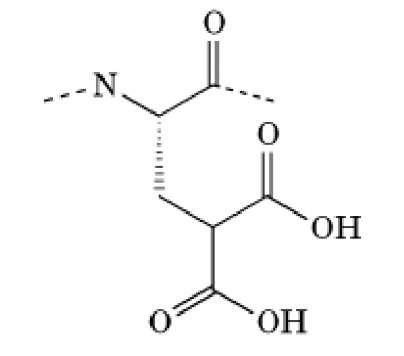
G-Carboxyglutamic acid residues are found within the highly homologous N-terminal domains of various vitamin K_dependent proteins (see Calcium-Binding Proteins). Such residues are generally abbreviated as "Gla"; their structure is depicted in Figure 1. Gla residues are the result of a post- translational modification of glutamic acid residues by a vitamin K-dependent carboxylase, also known as g-glutamyl carboxylase, which introduces a second carboxyl group into the side chain. The two carboxyl groups give this amino acid considerable affinity for cations, especially Ca , as in the chelators EDTA and EGTA. This modification is required for the calcium-mediated interaction of the Gla proteins with the negatively charged phospholipid membrane and is also essential for the formation of the native protein conformation.
Figure 1. Molecular structure of a g-carboxyglutamic acid residue.