20.14.
Valve Adjustment
If the engine is fitted with solid tappets, the valves on each cylinder are adjusted when the cylinder is on the compression stroke and both valves are closed. Many manufacturers recommend that the valve adjustment be done with the cold engine. The adjusting screw in each rocker arm is turned until the specified feeler gauge slides lightly between the rocker arm and the valve stem. The adjusting screw lock nut is tightened once the specified clearance is obtained (Fig. 20.156).
The following sequence is applicable for adjusting the hydraulic valve lifters in a typical 2.8 L V6 engine.
(a) The engine is rotated until the number 1 piston is at TDC of the compression stroke and the timing mark on the pulley is lined up with the 0 degree position on the timing indicator.
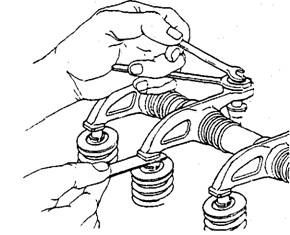
Fig. 20.156. Valve adjustment with solid tappets
(6) In this engine position the exhaust valves on cylinders 1,2, and 3, and the intake valves on cylinders 1, 5, and 6 are adjusted. Each rocker arm adjusting nut is retreated until there is clearance between the rocker arm and the valve stem.
(c) The rocker arm adjusting nut is slowly tightened until there is no clearance between the rocker arm and the valve stem. When this clearance is removed, the pushrod becomes more difficult to rotate.
(d) Continue to turn the adjusting nut one and half turns from the point where the clearance is removed.
(c) The engine is rotated one revolution until the timing mark is lined up with the 0 degree position on the timing indicator. This is the number 4 cylinder firing position, in which the exhaust valves on cylinders 4,5, and 6 and the intake valves on cylinders 2, 3 and 4 are adjusted.
On some rocker arms (Fig. 20.146) there is no adjustment but a bottomed measurement is performed. When each piston is on the compression stroke and both valves are closed, each lifter is bottomed by prying down on the outer end of the rocker arm. At this stage, a specific clearance must be available between the rocker arm and the valve stem. When this clearance is less than that specified, the installed height of the valve is not correct. Excessive clearance may be due to worn components of the valve mechanism, such as rocker arms, push-rods or lifters.
