Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
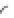
Gerade
g
in vektorieller Darstellung
mit einem Geradenpunkt
A
und Richtungsvektor
R
:
r
=
r
A
+
t
R
Da A der Koordinatenursprung ist, gilt hier
r
A
=
0
und damit
(II)
r
=
t
R
sinsin
cossin
a
G
b
G
c
G
mit Richtungsvektor
R
=
cos
=
Parameter
t
Gemeinsamer Punkt
P
von Gerade
g
und Ebene
E
, dazu (II) in (I) eingesetzt:
t
R
n
=
r
1
n
r
1
n
R
n
y
1
a
E
+
x
1
b
E
+
z
1
c
E
t
=
t
=
damit Parameter
oder
a
G
a
E
+
b
G
b
E
+
c
G
c
E
Skalares Produkt
r
1
n
in Matrizenschreibweise
T
y
1
x
1
z
1
a
E
b
E
c
E
=
y
1
a
E
+
x
1
b
E
+
z
1
c
E
Skalares Produkt
R
n
in Matrizenschreibweise
T
a
G
b
G
c
G
a
E
b
E
c
E
=
a
G
a
E
+
b
G
b
E
+
c
G
c
E
Koordinaten für Punkt
P
mit
r
=
t
R
y
P
x
P
z
P
a
G
b
G
c
G
y
P
=
t
sinsin
=
t
x
P
=
t
cossin
oder
z
P
=
t
cos