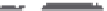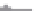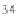Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
90°N
31
60°N
34
36
30°N
35
37
35
34
Equator
35
35
35
36
30°S
36
35
35
34
35
34
34
34
60°S
34
34
90°S
30°E
60°E
90°E 120°E 150°E 180° 150°W 120°W 90°W 60°W 30°W 0°
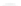
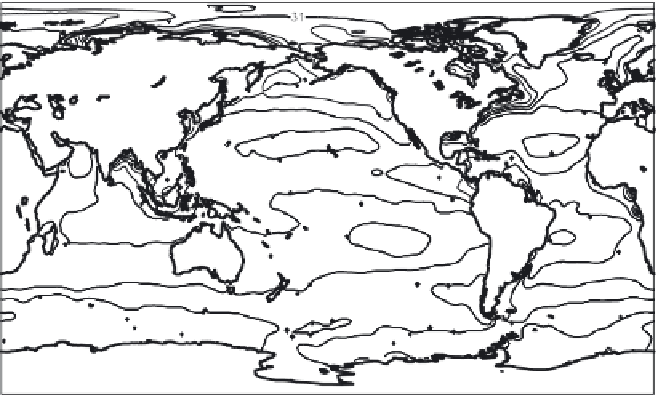
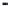
Figure 2.19 Annual mean sea surface salinity. The contour interval is 1 psu.
Oceanographers also define salinity in terms of the conductivity of a sample of
water, since a higher conductivity is associated with the presence of more ions
and dissolved salts. The
practical salinity unit
(psu) is the standard measure of
salinity, although it is technically not a unit because it is dimensionless. Values
indicate the ratio of the conductivity of a sample of seawater to the conductiv-
ity of a standard potassium chloride solution. A salinity value of 35 psu is very
close to 35 g/kg of salt at 15°C (about 258 K).
Figure 2.19
displays the annual mean salinity of surface waters.
Isohaline
values range from about 29 psu in the Arctic to more than 37 psu in the sub-
tropical Atlantic Ocean. Note the following:
• The Atlantic Ocean is saltier than the Paciic and Indian Oceans.
• Salinity tends to be highest in the subtropics.
• Lower salinity values occur near the coasts where large rivers low into
the sea. Examples are the northern Gulf of Mexico near the mouth of the
Mississippi River, and off the northeast coast of South America where the
Amazon and Orinoco Rivers empty into the Atlantic.
• High salinity gradients are located off the east coast of North America, north
of about 30°N, similar to the strong gradients in temperature in this region
(
Fig. 2.15)
.
• Atlantic waters with high salinity extend far north into the Arctic east of
Greenland.
The latitudinal dependence of surface water salinity is apparent in the zonal
mean plot in
Figure 2.20
. In the global average, subtropical surface salinity is
about 1.5 psu greater than that close to the equator. The black line in the figure
is the zonal mean excess of evaporation (E) over precipitation (P), illustrating the
association of their difference (E P) with ocean surface salinity. When water