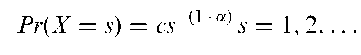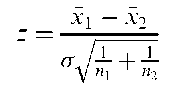Zelen’s exact test:
A test that the odds ratios in a series of two-by-two contingency tables all take the value one.
Zelen’s single-consent design:
An alternative to simple random allocation for forming treatment groups in a clinical trial. Begins with the set of N eligible patients. All N of these patients are then randomly subdivided into two groups say G1 and G2 of sizes n1 and n2. The standard therapy is applied to all the patients assigned to G1. The new therapy is assigned only to those patients in G2 who consent to its use. The remaining patients who refuse the new treatment are treated with the standard.
Zero-inflated binomial regression:
An adaptation of zero-inflated Poisson regression applicable when there is an upper bound count situation. It assumes that with probability p an observation is zero and with probability 1 — p a random variable with a binomial distribution with parameters n and n.
Zero-inflated Poisson regression:
A model for count data with excess zeros. It assumes that with probability p the only possible observation is 0 and with probability 1 — p a random variable with a Poisson distribution is observed. For example, when manufacturing equipment is properly aligned, defects may be nearly impossible. But when it is misaligned, defects may occur according to a Poisson distribution. Both the probability p of the perfect zero defect state and the mean number of defects X in the imperfect state may depend on covariates. The parameters in such models can be estimated using maximum likelihood estimation.
Zero sum game:
A game played by a number of persons in which the winner takes all the stakes provided by the losers so that the algebraic sum of gains at any stage is zero. Many decision problems can be viewed as zero sum games between two persons.
ZIP: Abbreviation for zero-inflated Poisson regression.
Zipf-Estoup law:
Synonymous with ZipPs law.
Zipf’s law:
A term applied to any system of classification of units such that the proportion of classes with exactly s units is approximately proportional to s—^1+a) for some constant a > 0. It is familiar in a variety of empirical areas, including linguistics, personal income distributions and the distribution of biological genera and species. A probability distribution appropriate to such situations can be constructed by taking
where
This is known as the Zipf distribution.
Z-scores:
Synonym for standard scores.
z-test:
A test for assessing hypotheses about population means when their variances are known.
For example, for testing that the means of two populations are equal, i.e. H0 : fi1 = fi2, when the variance of each population is known to be a2, the test statistic is
where xx1 and x2 are the means of samples of size n1 and n2 from the two populations. If H0 is true, z, has a standard normal distribution.
Zygosity determination:
The determination of whether a pair of twins is identical or fraternal. It can be achieved to a high (over 95%) level of certainty by questionnaire, but any desired level of accuracy can be achieved by typing a number of genetic markers to see if the genetic sharing is 100% or 50%. Important in twin analysis.