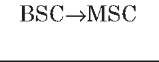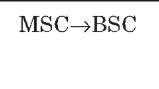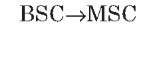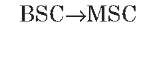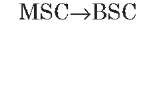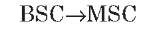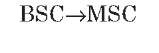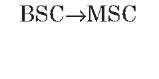A interface
The A interface is the interface between the BSC and the MSC. At the physical layer, it uses a 2-Mbps PCM30 link. One or more 64-Kbps timeslots are used to carry signaling information. Typically, more than one 2-Mbps link is required to handle the traffic between the BSC and the MSC.
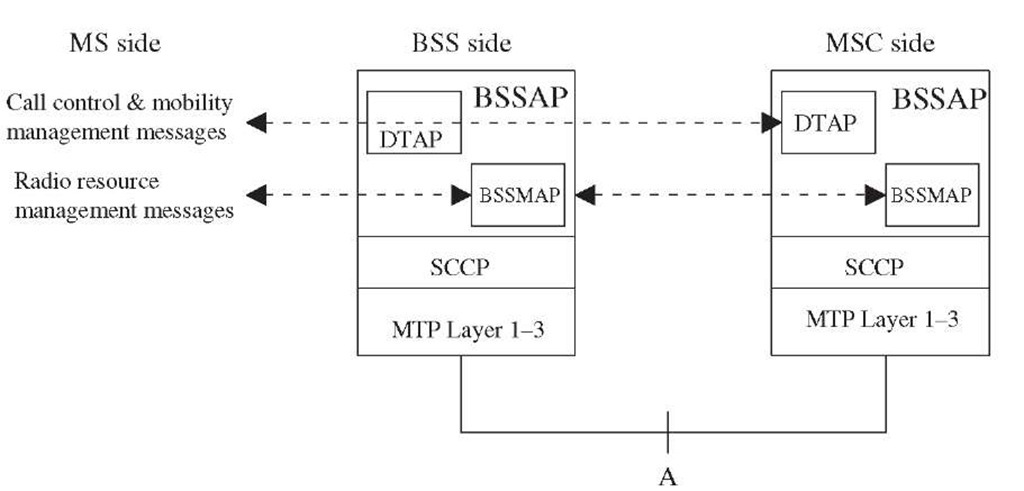
The Base Station System Application Part (BSSAP) is a GSM-specific protocol designed for signaling over the A interface. The BSSAP uses CCS7 MTP and SCCP transport and addressing services for the signaling message transfer. The BSSAP supports both connectionless and connection-oriented services provided by the SCCP. The connectionless services are used to support global procedure such as PAGING (for MS) and RESET (a circuit). The connection-oriented services are used for dedicated procedures such as handover and assignment procedures. The BSSAP supports messages sent between the MSC and the BSS, as well as transparent message transfer between the MSC and the MS. To enable this functionality, the BSSAP is divided into two parts, i.e., the Base Station Subsystem Management Application Part (BSSMAP) and Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP).
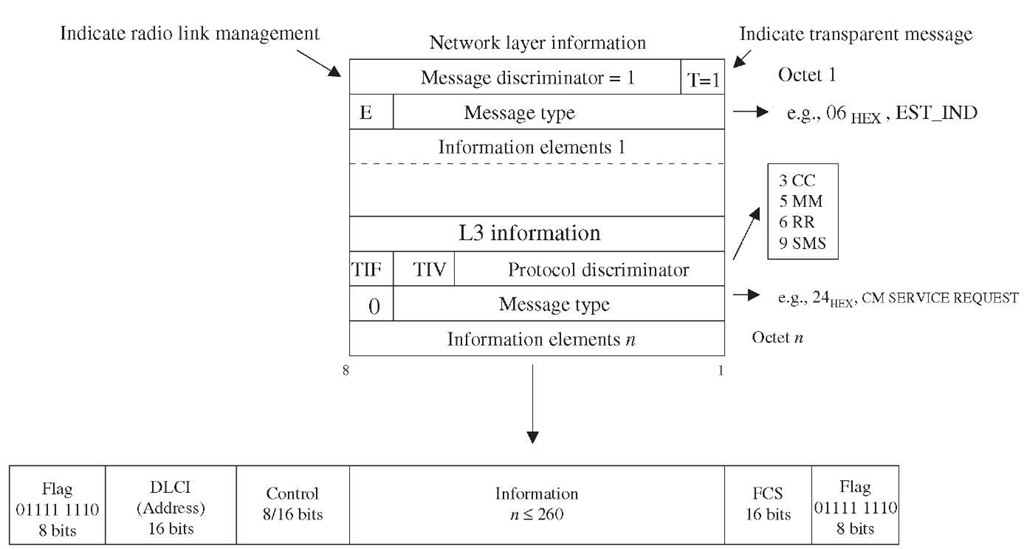
Figure 3-17 Transparent Layer 3 message over Abis.
TABLE 3-10 Abis Layer 3 Messages
|
RLM |
CCM |
TRXM |
DCM |
|
DATAREQuest |
BCCH |
RF REsource |
CHANnel ACTivation |
|
INFOrmation |
INDication |
||
|
DATAINDication |
CCCH LOAD |
SACCH |
CHANnel ACTivation |
|
INDication |
FILling |
ACKnowledge |
|
|
ERROR |
CHANnel |
OVERLOAD |
CHANnel ACTivation |
|
INDication |
REQuired |
Negative ACKnowledge |
|
|
ESTablish |
DELETE |
ERROR |
CONNection FAILure |
|
REQuest |
INDication |
REPORT |
INDication |
|
ESTablish |
PAGING |
DEACTivate SACCH |
|
|
CONFirm |
CoMmand |
||
|
ESTablish |
IMMEDIATE |
ENCRyption CoMmand |
|
|
INDication |
ASSign CoMmand |
||
|
RELease |
SMS Broadcast |
HANDOver DETection |
|
|
REQuest |
REQuest |
||
|
RELease |
MEASurement RESult |
||
|
CONFirm |
|||
|
RELease |
MODE MODIFY |
||
|
INDication |
REQuest |
||
|
UNIT DATA |
MODE MODIFY |
||
|
REQuest |
ACKnowledge |
||
|
UNIT DATA |
PHYsical CONTEXT |
||
|
INDication |
REQuest |
||
|
PHYsical CONTEXT |
|||
|
CONFirm |
|||
|
RF CHANnel RELease |
|||
|
MS POWER |
|||
|
CONTROL |
|||
|
BS POWER |
|||
|
CONTROL |
|||
|
PREPROCess |
|||
|
CONFIGure |
|||
|
PREPROCessed |
|||
|
MEASurement RESult |
|||
|
RF CHANnel RELease |
|||
|
ACKnowledge |
Figure 3-18 illustrates the protocol stack on the MSC and the BSC side. The MM and CM sublayer signaling information from the MS is routed to the BSS transparently over the signaling channels (FACCH, DACCH, SACCH). From the BSS, this information is relayed to the MSC by DTAP. The DTAP uses SCCP logical connection to transfer the information to the peer MM or CC entity in the MSC.
BSS management application part. The BSSMAP data are part of Layer 3 and carry messages related to radio resource and the BSC management. The BSSMAP process within the BSC controls the radio resources in response to the instructions given by the MSC. Examples of BSSMAP messages are paging, handover request, reset, and block. Table 3-11 lists the BSSMAP messages.
Figure 3-18 A-interface signaling protocol.
Direct transfer application part. The DTAP data is user information and carries messages related to call control and mobility management between two users, i.e., MS and any subsystem of NSS such as the MSC. The messages are transparent to BSS except for a few exceptions. These exceptions are location update request, CM service request, and IMSI detach indication. These messages are partially processed by the BSC to add necessary information required for other entities to process these requests.
The DTAP messages are identical to the transparent MM and CM messages listed in the previous section.
Inter-MSC signaling
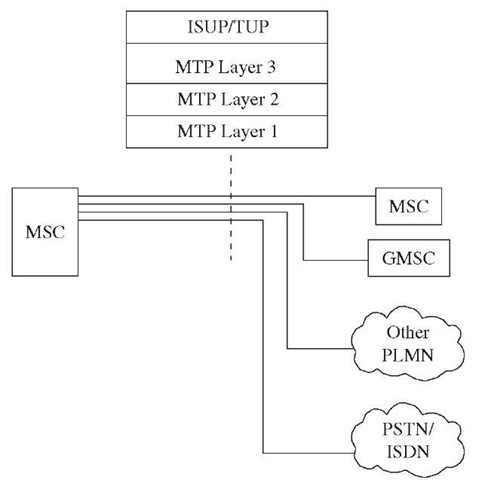
For call control, an MSC may have signaling interfaces to other MSC, GMSC, PLMN, and PSTN. Figure 3-19 shows the protocol stack used on these interfaces. ITU-T ISUP or TUP protocol is used for call setup and supervision. TUP is an old protocol and may not be used in newer implementations. ISUP is used for both speech and data call setup. ISUP relies on the MTP protocol for transportation, addressing, and routing of call control messages.
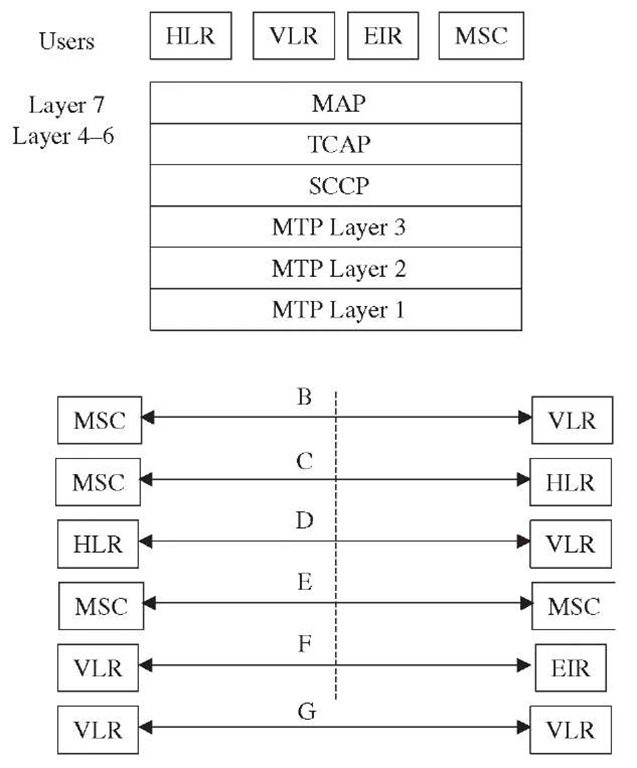
The MSC also has interfaces with the VLR, HLR, EIR ,GMSC, and interworking MSCs for non-circuit-related call control. Figure 3-20 shows this interface and protocol stack. The GSM Mobile Application Part (MAP) has been specifically designed for transfer of non-circuit-related signaling information between MSCs and between MSCs and databases. MAP relies on TCAP capabilities to establish non-circuit-related communication between two entities in the signaling network to exchange data and control information.
TABLE 3-11 BSSMAP Messages
TABLE 3-11 BSSMAP Messages
TABLE 3-11 BSSMAP Messages
An unsuccessful response to the previously received CIPH MOD CMD.
Figure 3-19 Circuit-switched call—protocol stack.
Figure 3-20 Noncircuit call control protocol stack.
TCAP in turn relies on SCCP addressing and MTP transport capabilities.
MAP is also used between the VLR and the HLR. The B interface between the MSC and the VLR is an internal interface in most of the implementations.
The communication between applications and the MAP is done via MAP services or local operation codes defined in the GSM MAP specification. Table 3-12 lists local operation codes and their functions.
The local operation codes defined for the MAP operation on the B interface (MSC-VLR) are not listed in Table 3-12. The B interface is an internal interface and is not visible in most implementations. The GSM recommendations do not encourage the use of this interface and have not updated specifications for this interface since Release 99.