Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
growth phase. In the Maldives on the other hand, tourism is
exclusively related to beach resorts and contributes to a third of the
GNP and to three quarters of foreign currency influx. If we look at the
situation at a finer scale, all the Maldivian islands did not react in the
same way to the tsunami wave both in terms of damage and in terms
of population evacuation. Differences were very striking between
islands which were only distant less than one kilometer [MAG 06,
DUV 14]. So the vulnerability level varies in space sometimes at a
very fine scale.
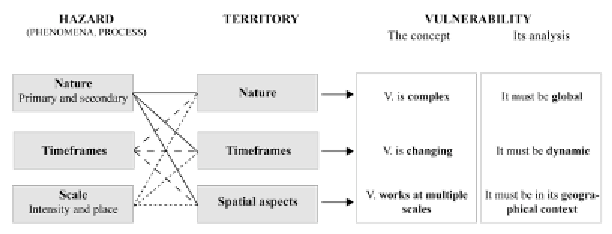
Figure 6.3.
Spatial components of the territory
On a different level, the timeframes of the hazard have an effect on
the timeframes of the territory, more precisely on spatial planning.
Indeed, hazards are expressed as a threat which are either limited in
time, or gradual, so it is more or less pressing in terms of reducing risk
and of planning space. This can bring a given society to settle on the
coasts protected from recurrent storms but situated in a region which
will be subject, in a few decades, to problems of groundwater
depletion, as the latter will be poorly-replenished due to a flawed
hydrological regime. In this case, risk in the short term is usually seen
as more important in terms of public policy than the risk in the longer
term.
The case of the creation of new tourist attraction poles on
mediterranean coasts is a perfect example of the limited ability of
planners and economic operators to take the long term into account.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search