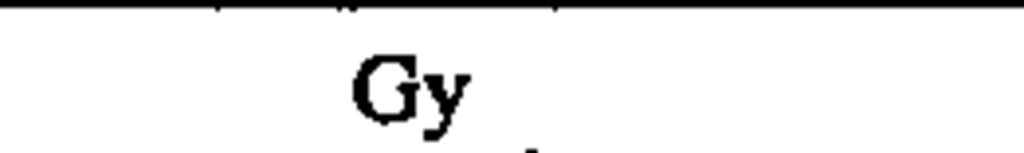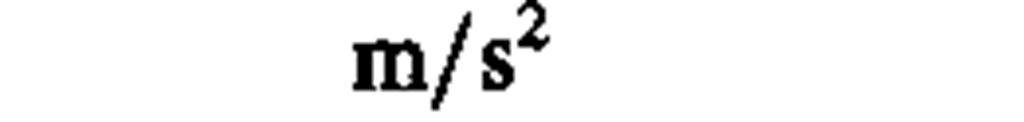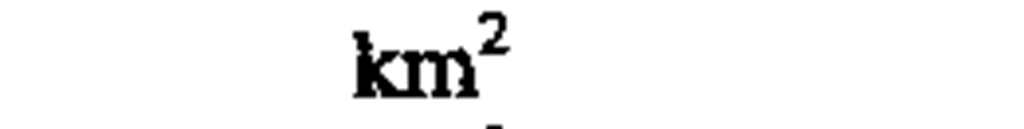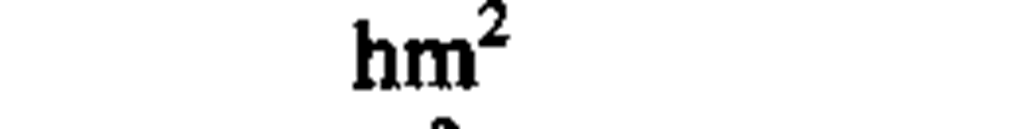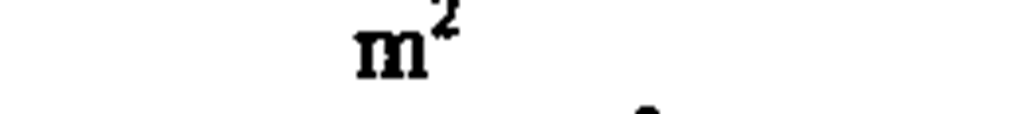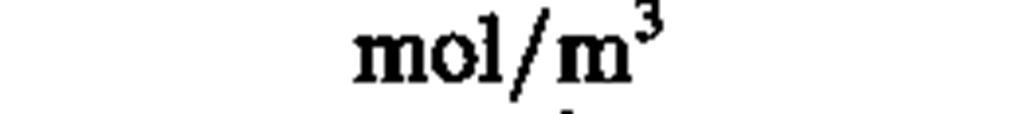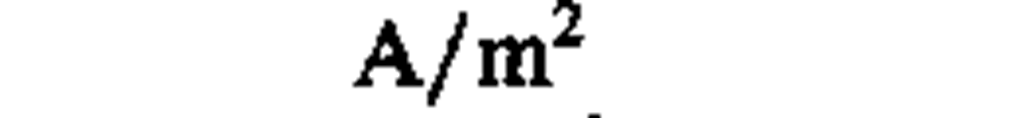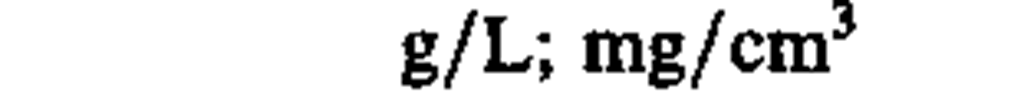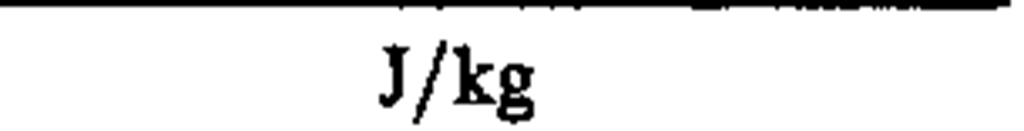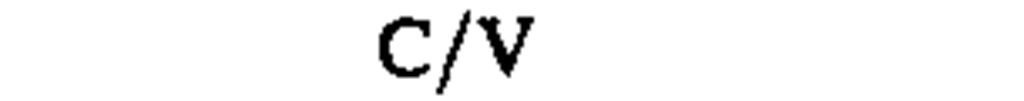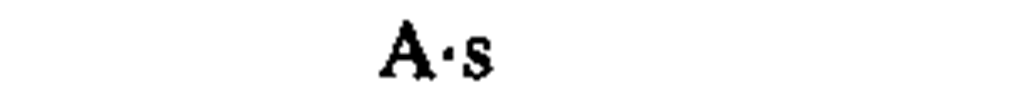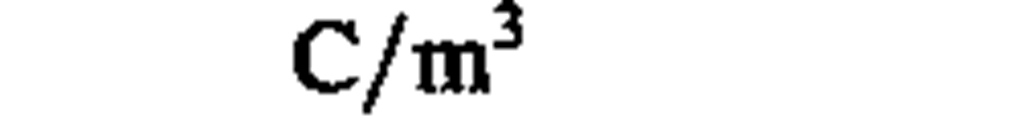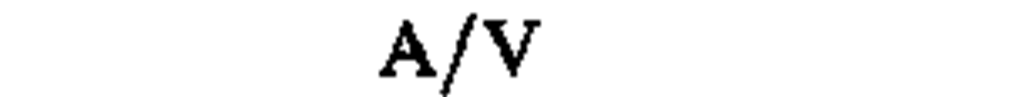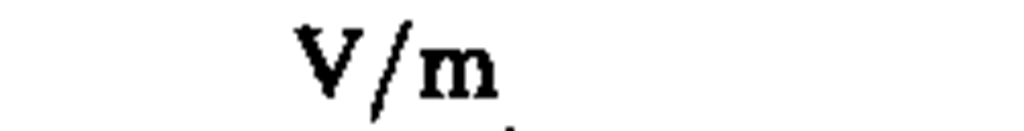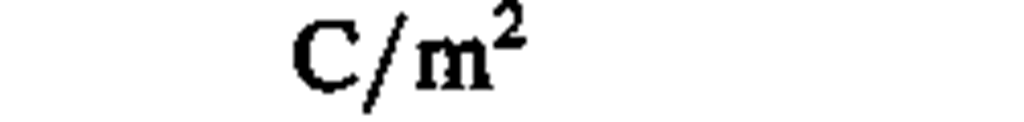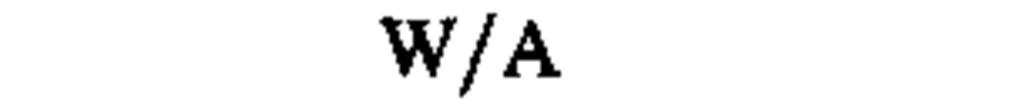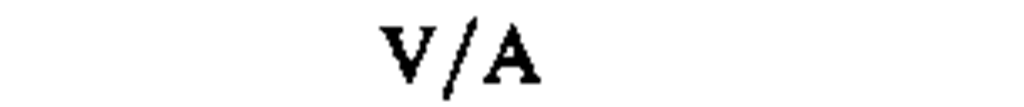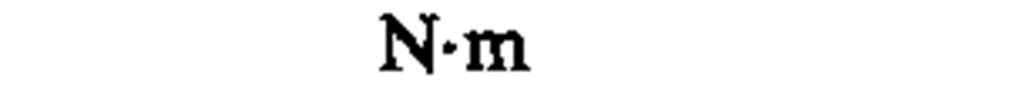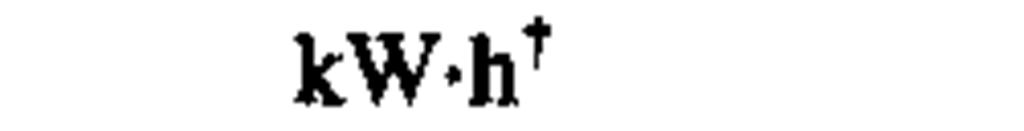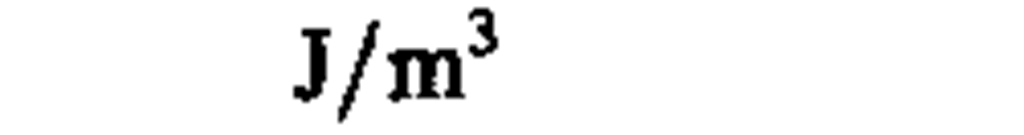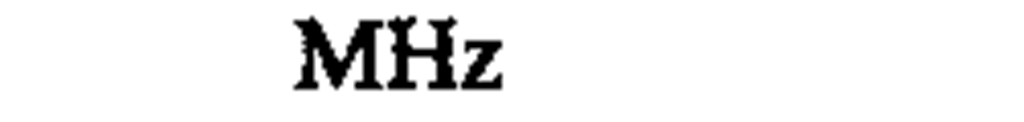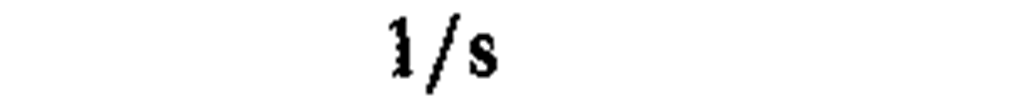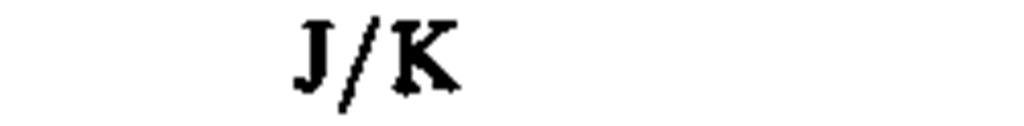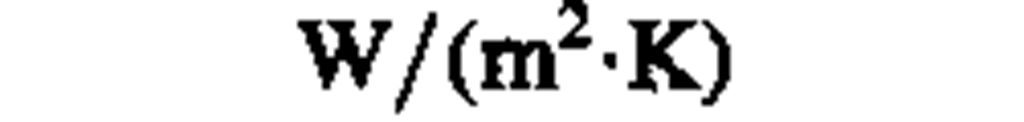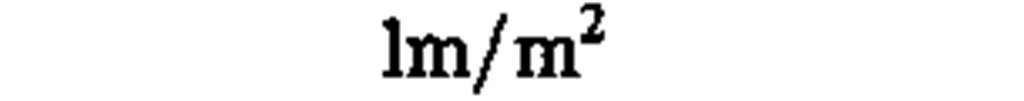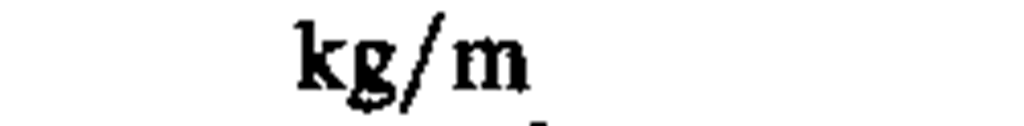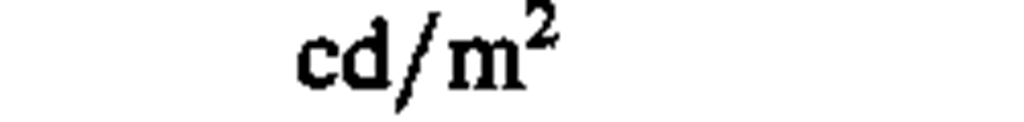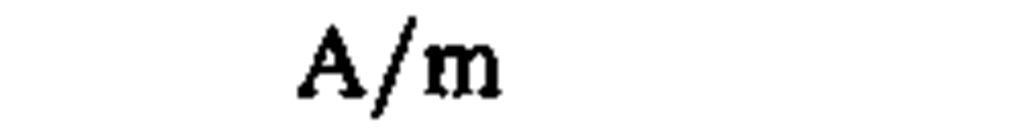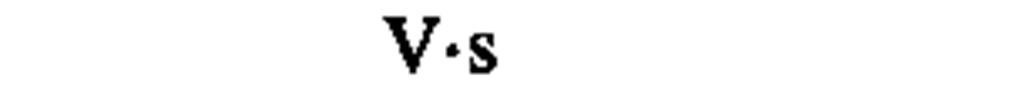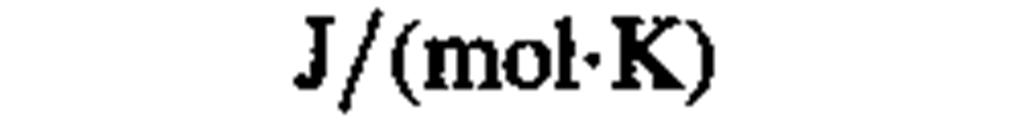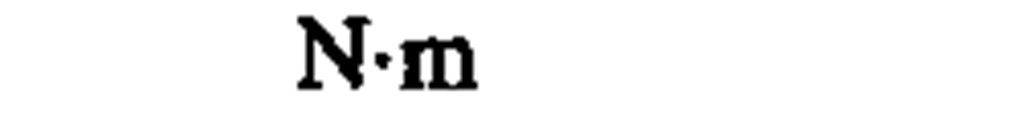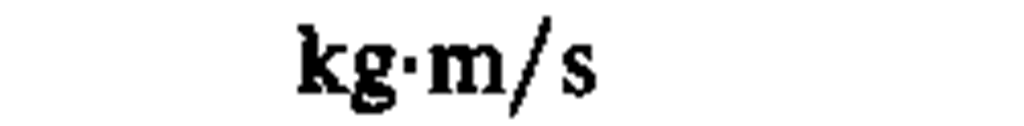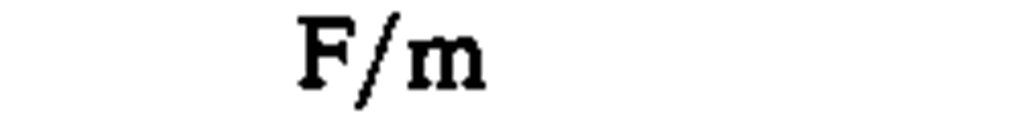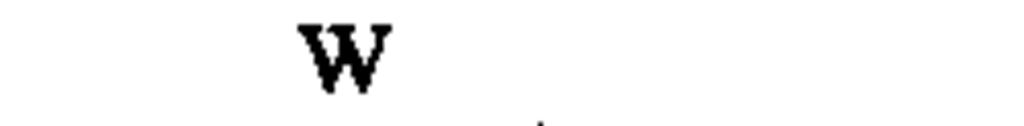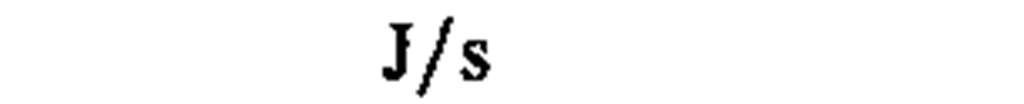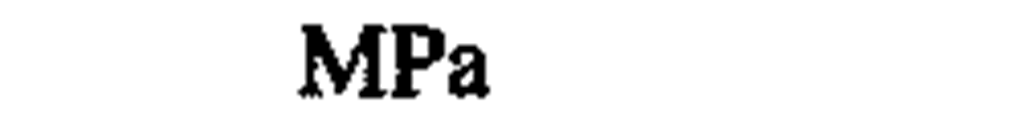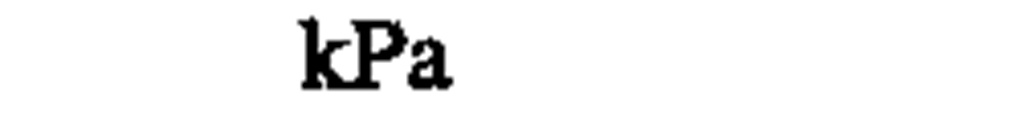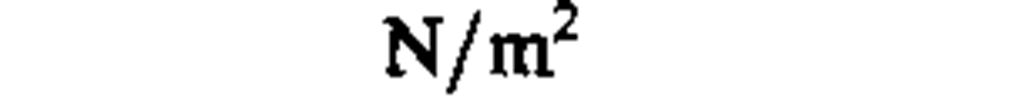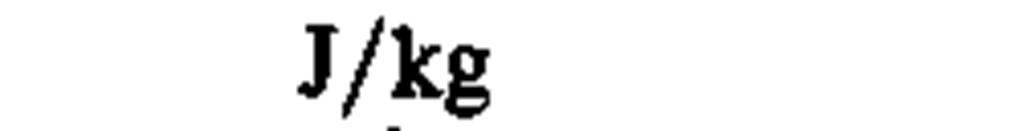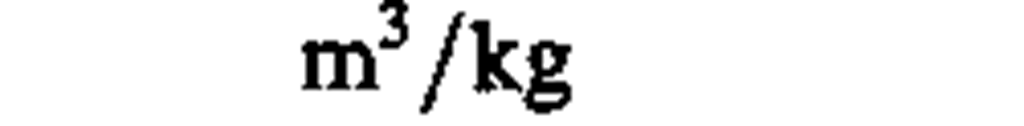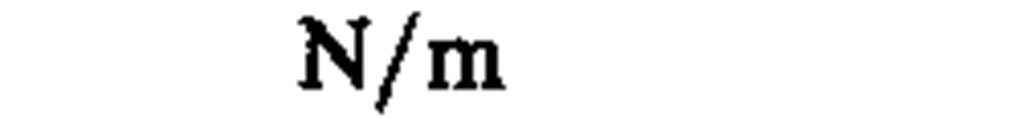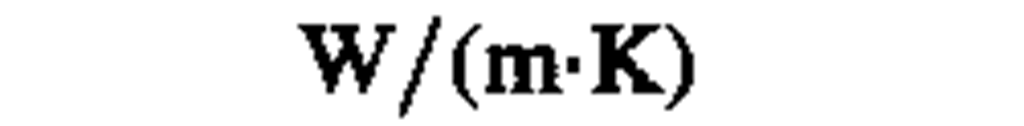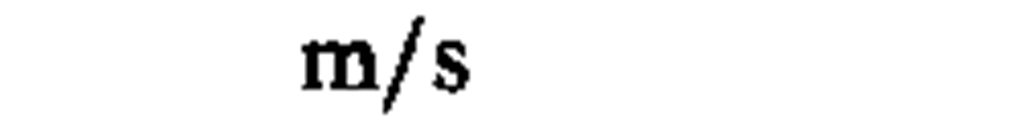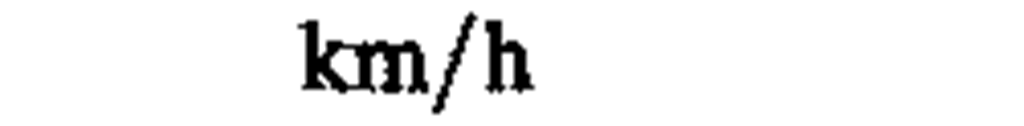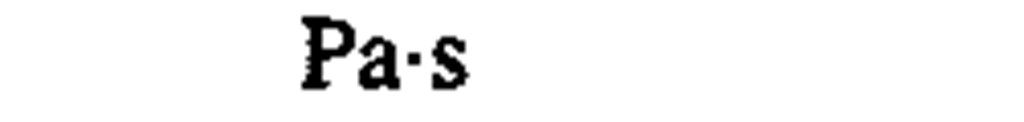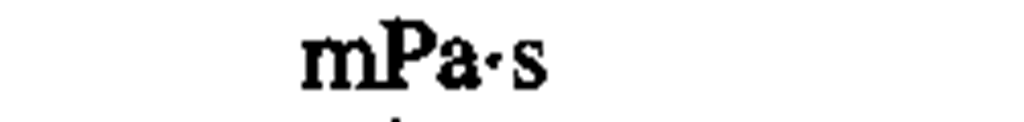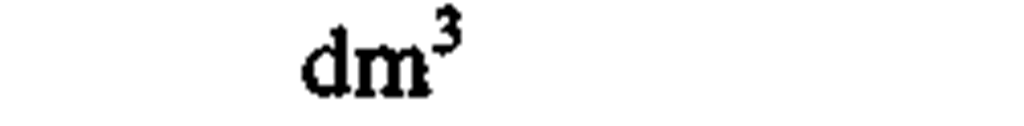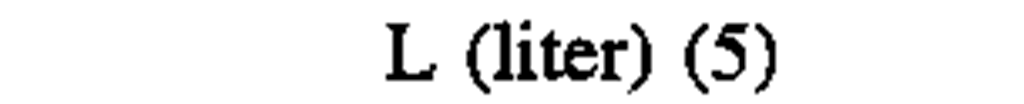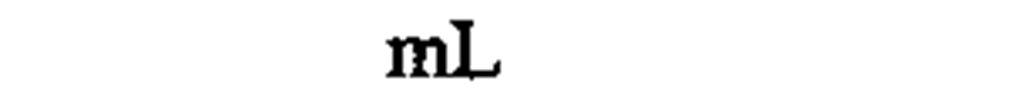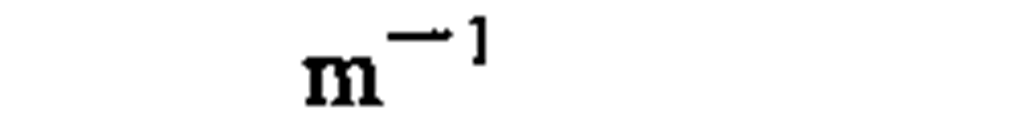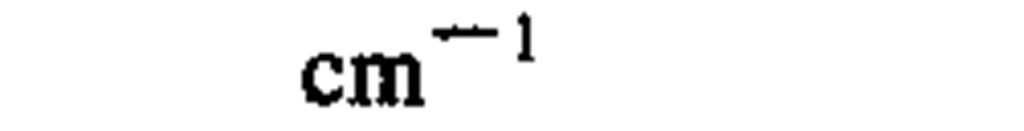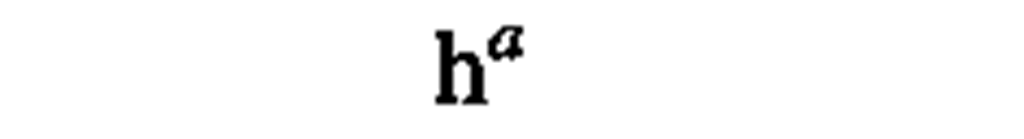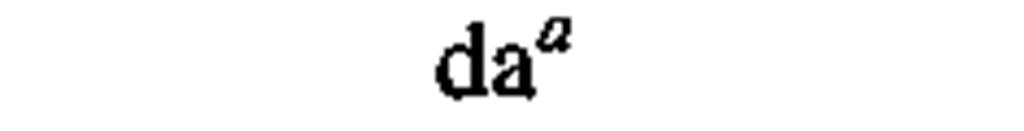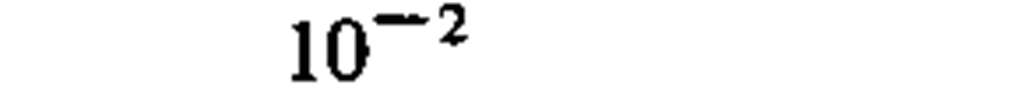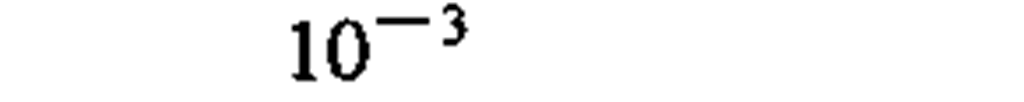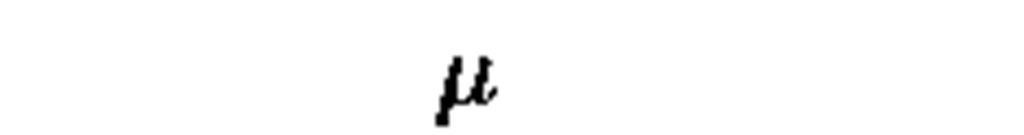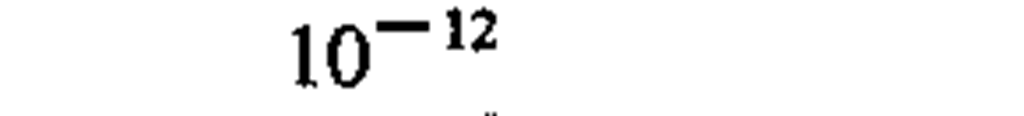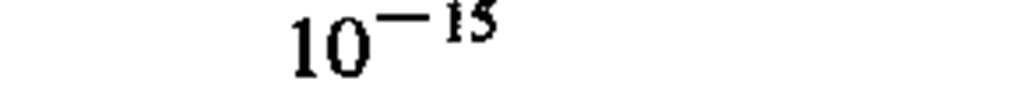CONVERSION FACTORS Part 1 (Molecular Biology)
SI Units (Adopted 1960)
The International System of Units (abbreviated SI), is being implemented throughout the world. This measurement system is a modernized version of the MKSA (meter, kilogram, second, ampere) system, and its details are published and controlled by an international treaty organization (The International Bureau of Weights and Measures) (1). SI units are divide^ into three classes:
BASE UNITS
|
length
|
 |
|
mass "
|
kilogram (kg)
|
|
time
|
second (s)
|
|
electric current
|
ampere (A)
|
|
thermodynamic temperature*
|
kelvin (K)
|
|
amount of substance
|
mole (mol)
|
|
luminous intensity
|
candela (cd)
|
SUPPLEMENTARY UNITS
|
plane angle
|
radian (rad)
|
|
solid angle
|
steradian (sr)
|
DERIVED UNITS AND OTHER ACCEPTABLE UNITS
These units are formed by combining base units, supplementary units, and other derived units (2-4). Those derived units having special names and symbols are marked with an asterisk in the list below.
|
Quantity
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Acceptable equivalent
|
|
absorbed dose
|
gray
|
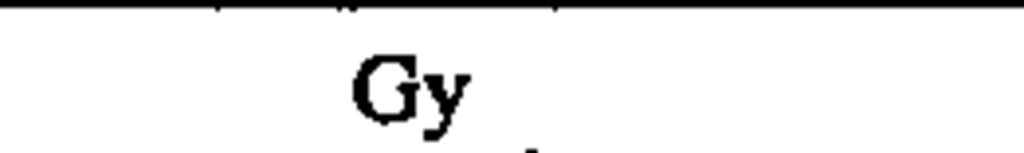 |
J/kg
|
|
acceleration
|
meter per second squared
|
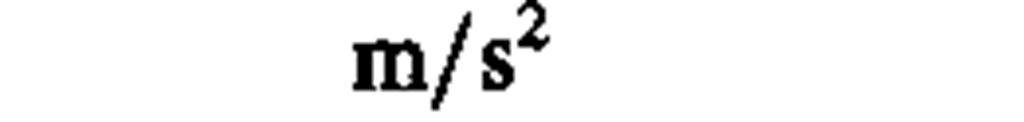 |
|
|
activity (of a radionuclide)
|
becquerel
|
 |
1/8
|
|
area
|
square kilometer
|
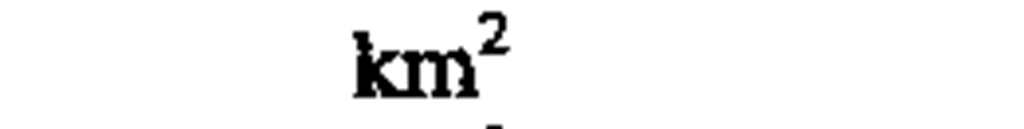 |
|
|
|
square hectometer
|
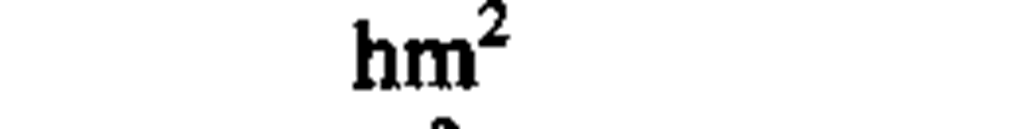 |
ha (hectare)
|
|
|
square meter
|
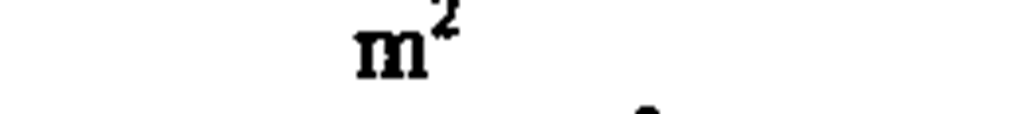 |
|
|
concentration (of amount of substance)
|
mole per cubic meter
|
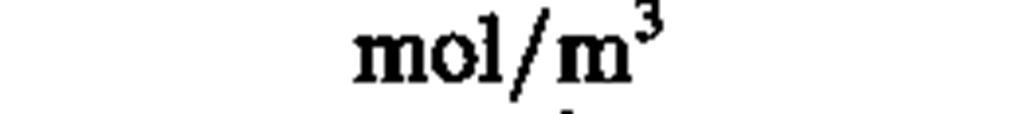 |
|
|
current density
|
ampere per square meter
|
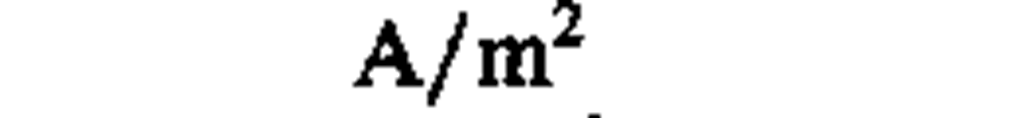 |
|
|
density, mass density
|
kilogram per cubic meter
|
 |
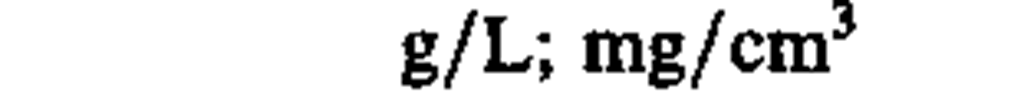 |
|
dipole moment (quantity)
|
coulomb meter
|
 |
|
|
Quantity
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Acceptable equivalent
|
|
dose equivalent
|
sievert
|
 |
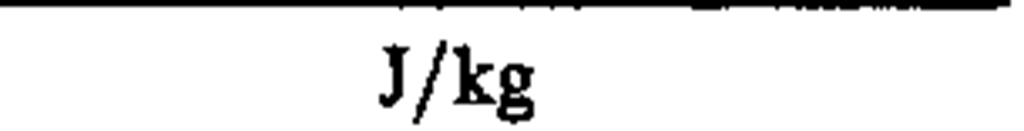 |
|
electric capacitance
|
farad
|
 |
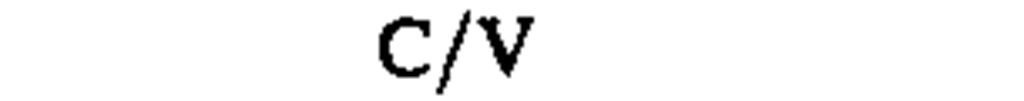 |
|
electric charge, quantity of electricity
|
coulomb
|
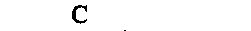 |
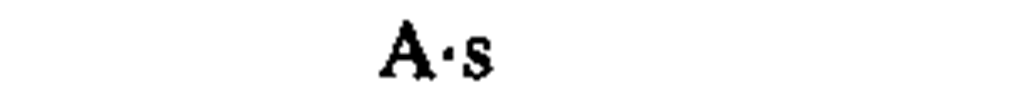 |
|
electric charge density
|
coulomb per cubic meter
|
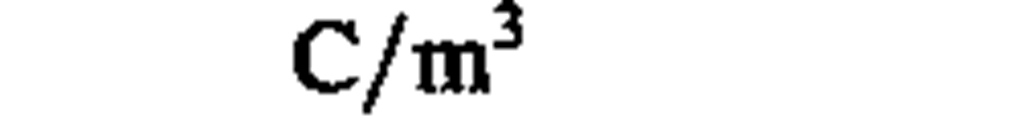 |
 |
|
♦electric conductance
|
siemens
|
 |
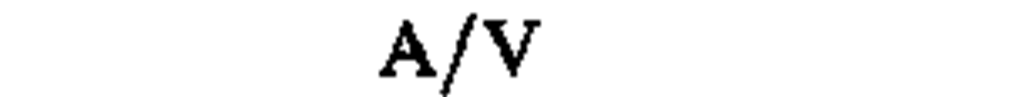 |
|
electric field strength
|
volt per meter
|
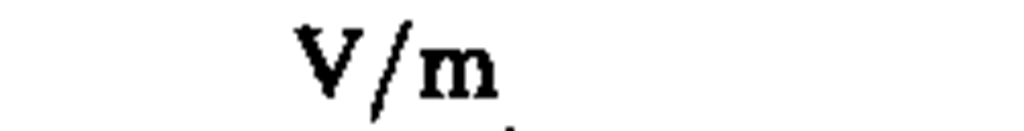 |
 |
|
electric flux density
|
coulomb per square meter
|
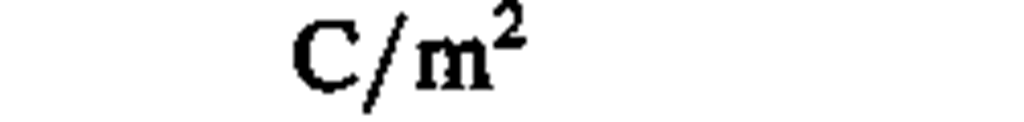 |
 |
|
♦electric potential, potential difference,
|
volt
|
 |
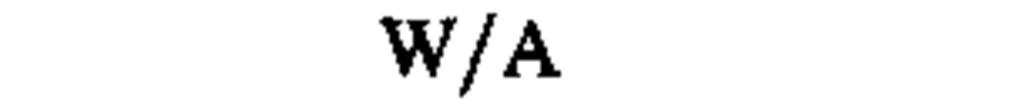 |
|
electromotive force
|
|
 |
 |
|
♦electric resistance
|
ohm
|
 |
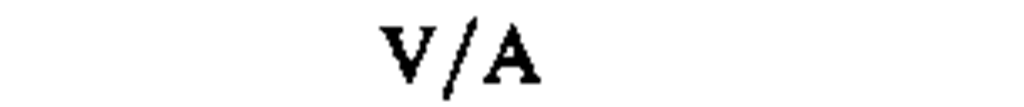 |
|
♦energy, work, quantity of heat
|
megajoule
|
 |
 |
|
|
kilojoule
|
 |
 |
|
|
joule
|
 |
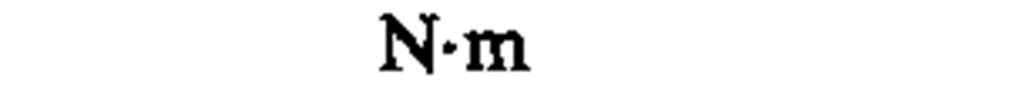 |
|
|
electronvolt1
|
 |
 |
|
|
kilowatt-hour*
|
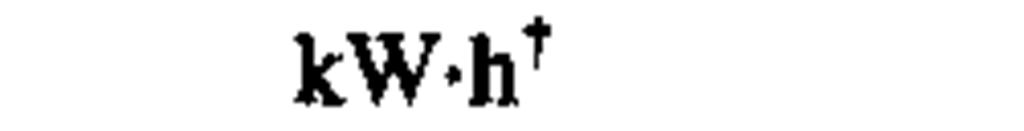 |
 |
|
energy density
|
joule per cubic meter
|
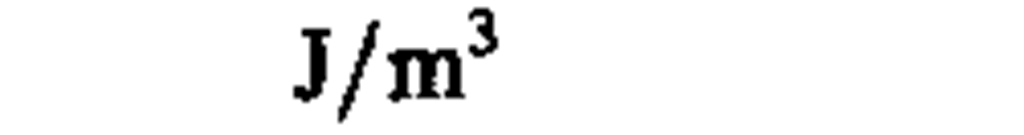 |
 |
|
♦force
|
kilonewton
|
 |
 |
|
|
newton
|
 |
 |
|
♦frequency
|
megahertz
|
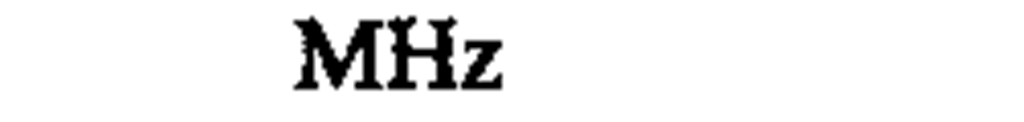 |
 |
|
|
hertz
|
 |
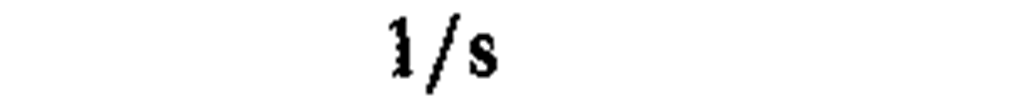 |
|
heat capacity, entropy
|
joule per kelvin
|
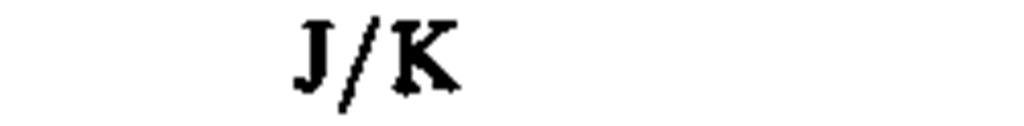 |
 |
|
heat capacity (specific), specific entropy
|
joule per kilogram kelvin
|
 |
 |
|
heat-transfer coefficient "
|
watt per square meter kelvin
|
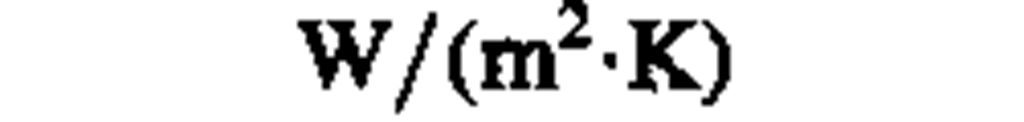 |
 |
|
♦illuminance
|
lux
|
 |
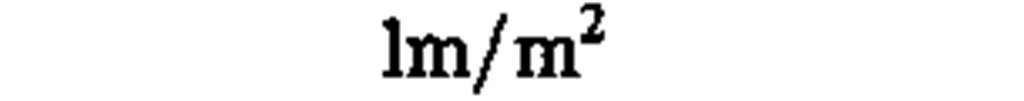 |
|
♦inductance
|
henry
|
 |
 |
|
linear density
|
kilogram per meter
|
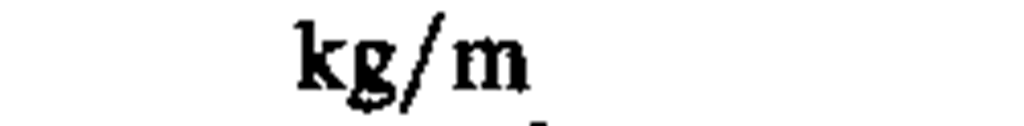 |
 |
|
luminance
|
candela per square meter
|
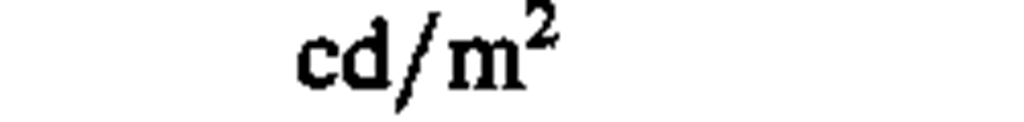 |
 |
|
♦luminous flux
|
lumen
|
 |
 |
|
magnetic field strength
|
ampere per meter
|
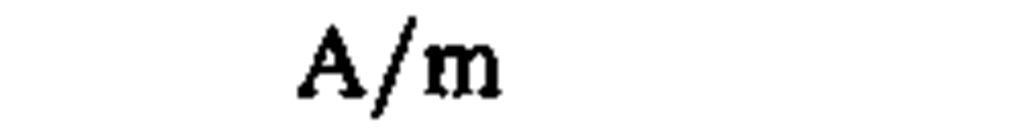 |
 |
|
♦magnetic flux
|
weber
|
 |
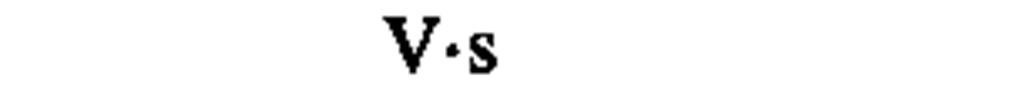 |
|
♦magnetic flux density
|
tesla
|
 |
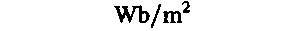 |
|
molar energy
|
joule per mole
|
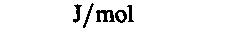 |
 |
|
molar entropy, molar heat capacity
|
joule per mole kelvin
|
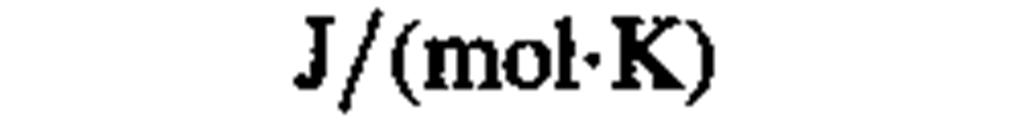 |
 |
|
moment of force, torque
|
newton meter
|
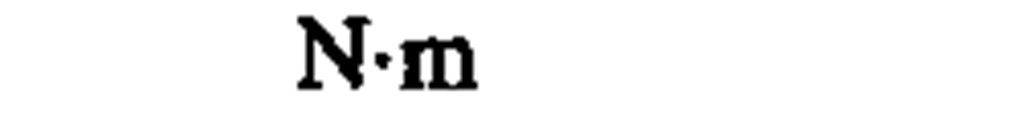 |
 |
|
momentum
|
kilogram meter per second
|
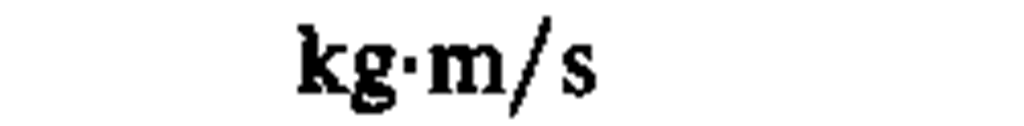 |
 |
|
permeability
|
henry per meter
|
 |
 |
|
permittivity
|
farad per meter
|
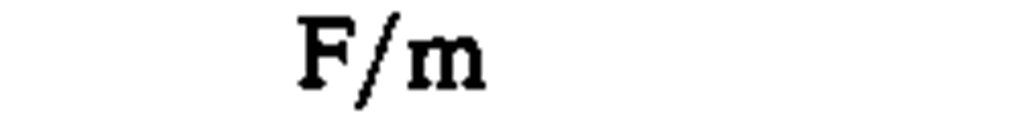 |
 |
|
♦power, heat flow rate, radiant flux
|
kilowatt
|
 |
 |
|
|
watt
|
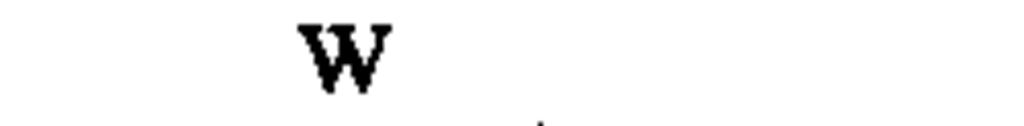 |
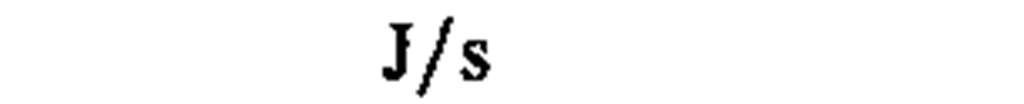 |
|
power density, heat flux density,
|
watt per square meter
|
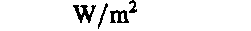 |
 |
|
irradiance
|
|
 |
 |
|
♦pressure, stress
|
megapascal
|
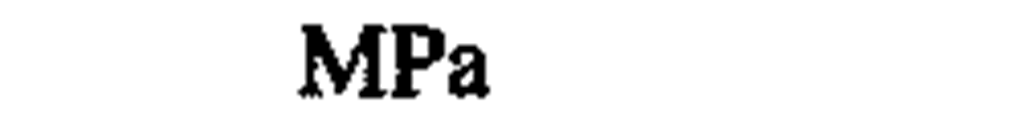 |
 |
|
|
kilopascal
|
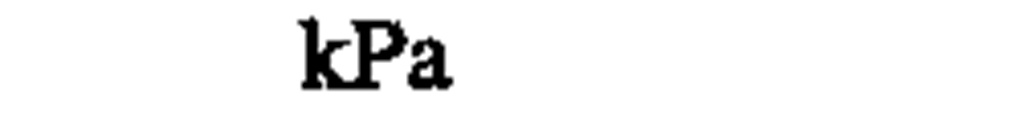 |
 |
|
|
pascal
|
 |
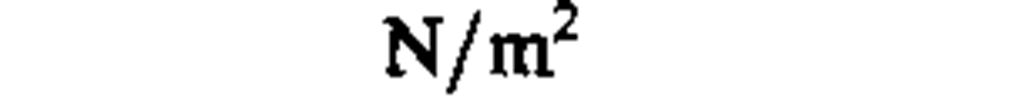 |
|
sound level
|
decibel
|
 |
 |
|
specific energy
|
joule per kilogram
|
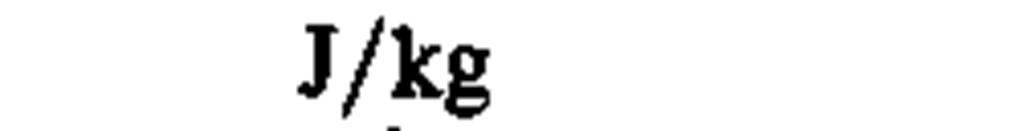 |
 |
|
specific volume
|
cubic meter per kilogram
|
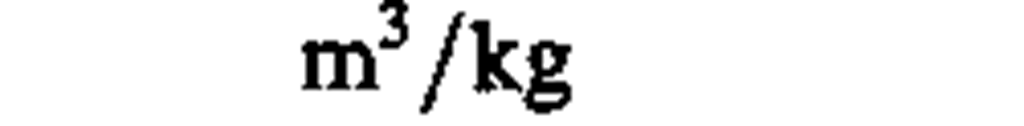 |
 |
|
surface tension
|
newton per meter
|
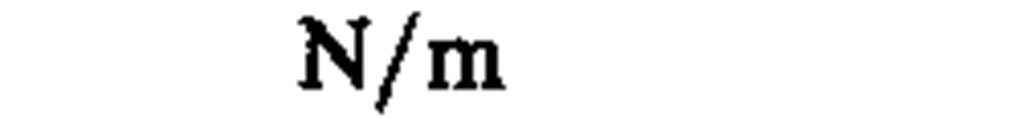 |
 |
|
thermal conductivity
|
watt per meter kelvin
|
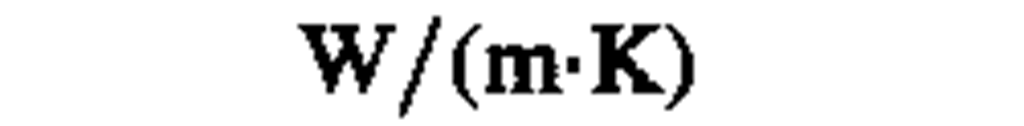 |
 |
|
velocity
|
meter per second
|
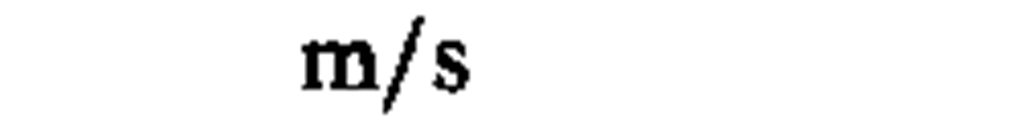 |
 |
|
|
kilometer per hour
|
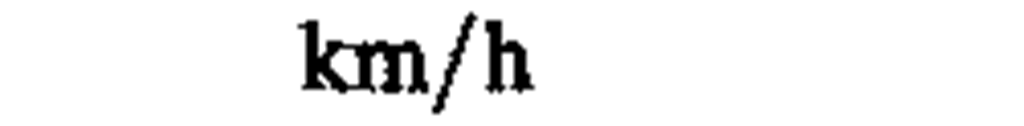 |
 |
|
viscosity, dynamic
|
pascal second
|
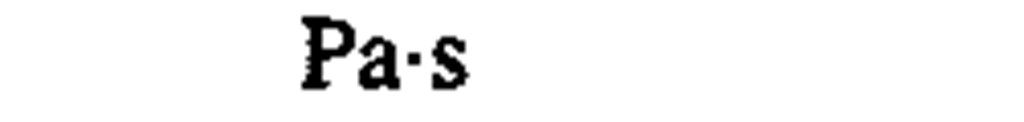 |
 |
|
|
millipascal second
|
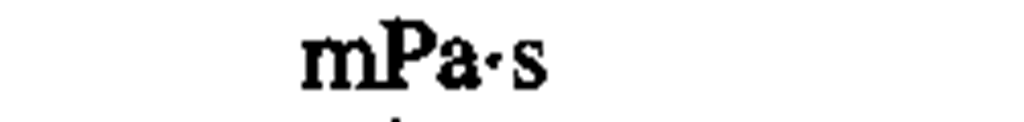 |
 |
|
viscosity, kinematic
|
square meter per second
|
 |
 |
|
|
square millimeter per second
|
 |
 |
|
volume
|
cubic meter
|
 |
 |
|
|
cubic diameter
|
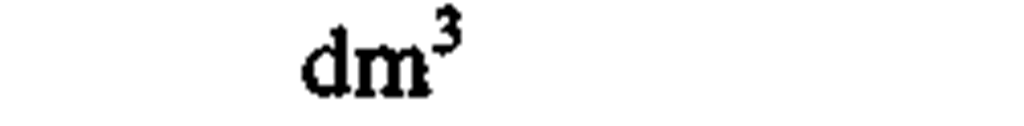 |
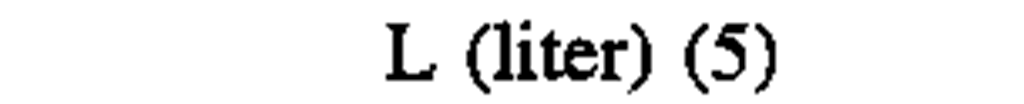 |
|
|
cubic centimeter
|
 |
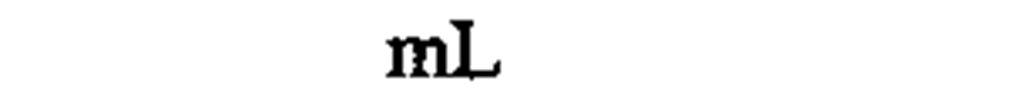 |
|
wave number
|
1 per meter
|
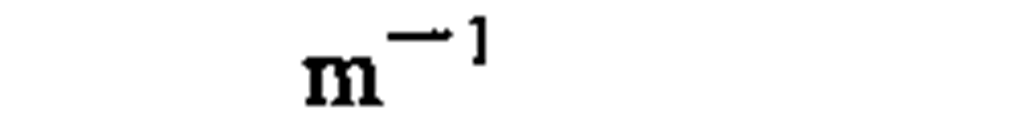 |
 |
|
|
1 per centimeter
|
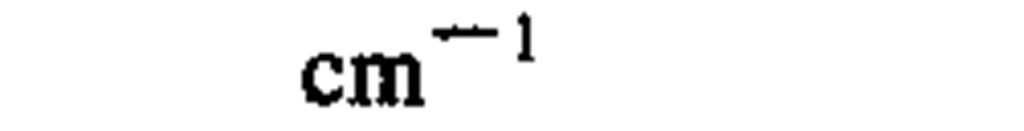 |
 |
tThis non-SI unit is recognized by the CIPM as having to be retained because of practical importance or use in specialized fields (1).
In addition, there are 16 prefixes used to indicate order of magnitude, as follows:
|
Multiplication factor
|
Prefix
|
Symbol
|
Note
|
 |
exa
|
E
|
|
 |
peta
|
P
|
|
 |
tera
|
T
|
|
 |
giga
|
G
|
|
 |
mega
|
M
|
|
 |
kilo
|
k
|
|
 |
hecto
|
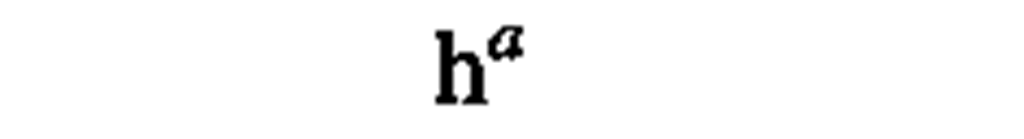 |
"Although hecto, deka, deci, and centi are SI prefixes, their use
|
 |
deka
|
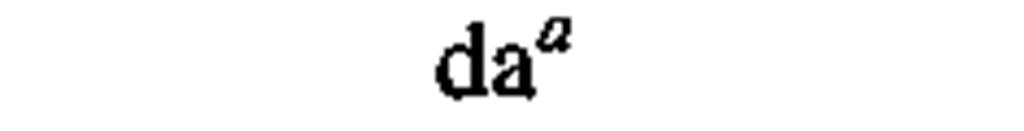 |
should be avoided except for SI unit-multiples for area and
|
 |
deci
|
 |
volume and nontechnical use of centimeter, as for body and
|
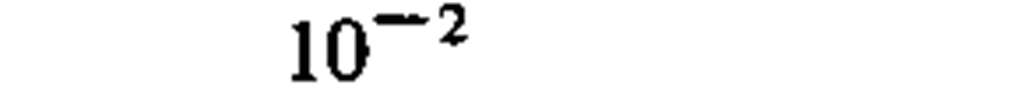 |
centi
|
ca
|
clothing measurement.
|
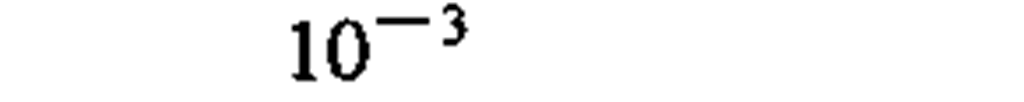 |
milli
|
m
|
|
 |
micro
|
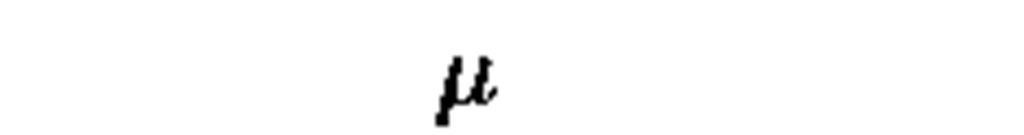 |
|
 |
nano
|
n
|
|
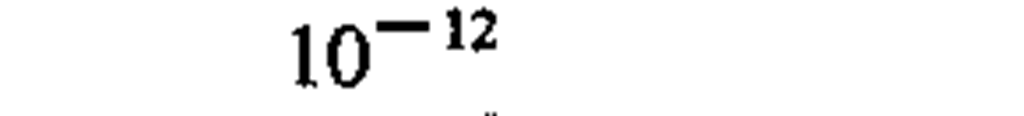 |
pico
|
P
|
|
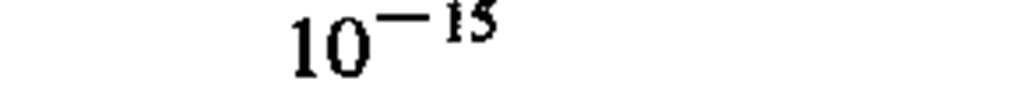 |
femto
|
f
|
|
 |
atto
|
a
|
|
For a complete description of SI and its use the reader is referred to ASTM E380 (4).
A representative list of conversion factors from non-SI to SI units is presented herewith. Factors are given to four significant figures. Exact relationships are followed by a dagger. A more complete list is given in the latest editions of ASTM E380 (4) and ANSI Z210.1 (6).