12.6.
Temperature Indicators
Temperature indicators are used to indicate the driver regarding overheating or an abnormal condition of the cooling system. For this purpose, a temperature indicating light and/or gauge is installed in the instrument panel of the car. Both balancing-coil and bimetal thermostat type gauges are in use for temperature indication. The indicator light warns the driver about the abnormal situation.
12.6.1.
Indicator Light
The warning light system consists of the indicator light (mounted on the instrument panel), a temperature switch (mounted in the water jackets), a “prove’Vtest circuit in the ignition switch, and the wires to connect these parts (Fig. 12.31.). The temperature switch is a single contact switch which serves as a ground for the light through the engine block. This switch is normally open (very high resistance) and closes (very low resistance) to switch the light on at about 391 to 394 K or at a temperature about 5.5 K below the boiling point of the coolant.
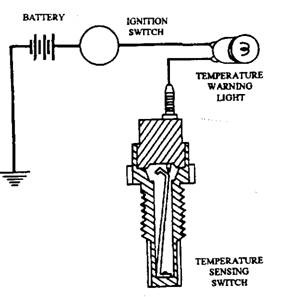
Fig. 12.31. Temperature warning light.

Fig. 12.32. Typical temperature sending unit.
12.6.2.
Indicator Gauges
The indicator gauges are similar to that used in the fuel system (section 9.7) and oil systems (section 11.12.1) except for the difference in the sending unit. The temperature gauge sending unit (Fig. 12.32) has a bimetal spring that changes resistance in proportion to engine heat. The free end of the bimetal spring is attached to a variable resistance so that the instrument circuit resistance is changed proportionately to the engine temperature. When the engine is hot, the engine unit resistance is low giving a high instrument reading. Figures 12.33 and 12.34 respectively illustrate the balancing coil gauge and the bimetal-thermostat gauge.

Fig. 12.33. A balance-coil or magnetic temperature gauge.
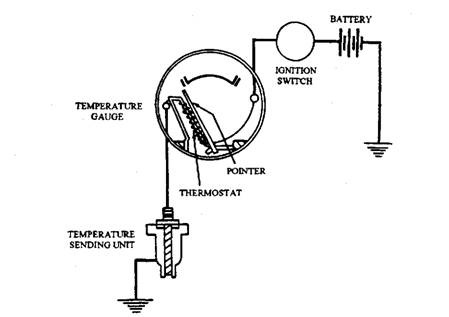
Fig. 12.34. A thermostatic heating or bimetal-thermostat temperature gauge.
