturing (value of export production in B$’000; 2004): rum 31,344; chemical products (2001) 13,842. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,087,000,000 (2,087,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (652,000). Households. Average household size (2000) 3.5; income per household (2004) B$39,626 (US$39,626); expenditure (1995): housing 32.8%, transportation and communications 14.8%, food and beverages 13.8%, household furnishings 8.9%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.8%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 0.2%; overall forest area (2005) 51.5%. Gross national income (2006): US$6,077,000,000 (US$18,570 per capita). Population economically active (2004): total 176,330; activity rate of total population 55.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2000] 76.6%; female 48.8%; unemployed [2005] 10.2%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,072; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 216. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 344; remittances (2006) 144.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): B$2,567,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 22.1%; mineral fuels 19.8%; food products 13.2%; chemicals and chemical products 7.0%). Major import sources (2005): US 83.9%; Curagao 7.1%; Puerto Rico 1.9%; Japan 1.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): B$450,800,000 (domestic exports 60.1%, of which plastics 25.7%, fish, crustaceans, and mollusks [mainly crayfish] 17.2%, alcoholic beverages [mainly rum] 3.7%; reexports 39.9%, of which petroleum 9.0%, nonelectrical machinery 5.1%). Major export destinations (2005): US 68.9%; France 8.3%; Germany 7.0%; UK 4.6%; Canada 4.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads(2000): total length 2,693 km (paved 57%). Vehicles (2001): passengercars 80,000; trucks and buses 25,000. Air transport (2001; Bahamasair only): passenger-km 374,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,764,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 39,000 (122); televisions (2001): 77,000 (247); telephone landlines (2005): 133,000(412); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 228,000 (705); total Internetusers(2005): 103,000(319); broadband Internet subscribers (2004): 13,000 (40).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 1.5%; primary education 8.7%; incomplete secondary 19.9%; complete secondary 53.7%; incomplete higher 8.1%; complete higher 7.1%; not stated 1.0%. Literacy (2005): total percentage ages 15 and over literate 95.8%; males literate 95.0%; females literate 96.7%. Health (2001): physicians 458 (1 per 672 persons); hospital beds 1,540 (1 per 200 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 24.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,520 (vegetable products 68%, animal products 32%); 130% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 860 (paramilitary coast guard 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$121.
Background
The islands were inhabited by Lucayan Indians when Christopher Columbus sighted them on 12 Oct 1492. He is thought to have landed on San Salvador (Watling) Island. The Spaniards made no attempt to settle but carried out slave raids that depopulated the islands; when English settlers arrived in 1648 from Bermuda, the islands were uninhabited. They became a haunt of pirates, and few of the ensuing settlements prospered. The islands enjoyed some prosperity following the American Revolution, when Loyalists fled the US and established cotton plantations. The islands were a center for blockade runners during the American Civil War. Not until the development of tourism after World War II did permanent economic prosperity arrive. The Bahamas was granted internal self-government in 1964 and became independent in 1973.
Recent Developments
The Bahamas in May 2007 by a relatively comfortable margin, and in his first policy statement, Prime Minister Ingraham announced the privatization of Bahamasair, the money-losing government-owned airline.
Bahrain
Official name: Mamlakat al-Bahrayn (Kingdom of Bahrain). Form of government: constitutional monarchy (declared 14 Feb 2002) with two legislative houses (Council of Representatives [40] and Shura Council [40]). Chief of state: King Hamad ibn ‘Isa al-Khalifah (from 2002). Head of Government: Prime Minister Sheikh Khalifah ibn Sulman al-Khalifah (from 1970). Capital: Manama. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Bahrain dinar (BD) = 1,000 fils; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = BD 0.38.
Demography
Area: 278 sq mi, 720 sq km. Population (2007): 749,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 2,665.5, persons per sq km 1,028.8. Urban (2005): 96.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 57.52%; female 42.48%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 27.2%; 15-29, 23.2%; 30-44, 29.9%; 45-59, 15.2%; 60-74, 3.6%; 75-84, 0.8%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Bahraini Arab 63.9%; Indo-Pakistani 14.8%, of which Urdu 4.5%, Malayali 3.5%; Persian 13.0%; Filipino 4.5%; British 2.1%; other 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 82.4%, of which Shi’i 58.0%, Sunni 24.0%; Christian 10.5%; Hindu 6.3%; other 0.8%. Major urban areas (2001): Manama 143,035; Muharraq 91,307; Ar-Rifa’ 79,550; Madinat Hamad 52,718; Al-’Ali 47,529. Location: the Middle East, archipelago in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.63. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.7 years; female 76.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: BD 1,671,400,000 (petroleum and natural gas revenue 75.7%; other 24.3%). Expenditures: BD 1,289,200,000 (current expenditure 79.4%; development expenditure 20.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): dates 15,000, vegetables 7,703 (of which tomatoes 2,100, onions 1,149), fruit (excluding dates) 5,010; livestock (number of live animals) 40,000 sheep, 26,000 goats, chickens 470,000; fisheries production (2004) 14,267. Manufacturing (barrels; 2005): jet fuel 19,956,000; distillate fuel oil 19,278,000; gasoline 7,309,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005-06) 9,567,000,000 ([2004] 7,198,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005-06) 66,400,000 ([2004] 93,100,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 10,939,000 (1,018,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 10,278,000,000 ([2004] 7,030,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$15,229,000,000 (US$20,609 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 350,000; activity rate of total population 48.3% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 67%; female 23.2%; unemployed [citizens only; 2006] 16-18%). Public debt (December 2004): US$3,866,000,000. Households. Average household size (2001) 5.9. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3%, in permanent crops 6%, in pasture 6%; overall forest area (2005) 1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 920; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 546. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 414; remittances (2006) 1,531; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 661.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): BD 2,988,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 52.5%; machinery and apparatus 9.0%; transport equipment 7.3%; chemicals and chemical products 6.4%). Major import sources (2004): Saudi Arabia 47.7%; Japan 6.2%; UK 3.7%; Germany 3.6%; France 3.6%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): BD 3,769,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 77.6%; base and fabricated metals, including aluminum [all forms] 12.9%; chemicals and chemical products 2.6%). Major export destinations (2004): unknown destinations for petroleum exports 76.5%; Saudi Arabia 6.4%; US 3.2%; Taiwan 2.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2003): total length 3,498 km (paved 79%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 241,813; trucksand buses 44,811. Airtransport (2005; Gulf Air, the national airline of both Bahrain and Oman, only): passenger-km 17,467,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 674,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 198,000 (284); televisions (2002): 273,000 (411); telephone landlines (2006): 190,000(262); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 835,000 (1,148); personal computers (2004): 121,000 (164); total Internet users (2006): 157,000(230); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 39,000 (52).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education 24.0%; primary education 37.1%; secondary 26.4%; higher 12.5%. Literacy (2005): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 90.0%; males literate 92.6%; females literate 86.4%. Health (2005): physicians 1,973 (1 per 362 persons); hospital beds 2,033 (1 per 352 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 17.3.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 11,200 (army 75.9%, navy 10.7%, air force 13.4%); US troops (2006) 3,000. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.6%; per capita expenditure US$675.
Background
The area has long been an important trading center and is mentioned in Persian, Greek, and Roman references. It was ruled by Arabs from the 7th century ad but was then occupied by the Portuguese in 1521-1602. Since 1783 it has been ruled by the Khalifah family, though through a series of treaties its defense remained a British responsibility from 1820 to 1971. After Britain withdrew its forces from the Persian Gulf (1968), Bahrain declared its independence in 1971. It served as a center for the allies in the Persian Gulf War (1990-91). Since 1994 it has experienced bouts of political unrest, mainly by Shi-’ites, who attempted to get the government to restore the parliament (abolished in 1975).
Recent Developments
Some progress was made in Bahrain in the realm of women’s affairs in 2007. On 28 March Bahraini diplomat Haya Rashid Al-Khalifa, president of the 61st session of the UN General Assembly, became the first woman to deliver a speech at the Arab League summit conference, which was held in conservative Saudi Arabia.
Bangladesh
Official name: Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh (People’s Republic of Bangladesh). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [300]). Chief of state: President Iajuddin Ahmed (from 2002). Head of government: Chief Adviser Fakhruddin Ahmed (from 2007). Capital: Dhaka. Official language: Bengali. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Bangladesh taka (Tk) = 100 paisa; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Tk 68.52.
Demography
Area: 56,977 sq mi, 147,570 sq km. Population (2007): 140,661,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 2,614.7, persons per sq km 1,009.5. Urban (2003): 24.2%. Sexdistribution (2005): male 51.09%; female 48.91%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 35.5%; 15-29, 28.6%; 30-44, 19.5%; 45-59, 10.8%; 60-74, 4.6%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (1997): Bengali 97.7%; tribal 1.9%, of which Chakma 0.4%, Saontal 0.2%, Marma 0.1%; other 0.4%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 88.3%; Hindu 10.5%; Christian 0.3%; Buddhist 0.6%; other 0.3%. Major urban areas (2004): Dhaka 10,550,000; Chittagong 2,640,000; Khulna 1,230,000; Rajshahi 725,200; Narayanganj 363,600. Location: South Asia, bordering India, Myanmar (Burma), and the Bay of Bengal.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 29.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 21.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.11. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 61.9 years; female 59.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue: Tk 448,700,000,000 (tax revenue 80.6%, of which VAT 27.6%, import duties 18.4%, taxes on income and profits 15.5%; nontax revenue 19.4%). Expenditures:Tk 610,600,000,000 (current expenditure 57.0%, of which education 10.4%, domestic interest payments 10.2%, defense 5.5%, health 3.3%; development expenditure 35.2%; other 7.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): paddy rice 41,104,000, sugarcane 6,500,000, potatoes 4,855,000; livestock (number of live animals) 36,900,000 goats, 24,500,000 cattle, 142,000,000 chickens; roundwood 27,944,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 99%; fisheries production (2004) 2,102,026 (from aquaculture 43%). Mining and quarrying (2004-05): marine salt 350,000; kaolin 8,400. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1998): wearing apparel 839; tobacco products 634; textiles 567. Energy production (con-sumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 21,466,000,000 (21,466,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) n.a. (700,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 1,900,000 ([2004] 9,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 842,000 (3,209,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 13,300,000,000 (13,300,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.3; average annual income per household (2000) Tk 70,103 (US$1,344); sources of income: self-employment 56.9%, wages and salaries 28.1%, transfer payments 9.1%, other 5.9%; expenditure (2000): food and beverages 54.6%, housing 9.0%, energy 6.8%, clothing and footwear 6.3%. Population economically active (2002-03): total 46,324,000; activity rate of total population 34.7% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 58.6%; female 22.3%; officially unemployed 4.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$17,938,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$72,050,000,000 (US$462 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 61.3%, in permanent crops 3.4%, in pasture 4.6%; overall forest area (2005) 6.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 70; remittances (2006) 5,922; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 437; official development assistance (2005) 1,321. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 132; remittances (2005) 6.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$14,746,-000,000 (textile yarn, fabrics, and made-up articles 15.1%; capital machinery 10.4%; imports for export processing zone 7.2%; base metals 6.6%; cotton 5.0%). Major import sources (2004): India 18.5%; China 13.1%; Singapore 10.5%; Japan 5.4%; Hong Kong 5.0%. Exports (2005-06): US$10,526,-300,000 (woven garments 38.8%; hosiery and knitwear 36.3%; frozen fish and shrimp 4.4%; jute manufactures 3.4%). Major export destinations (2004): US 25.6%; Germany 17.6%; UK 12.0%; France 7.5%; Italy 4.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length 2,768 km; passenger-km 3,970,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 908,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 239,226 km (paved 10%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 185,000; trucks and buses 88,000. Air transport (2005; Biman Bangladesh only): passenger-km 5,163,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 181,034,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 913,000 (6.8); televisions (2004): 11,531,000 (85); telephone landlines (2006): 1,134,000 (7.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 19,131,000 (133); personal computers (2004): 1,650,000 (12); total Internet users (2006): 450,000 (3.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004; estimated). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 48.8%; incomplete primary education 17.9%; complete primary 7.7%; incomplete secondary 15.1%; complete secondary or higher 10.5%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 41.1%; males literate 50.3%; females literate 31.4%. Health (2002): physicians 32,498 (1 per 4,049 persons); hospital beds 45,607 (1 per 2,886 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 60.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,388 (vegetable products 98%, animal products 2%); 130% of FAO recommended minimum.
Background
In its early years Bangladesh was known as Bengal. When the British left the subcontinent in 1947, the area thatwas East Bengal became the part of Pakistan called East Pakistan. Bengali nationalistsentiment increased after the creation of an independent Pakistan. In 1971 violence erupted; some one million Bengalis were killed, and millions more fled to India, which finally entered the war on the side of the Bengalis, ensuring West Pakistan’s defeat. East Pakistan became the independent nation of Bangladesh. Little of the devastation caused by the war has been repaired, and political instability, including the assassination of two presidents, has continued. In addition, the low-lying country has been repeatedly battered by natural disasters, notably tropical storms and flooding.
Recent Developments
The volatility of the situation in Bangladesh was highlighted in August 2007 when a brawl between university students and soldiers turned into countrywide violence. The country also faced economic challenges. Officially, in June inflation stood at 9.2%, but steeper price hikes were reported for food items, and the ready-made-garment sector faced an order dearth. In addition back-to-back floods caused more than 1,000 fatalities, along with huge losses to infrastructure and crops. Thousands more deaths were caused by a cyclone that struck southern Bangladesh in mid-November. (See Disasters.)
Barbados
Official name: Barbados. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [21]; House of Assembly [30]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Clifford Husbands (from 1996). Head of government: Prime Minister David Thompson (from 2008). Capital: Bridgetown. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Barbados dollar (BDS$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = BDS$2.00.
Demography
Area: 166 sq mi, 430 sq km. Population (2007): 294,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,771, persons per sq km 683.7. Urban (2005): 52.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.26%; female 51.74%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 19.0%; 15-29, 22.8%; 30-44, 26.1%; 45-59, 19.0%; 60-74, 8.2%; 75-84, 3.8%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): local black 87.1%; mulatto 6.0%; British expatriates 4.3%; US white 1.2%; Indo-Pakistani 1.1%; other 0.3%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 72.5%, of which Anglican 28.3%, Pentecostal 18.7%, Adventist 5.5%, Methodist 5.1%; Rastafarian 1.1%; Muslim 0.7%; Hindu 0.3%; nonreligious 17.3%; other/unknown 8.1%. Major urban areas (2004): Bridgetown 99,100; Speightstown 3,600; Oistins (2000) 1,203; Holetown (2000) 1,087. Location: northeast of Venezuela at the eastern edge of the Caribbean Sea where it adjoins the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.65. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.8 years; female 74.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:BDS$2,145,000,000 (tax revenue 95.2%, of which VAT 31.8%, corporate taxes 16.8%, personal income taxes 14.3%; nontax revenue 4.8%). Expenditures: BDS$2,328,500,000 (current expenditure 85.2%, of which education 18.3%, general public service 14.6%, debt payments 12.8%, health 11.3%, defense 2.2%; development expenditure 14.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; December 2005): US$763,500,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): raw sugar 38,240, sweet potatoes 2,000, coconuts 1,950; livestock (number of live animals) 19,000 pigs, 10,800 sheep, 3,400,000 chickens; roundwood 6,000 cu m; fisheries production (2004) 2,500. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1997): industrial chemicals 87; food products 63; beverages (significantly rum and beer) 58. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 793,000,000 (793,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 612,000 (negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,000 (346,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 25,000,000 (25,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 2.8; expenditure (2001): food 33.8%, medical and personal care 17.0%, housing 12.3%, household furnishings and operations 10.1%, education and recreation 7.4%, energy 6.3%. Population economically active (December 2005): total 145,800; activity rate of total population 53.1% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 69.0%; female 49.5%; unemployed [March 2006] 8.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$3,307,000,000 (US$11,291 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 897; remittances (2005) 140; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 48. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 96; remittances (2005) 40. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 37%, in permanent crops 2%, in pasture 5%; overall forest area (2005) 4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): BDS$3,209,000,000 (machinery 17.0%; food and beverages 13.8%; mineral fuels 11.7%; construction materials 7.5%). Major import sources: US 36.5%; Trinidad and Tobago 22.0%; UK 5.5%; Canada 3.6%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): BDS$719,000,000 (domestic exports 58.6%, of which manufactured goods [other than rum] 27.6%, rum 7.1%, sugar 6.2%; reexports 41.4%). Major export destinations: Caricom (Caribbean Community and Common Market) 37.8%, of which Trinidad and Tobago 9.3%, Jamaica 4.8%; US 12.8%; UK 8.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 1,600 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 92,195; trucks and buses 8,597. Air transport (2003): metric ton-km cargo 200,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 35,000 (130); televisions (2004): 78,000 (291); telephone landlines (2005): 135,000 (501); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 206,000 (766); personal computers (2005): 40,000 (148); total Internet users (2005): 160,000 (593); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 32,000 (118).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of employed labor force having: no formal schooling 0.5%; primary education 14.9%; secondary 58.7%; technical/vocational 5.4%; university 19.6%; other/unknown 0.9%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 99.7%. Health (2002): physicians 376 (1 per 721 persons); hospital beds 501 (1 per 541 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 11.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,727 (vegetable products 83%, animal products 17%); 151% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 610 (army 82.0%, navy 18.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.5%; per capita expenditure US$52.
Background
The island of Barbados was probably inhabited by Arawak Indians who originally came from South America. Spaniards may have landed by 1518, and by 1536 they had apparently wiped out the Indian population. Barbados was settled by the English in the 1620s. Slaves were brought in to work the sugar plantations, which were especially prosperous in the 17th-18th centuries. The British Empire abolished slavery in 1834, and all the slaves in Barbados were freed by 1838. In 1958 Barbados joined the West Indies Federation. When the latter dissolved in 1962, Barbados sought independence from Britain; it achieved it and joined the Commonwealth in 1966.
Recent Developments
Barbadian officials announced in May 2007 that Barbados would import natural gas by pipeline from Trinidad and Tobago and in June launched an open-bid round for offshore exploration.
Belarus
Official name: Respublika Belarus (Republic of Belarus). Form of government: republic with two legislative bodies (Council of the Republic [64]; House of Representatives [110]). Head of state and government: President Alyaksandr H. Lukashenka (from 1994), assisted by Prime MinisterSyarheySidorski (from 2003). Capital: Minsk. Official languages: Belarusian; Russian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: Belarusian ruble (Br); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Br 2,125.50; ruble re-denominated 1 Jan 2000; as of that date 1,000 (old) rubles = 1 (new) ruble.
Demography
Area: 80,153 sq mi, 207,595 sq km. Population (2007): 9,692,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 120.8, persons per sq km 46.7. Urban (2007): 72.8%. Sex distribution (2007): male 46.69%; female 53.31%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 15.2%; 15-29, 24.1%; 30-44, 22.0%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74, 12.8%; 75-84, 5.0%; 85 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (1999): Belarusian 81.2%; Russian 11.4%; Polish 3.9%; Ukrainian 2.4%; Jewish 0.3%; other 0.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Be-larusian Orthodox 48.7%; Roman Catholic 13.2%; unaffiliated Christian 5.9%; other Christian 2.4%; Jewish 0.6%; Muslim 0.3%; nonreligious 24.0%; atheist 4.9%. Major cities (2005): Minsk 1,765,800; Homyel 481,200; Mahilyow 366,900; Vitsyebsk 342,700; Hrodna 316,700. Location: eastern Europe, bordering Latvia, Russia, Ukraine, Poland, and Lithuania.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 75.9%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): -5.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.21. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 62.9 years; female 75.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: Br 17,417,000,000 (tax revenue 72.7%, of which VAT 21.9%, tax on profits 9.3%, personal income tax 8.1%, excise tax 6.4%; nontax revenue 5.7%; other 21.6%). Expenditures: Br 17,595,000,000 (current expenditure 75.1%; development expenditure 4.6%; other 20.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$783,000,000. Households (2004). Average household size 3.1; sources of money income: wages and salaries 49.2%, transfers 18.1%, other 32.7%; expenditure (2001): food and nonalcoholic beverages 53.6%, clothing and footwear 9.4%, housing and energy 7.2%, transport 6.3%, alcoholic beverages and tobacco products 5.9%. Population economically active (2005): 4,426,300; activity rate of total population 45.4% (participation rate [1999]: ages 15-64, 69.7%; female 53.1%; officially unemployed [December 2006] 1.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): maize for forage 9,227,000, potatoes 8,185,000, sugar beets 3,065,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,962,600 cattle, 3,406,800 pigs, 24,600,000chickens; roundwood 7,542,800 cu m, of which fuelwood 15%; fisheries production (2004) 5,040 (from aqua-culture 82%). Mining and quarrying (2004): potash 4,650,000; peat 2,100,000. Manufacturing (2006): fertilizers 5,469,000; cement 3,495,000; steel (2002) 1,607,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 31,800,000,000 ([2005] 34,999,000,000); coal (2004) none (234,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 13,100,000 (145,400,000); petroleum products (2004) 15,200,000 (5,049,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 228,000,000 (20,407,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$36,838,000,000 (US$3,781 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 26.8%, in permanent crops 0.6%, in pasture 15.4%; overall forest area (2005) 38.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 253; remittances (2005) 370; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 197. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 604; remittances (2005) 94.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$22,323,000,000 (mineral products 33.4%; machinery, equipment, and vehicles 24.1%; chemicals and chemical products 12.6%; food and beverages 9.4%). Major import sources (2004): Russia 68.2%; Germany 6.6%; Ukraine 3.3%; Poland 2.9%; Italy 1.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$19,739,000,000 (mineral products [significantly refined petroleum] 38.8%; machinery, equipment, and vehicles 20.0%; chemicals and chemical products 14.4%; food and beverages 7.5%). Major export destinations (2004): Russia 47.0%; UK 8.3%; The Netherlands 6.7%; Poland 5.3%; Ukraine 3.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length (2002) 5,533 km; passenger-km 9,968,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 45,723,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 93,310 km (paved 87%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2004) 1,707,888; trucks and buses (2001) 85,791. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 754,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 92,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 887,000 (90); televisions (2003): 3,809,000 (386); telephone landlines (2006): 3,368,000 (347); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,960,000 (614); total Internet users (2006): 4,200,000 (512); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 11,000 (1.2).
Education and health
Literacy (2001): total population ages 15 and over literate, virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 45,600 (1 per 214 persons); hospital beds 108,800 (1 per 90 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 6.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,885 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%); 146% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 72,940 (army 40.6%, air force and air defense 24.9%, centrally controlled units 34.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 7.2%; per capita expenditure US$38.
Background
While Belarusians share a distinct identity and language, they did not enjoy political sovereignty until the late 20th century. The territory that is now Belarus underwent partition and changed hands often; as a result its history is entwined with those of its neighbors. In medieval times the region was ruled by Lithuanians and Poles. Following the Third Partition of Poland, it was ruled by Russia. After World War I, the western part was assigned to Poland, and the eastern part became Soviet Russian territory. After World War II, the Soviets expanded what had been the Belorussian SSR by annexing more of Poland. Much of the area suffered contamination from the Chernobyl accident in 1986, forcing many to evacuate. Belarus declared its independence in 1991 and later joined the Commonwealth of Independent States. Amid increasing political turmoil in the 1990s, it proposed a union with Russia in 1997 that was still being debated at the start of the 21st century.
Recent Developments
In 2007 Belarus resolved two fractious disputes with Russia over natural gas prices and petroleum. Belarus agreed to pay US$100 per 1,000 cu m for imported Russian gas, more than double the 2006 rate, and to increase the price each year to reach the European rate (at that time about US$265) by 2011. Minsk and Moscow also signed an agreement on oil transit. The tax Belarus was paying on oil imported from Russia was reduced from US$180 to US$53 per ton, though it was to pay an additional tariff on exports of Belarusian products that were produced from imported Russian oil. Despite the energy problems, economic performance was positive. Official estimates put GDP growth at 21% in 2007. Industrial output rose by 8.2% and consumer goods by 7.3%.
Belgium
Official name: Koninkrijk Belgie (Dutch); Royaume de Belgique (French) (Kingdom of Belgium). Form of government: federal constitutional monarchy with two legislative chambers (Senate [71]; House of Representatives [150]). Chief of state: King Albert II (from 1993). Head of government: Prime Minister Yves Leterme (from 2008). Capital: Brussels. Official languages: Dutch; French; German. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; US$1 = €0.63 (1 Jul 2008).
Demography
Area: 11,787 sq mi, 30,528 sq km. Population (2007): 10,597,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 899.0, persons per sq km 347.1. Urban (2005): 97.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.94%; female 51.06%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 16.8%; 15-29, 18.1%; 30-44, 21.9%; 45-59, 20.8%; 60-74, 14.1%; 75-84, 6.5%; 85 and over, 1.8%. Ethnic composition (2000): Flemish 53.7%; Walloon (French) 31.6%; Italian 2.6%; French 2.0%; Arab 1.8%; German 1.5%; Berber 0.9%; other 5.9%. Religious affiliation (2001): self-identified Roman Catholic 46.7%; other Christian 2.6%; Muslim 3.9%; nonreligious/secular/other 46.8%. Major cities (2006): Brussels (population of capital region) 1,024,492; Antwerp 464,038; Ghent 233,925; Charleroi 201,456; Liege 187,432. Location: western Europe, bordering The Netherlands, Germany, Luxembourg, France, and the North Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 11.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 73.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.72. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 76.7 years; female 82.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:€149,218,000,000 (social security contributions 28.2%; personal income tax 24.3%; taxes on goods and services 23.0%). Expenditures: €149,504,000,000 (social insurance benefits 46.3%, of which health 12.6%; wages 24.1%; interest on debt 9.1%; capital expenditure 5.4%). Public debt (December 2006): US$357,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugar beets 5,606,000, potatoes 2,654,000, wheat 1,768,000; livestock (number of live animals) 6,332,000 pigs, 2,695,000 cattle; roundwood 4,950,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 13%; fisheries production (2004) 27,775 (from aquacul-ture 4%). Mining and quarrying (2005): Belgian blue-stone 1,200,000 cu m. Manufacturing (value added in €’000,000; 2005): chemicals and chemical products 8,903; base and fabricated metals 7,116; food/beverages/tobacco 6,046; value of traded polished diamonds handled in Antwerp (2005) US$15,900,000,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004-05) 82,665,000,000 ([2004] 85,643,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (8,244,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (252,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 30,086,000 (17,694,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) negligible (21,300,000,000). Households. Avg. household size (2005) 2.4; average net income per household (2003) €24,455 (US$27,602); sources of income (2003): wages and transfer payments 69.3%, property income 11.1%; expenditure (2004): housing 21.0%, food, beverages, tobacco 15.8%, transportation 13.4%, recreation and culture 8.6%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 27.6%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 17.7%; overall forest area (2005) 22.0%. Population economically active (2004): total 4,797,000; activity rate 46.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.3%; female [2002] 43.0%; unemployed [2006] 8.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$395,886,000,000 (US$37,955 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 9,845; remittances (2006) 7,154; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 23,072. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14,787; remittances (2006) 2,548; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 21,525.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): €208,539,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 16.0%; road vehicles 12.6%; medicine and pharmaceuticals 10.1%; food 7.1%). Major import sources (2005-06): The Netherlands 23.0%; Germany 15.8%; France 12.9%; UK 7.6%; US 4.5%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): €226,196,000,000 (road vehicles 14.0%; machinery and apparatus 13.4%; pharmaceuticals 10.0%; food 7.6%; organic chemicals 6.6%; diamonds 4.6%). Major export destinations (2005-06): France 17.8%; Germany 16.7%; The Netherlands 12.7%; UK 8.1%; Italy 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 3,536 km; passenger-km 9,117,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 8,130,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 150,567 km (paved 78%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 4,976,286; trucks and buses 638,579. Airtransport (2005; SN Brussels, European Air Transport, and TNT Airways S.A. only): passenger-km 4,918,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 705,130,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,706,000 (164); televisions (2004): 5,800,000 (557); telephone landlines (2006): 4,719,000 (452); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 9,660,000 (926); personal computers (2004): 3,627,000 (351); total Internet users (2005): 4,800,000 (458); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 2,005,000 (191).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling through lower-secondary education 39%; upper secondary/higher vocational 33%; university 28%. Health: physicians (2005) 42,176 (1 per 248 persons); hospital beds (2004) 70,865 (1 per 147 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 4.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,109 (vegetable products 63%, animal products 37%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 37,000 (army 67.0%, navy 6.9%, air force 17.2%, medical service 4.9%, other 4.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$403.
Background
Inhabited in ancient times by the Belgae, a Celtic people, the area was conquered by Caesar in 57 BC; under Augustus it became the Roman province of Gallia Belgica. Conquered by the Franks, it later broke up into semi-independent territories, including Brabant and Luxembourg. By the late 15th century AD, the territories of The Netherlands, of which the future Belgium was a part, had gradually united and passed to the Habsburgs. In the 16th century, it was a center for European commerce. The basis of modern Belgium was laid in the southern Catholic provinces that split from the northern provinces after the Union of Utrecht in 1579. Overrun by the French and incorporated into France in 1801, it was reunited to Holland and with it became the independent Kingdom of The Netherlands in 1815. After the revolt of its citizens in 1830, it became the independent Kingdom of Belgium. Under Leopold II it acquired vast lands in Africa. Overrun by the Germans in World Wars I and II, Belgium was the scene of the Battle of the Bulge. Internal discord led to legislation in the 1970s and 1980s that created three nearly autonomous regions in accordance with language distribution: Flemish Flanders, French Wallonia, and bilingual Brussels. In 1993 it became a federation comprising the three regions. It is a member of the European Union.
Recent Developments
Belgium experienced its most serious political crisis in decades following the country’s general election in June 2007, as political parties struggled to form a government. In Dutch-speaking Flanders there were major gains for the Christian Democrats, while in Francophone Wallonia the Christian Democrats made modest gains and the Liberals emerged as the largest political force. The clear winner was Yves Leterme, the leader of the Flemish Christian Democrats. His demands for wide-ranging constitutional reforms and increased autonomy for the regions, notably Flanders, met firm opposition from potential French-speaking partners, however, and stalled the formation of a coalition. After nine months of stalemate, Leterme was made prime minister in March 2008. The economy was strong in 2007. Public debt was declining as a percentage of GDP, the unemployment rate dropped to 7.5% (and further, to 6.7% by May 2008), and economic growth was 4.5%.
Belize
Official name: Belize. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [12]; House of Representatives [32]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Colville Young (from 1993). Head of government: Prime Minister Dean Barrow (from 2008). Capital: Belmopan. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Belize dollar (BZ$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = BZ$1.97 (pegged to the US dollar).
Demography
Area: 8,867 sq mi, 22,965 sq km. Population (2007): 306,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 34.5, persons persq km 13.3. Urban (2005): 50.2%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.51%; female 49.49%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 41.0%; 15-29, 27.7%; 30-44, 17.4%; 45-59, 8.1%; 60-74, 4.2%; 75-84, 1.2%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo (Spanish-Indian) 48.7%; Creole (predominantly black) 24.9%; Mayan Indian 10.6%; Garifuna (black-Carib Indian) 6.1%; white 4.3%; East Indian 3.0%; other or not stated 2.4%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 49.6%; Protestant 31.8%, of which Pentecostal 7.4%, Anglican 5.3%, Seventh-day Adventist 5.2%, Mennon-ite 4.1%; other Christian 1.9%; nonreligious 9.4%; other 7.3%. Major cities (2005): Belize City 60,800; San Ignacio/Santa Elena 16,800; Orange Walk 15,300; Belmopan 13,500; Dangriga 10,800. Location: Central America, bordering Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and Guatemala.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 29.3 (world avg. 20.3); (1997) within marriage 40.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 23.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.68. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 66.5 years; female 70.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006-07). Revenue:BZ$598,048,000 (tax revenue 85.9%, of which taxes on goods and services 33.8%, taxes on international trade 28.5%, taxes on income and profits 22.6%; other revenue 14.1%). Expenditures: BZ$667,943,000 (current expenditure 84.1%; capital expenditure 15.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane (2006) 1,188,000, oranges 213,400, bananas (2006) 69,600; livestock (number of live animals) 57,800 cattle, 1,600,000 chickens; roundwood 187,600 cu m, of which fuelwood 67%; fisheries production (2004) 14,335 (from aqua-culture 80%). Mining and quarrying (2004): limestone 571,000; sand and gravel 162,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food products and beverages (significantly citrus concentrate, flour, sugar, and beer) 69.2; textiles, clothing, and footwear 7.2; other (including cigarettes) 11.5. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 169,000,000 (194,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 810,000 (n.a.); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (292,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.4; average annual income of employed head of household (1993) BZ$6,450 (US$3,225); expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 34.7%, transportation 17.0%, housing and energy 16.8%, clothing and footwear 9.2%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3.1%, in permanent crops 1.4%, in pasture 2.2%; overall forest area (2005) 72.5%. Population economically active (2005): total 110,786; activity rate of total population 38.2% (participation rates: ages 14 and over 59.4%; female 36.7%; unemployed 11.0%). Gross national income (2006): US$1,003,000,000 (US$3,560 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; September 2006): US$929,600,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 208; remittances (2006) 96; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 34; official development assistance (2005) 23 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 42; remittances (2005) 20.
Foreign trade
Transport equipment 16.3%; direct imports to commercial free zone 15.0%; food and live animals 9.8%; chemicals and chemical products 7.2%). Major import sources: US 39%; Central American countries 19%; Mexico 9%; EU 7%; Caricom (Caribbean Community and Common Market) 2%. Exports (2005): BZ$643,800,000 (domestic exports 60.4%, of which seafood products [significantly shrimp] 14.1%, citrus [mostly oranges] concentrate 11.9%, rawsugar 10.8%, bananas 7.9%, garments 5.3%; reexports [principally to Mexico] 39.6%). Major export destinations (domestic exports only): US 52%; UK 22%; other EU 7%; Caricom 11%; Mexico 4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 2,984 km (paved 14%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 36,952; trucks and buses 7,380. Air transport (2001; Belize international airport only): passenger arrivals 256,564, passenger departures 240,900; cargo loaded 186 metric tons, cargo unloaded 1,272 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 52,000 (190); telephone landlines (2006): 34,000 (137); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 118,000 (430); personal computers (2002): 35,000 (132); total Internet users (2006): 34,000 (124); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 5,600 (19).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 36.6%; primary education 40.9%; secondary 11.7%; postsecondary/advanced vocational 6.4%; university 3.8%; other/unknown 0.6%. Literacy (2001): total population ages 14 and over literate 93.4%; males 93.6%; females 93.3%. Health (2004): physicians 221 (1 per 1,279 persons); hospital beds 650 (1 per 435 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 25.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,921 (vegetable products 80%, animal products 20%); 161% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,050 (army 100%); foreign forces (2006): British army 30. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$55.
Background
The area was inhabited by the Maya c. 300 bc-ad 900; the ruins of their ceremonial centers, including Caracol and Xunantunich, can still be seen. The Spanish claimed sovereignty from the 16th century but never tried to settle Belize, though they regarded as interlopers the British who did. British logwood cutters arrived in the mid-17th century; Spanish opposition was finally overcome in 1798. When settlers began to penetrate the interior they met with Indian resistance. In 1871 British Honduras became a crown colony, but an unfulfilled provision of an 1859 British-Guatemalan treaty led Guatemala to claim the territory. The situation had not been resolved when Belize was granted its independence in 1981. A British force, stationed there to ensure the new nation’s security, was withdrawn after Guatemala officially recognized the territory’s independence in 1991.
Recent Developments
The government of Belize addressed its unsustainable debt burden in 2007. Most of its creditors agreed to exchange their claims for new bonds, with a face value of US$546.8 million, that would mature in 2019. Unfortunately, the devastation inflicted in August by Hurricane Dean resulted in an estimated US$98.6 million loss, about one-third of the government revenues for the April 2007-March 2008 period.
Benin
Official name: Republique du Benin (Republic of Benin). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [83]). Head of state and government: President Yayi Boni (from 2006). Capital: Porto-Novo (official capital and seat of legislature; administrative seat in Cotonou). Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged since 1 Jan 2002 to the euro (€) at €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 43,484 sq mi, 112,622 sq km. Population (2007): 8,079,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 185.8, persons per sq km 71.7. Urban (2005): 38.8%. Sex distribution (2002): male 48.51%; female 51.49%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 44.5%; 15-29, 28.5%; 30-44, 15.6%; 45-59, 7.5%; 60-74, 3.3%; 75 and over, 0.6%. Ethnic composition (2002): Fon 39.2%; Adjara 15.2%; Yoruba (Nago) 12.3%; Bariba 9.2%; Fulani 7.0%; Somba (Otomary) 6.1%; Yoa-Lokpa 4.0%; other 7.0%. Religious affiliation (2002): Christian 42.8%, of which Roman Catholic 27.1%, Protestant 5.4%, indigenous Christian 5.3%; Muslim 24.4%; traditional beliefs 23.3%, of which voodoo 17.3%; nonreligious 6.5%; other 3.0%. Major cities (2004): Cotonou 818,100; Porto-Novo 234,300; Parakou 227,900; Djougou 206,500; Abomey 126,800. Location: western Africa, bordering Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, the Atlantic Ocean, and Togo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 38.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 26.6 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.20. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 51.9 years; female 54.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 422,100,000,000 (tax revenue 79.2%; nontax revenue 11.7%; grants 9.1%). Expenditures: CFAF 455,300,000,000 (current expenditures 73.4%, of which interest on public debt 1.5%; development expenditure 26.8%; net lending -0.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,762,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$4,649,000,000 (US$531 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 2,861,000, yams 2,084,000, corn (maize) 865,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,800,000 cattle, 1,380,000 goats, 750,000 sheep; roundwood 6,393,188 cu m, of which fuelwood 95%; fisheries production (2004) 39,995. Mining (2005): insignificant production of clay and gold. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1999): food products 74; textiles 42; beverages 36. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 81,000,000 (659,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 137,000 (negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (737,000). Population economically active (2002): total 2,830,900; activity rate of total population 41.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [1997] 84.3%; female [1998] 50.8%; unemployed in Cotonou [April 2003] 6.8%). Households. Average household size (2002) 5.6; expenditure (1996): food and nonalcoholic beverages 38.2%, transportation 10.1%, expenditures in cafes and hotels 9.8%, housing and energy 9.5%, clothing and footwear 6.9%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 24.0%, in permanent crops 2.4%, in pasture 5.0%; overall forest area (2005) 21.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 106; remittances (2005) 63; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 38; official development assistance (2005) 349. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 29; remittances (2005) 7.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 454,600,000,000 (food products 31.2%; petroleum products 14.7%; machinery and transport equipment 13.6%). Major import sources (2004): China 32%; France 13%; Thailand 7%; Cote d’Ivoire 5%. Exports (2005): CFAF 300,000,000,000 (domestic exports 59.5%, of which cotton 30.4%; reexports 40.5%). Major export destinations (2004): China 30%; India 19%; Ghana 6%; Niger 6%; Nigeria 4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): length (2004) 578 km; passenger-km 62,194,000; metric ton-km cargo 88,832,000. Roads (2004): total length 19,000 km (paved 9.5%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 37,772; trucks and buses 8,058. Air transport (2003): passengers carried 46,000; metric ton-km cargo 7,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 16,000 (2.2); televisions (2004): 431,000 (59); telephone landlines (2006): 77,000 (8.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,056,000 (121); personal computers (2005): 32,000 (4.2); total Internet users (2006): 700,000 (80); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 100 (0.03).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 63.5%; primary education 18.7%; secondary 15.9%; postsecondary 1.9%. Literacy (2005): total percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 43.2%; males literate 58.8%; females literate 28.4%. Health (2001): physicians 923 (1 per 7,183 persons); hospital beds 590 (1 per 11,238 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 79.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,437 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 135% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 4,550 (army 94.5%, navy 2.2%, air force 3.3%). Military expenditure as percentage of GNP (2005): 1.7%; per capita expenditure US$10.
Background
In southern Benin, the Dahomey, or Fon, established the Abomey kingdom in 1625. In the 18th century, the kingdom became known as Dahomey when it expanded to include Allada and Ouidah, where French forts had been established in the 17th century. In 1857 the French reestablished themselves in the area, and eventually fighting ensued. In 1894 Dahomey became a French protectorate; it was incorporated into the federation of French West Africa in 1904. It achieved independence in 1960. The area called Dahomey was renamed Benin in 1975. At the end of the 20th century, its chronically weak economy produced tension between laborers and the government.
Recent Developments
Pres. Thomas Yayi Boni organized a “march against corruption” in July 2007, and he later vowed to fulfill his election promises by wiping it out. In June it was announced that the Benin scientist Jerome Fagla Medegan had been granted a patent for his new treatment for a strain of sickle-cell anemia, marking the first time that an African had been given a patent for a new drug.
Bermuda
Official name: Bermuda. Political status: overseas territory of the UK with two legislative houses (Senate [11]; House of Assembly [36]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor Sir Richard Gozney (from 2007). Head of government: Premier Ewart Brown (from 2006). Capital: Hamilton. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Bermuda dollar (Bd$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Bd$1.00.
Demography
Area: 20.5 sq mi, 53.1 sq km. Population (2007): 64,900. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 3,166, persons per sq km 1,222. Urban (2005): 100%. Sex distribution (2006): male 47.81%; female 52.19%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 18.1%; 15-29, 17.6%; 30-44, 24.8%; 45-59, 22.7%; 60-74, 11.9%; 75-84, 3.9%; 85 and over, 1.0%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 50.4%; British expatriates 29.0%; mulatto 10.0%; US white 6.0%; Portuguese 4.5%; other 0.1%. Religious affiliation (2000): Protestant 64.3%, of which Anglican 22.6%, Methodist 14.9%; Roman Catholic 14.9%; nonreli-gious 13.8%; other 6.0%; unknown 1.0%. Major cities (2000): St. George 1,752; Hamilton 969. Location: North Atlantic Ocean, east of North Carolina (US).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2004): 13.1 (world avg. 21.1); (2002) within marriage 64.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2004): 7.2 (world avg. 8.8). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2004): 5.9 (world avg. 12.3). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.89. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.8 years; female 80.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue:Bd$782,500,000 (payroll taxes 31.6%; customs duties 27.1%; taxes on international companies 6.3%; stamp duties 6.1%; taxes on land 5.4%; other 23.5%). Expenditures: Bd$809,000,000 (current expenditure 89.3%; development expenditure 10.7%). Public debt (2004-05): US$128,000,000. Production (value in Bd$’000 except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): vegetables 4,709, fruits 334, flowers 228; livestock (number of live animals) 900 horses, 600 cattle, 45,000 chickens; fisheries production 379. Mining and quarrying:crushed stone for local use. Manufacturing: industries include pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, electronics, fish processing, handicrafts, and small boatbuilding. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 661,000,000 (661,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (198,000). Households (2004). Average household size 2.3; average annual income per household Bd$106,233 (US$106,233); sources of income: wages and salaries 65.1%, imputed income from owner occupancy 14.4%, self-employment 9.2%, net rental income 4.1%, other 7.2%; expenditure: housing 33.3%, household furnishings 13.8%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 13.7%, health and personal care 8.7%, transportation 8.0%, foreign travel 5.4%. Population economically active (2000): total 37,879; activity rate of total population 61.0% (participation rates: ages 16-64, 84.8%; female 48.3%; unemployed [2005] 2.1%). Gross national income (at 2005 market prices): US$5,056,000,000 (US$78,538 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005-06) 453; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 8,620. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (1997) 148. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2%; overall forest area (2005) 20%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2002): Bd$746,000,000 (food, beverages, and tobacco 20.2%; machinery 16.5%; chemicals and chemical products 13.9%; mineral fuels 7.8%; transport equipment 6.0%). Major import sources: US 76%; Canada 5%; UK 5%; Caribbean countries (mostly Netherlands Antilles) 3%. Exports (2002): Bd$57,000,000 (nearly all reexports [including sales of fuel to aircraft and ships and pharmaceuticals]; diamond market was established in 1990s). Major export destinations: mostly US, UK, Norway, and Spain.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2002): total length 225 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 21,978; trucks and buses 4,873. Air transport: passenger arrivals and departures (2005) 900,000; cargo loaded (2001) 909 metric tons, cargo unloaded (2001) 4,862 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 17,000 (268); televisions (2001): 68,000 (1,077); telephone landlines (2006): 58,000 (889); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 60,000 (916); personal computers (2002): 34,000 (535); total Internet users (2005): 42,000 (646); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 24,000 (360).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of total population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 0.4%; primary education 7.0%; secondary 39.3%; postsecondary technical 25.7%; higher 26.8%; not stated 0.8%. Literacy (1997): total population ages 15 and over literate 98%. Health: physicians (2005) 135 (1 per 482 persons); hospital beds (2005-06) 351 (1 per 186 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2001-03) 2.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,083 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 530; part-time defense force assists police and is drawn from Bermudian conscripts.
Background
The Bermuda archipelago was named for Juan de Bermudez, who may have visited the islands in 1503. Colonized by the English in 1612, Bermuda became a crown colony in 1684 and a British overseas territory in 2002. Its economy is based on tourism and international finance; its per capita gross national product is among the world’s highest.
Recent Developments
In the local elections on Bermuda on 18 December 2007, Premier Ewart Brown’s Progressive Liberal Party (PLP) won 52.35% of the vote and 22 seats, compared with 47.25% and 14 seats for the United Bermuda Party. It was the PLP’s third successive election victory and left the balance of parliamentary power unchanged.
Bhutan
Official name: Druk-Yul (Kingdom of Bhutan). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (National Council [25]; National Assembly [47]). Chief of state: King Jigme Khesar Namgyal Wangchuk (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Lyonchen Jigme Thinley (from 2008). Capital: Thimphu. Official language: Dzongkha (a Tibetan dialect). Official religion: Mahayana Buddhism. Monetary unit: 1 ngultrum (Nu) = 100 chetrum; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Nu 43.35; the Indian rupee is also accepted legal tender.
Demography
Area: 14,824 sq mi, 38,394 sq km. Population (2007): 658,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 44.4, persons per sq km 17.1. Urban (2005): 30.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 54.20%; female 45.80%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 33.2%; 15-29, 32.1%; 30-44, 17.6%; 45-59, 10.4%; 60-74, 5.5%; 75-84, 1.1%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2005): Bhutia (Ngalops) 50%; Nepalese (Gurung) 35%; Sharchops 15%. Religious affiliation (2005): Buddhist 74%; Hindu 25%; Christian 1%. Major towns (2001): Thimphu 50,510; Phuentsholing 13,292; Gedu 7,826; Gelaphu 6,384; Samtse 3,703. Location: southern Asia, bordering China and India.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 13.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.55. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 62.9 years; female 66.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:Nu 13,534,000,000 (grants 47.2%; tax revenue 27.8%; nontax revenue 22.5%; other 2.5%). Expenditures: Nu 16,151,000,000 (capital expenditures 55.1%; current expenditures 44.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; September 2006): US$691,100,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): corn (maize) 70,000, potatoes 47,000, rice 45,000; livestock (number of live animals) 372,000 cattle, 41,000 pigs, 28,000 horses; roundwood 4,679,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 97%; fisheries production (2004) 300. Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 536,000; dolomite 388,700; gypsum 150,600. Manufacturing (value of sales in Nu ’000,000; 2005): chemical products 857; cement 807; ferroalloys 651. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 2,355,000,000 (739,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2005) 85,300 ([2004] 65,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (51,000). Households. Average household size (2005) 4.6; expenditure (2003): food 36%, housing 27%, clothing 10%, education 3%, health care 1%. Population economically active (2005): total 257,000; activity rate of total population 38.2% (officially unemployed 3.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$921,000,000 (US$1,420 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 3.2%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 8.8%; overall forest area (2005) 68.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005-06) 21; remittances (2005) 1.5; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 38; official development assistance (2005) 90.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): Nu 17,035,000,000 (machinery, transport equipment, and base and fabricated metals 45.5%; mineral fuels 16.1%; food and beverages 14.9%; textiles 4.2%). Major import sources: India 75.1%; Japan 3.8%; Singapore 2.6%; Thailand I.6%; South Korea 1.5%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): Nu II,386,000,000 (electricity 30.2%; copper wire and cable 9.6%; calcium carbide 6.2%; ferroalloys 6.0%; cement5.4%; polyester yarn 4.2%). Major export destinations:India 87.6%; Hong Kong 6.0%; Bangladesh 4.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 4,153 km (paved 59%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 10,574; trucks and buses 3,852. Air transport (2002): passenger-km 61,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,700,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 25,000 (33); telephone landlines (2006): 32,000 (49); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 82,000 (128); personal computers (2005): 13,000 (16); total Internet users (2006): 30,000 (47).
Education and health
Literacy (2005): total population ages 6 and over literate 59.5%; males literate 69.1%; females literate 48.7%. Health (2003): physicians 140 (1 per 5,245 persons); hospital beds 1,093 (1 per 672 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 48.8.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2002): about 6,000 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$11.
Background
Bhutan’s mountains and forests long made it inaccessible to the outside world, and its feudal rulers banned foreigners until well into the 20th century. It nevertheless became the object of foreign invasions; in 1865 it came under British influence, and in 1910 it agreed to be guided by Britain in its foreign affairs. It later became oriented toward British-ruled India, though much of its trade was with Tibet. India took over Britain’s role in 1949, and China’s 1950 occupation of neighboring Tibet further strengthened Bhutan’s ties with India. The apparent Chinese threat made Bhutan’s rulers aware of the need to modernize, and it embarked on a program to build roads and hospitals and to create a system of secular education.
Recent Developments
In 2008 Bhutan transitioned from an absolute monarchy to a multiparty democracy. Bhutan’s first general elections were held in March, resulting in the election of Lyonpo Jigme Thinley as prime minister with real executive powers. The fate of more than 100,000 Bhutanese refugees staying in UN High Commissioner for Refugees-administered camps in eastern Nepal remained uncertain. Following the completion in 2007 of the Tala Hydroelectric Project, which supplied India with power, plans were approved for work to begin in 2008 on the Punatsangchu-I project.
Bolivia
Official name: República de Bolivia (Republic of Bolivia).Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Chamber of Senators[27]; Chamber of Deputies [130]). Head of state and government: President Evo Morales (from 2006). Capitals: La Paz (administrative); Sucre (judicial). Official languages: Spanish; Aymara; Quechua. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 boliviano (Bs) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Bs 7.20.
Demography
Area: 424,164 sq mi, 1,098,581 sq km. Population (2007): 9,525,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 22.5, persons per sq km 8.7. Urban (2005): 64.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.85%; female 50.15%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 38.1%; 15-29, 27.1%; 30-44, 17.6%; 45-59, 10.4%; 60-74, 5.3%; 75-84, 1.3%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2001): Amerindian 62%, of which Quechua 31%, Aymara 25%; mestizo 28%; white 10%, of which German 3%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 78%; Protestant/independent Christian 16%; other Christian 3%, of which Mormon 1.8%; nonreligious 2.5%; other 0.5%. Major cities (2001): Santa Cruz 1,116,059 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,320,000); La Paz 789,585 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,527,000); El Alto (within La Paz urban agglomeration) 647,350; Cochabamba 516,683; Oruro 201,230. Location: central South America, bordering Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, Chile, and Peru.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.85. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 63.2 years; female 68.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: Bs 30,071,900,000 (taxes on hydrocarbons 35.4%; other tax income 49.5%; other 15.1%). Expenditures: Bs 26,876,500,000 (current expenditure 65.3%; capital expenditure 34.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,664,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 5,112,000, soybeans 1,689,000, corn (maize) 816,700 (Bolivia was the third largest producer of coca in the world in 2005); livestock (number of live animals) 8,550,000 sheep, 6,822,200 cattle, 2,984,000 pigs, (2004) 1,900,000 llamas and alpacas; roundwood 3,061,337 cu m, of which fuelwood 74%; fisheries production (2004) 7,196 (from aquaculture 6%). Mining and quarrying (metal content; 2005): zinc 157,019; tin 18,694; silver 420. Manufacturing (value added in Bs ’000,000; 2004, in 1990 prices): food products 1,545; beverages and tobacco products 581; petroleum products 497. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 4,778,000,000 ([2004] 4,547,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 15,300,000 (10,700,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,618,000 (1,454,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 9,544,000,000 (1,732,000,000). Population economically active (2000): total 3,823,937; activity rate of total population 46.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 71.8%; female 44.6%; unemployed [2006] 8% in urban areas). Gross national income (2006): US$10,163,000,000 (US$1,087 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.3; annual income per household (1999): Bs 16,980 (US$2,920); expenditure (2000): food 28.6%, transportation and communications 23.1%, rent and energy 10.3%, expenditures in cafes and hotels 9.5%, recreation and culture 7.1%, household furnishings 6.3%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 239; remittances (2006) 1,030; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 274; official development assistance (2005) 547 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 186; remittances (2005) 66. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.8%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 31.2%; overall forest area (2005) 54.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$2,343,300,000 (machinery and apparatus 20.1%; chemicals and chemical products 14.6%; base and fabricated metals 11.0%; mineral products 10.9%; transport equipment 10.1%). Major import sources: Brazil 21.9%; Argentina 16.7%; US 13.8%; Chile 6.9%; Peru 6.5%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): US$2,810,400,000 (natural gas 35.0%; soybeans 13.3%; petroleum 12.7%; zinc 7.1%; tin 4.5%; silver 2.8%). Major export destinations: Brazil 36.8%; US 14.0%; Argentina 9.5%; Colombia 6.6%; Venezuela 5.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 3,519 km; (1997) passenger-km 224,900,000; (1997) metric ton-km cargo 838,900,000. Roads (2004): total length 62,479 km (paved 7%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 171,642; trucks and buses 173,864. Air transport (2003): passenger-km 1,704,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 24,348,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 139,000 (16); televisions (2004): 1,210,000 (134); telephone landlines (2006): 667,000 (71); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,698,000 (289); personal computers (2004): 210,000 (23); total Internet users (2006): 580,000 (62); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 11,000 (1.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 19 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 14.8%; primary education 44.9%; secondary 24.8%; higher 15.5%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 87.2%; males literate 93.1%; females literate 81.6%. Health: physicians (2002) 2,987 (1 per 2,827 persons); hospital beds (2005) 9,886 (1 per 954 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 51.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,128 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 118% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 33,000 (army 75.8%, navy 15.1%, air force 9.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.6%; per capita expenditure US$16.
Background
The Bolivian highlands were the location of the advanced Tiwanaku culture in the 7th-11th centuries and, with its passing, became the home of the Ay-mara, an Indian group conquered by the Incas in the 15th century. The Incas were overrun by the invading Spanish under Francisco Pizarro in the 1530s. By 1600 Spain had established the cities of Charcas (now Sucre), La Paz, Santa Cruz, and what would become Cochabamba, and had begun to exploit the silver wealth of Potosf. Bolivia flourished in the 17th century, and for a time Potosf was the largest city in the Americas. By the end of the century, the mineral wealth had dried up. Talk of independence began as early as 1809, but not until 1825 were Spanish forces finally defeated. Bolivia shrank in size when it lost Atacama province to Chile in 1884 at the end of the War of the Pacific and again in 1939 when it lost most of Gran Chaco to Paraguay. One of South America’s poorest countries, it was plagued by governmental instability for much of the 20th century. By the 1990s Bolivia had become one of the world’s largest producers of coca, from which cocaine is derived. The government subsequently instituted a largely successful program to eradicate the crop, although such efforts were resisted by the many poor farmers who depended on coca.
Recent Developments
As South America’s first Indian president, Bolivia’s Evo Morales forged ahead in 2007 with bold attempts to restructure Bolivia on terms more favorable to its impoverished Indian majority. He scored some successes, significantly boosting the government’s share of revenue from natural gas and mineral resources. The constituent assembly made little progress in drafting a new constitution, however, and tension increased between the Indian-dominated western highlands and the resource-rich eastern lowlands. The rivalry between the regions was further aggravated by a proposal to transfer the political capital back to Sucre (the sole capital until 1899), sparking massive protests in La Paz.