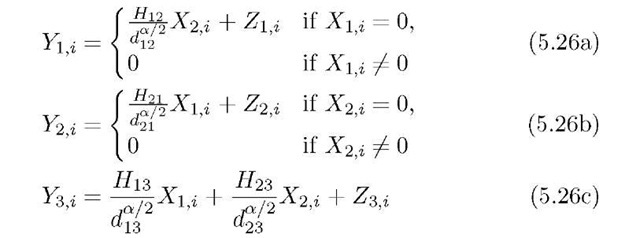We study the performance of cooperative protocols for the network shown in Figure 5.2. The network outputs are
for i = 1,2,… ,n. The transmitting nodes have half-duplex constraints. The noise variables Zu,i, u = 1,2,3, i = 1,2,…,n, and channel gains Huv are the usual complex, Gaussian random variables (see Section 3.2 and (3.3a) and (3.3b)). Note that the Huv change on a slow timescale as compared to the and Zu,j. The transmitters have the average power constraints (3.5) and we set P1 = P2 = P for simplicity. We will usually view the network of Figure 5.2 as either a RC with node 1 as the source, or a RC with node 2 as the source. Of course, this means that all the relaying strategies developed in topic 4 will apply here.
We add some remarks about channel and network knowledge. The DF protocols usually require CSIR only. The AF protocols additionally require the destination to know the source-to-relay channel gain to perform maximal ratio combining [148, p. 721].
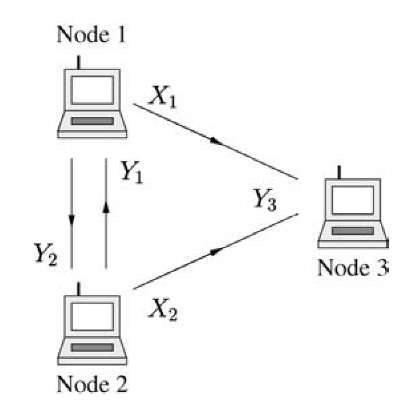
Fig. 5.2 A three-node wireless network. Nodes 1 and 2 have messages destined for node 3.
The CF protocols require both the relay and destination to know all channel gains, i.e., the relay must have CSI available before transmitting (CSIT). The CSIT usually has low rate as compared to the data, and requires feedback from the destination once this node determines the channel gains on its incoming links. Keeping this in mind, we will see that CF achieves the best possible diversity-multiplexing tradeoff in both the high and low SNR regimes. Low rate feedback in the form of an ARQ bit from the destination to the relay can also improve performance, as shown in Section 5.4.2.5.
Finally, we remark that from now on we work with
rather than the received SNRs![]() For convenience, we abuse notation and generically write mutual information expressions parameterized by 7 as I(7) and then define
For convenience, we abuse notation and generically write mutual information expressions parameterized by 7 as I(7) and then define![]()