Cost
Prices for laser printers continue to drop significantly, so the cost of a laser printer is no longer the issue it once was. The question becomes cost of supplies vs. quality of print. Laser cartridges are more expensive than inkjet ones, but they last longer. While color laser printers are now inexpensive enough to use in offices, the cost of color cartridges is still high.
At the moment, businesses that need to print only in black and white find that laser printers are more economical than inkjet. Businesses that need to print in color (particularly photographs) generally use an inkjet printer. One of the decisions you must make in the business of desktop publishing is which printing option is the most cost-effective for your purpose.
Printer Drivers
A printer driver is software that allows the computer to output files to a printer. Sometimes printer drivers need to be specifically installed on a computer in order for the printer to work. However, most computers have the necessary printer drivers built into the operating system.
PPD (PostScript printer description) is a postscript printer file that sends essential information to a laser printer allowing it to produce the expected product. It includes both postscript information as well as design details.
Inkjet is a printing method that sprays a series of ink dots onto a page, allowing it to reproduce both text and images with fine detail.
A printer driver is software installed on a computer that allows a printer and computer to communicate.
PPD is a file sent to a printer that provides it with all the information it needs to create a postscript document.
Figure 1.16
CAT5 is a type of cable that can be used to connect one computer to another to create a network.
This file is usually produced by your DTP software without any decision on your part.
Networks
The growth of networks both at home and at work has changed completely the way businesses function. No longer is a person tied to a single, stationary computer, working alone. Now all computers within an organization, or even throughout the world using the Internet, are connectable. A file on one person’s computer can be accessible to anyone with access to that computer through a network.
A network can be wired using Ethernet cables such as a CAT5, shown in Figure 1.16, or wireless using wireless access points that broadcast signals using Wi-Fi. In both cases, equipment such as a router or a hub or switch acts as the central point connecting all the computers on the network.
Laptop computers today usually come with built-in wireless capability. A laptop can also be wireless using a card that is inserted into a slot on the computer called a PC card. Other wireless devices such as PDAs and cell phones also have wireless capabilities. Many businesses now offer hot spots that provide a wireless network to anyone in the vicinity.
LAN
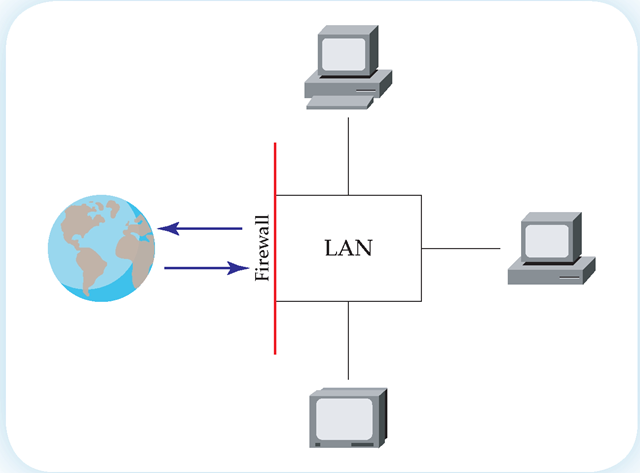
A local area network (LAN) connects computers in a single building or within a single organization. Often a firewall blocks the outside world from having access to the LAN, as shown in Figure 1.17. Firewalls can also be installed on individual computers to block unwanted access.
Wired networks are those that are connected using Ethernet cables such as CAT5.
Wireless access points are locations from which network signals are transmitted using an antenna.
Wi-Fi is a term used to describe a wireless network.
A router is one type of hardware that connects computers in a network.
Hubs and switches are also used to connect networks.
Hot spots are locations that transmit a wireless signal for use by those in the vicinity.
LAN is a local area network that connects computers located in proximity to one another. Since cables are required to connect each to a single connection point, the physical distance limits the size of a LAN.
A firewall is a means of preventing access to a network
Figure 1.17
A firewall is a means of preventing unwanted access to a computer on a network. It is one of the means of providing network security.
WAN
A wide area network WAN connects computers over a large geographical area. The Internet is a good example of a WAN, but it is not the only one. A VPN (virtual private network) is another type of WAN that connects all the computers in a single organization. VPNs block access to anyone not part of this widespread network by running the system in parallel to the Internet.
Online Security
With the advancements in computer accessibility, the issue of security has become of prime concern for businesses. Not everyone with the ability to access a computer may have the best of intentions. As a result, passwords and logins are usually required to use a networked computer. Passwords should not be shared and should be stored in a safe location. Unfortunately, with the proliferation of passwords, it has become difficult for users to keep track of all their passwords without writing them down.
Although good passwords should not include easily guessed words, they should be easy enough for their user to remember. They should include both upper- and lowercase letters as well as numbers. Ideally, even with these restrictions, passwords should be changed periodically. In addition, it’s important not to use the same password for every situation.
Viruses
Online security is not limited to preventing access to files. Destructive programs (called malware) such as computer viruses, worms, Trojans, adware, or spyware can invade a computer. This invasion usually occurs through e-mail links and attachments, or as the result of visiting a website.
Antivirus software has been developed to protect computers against malware, but it must be continually updated. To maintain a secure computer, it is important to use current anti-virus software, to not open e-mail attachments that you did not request, and to closely monitor both e-mail and web usage.
WAN is a wide area network that uses devices such as telephone lines, satellite dishes, and radio waves to connect computers to a network.
VPN is a virtual private network that provides a WAN to members of a widespread organization.
Malware is a broad term that describes software designed to be destructive to a computer.
It can include viruses, worms, Trojans, adware, or spyware.
SUMMARY
In this topic you learned how desktop publishing began. You read about the operating systems and software that you will use as you study desktop publishing. You saw various input and output devices that are required to enter and then to publish a document. You briefly studied how networks are established and how to maintain security while using them. Now it is time to begin using digital desktop publishing tools.
KEY TERMS
|
Acrobat Reader |
Linux |
PostScript |
|
cross-platform |
Mac |
PPD |
|
desktop publishing |
malware |
printer driver |
|
dot matrix |
OCR |
router |
|
DTP |
open source |
VPN |
|
firewall |
operating system |
WAN |
|
GUI |
output device |
Wi-Fi |
|
high-end program |
PageMaker |
Windows |
|
hot spots |
PC |
wired |
|
inkjet |
|
wireless access point |
|
input device |
platform |
WYSIWYG |
|
LAN |