Troubleshooting CAPWAP Session Establishment/AP Discovery and Join
Usually, in failures in which the DTLS is never established, you have to identify at what step the process is failing. Once again, you usually have to defer to a packet trace to determine that. You have to look at two different views:
■ At the WLC port
■ At the switch port the AP is plugged into
In most cases, something happens between these two segments; however, you must understand that these points in the network are crucial. Technically, these are the starting and finishing points.
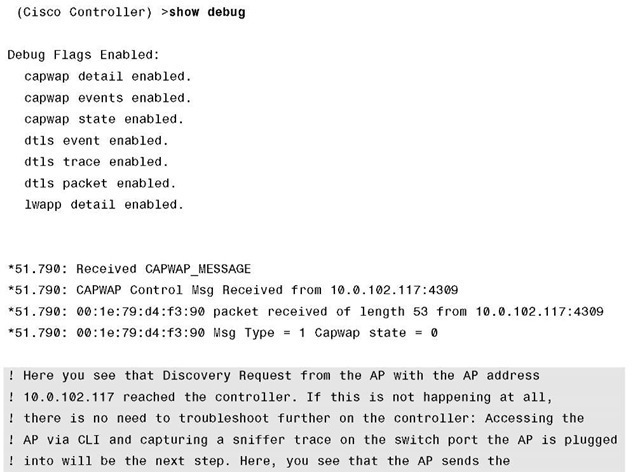
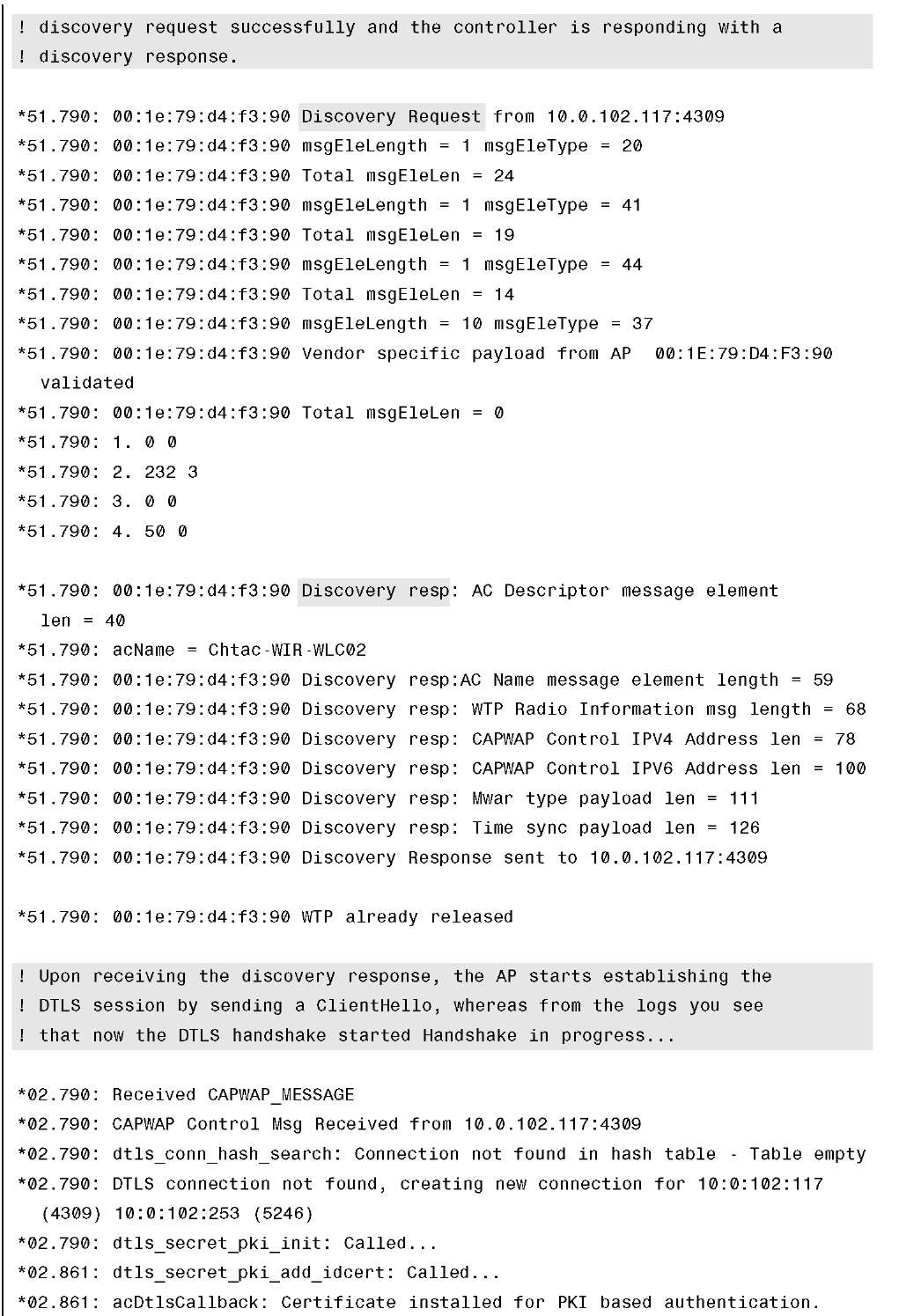
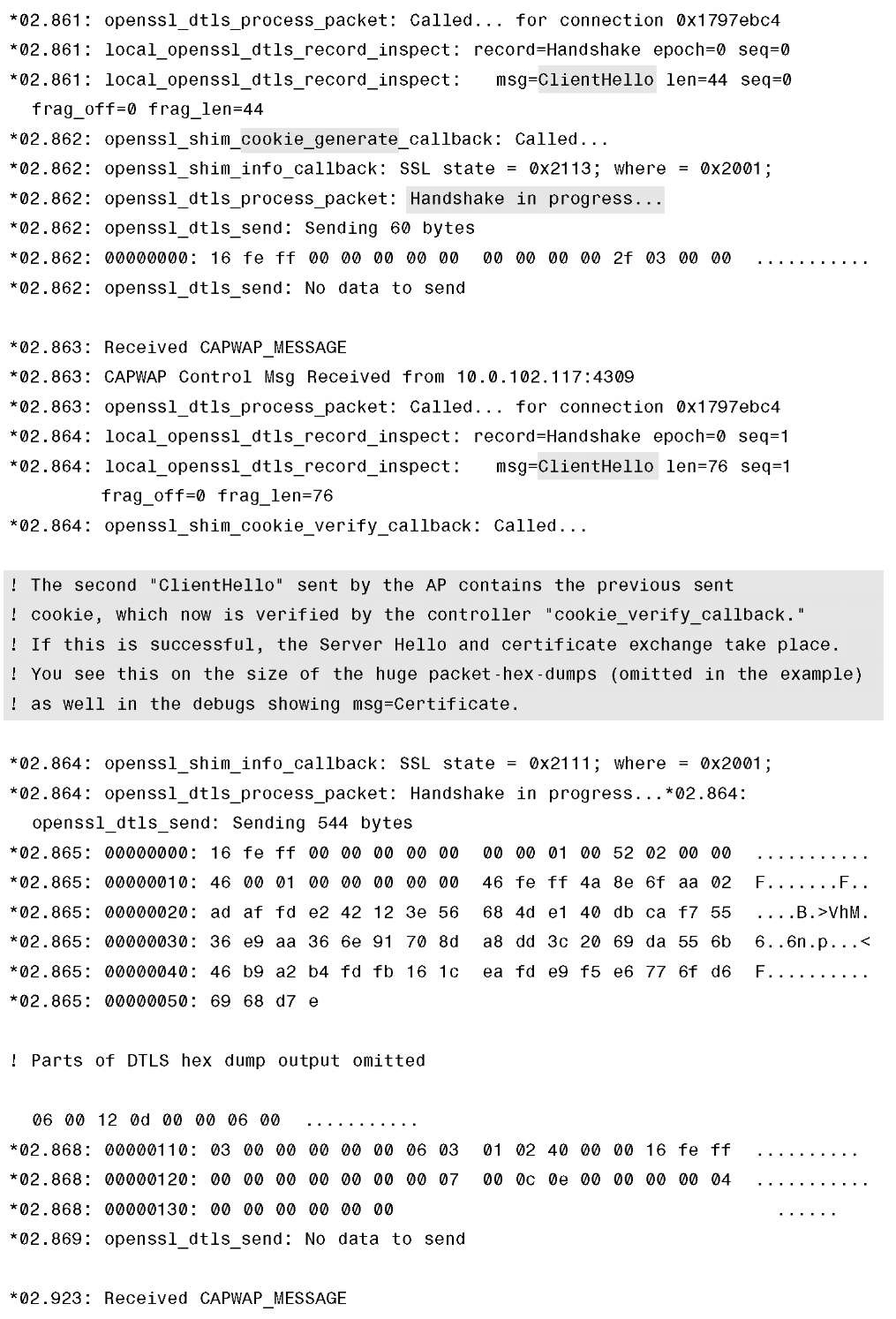
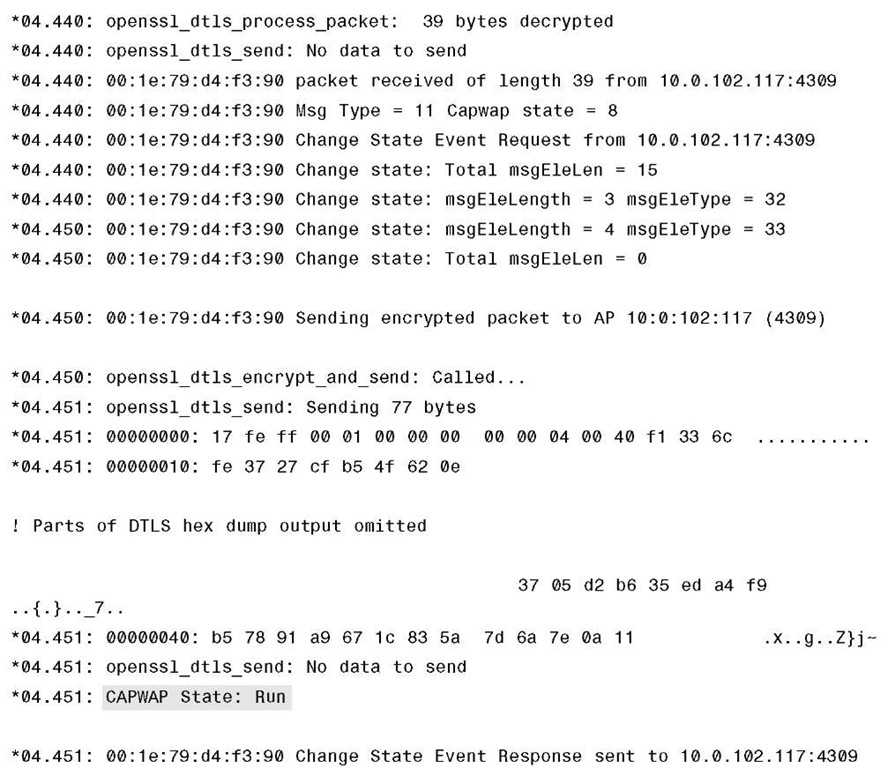
To get a good grasp on troubleshooting the issue, you must comprehend and understand the CAPWAP join process. On paper it is pretty straightforward, but you can take another look at it from a different angle. Looking at the process from a debug output perspective might be a better approach. This approach might also help solidify the foundation of what you have already learned. The commented output in Example 4-3 is with CAPWAP and DTLS debugs enabled at the same time. To read the debugs and explanations that follow, please refer to the CAPWAP packet flow in Figure 4-4.
Example 4-3 CAPWAP and DLTS Debugs on the Controller
Example 4-3 CAPWAP and DLTS Debugs on the Controller
Example 4-3 CAPWAP and DLTS Debugs on the Controller
Example 4-3 CAPWAP and DLTS Debugs on the Controller
Example 4-3 CAPWAP and DLTS Debugs on the Controller