1.4
Telephone line electrical signal power levels are presented in dBm units. Power level expressed in dBm is the power in decibel (dB) with reference to one milliwatt (mW). Power 0 dBm represents one milliwatt of power. One mW is a strong speech level for listening. Usual telephone conversion levels are close to -16dBm (25|^W; |jW is microwatt). ITU-T-G.711 and ITU-T-G.168 (2004) recommendations listed speech power levels and corresponding digital quantization mapping for 8-bit A-law and | – law. A – law and | – law (pronounced as Mu) are logarithmic compression methods explained in topic 3 under G.711 compression. Telephone interfaces have SLIC and SLAC for converting TIP-RING signals to digital samples. SLIC converts a signal from two-wire TIP-RING interface to a four- wire interface to SLAC. In recent literature, the hardware CODEC name is used instead of SLAC. CODEC consists of a COder, DECoder hardware with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a digital- t o – analog converter (DAC) that samples the signals at 8 or 16 kHz. Sampled signals are given to the processor for additional processing. In this topic, signal levels and the mapping to 16-bit numbers in A-law and | – law, are given with reference to dB and dBm scale.
1.4.1
µ -Law Power Levels and Quantization
The maximum | (read as Mu)-law undistorted power level for the sine wave is 3.17dBm. Power of 3.17dBm is 2.0749mW in 600 Ohms (Q) of telephone impedance. Impedance of 600 Q is applicable to North America and a few other countries like Japan and Korea. A sine wave of 2.0749mW in 600 Q develops 1578 millivolts (mV) peak or a 3.156 Volts peak-to-peak sine wave amplitude. Voltage of 1578mV has to be quantized as 8159 amplitude [ITU-
T-G.711 (1988), ITU-T-G.168 (2004)] in 16-bit binary numbering format. Assuming linear mapping for calculation purposes, the quantization level is 1578 mV/8159 = 0.1934 mV. Once voice samples are available as per the above quantization of one level per 0.1934 mV, the following formula given in ITU-T-G.168 is used for estimating the voice power over a block of samples:
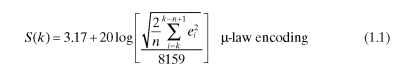
S(k) = signal level in dBm
e = linear equivalent of the pulse codec modulation (PCM) encoded
signal at sample index l k = discrete time index or starting index for block of samples n = block size of samples or number of samples over which root mean
square (RMS) measurement is made.
In general, N will be used in signal processing literature for representing blocks of samples and n will be used for an index within the block of samples. In the above equation, to maintain consistency with the ITU recommendations, n is used for denoting block size and is used for the index.
A sine wave with a peak amplitude of 8159 results in 3.17 dBm without any dependency on frequency. |>law coding distorts the sine wave if it exceeds 3.17 dBm. Square wave power is 3dB more than sine wave power, and an amplitude of 8159 of square wave results in 6.17 dBm. Alternatively, a constant value of 8159 (constant voltage) is 3 dB more power than a sine wave of 8159. Sometimes use of a constant value and calibrating with reference to a constant of 8159 as 6.17 dBm can help for calibration of the algorithms and power estimation blocks. In practice, lower amplitude is used for such calibrations in the range of -13 to -10 dBm instead of 6.17 dBm. Coding with |>law supports the SNR up to 37 to 41 dB (for a 0- to -30-dBm signal power level) for the useful speech signal levels.
1.4.2
A-Law Power Levels and Quantization
An A-law maximum undistorted power level for the sine wave is 3.14dBm. Power of 3.14dBm is 2.06 mW in 600 Q of telephone impedance. A sine wave of 2.06 mW in 600 Q will develop 1572 mV peak or a 3.144 Volts peak-to-peak sine wave amplitude. Voltage of 1572 mV has to be quantized to 4096 amplitude levels. Quantization level is 1572 mV/4096 = 0.3838 mV. Once voice samples are available as per the above quantization of one level per 0.3838 mV, the following formula given in ITU-T G.168 (2004) is used for estimating the voice power over a block of samples:
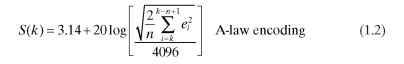
The symbols used in this equation are the same as those used in the |>law power representation in Eq. (1.1). For a sine wave of peak 4096, this calculation results in 3.14 dBm with out any dependency on frequency. A-law starts distortion to sine wave if it exceeds 3.14dBm. An amplitude of 4096 for the square wave results in 6.14 dBm. As an example, substituting one complete cycle of a 2-kHz sine wave at 4096 amplitude (four samples for one complete cycle are 0, 4096, 0, -4096) in A-law power calculation gives 3.14 + 0dBm = 3.14dBm. Substituting four constant values of 4096 in A-law power calculation will give 3.14 + 3.0dBm = 6.14dBm. A-law supports SNR up to 37 to 41 dB (this varies with signal power level) for the useful speech signal levels.
