Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
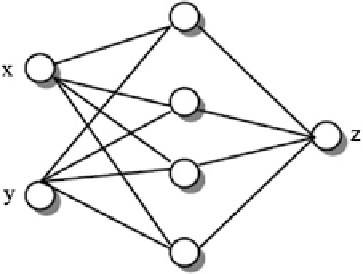
Fig. 1
Network perceptron
with a hidden layer for the
interpolation heights
is compared with the actual height. Finally, the extent of errors that exist in the cal-
culated elevations through standard interpolation methods can be determined by
using RMSE rate. The measurement of RMSE can be expressed as follows:
i
=
1
z
comp
−
z
actual
2
n
−
1
RMSE
=
where, Z
comp
is calculated height values and Z
actual
is actual checkpoint height.
6 Using Neural Networks in Heights Interpolation
Interpolation of elevations based on ANN uses the Perceptron network, which
consists of three layers; an input layer, an intermediate layer and an output layer.
Structure and network topology is shown in Fig.
1
. Two neurons in the input layer
are components of x and y and the output layer of neuron is component of z.
Training is based on the gradient method. In the network learning process in both
data points for training and a set of checkpoints; checkpoints (1) are areas of valida-
tion and checkpoints (2) is the independent checkpoints, these are used for testing
and evaluating the precision interpolation networks. The error signal based on the
RMSE is created and the sum of weight is used to achieve the minimum RMSE.
7 Using Genetic Algorithms in Heights Interpolation
Unlike NN that is able to create a network for elevation interpolation method of genetic
algorithm optimisation routine can only be used for interpolation. The usual methods
of interpolation used in this study along with GA have been optimised and consisting
of polynomials and the inverse distance weighting method, which will be described
below. Due to this comparison, the Tournament function can be used for selecting and
the Gaussian function is used for single-point mutation and combination for this gen-
eration. Fusion and selection function are considered equal to 500 generations.