Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
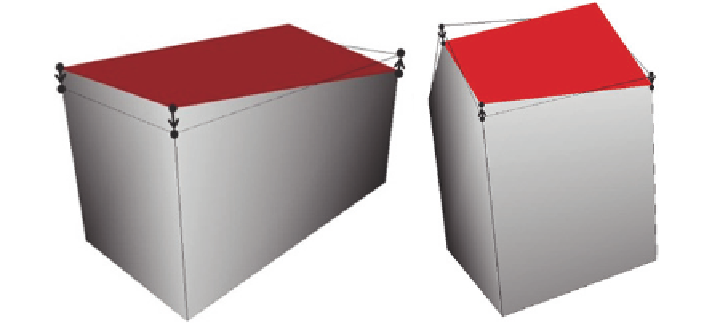
Fig. 8
Healing of the LOD1 and LOD2 RoofSurface
least deviation according to
n
z
and maximal z-value. Additionally, it is not adja-
cent to the GroundSurface. We are projecting all points of the
LinearRing
of the
RoofSurface
onto a plane parallel to P
xy
, passing through the average z-value of all
points in the ring (Fig.
8
).
The second algorithm handles all other LoD2 roof types and calculates the
least square fitting plane for all
RoofSurfaces
. Each point of a linear ring of the
corresponding RoofSurface is projected along the z-axis into the according least
square fitting plane of its linear ring. This procedure will be repeated until all
RoofSurfaces
are planar or a maximum number of iterations is reached. Note that
the points are only projected along the z-axis. Hence already healed
WallSurfaces
remain planar, even if shared points with
RoofSurfaces
are moved (Fig.
8
).
3.1.2 Solid Healing
In this phase one error is healed at a time. That means each iteration heals an error
and checks the result for validation.
CS_NUMFACES
: To form a solid minimum four surface is required. Any
solid having less than four valid polygons has insufficient number of face error. If
a solid has less than 4 polygons then it is not possible to repair, only exception is
a triangular pyramid with one missing triangle. For all other cases the solid would
be invalid and deleted from the model by the healing process.
CS_SELFINT
: Polygons of a solid must meet each other only through edges.
Any other intersection of polygons will be considered as a self-intersection error
of solid. We assume that the polygons of a solid, in the sense of CP_PLANAR,
are planar, hence the user defined tolerance for the intersection algorithm should
not be greater than the one used for CP_PLANAR. This might lead otherwise to
false positives and/or irrational results. The Tolerance i.e. is used to determine if