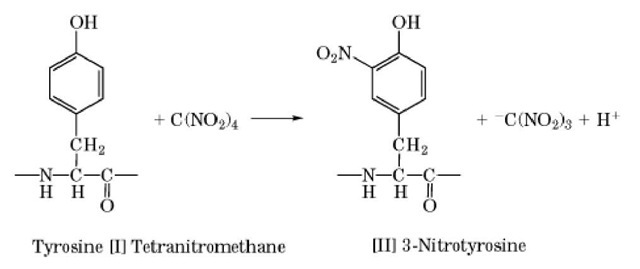
Tyrosine residues are nitrated with tetranitromethane (TNM) [I] to form 3-nitrotyrosine residues [II] under mild conditions (Scheme 1) (1):3-Nitrotyrosine is colored, with an absorbance maximum at 428 nm at alkaline pH, and can be utilized as a reporter group. TNM also oxidizes thiol groups at low pH. The nitration reaction often causes protein polymerization, especially at high protein concentration. The modified nitrotyrosine residue is reduced with sodium hydrosulfite to an aminotyrosine residue, which then can be subjected to further modifications.
Nitration (Molecular Biology)
Next post: Nitric Oxide Part 1 (Molecular Biology)
Previous post: Ninhydrin (Molecular Biology)