ORDER
Galliformes
FAMILY
Phasianidae
GENUS & SPECIES
Phasianus colchicus
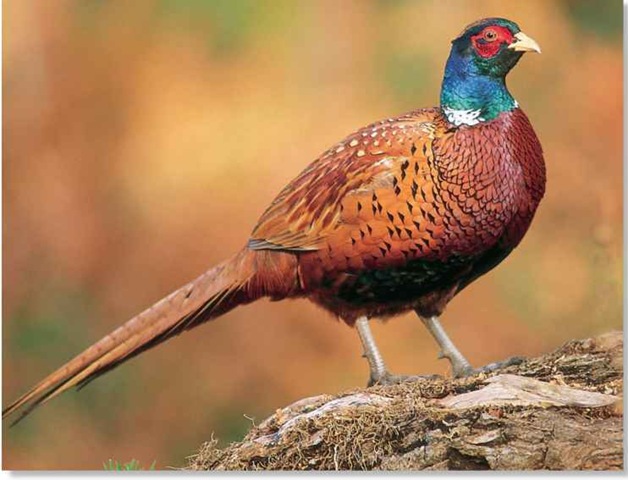

• This ground-dwelling bi
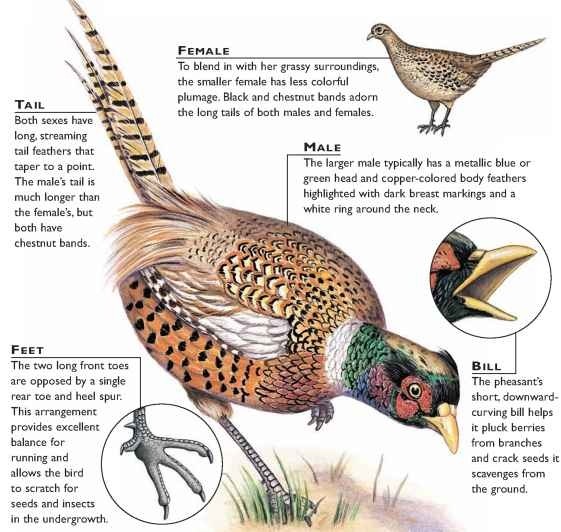
key features
rd rarely ranges more than 6 miles from its breeding ground
• Flies low and fast, skimming over thickets and brush, but only for short distances
• Males have a bright red inflatable pouch, called a wattle, that is extended during breeding
where in the world?
southeast Europe and central Asia to China, Korea and Japan; introduced to western Europe, North America and New Zealand

Lifecycle
Though a fast flier over short distances, the common pheasant spends most of its life on the ground, foraging in undergrowth, taking dust baths and building its nest amid shrubs.
HABITAT
The common pheasant is most often found in open, lightly wooded areas, parks and farmlands of Asia, Europe and North America. But it also populates desert oases of the western U.S. as well as the cool mountain forests of China, where it lives at altitudes of up to 3,000′. It prefers to nest under protective cover and thrives along river and lake banks, hiding in reed beds or riverside thickets of tamarisks, poplars, wild olives and other trees and shrubs. Rice fields provide cover and ready food in China, Korea and Japan.
Open house The pheasant mostly lives out In the open.

BREEDING
Common-pheasant breeding is based on dominance. The dominant male will attract a harem of several females, then woo them with a complex courtship ritual of movement and sound. Standing tall and straight, the male struts around the female in semicircles, feathers fluffed and wattle inflated. To attract the attention of a female, he will hiss, flutter his tail feathers and crouch low to the ground with his tail held high, while making a soft, guttural cooing sound. After mating,the female lays I -2 eggs a day until she has a full clutch of around 10. After
a 3-4 week incubation, the chicks are born virtually ready to start feeding themselves. The male takes no responsibility for the young birds, leaving their care entirely to the female. At 12 days the young make their first flights, and at 10 ‘y Early flight weeks the brood leaves its The chick is able to fly at mother as young as 12 days old.

A First born Pheasant eggs hatch at different intervals.

The state bird of South Dakota is the common pheasant.
# The common pheasant can fly up to 60 mph.
# The ring-necked pheasant is another name for the common pheasant because of the typical white ring around its neck.
FOOD & FEEDING
The common pheasant is an omnivore, feeding on what is most readily available in each season and habitat. Farmlands provide an abundance of energy-rich grains and fruits, while wooded areas offer berries, roots, insects, worms and slugs.Young pheasants (up to 4 months old) eat more animal matter than adults to obtain the protein necessary for growth.The common pheasant spends most of its time on the ground scratching for food. It makes use of both its bill and its feet for digging, but in spring, it alights in high tree branches to feast on tasty buds and flowers. During winter, pheasants may feed together in large flocks.
VERSATILE FORAGER

1 Dig…
A male pheasant uses his bill like a shovel, throwing soil aside as he forages for food such as seeds, berries, worms and insects.
2 Peck…
The common pheasant’s sharp bill also allows it to unearth items buried in the ground, including roots and tubers.


3 Jump…
A powerful jumper, the pheasant flutters its wings and easily reaches berries in the highest branches of a blackberry bush.

4 A Perch
When food is scarce on the ground during the spring, the pheasant flies up to a lofty limb for a hearty meal of leaf buds.
BEHAVIOR
Active both night and day, the common pheasant begins calling well before sunrise. The birds often leave their roosting sites at that time to forage for 2-3 hours, then move to a nearby source of water for a short time. Pheasants like to spend the warmest part of the day relaxing in the shade, preening, dustbathing and sleeping. The birds then
continue their search for food until dusk, when they settle for the night.They roost most often in dense ground cover, but they may also adopt nests abandoned by squirrels or other birds. Roosting groups in the cold winter months may vary from 2-24 birds.

A Bath time The pheasant regularly takes dust baths to remove oil from its feathers.
CONSERVATION
The common pheasant is a hardy and adaptable species. Clearing forests for farmland in the U.S. earlier this century reduced pheasant populations, but through the efforts of organizations such as the Conservation Reserve Program, it now thrives in many midwestern states. It continues to flourish in its native Asian environment, as well as in the other diverse geographical areas where it has been introduced.
Profile
Common Pheasant
The common pheasant is a speedy runner and, over short distances, a powerful, low-altitude flier.
CREATURE COMPARISONS
The green pheasant (Phasianus versicolor) is slightly smaller than the common pheasant, but otherwise is remarkably similar to its close relative. However; female green pheasants have darker mantle feathers than the the female common pheasant, and green wingtips. While the common pheasant, as its name implies, ranges over broad ranges in Asia, Europe and North America, the green pheasant is confined to Japan and the Hawaiian islands.

| vital | |
| statistics | |
| Weight | 1.5-3 lbs. Male 20-36″; female 20-26″ |
| Length | |
| Wingspan | About 32″ |
| Sexual Maturity | 1 year |
| Breeding Season | Varies, but majority from March-June’. ‘r |
| Number of Eggs | 8-15 |
| Incubation f Period | 23-28 days |
| Fledging Period | 70-80 days |
| Birth j- Interval | 1 year |
| Typical Diet | Seeds, berries, shoots and invertebrates |
| Lifespan | Average 10-20 months |
Related species
• The common pheasant is one of two species in the genus Phasianus; the other member, the green pheasant (P. versicolor), is often considered a subspecies. Other relatives include the reeves pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesi) and the copper pheasant (S. soemmeringi). The family Phasianidae includes about 174 species of pheasant, francolin, peafowl, partridge and quail.
