Mobility management
Location update. GSM allows a subscriber to move throughout the coverage area with a capability to make or receive calls. This is possible because the GSM network continuously tracks the movement of a mobile and updates its location all the time. There are three different location-updating scenarios.
■ Attach/initial registration, used when a mobile is turned on
■ Normal/forced registration, initiated when a mobile station moves to a new location area
■ Periodic updates, regular location updates on expiry of a timer. This is required to track those mobile stations the locations of which may be lost because of some reason.
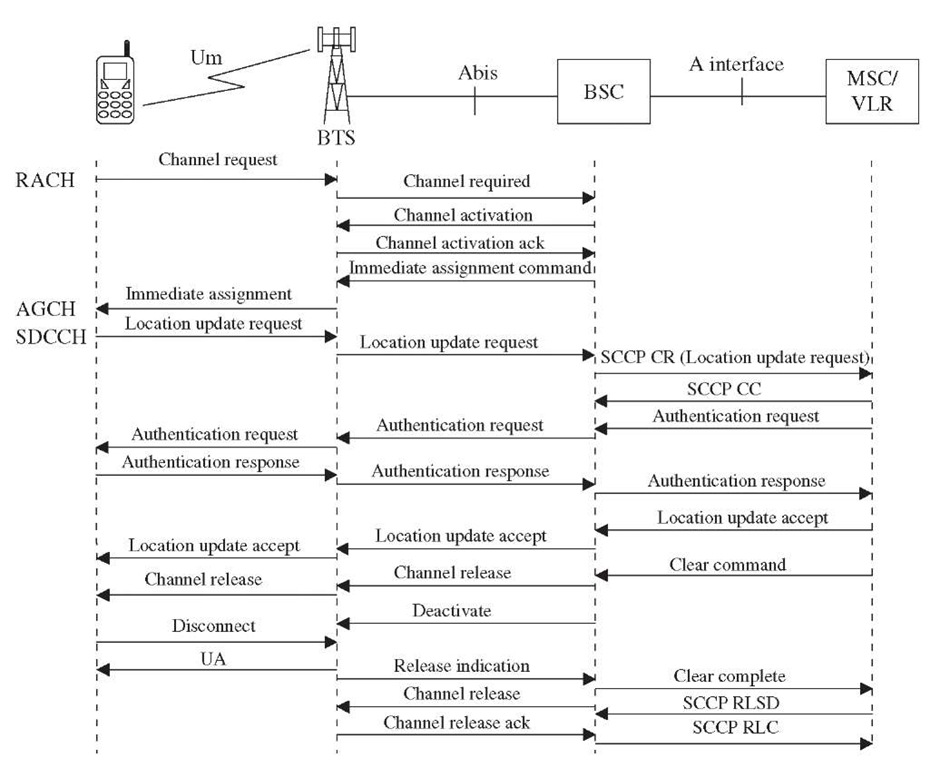
Figure 3-21 shows a location update (LU) procedure involving a mobile station, BTS, BSC, and MSC/VLR. In cases where the LU procedure is triggered because of VLR area change, the HLR and the old MSC/VLR are also involved. In GSM networks, where EIR is implemented and the IMEI check is turned on, additional signaling for verification is involved but is not shown in the figure.
The mobile station initiates the update location procedure by sending a channel request message on the random access channel toward the BTS. The reason for this request is also indicated in the request message. The reason, or establishment cause, in this case is update location. Other examples of establishment causes are voice call establishment and emergency call establishment. The BTS then sends a channel required message to the BSC.
The BSC checks the availability of a free SDCCH and activates it for the MS, using a channel activation message toward the BTS. This message contains the information on reserved channel type and number.
TABLE 3-12 MAP Local Operation Code {Continued)
|
Operation |
Op code |
Description |
|
Mobility management |
||
|
updateLocation |
2 |
This operation code is send by the VLR to update location information stored in the HLR. |
|
cancelLocation |
3 |
The HLR uses this operation code to delete a subscriber record from a VLR/SGSN. For example, when a MS moves to a new VLR area, the HLR informs the old VLR to remove data for the MS. |
|
sendIdentification |
55 |
The new VLR uses this to retrieve the IMSI and authentication data from the old VLR for a subscriber registering in that VLR. |
|
purgeMS |
67 |
The VLR/SGSN sends this to the HLR to request the HLR to mark this MS as not reachable in case of MT call, MT-SMS, or network-initiated PDP context. |
|
updateGprsLocation |
23 |
The SGSN sends this message to update location information stored in the HLR. |
|
noteMMEvent |
89 |
The VLR/SGSN sends this message to the gsmSCF to indicate that a mobility management event has been processed successfully |
|
prepareHandover |
68 |
This is sent by an MSC that needs to hand over a call to another MSC. |
|
sendEndSignal |
29 |
This message is sent by an MSC to another MSC during the process of handover, indicating that radio path has been established to the MS and the recipient MSC can now release the resources. |
|
processAceessSignaling |
33 |
This message is sent by an MSC to pass information received on A interface or Iu interface to another MSC. |
|
forwardAccessSignaling |
34 |
This message is sent by an MSC to forward information to the A interface or Iu interface of another MSC. |
|
prepareSubsequentHandover |
69 |
This message is used by an MSC to inform another MSC that it has been decided to handover to a third MSC. |
|
sendAuthenticateInfo |
56 |
This message is used by the VLR/SGSN to request authentication information from the HLR. |
|
authenticationFailureReport |
15 |
This message is used between VLR/SGSN and the HLR to report authentication failure. |
|
checkIMEI |
43 |
This is used between MSC/SGSN and EIR to request IMEI check. |
|
insertSubscriberData |
7 |
This message is send by an HLR to update a VLR/SGSN with certain subscriber data. |
|
deleteSubscriberData |
8 |
This message is used by an HLR to remove certain subscriber data from the VLR/SGSN. |
TABLE 3-12 MAP Local Operation Code
|
Operation |
Op code |
Description |
|
Mobility management |
||
|
reset |
37 |
This operation code is used by the HLR in case of restart after failure. This is sent to all VLRs and SGSNs for which mobile stations were registered before restart. |
|
forwardCheckSSIndication |
38 |
This operation code is used by the HLR after restart to MS to indicate that a supplementary service parameter may have been altered. This message is sent by the HLR via VLR/MSC. This is an optional capability and implementation dependent. |
|
restoreData |
57 |
This is used by the VLR to synchronize the data with the HLR for a particular IMSI in certain cases. For example, this is invoked by the VLR if it receives a provideRoaming-Number operation code from the HLR for an IMSI that is unknown to the VLR. |
|
anyTimeInterrogation |
71 |
This is used by the gsmSCF to interrogate the HLR for the current state or location of an MS. |
|
provideSubscriberInfo |
70 |
This is used by the HLR to retrieve the MS state or location from the VLR/SGSN. |
|
anyTimeModification |
65 |
This is used by the gsmSCF to request subscription information from the HLR. |
|
anyTimeSubscription-Interrogation |
62 |
This is used by the gsmSCF to request subscription information from the HLR. |
|
noteSubscriberDataModified |
5 |
This is used by the HLR to inform the gsmSCF that the subscriber data has been modified. |
|
Operation and maintenance |
||
|
activateTraceMode |
50 |
When an operator executes a command in an OMC to trace a subscriber, the HLR requests that the VLR/SGSN activate subscriber tracing. The VLR/SGSN waits for the subscriber to become active before tracing can begin in the MSC/SGSN. |
|
deactivateTraceMode |
51 |
This is to deactivate the subscriber tracing in the MSC/SGSN. This operation code is sent by the HLR to the VLR/SGSN on request from the OMC. |
|
sendIMSI |
58 |
On request from the OMC, the VLR in a VPLMN requests the HPLMN HLR to get the IMSI for the subscriber whose MSISDN is known. |
|
Call handling |
||
|
sendRoutingInformation |
22 |
The GMSC/gsmSCF uses this operation in case of a mobile terminating call to interrogate the HLR for routing information. The HLR returns information such as VMSC address and the MSRN assigned to the subscriber. |
TABLE 3-12 MAP Local Operation Code
|
Operation |
Op code |
Description |
|
Call handling |
||
|
provideRoamingNumber |
4 |
On receiving sendRoutingInfo request from the GMSC/gsmSCF, the HLR requests the VLR where the subscriber is currently registered to send assigned MSRN. |
|
Supplementary services |
||
|
registerSS |
10 |
The VLR uses this operation code to enter the supplementary service data for a specific subscriber in the HLR. For example, if a subscriber registers any SS service on the phone, the registration will be passed to the HLR by the MSC and VLR transparently. The SS code parameter in this operation determines the supplementary service to be registered. |
|
eraseSS |
11 |
This is used to delete SS-related data for a specific subscriber in the HLR. |
|
activateSS |
12 |
This is used between VLR and HLR to activate an SS for a specific subscriber. |
|
deactivateSS |
13 |
This is used between VLR and HLR to deactivate an SS that was previously activated for a specific subscriber. |
|
interrogateSS |
14 |
This is used by the VLR to interrogate the status a specified supplementary service in the HLR. |
|
registerPassword |
17 |
This operation is invoked by the VLR toward the HLR on requests from the MS to register a new password or change an existing password. |
|
getPassword |
18 |
This operation is invoked by the HLR to get the password from the MS. This may be required if an MS tries to register an SS that requires a password from the subscriber. The VLR acts transparently and relays the message to the MSC. |
|
processUnstructured-ssRequest |
59 |
This operation is used to handle unstructured supplementary service between two entities. Unstructured SS is an additional means to build new supplementary services not defined by the GSM specifications. This request is sent between MSC and VLR, VLR and HLR, HLR and HLR, or HLR and gsmSCF. |
|
unstructuredSSRequest |
60 |
This operation is used by the requesting entity to get the information from the MS in connection with the handling of an unstructured supplementary service handling. This request is sent between MSC and VLR, VLR and HLR, or HLR and gsmSCF. |
|
unstructuredSSNotify |
61 |
This operation is used by the requesting entity to send a notification to the MS in connection with an unstructured supplementary service handling. This |
TABLE 3-12 MAP Local Operation Code
|
Operation |
Op code |
Description |
|
|
Supplementary services |
|
|
request is sent between MSC and VLR, VLR and HLR, or HLR and gsmSCF. |
||
|
ssInvocationNotify |
72 |
The MSC sends this operation code to the gsmSCF when a subscriber invokes one of the following supplementary services: ■ Call deflection (CD) ■ Explicit call transfer (ECT) ■ Multiparty (MP) |
|
registerCcEntry |
76 |
When a subscriber registers for call completion supplementary service, this operation code is send by the VLR to register the data in the HLR. |
|
eraseCcEntry |
77 |
This is used by the VLR to delete call completion supplementary service data for a specific subscriber in the HLR. |
|
Short message service management |
||
|
sendRoutingInfoForSM |
45 |
In case of MT-SMS, the GMSC sends this message to the HLR to get routing information needed for routing the short message to the serving MSC. |
|
moForwardShortMessage |
46 |
This is used by the serving SGSN/MSC to forward a mobile-originated short message to the interworking MSC for ultimate submission to the SMSC. |
|
reportSmDeliveryStatus |
47 |
This operation code is used between the GMSC and the HLR in case of unsuccessful delivery of SM to a MS. The HLR, on receiving this message, sets the message waiting flag for the MS. Once the serving VLR informs the HLR of contact renewal with the MS by sending the readyForSM message, the HLR resets the flag and sends an alertService Center message to the interworking MSC. |
|
readyForSM |
66 |
See description for reportSmDeliveryStatus. |
|
alertServiceCenter |
64 |
See description for reportSmDeliveryStatus. |
|
informServiceCenter |
63 |
This is used by the HLR to inform GMSC that the status of the subscriber for whom routing information is requested is not reachable. |
|
mtForwardShortMessage |
44 |
This is used by the GMSC to forward a mobile terminating short message to the serving MSC/SGSN. |
|
Network requested PDP context activation |
||
|
sendRoutingInfoForGPRS |
24 |
This operation is invoked by the GGSN to get the routing information from the HLR. |
|
failureReport |
25 |
This is used by the GGSN to inform the HLR that network-initiated PDP context activation was not successful. |
|
noteMsPresentForGPRS |
26 |
This is used by the HLR to inform the GPRS of the availability of an MS. |
TABLE 3-12 MAP Local Operation Code
|
Operation |
Op code |
Description |
|
Location service management |
||
|
sendRoutinglnforforLCS |
85 |
This operation code is sent to the HLR by the GMLC to retrieve the routing information needed for routing a location service request to serving MSC/SGSN. |
|
provideSubscriberLocation |
83 |
This is used by the GMLC to request the location of a specified MS from the SGSN/VLR. |
|
subscriberLocationReport |
86 |
This message is sent by the SGSN/MSC to the GMLC to provide the location of a specified MS. This is invoked in response to the message provideSubscriberLocation. |
On receiving the acknowledgment from the BTS on channel activation, the BSC sends the immediate assignment command on the AGCH. The MS then moves to the assigned SDCCH and activates a Layer 2 connection by sending a LAPD SABM message, which also includes location update request. The location update request message contains several information elements, including the type of update location (attach, periodic, or normal), old LAI, IMSI, or TMSI. The BTS confirms the LAPD connection by sending an unnumbered acknowledgment. The BTS then passes the location update request to the BSC in an establish indication message.
The BSC processes the establish indication message, adds necessary information such as new LAI, and then establishes the SCCP connection (connection-oriented) with the MSC by sending a connection request (CR) message. The CR message also carries a location update request. The MSC acknowledges the CR message by sending a connection confirmed (CC) message.
The MSC/VLR sends the authentication request to the BSC, using the previously established SCCP connection. The BSC passes this request to the MS transparently. The authentication request message contains two important parameters: a 128-bit random number (RAND) and a 3-bits ciphering key sequence number (CKSN). The SIM within MS uses RAND and Ki, which is stored in SIM to calculate signed response (SRES) based on the A3 algorithm. The MS sends the SRES value as a parameter within the authentication response message to the MSC/VLR.
The VLR compares the SRES received from the MS to the SRES value available within it as a result of a previous send authentication procedure with the HLR/AuC. The MS is successfully authenticated if the two values match.
Figure 3-21 Location update procedure.
On successful authentication, if the ciphering is active, then the MSC/ VLR initiates a ciphering mode setting procedure by sending a ciphering mode command to the BTS. This message contains the cipher key (Kc) and algorithm to calculate ciphering key. The BTS extracts and stores the cipher key before passing this message to the MS. The MS, on receiving this message, calculates the value of Kc, using Ki and RAND. The Ki and RAND are the same parameters, which were received previously during the authentication procedure. The algorithm used for the Kc computation is A8.
From this point onward, the MS starts ciphering all the data toward the BTS, using the A5 algorithm, as shown in Figure 3-22. The MS indicates to the BTS that ciphering has started by sending a ciphering mode complete message. The network also started ciphering all the data toward the MS. The BTS then sends ciphering mode complete in the Layer 3 data indication (DI) frame.
In cases where an IMEI check is enabled, then MSC/VLR requests the MS to provide its IMEI by sending an identity request message. The IMEI check, however, can be performed any time during the Update Location scenario. The MS responds back with an identity response message, which contains the MS’s IMEI. The received IMEI is compared with the IMEI stored in the EIR.
Any time during the update location procedure, MSC/VLR assigns a new TMSI to the MS for security reasons, using the TMSI reallocation command. The TMSI can also be assigned at the end within a location update accepted message from the MSC/VLR. In any case, the MS acknowledges receipt of the new TMSI by sending a TMSI reallocation complete message to the MSC/VLR.
The MSC/VLR concludes the location update procedure by sending location update accepted message transparently to the MS. The VLR is now updated with the new LAI.
The network (MSC/VLR) initiates the release of the control channel by sending a clear command message to the BSC. The BSC then instructs the BTS to release the channel by sending a channel release message in a data request frame. The BTS passes this message to the MS. The BSC also requests the BTS to stop sending SACCH messages by sending deactivate SACCH message. The MS, on receiving the channel release message from the BTS, confirms the release by sending a LAPDm disconnect message. The BTS sends a release indication message to the BSC. After link disconnection is achieved, the RF channel is released on instructions from the BSC using RF channel release message. On receiving acknowledgment from the BSC with the RF channel release acknowledge message, the BSC informs the MSC, using a clear complete message.