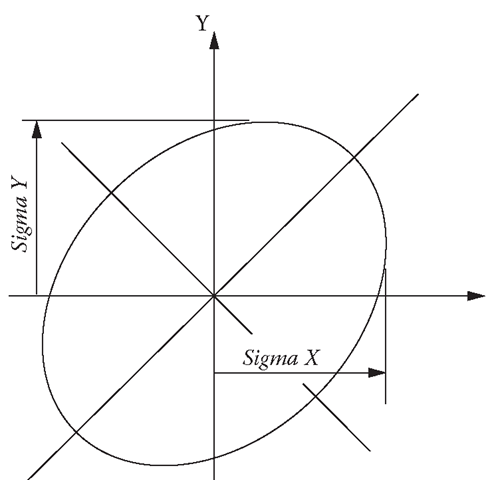
Error ellipses are a graphical tool used to illustrate the pair-wise correlation that exists between computed values. Using 2-D plane coordinates as an example, if the correlation between the computed coordinates is zero, then the orientation of the error ellipse corresponds to that of the host coordinate system. Special case: if the correlation is zero and the standard deviations are the same for both coordinates, then the error ellipse is a circle (and orientation is immaterial). However, if the standard deviation is the same for both coordinates and the correlation is not zero, then the maximum and minimum standard deviations will occur with some other orientation.
FIGURE 3.16 General Error Ellipse
The general case, illustrated in Figure 3.16, accommodates standard deviations of coordinates that are not the same with respect to the X and Y axes and in which correlation does exist. The respective x/y standard deviations and orientation of the ellipse major axis are obtained from the point covariance matrix. Additional material on error ellipses is given in Wolf and Ghilani (1997) and should be studied carefully in order to fully understand their usefulness. An incidental point is that error ellipses provide excellent visualization of correlation in two dimensions, typically in the horizontal plane. Visualization of 3-D error ellipsoids needs more study and discussion.