Example scenario
Problem definition. Inbound roamers from a partner network X, roaming in a business district, are unable to receive incoming calls. However, they are able to make outgoing calls and send/receive SMS.
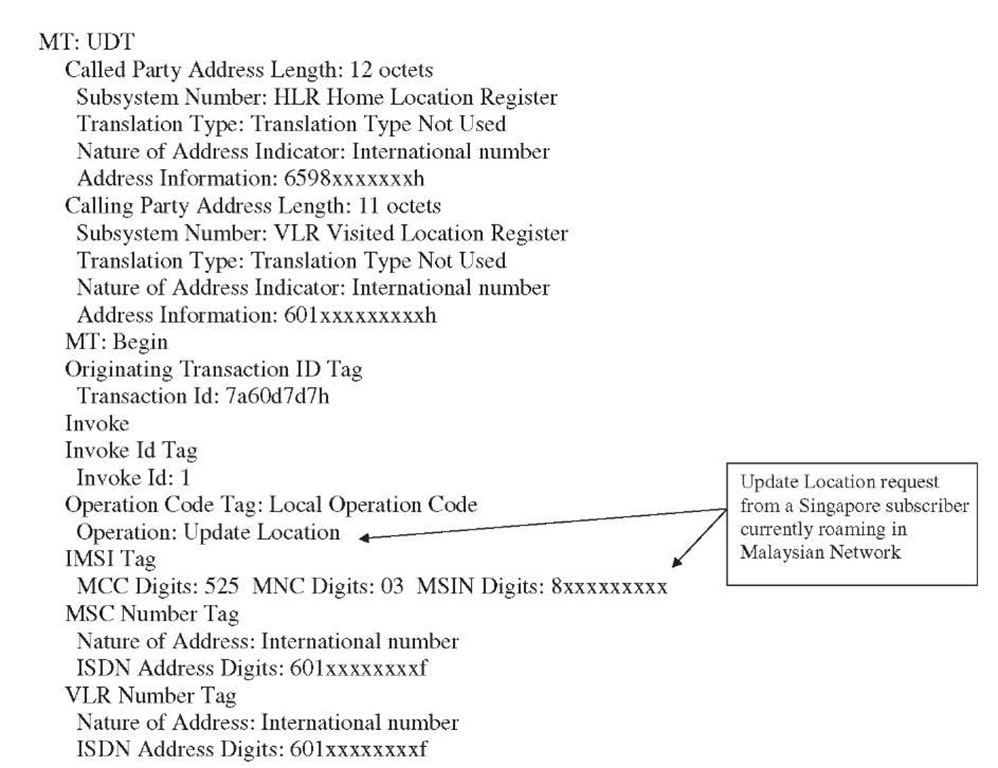
Figure 10-16 Update location.
Figure 10-17 Update location response.
TABLE 10-8 MAP Operation and Return Error Component
|
Operation |
Opcode decimal (hex) |
MAP return errors |
|
Update location |
2 (02) |
System failure Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber Roaming not allowed |
|
Cancel location |
3 (03) |
Data missing Unexpected data value |
|
Purge MS |
67 (43) |
Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber |
|
Update GPRS location |
23 (17) |
System failure Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber Roaming not allowed |
|
Provide subscriber info |
70 (46) |
Data missing Unexpected data value |
|
Send identification |
55 (37) |
Data missing Unidentified subscriber |
|
Send authentication info |
56 (38) |
Data missing Unexpected data value System failure Unknown subscriber |
|
Insert subscriber data |
7 (07) |
Data missing Unexpected data value Unidentified subscriber |
|
Restore data |
57 (39) |
Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber System failure |
|
Send routing info for GPRS |
24 (18) |
Absent subscriber Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber System failure |
|
Provide roaming number |
4 (04) |
Absent subscriber Facility not supported/not allowed Data missing Unexpected data value No roaming number available System failure |
|
Register SS |
10 (0a) |
Absent subscriber Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Bearer services not provisioned Teleservices not provisioned |
TABLE 10-8 MAP Operation and Return Error Component
|
Operation |
Opcode decimal (hex) |
MAP return errors |
|
Illegal SS operation SS error status SS incompatibility |
||
|
Erase SS |
11 (0b) |
Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Bearer services not provisioned Teleservices not provisioned Illegal SS operation System failure SS error status |
|
Deactivate SS |
13 (0d) |
System failure Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Bearer services not provisioned Teleservices not provisioned Illegal SS operation SS error status SS subscription violation Negative password check Number of password attempts violation |
|
Interrogate SS |
14 (0e) |
System failure Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Bearer services not provisioned Teleservices not provisioned Illegal SS operation SS not available |
|
Process unstructured SS request |
59 (3b) |
System failure Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown alphabet USSD busy |
|
Unstructured SS request |
60 (3c) |
System failure Data missing Absent subscriber Unexpected data value Unknown alphabet USSD busy Illegal subscriber Illegal equipment |
|
Unstructured SS notify |
61 (3d) |
System failure Call barred Absent subscriber Unexpected data value |
TABLE 10-8 MAP Operation and Return Error Component
|
Operation |
Opcode decimal (hex) |
MAP return errors |
|
Unknown alphabet |
||
|
USSD busy |
||
|
Illegal subscriber |
||
|
Illegal equipment |
||
|
Send routing info for SM |
45 (2d) |
System failure Call barred Data missing Unexpected data value Teleservices not provisioned Facility not supported Unknown subscriber Absent subscriber SM |
|
MO forward SM |
46 (2e) |
System failure Unexpected data value Facility not supported SM delivery failure |
|
MT forward SM |
44 (2c) |
System failure Unidentified subscriber Data missing Unexpected data value Facility not supported Unknown subscriber Absent subscriber SM Illegal subscriber Subscriber busy for MT-SMS SM delivery failure |
|
Report SM delivery status |
47 (2f) |
Data missing Unexpected data value Unknown subscriber Message waiting list full |
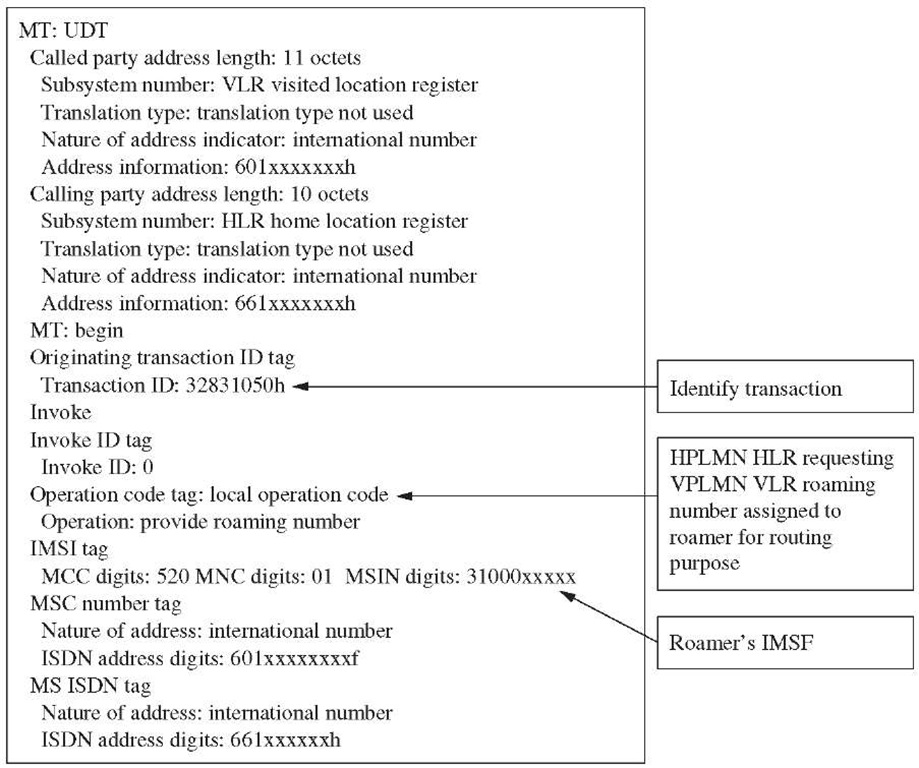
Analysis. By analyzing problem statement it is clear that either the provide roaming number procedure is not successful or incoming calls are not routed correctly.
Diagnostic. The first step is to isolate the fault between the roaming procedure and the ISUP call routing. A protocol session may help in this case. The recommended steps are as follows.
1. Select signaling links carrying traffic to partner network X.
2. Set up an appropriate filter to reduce the amount of captured traffic. This is required for efficiency purposes and to focus on the problem in hand.
■ SCCPMSUs only.
■ SCCP calling party address partner network X. For example, if the partner network is Vodafone, then it could be set to +4412-, where "-" is a wild character.
TABLE 10-9 MAP Error Codes
|
MAP errors |
Error code decimal (hex) |
Brief description |
|
Unknown subscriber |
1 (01) |
No subscription exists. |
|
Unknown MSC |
3 (03) |
|
|
Unknown location area |
4 (04) |
|
|
Unidentified subscriber |
5 (05) |
The database (HLR/VLR) does not contain any entry for this subscriber. It is not possible to determine whether the subscription exists. |
|
Absent subscriber SM |
6 (06) |
MT-SMS transfer cannot be completed because network cannot contact the MS. |
|
Unknown equipment |
7 (07) |
|
|
Roaming not allowed |
8 (08) |
The user is not allowed to roam in an area because of subscription. |
|
Illegal subscriber |
9 (09) |
The subscriber is not allowed to access services, as authentication failed. |
|
Bearer service not provisioned |
10 (a) |
|
|
Teleservices not provisioned |
11 (b) |
|
|
Illegal equipment |
12 (c) |
IMEI check procedure shows that MS is not white-listed. |
|
Call barred |
13 (d) |
|
|
Forwarding violation |
14 (e) |
|
|
CUG reject |
15 (f |
|
|
Illegal SS operation |
16 (10) |
|
|
SS error status |
17 (11) |
|
|
SS not available |
18 (12) |
|
|
SS subscription violation |
19 (13) |
|
|
SS incompatibility |
20 (14) |
|
|
Facility not supported |
21 (15) |
The PLMN/terminal does not support the requested facility. |
|
Invalid target base station |
23 (17) |
|
|
No radio resources available |
24 (18) |
|
|
No handover number available |
25 (19) |
|
|
Subsequent handover failure |
26 (1a) |
|
|
Absent subscriber |
27 (1b) |
|
|
Incompatible terminal |
28 (1c) |
|
|
Short-term denial |
29 (1d) |
|
|
Long-term denial |
30 (1e) |
|
|
Subscriber busy for MT-SMS |
31 (1f) |
MT-SMS transfer cannot be completed because another MT-SMS transfer is going on. |
|
SM delivery failure |
32 (20) |
|
|
Message waiting list full |
33 (21) |
|
|
System failure |
34 (22) |
The requested task cannot be completed because of a problem in another entity. The type of resource or entity may be given in the resource indicator parameter. |
|
Data missing |
35 (23) |
An optional parameter required by the context is missing. |
TABLE 10-9 MAP Error Codes
|
MAP errors |
Error code decimal (hex) |
Brief description |
|
Unexpected Data Value |
36 (24) |
The data type is valid as per specifications but its value or presence is unexpected in the current context. |
|
PW registration failure |
37 (25) |
|
|
Negative PW check |
38 (26) |
|
|
No roaming number available |
39 (27) |
A roaming number cannot be allocated because all available numbers are in use. |
|
Tracing buffer full |
40 (28) 41 (29) |
|
|
Target cell outside group area |
42 (2a) |
|
|
Number of PW attempt violations |
43 (2b) |
|
|
Number changed |
44 (2c) |
The subscription does not exist for that number anymore. |
|
Busy subscriber |
45 (2d) |
|
|
No subscriber reply |
46 (2e) |
|
|
Forwarding failed |
47 (2f) |
|
|
OR not allowed |
48 (30) |
|
|
ATI not allowed |
49 (31) |
Any time interrogation. |
|
No group call number available |
50 (32) |
|
|
Resource limitation |
51 (33) |
|
|
Unauthorized requesting network |
52 (34) |
|
|
Unauthorized LCS client |
53 (35) |
|
|
Position method failure |
54 (36) |
|
|
Unknown or unreachable |
58 (3a) |
|
|
LCS client |
||
|
MM event not supported |
59 (3b) |
|
|
ATSI not allowed |
60 (3c) |
Any time information handling. |
|
ATM not allowed |
61 (3d) |
|
|
Information not available |
62 (3e) |
|
|
Unknown alphabet |
71 (47) |
|
|
User busy |
72 (48) |
The wild character allows capturing of all MSUs with country code 44 and network code 12; the rest of the digits are insignificant. Note that protocol analyzers from different vendors support different wild characters.
■ SCCP called party address MSC serving business district.
3. Capture the traffic for a substantial time, say 15 minutes or more.
4. Stop the protocol analysis session and analyze the return errors.
Generate statistics on error distribution if PA supports this feature.
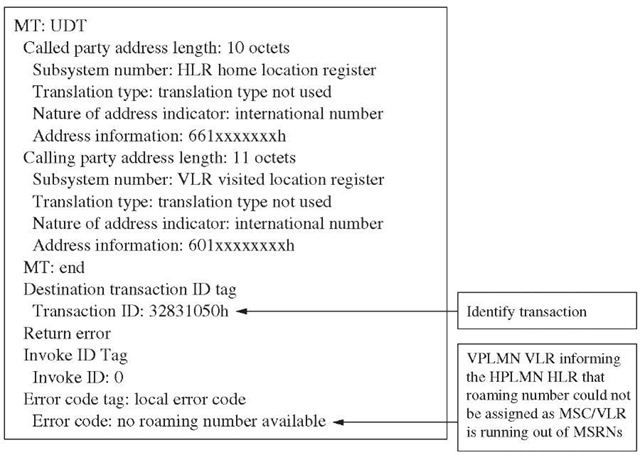
5. In this example (see Figures 10-18 and 10-19), most of the PRN transactions are returned with an error. The error type shows no roaming number available. On further analyzing the traffic by looking at transactions with errors, it is evident that the MSC is running out of roaming numbers.
Problem resolution. The next step is to resolve the problem. Further analysis is required to establish if this problem occurs all the time or occasionally. If it occurs occasionally, what is the pattern, which day of the week, which hour of the day, and so on. Once the facts are established, an appropriate action is taken. For example if the provide roaming number procedure is failing consistently with the return error no roaming number available, it is likely that the MSRN range assigned to the MSC/VLR is not sufficient. The problem can be resolved by adding number blocks to the existing MSRN range.
Figure 10-18 Provide roaming number protocol decodes.
Figure 10-19 Provide roaming number response protocol decodes.