Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
from Cherrapunji - 1563mm and 22992mm,
respectively.
High-intensity rain is associated with increased
drop size rather than an increased number of
drops. For example, with precipitation inten-
sities of 0.1, 1.3 and 10.2cm/hr (or
.
0.05, 0.5 and
4.0in/hr), the most frequent raindrop diameters
are 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3cm, respectively.
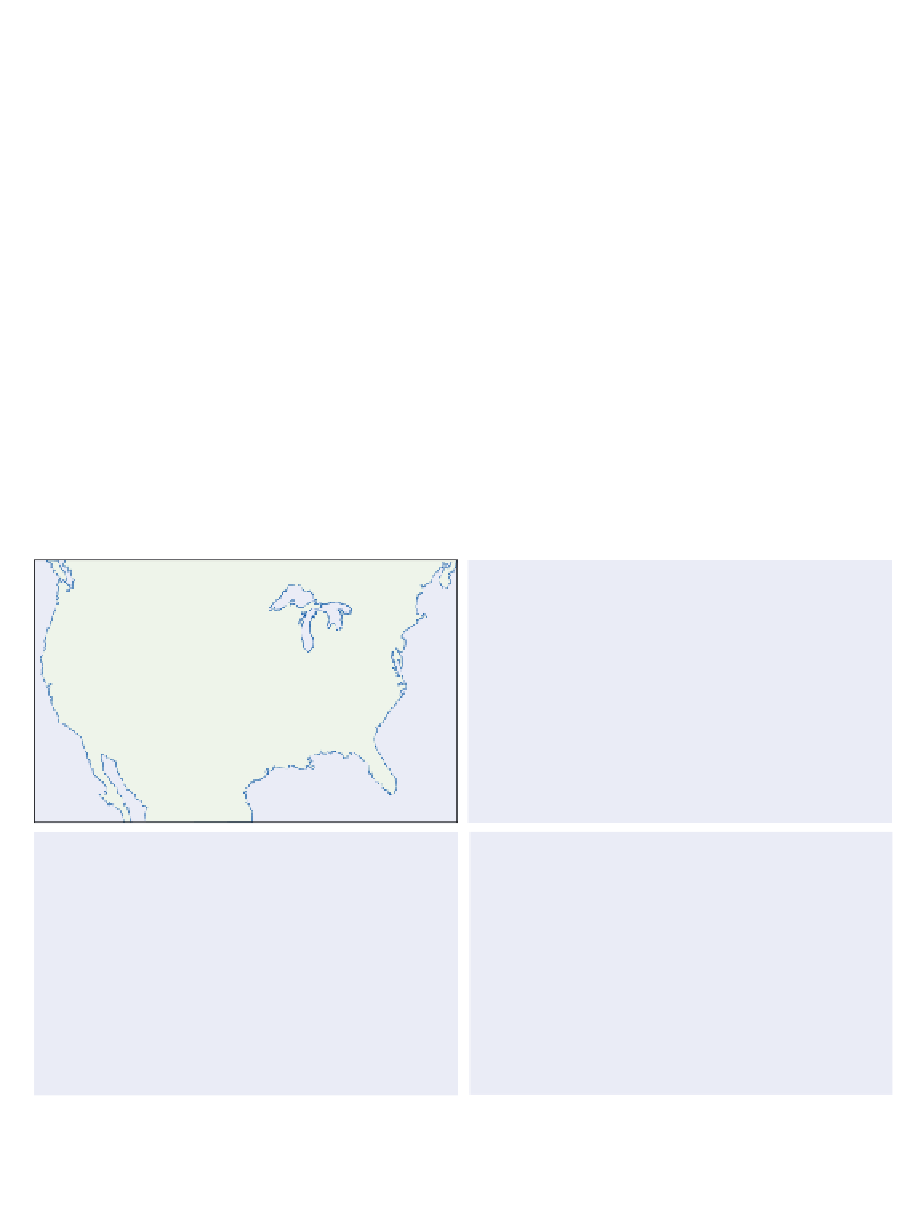
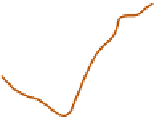
Figure 4.12
shows maximum expected precipitation for storms
of different duration and frequency in the USA.
The maxima are along the Gulf Coast and in
Florida.
linear relationship is similar to that for rainfall
duration and intensity.
Figure 4.13
illustrates the
relationship between rain area and frequency of
occurrence in Illinois, USA. Here a log-log plot
gives a straight line fit. For 100-year, or heavier falls,
the storm frequency in this region can be estimated
from 0.0011 (area)
0.896
where the area is in km
2
.
Frequency of rainstorms
It is useful to know the average time period within
which rainfall of a specified amount or intensity
may be expected to occur once. This is termed the
recurrence interval
or
return period
.
Figure 4.14
gives this type of information for six contrasting
stations. From this, it would appear that on
average, each 20 years, a 24-hour rainfall of at
least 95mm is likely to occur at Cleveland and
216mm at Lagos. However, this
average
return
period does not mean that such falls necessarily
Areal extent of a rainstorm
The rainfall totals received in a given time interval
depend on the size of the area that is considered.
Rainfall averages for a 24-hour storm covering
100,000km
2
may be only one-third to one-tenth of
those for a storm over a 25km
2
area. The curvi-
1-hour storm
24-hour storm
50
60
40
200
225
5
0
20
90
Figure 4.12
Maximum expected precipitation (mm) for storms of 1-hour and 24-hour duration occurring once in
10 years and once in 100 years over the continental United States, calculated from records prior to 1961.
Source: US National Weather Service courtesy NOAA.