Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
80°N
80°N
F
E
Boreal
zone
60°
60°
D
BS
D
C
40°
40°
Cs
BW
C
Tropical:
summer rainfall
20°
20°
Aw
ont
h
Equitorial
westerlies
0°
0°
Af (Am)
Tropical:
summer rainfall
20°
20°
Aw
Dry zone
and trades
Med.
BW
Cs
40°
40°
C
BS
(A)
(B)
60°S
60°S
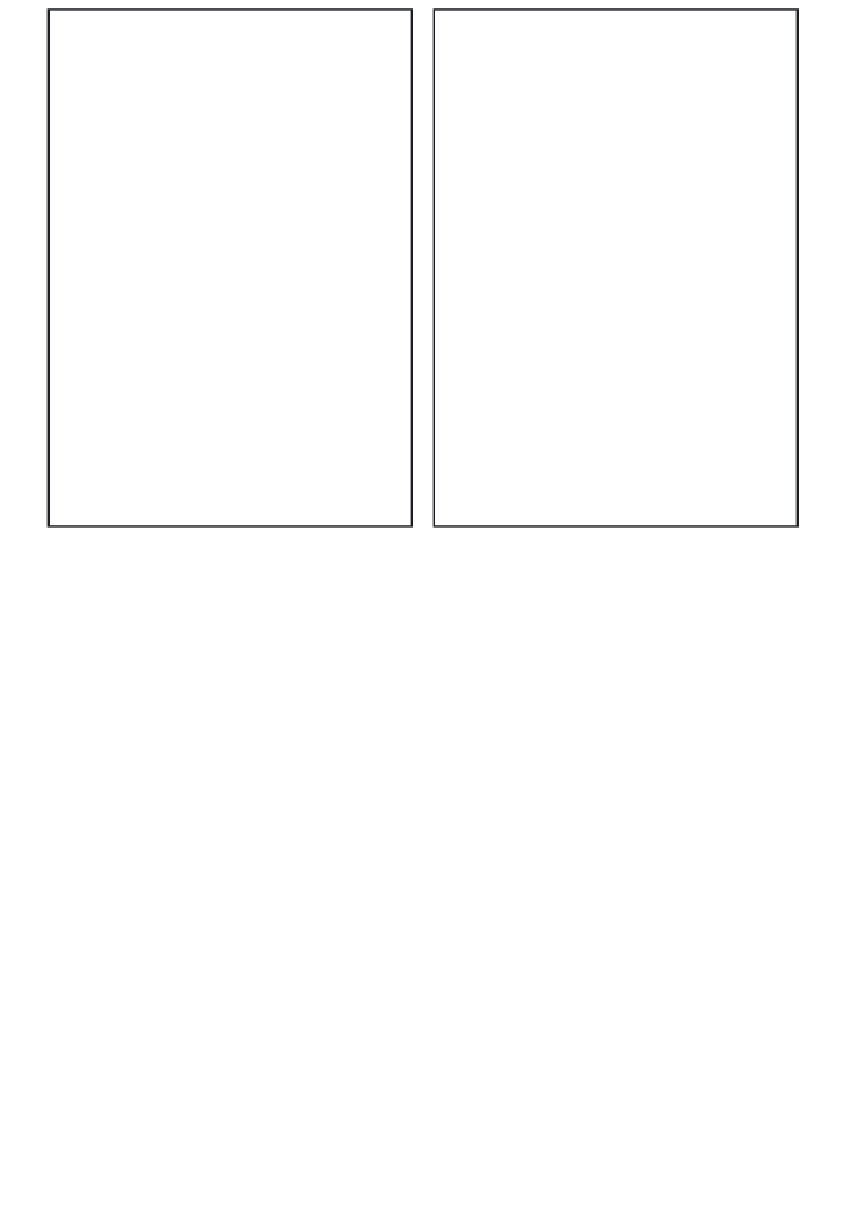
Figure A1.2
(A) The distribution of the major Köppen climatic types on a hypothetical continent of low
and uniform elevation. Tw = mean temperature of the warmest month, Tc = mean temperature of the
coldest month. (B) The distribution of Flohn's climatic types on a hypothetical continent of low and uniform
elevation.
Source: From Flohn (1950). Copyright © Erdkunde. Published by permission.
mean monthly temperature (in
C), with correc-
tions for day length. For a 30-day month (12-hour
days):
PE
(in cm) = 1.6(10
t/I
)
a
where:
I
= the sum for 12 months of (
t
/5)
1.514
a
= a further complex function of
I
.
Tables have been prepared for the easy computa-
tion of these factors.
The monthly water surplus (
S
) or deficit (
D
)
is determined from a moisture budget assess-
ment, taking into account stored soil moisture
(Thornthwaite and Mather 1955; Mather 1985). A
moisture index (
Im
) is given by:
Im
= 100(
S - D
)/
PE
.
°
actual soil moisture content. The average water
balance is calculated through a bookkeeping pro-
cedure. The mean values of the following variables
are determined for each month:
PE
, potential
evapotranspiration, precipitation minus
PE
;
and
Ws
, soil water storage (a value assumed
appropriate for that soil type at field capacity).
Ws
is reduced as the soil dries (D
Ws
).
AE
is actual
evapotranspiration. There are two cases:
AE
=
PE
,
when
Ws
is at field capacity, or (
P
-
PE
) >0;
otherwise
AE
=
P
+ D
Ws
. The monthly moisture
deficit,
D
, or surplus,
S
, is determined from
D
=
(
PE
-
AE
), or
S
= (
P
-
PE
) >0, when
Ws
< field
capacity. Monthly deficits or surpluses are carried
forward to the subsequent month.
A novel feature of the system is that the thermal
efficiency is derived from the
PE
value, which itself
is a function of temperature. The climate types
defined by these two factors are shown in
Table
This allows for variable soil moisture storage
according to vegetation cover and soil type, and
permits the evaporation rate to vary with the